 At the dawn of the web-era, there was much focus on how environmentally friendly websites were: we’d chop down fewer trees, ship fewer products, and travel less for business.
At the dawn of the web-era, there was much focus on how environmentally friendly websites were: we’d chop down fewer trees, ship fewer products, and travel less for business.
And because the web was small, any negative impact it had was relatively small. But the Internet’s no longer small, and neither is the impact it has on the environment. The average website uses 211,000g of CO2 per year, watching a video online outputs an estimated 0.2g of CO2 per second, and a single email can cost 50g of CO2.
In the next four years, the tech industry as a whole may use up to 20% of the world’s electricity and be responsible for 5.5% of global CO2 emissions.
The good news is that because websites are viewed many times, even small improvements can multiply into real change.
1. Reduce Energy Consumption
Through electricity use, the Internet generates around the same CO2 as most major countries. That carbon comes from two sources: the devices we use to access the Internet and the servers that host our data.
Computers heat up, and when they heat up, they slow down. Servers are especially vulnerable and use extraordinary amounts of energy to keep cool and functional, which is why Microsoft keeps throwing servers into the sea.
Make It Faster
The faster your site, the less data is used to serve it, and the less carbon it’s outputting; it’s that simple.
Reduce the Number of Resources Used
Everything you load on your site has an impact. You might think that a tiny PNG is too small to really impact your carbon footprint, but over thousands of page loads, its impact is multiplied. Anything you can do to reduce the number of actual files requested will reduce your carbon output. You can use sites like Ecograder to estimate your own site’s CO2 output.
Optimize Images
If there’s one thing you can do to reduce the size of your site, the amount of data that needs to be sent over the Internet to serve your site, and the resulting speed, it’s optimizing your images.
Nothing reduces a site’s footprint like optimizing images. It’s easy and free to reduce the size of JPGs and PNGs with a service like TinyPNG. Offer WebP to any browser that will accept them; it will boost your Lighthouse score and improve your CO2 usage.
Lazy Load Images
Lazy loading images means images are loaded as they are required; images at the top of a page always load, images further down only load when the user scrolls to them; if the user doesn’t scroll to the bottom of the page, they don’t load, saving you CO2.
Reduce The Amount Of JavaScript You Use
Yes, JavaScript is awesome. Yes, it can be hugely beneficial to UX. And yes, it munches on energy like it’s candy.
When a web page loads, it’s done, the total cost is in. If JavaScript keeps running in the background, redrawing the screen based on user interaction — as is the case with a parallax site — the web page keeps using up energy on the device.
Choose a Sustainable Hosting Company
You can reduce the power needs of a site, but you can’t eliminate them. One simple step is to opt for a hosting company that gets its electricity from sustainable sources such as wind power or solar.
Low←Tech Magazine is powered by a server that runs on solar energy and carries a warning that it may go offline. But it’s possible to host both reliably and sustainably. Many web hosts outsource their actual server management, so they have no control over how those servers are powered, but there are plenty of exceptions that guarantee green web hosting. Google Cloud aims to be the cleanest in the cloud industry. For green web hosting, I always recommend the all-round superb Kualo.
2. Be Inclusive
One of the biggest issues with the EV (Electric Vehicle) movement is that we’re replacing cars earlier than we normally would in a rush to move to “clean” driving.
A new EV certainly outputs less than a gas-powered vehicle when driven the same distance. Combine increased use — because owners think they are driving cleanly — with the fact that a new EV has to be manufactured, the minerals for batteries have to be mined (in horrific conditions), and it then needs to be shipped to you, and EVs are not as friendly as they appear — so go ahead, buy that vintage Porsche it’s probably better for the environment than a Tesla.
Support Legacy Devices
The same issue that applies to cars applies to devices. Every time we rush ahead to support the latest iPhone, we leave older generations behind. A device can and should last longer than two years.
This is not to say that you shouldn’t embrace modern web standards. Technologies like CSS Grid are excellent at reducing markup size and speeding up sites. CSS Grid has been well supported for over four years, and even “legacy” devices can handle it. If you can keep a phone for an extra six months, the environmental cost of that phone is reduced by 20%.
3. Help Users Make Good Choices
More and more people are trying to make good choices. We’re eating a healthier, balanced diet. We’re recycling clothes. We’re traveling by bike, and on foot, instead of by car. People want to do the right thing, and they seek out companies that aid them.
Improve Navigation
Anything that you can do to make your content more findable will mean fewer page loads and therefore consume fewer resources.
By improving your information architecture, improving your search accuracy, and improving on-page signposts like bread crumbs and link text, you help users find content faster.
Feelgood Feedback
When the environmental impact of a user’s actions are quantifiable, let them know. Users who care will appreciate it, and users who don’t will ignore it.
