User Experience is a crucial consideration for any web developer or designer; the only way to ensure that you’re delivering a successful website is to ensure that the end-user or customer will feel comfortable using it.
User Experience is a crucial consideration for any web developer or designer; the only way to ensure that you’re delivering a successful website is to ensure that the end-user or customer will feel comfortable using it.
A strong user experience increases your client’s chances of successful audience engagement and conversions.
What you might not realize, however, is that the strategies you use to enhance UX as a web developer or designer can also influence how the search engines respond to a website.
Though many designers assume that SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the work of a copywriter or content producer, there are design elements to consider too.
After all, the definition of optimization is “the action of making the best version of a resource.”
So, how are UX and SEO connected?
Adding UX to a Successful SEO Strategy
SEO used to be easy. To stand out on the search results, you just needed to stuff a page full of as many keywords and phrases as possible. Now, it’s a little more complicated.
Leaders in search engine development, like Google and Bing, know that they need to offer their customers excellent experiences to keep them. In this new experience-focused landscape, SEO and UX share common goals.
Search engines don’t just want to provide customers with any answers to their questions. Instead, Google and its competitors are using everything from artificial intelligence to machine learning algorithms to ensure that search results are accurate, relevant, and engaging.
In the same way, user experience is about providing users with easy access to the information and resources they want.
Now that SEO is a multi-disciplined approach, UX is just one of the essential tools that makes it possible for developers to optimize their websites properly.
Where UX Developers Influence SEO
There are plenty of connections between UX and site indexability.
We all know that since 2018, site speed has become a crucial ranking factor for companies in search of better search results. As a developer, it’s up to you to ensure that there aren’t too many elements weighing a website down that would prevent it from delivering fast results.
Bounce rate is another critical factor in search engine ranking algorithms. When customers click on a website, Google wants to see that they get the answers they want. If your navigation is difficult to understand, or the correct information isn’t easy to see on a page, end-users will just hit the back button.
Let’s take a closer look at how developers can influence SEO with their UX strategies.
1. Site Navigation and Ease of Use
It’s no secret that today’s digital consumers crave easy-to-use sites.
A complex website with pages ranking for different terms might seem like an excellent idea for SEO. However, from a UX perspective, the easier it is to navigate your website, the more your end-users will benefit.
According to a study from Ahrefs, well-optimized pages that rank for several keywords can be more beneficial than dozens of pages ranking for similar terms. At the same time, if the search engines have difficulty crawling all your pages due to a poor site navigation strategy, then some pages won’t get indexed.
So, how do you improve navigation and SEO at once? Follow the proper structure for your site first, categories and subcategories on the retail page help customers find exactly what they need. A solid internal linking structure allows the crawlers to examine your website and index each essential page individually.
Keep navigation simple when designing a website for both UX and SEO potential.
2. User-Friendly Page Layouts
There are countless cases where poor layout design and formatting disrupts SEO potential. For example, cluttering a page with too much information makes it tougher to read and index. At the same time, if your pages aren’t attractive and easy to navigate, customers are more likely to hit the back button.
If customers come to a website and immediately leave it again, this tells the search engines that they’re not finding what they need on those pages. That means Google will bump you to a lower position on the SERPs.
So, how do you make your layouts more UX and SEO-friendly?
- Get your category pages right: Say you’re creating a blog page for your client. They want to list all of their blogs on one main page while linking to separate locations for each article. A design that puts a large chunk of content from each blog on the main page can be problematic for UX and SEO. It means your customers have to scroll further to find what they need. At the same time, the search engines never know which words to rank that main page for. On the other hand, listing blogs on smaller cards, as Fabrik does in this example, makes sorting through content easier.
- Leverage headers and tags: Your customers and the search engines habitually “scan” your pages. When trying to improve UX and SEO simultaneously, you must ensure that it’s easy to find crucial information quickly. Header 1 or H1 tags can help by showing your audience your website’s critical sections. Title tags also give search engines more information on the term you want to rank for. Organizing your content into a structure that draws the eye down the page also means your customers are more likely to stay on your website for longer. That shows the search engines that you have quality, relevant content.
- Make the most of images and videos: Visual media isn’t just an excellent way to engage your audience. With videos and pictures, you can convey more vital information in a quick and convenient format. This leads to greater satisfaction from your audience from a UX perspective. However, visual content is also great for SEO. You can optimize every image with alt text and meta descriptions. That means you have a higher chance of ranking both in the main search results and the image searches on Google.
3. Using Search Data to Inform Site Architecture
Today, SEO is less about building hundreds of landing pages for individual queries. Now, it’s more important to take a simple, de-cluttered approach with your website. SEO can determine what kind of architecture you need to create for a successful website.