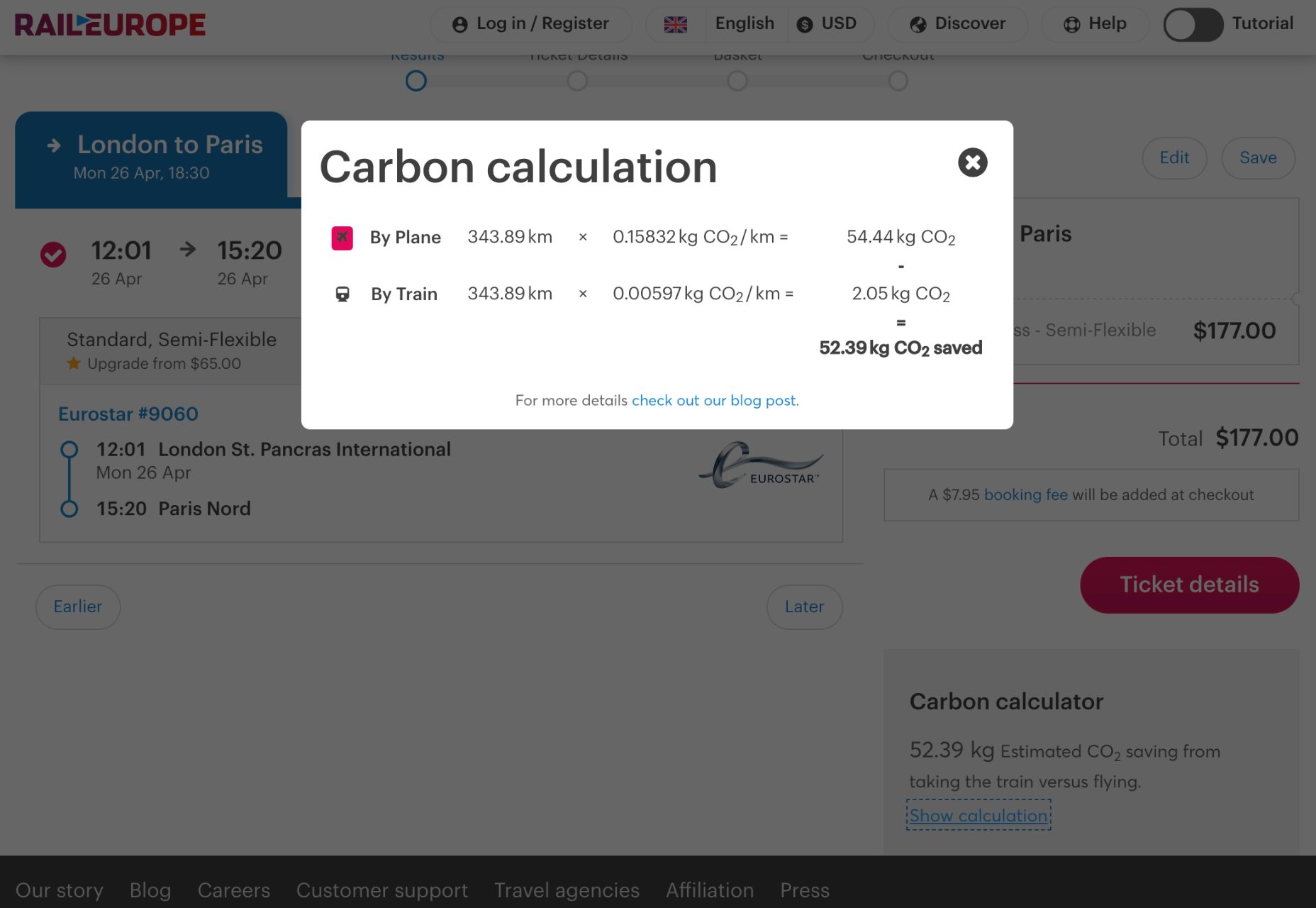
Raileurope.com adds a note to any quotation letting you know how much carbon you’ve saved by traveling by train instead of flying.
Don’t Remove the Shipping Rate
Many ecommerce sites offer free shipping, especially above a certain order value; it’s a good way to encourage higher sales. But absorbing the shipping cost implies that there is no shipping. By highlighting the shipping costs, even if they’re not passed on to the customer, you remind them that there is an environmental cost and a financial cost.
You can absorb the shipping rate without implying there is no cost by adding the shipping and then explicitly deducting it as a discount.
Sustainable Web Design Is Good For Business
The fundamentals of good web design are the fundamentals of sustainable web design.
Make it fast and usable, and you’ll also be making it energy efficient. Make it inclusive, and you’ll help the industry slow the ever-growing tendency to consume. Make it transparent, and you’ll help your users make good choices of their own. All of these things are not only good for the environment, but they also result in improved UX and SEO.
Featured image via Pexels.
The post 3 Effective Ways To Improve Your Site’s Carbon Footprint first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.


 Every week users submit a lot of interesting stuff on our sister site Webdesigner News, highlighting great content from around the web that can be of interest to web designers.
Every week users submit a lot of interesting stuff on our sister site Webdesigner News, highlighting great content from around the web that can be of interest to web designers.










 The digital world is a place of constant change. Just as you get used to a new design trend, another one appears, forcing you to rethink the way that you approach each client project.
The digital world is a place of constant change. Just as you get used to a new design trend, another one appears, forcing you to rethink the way that you approach each client project. 
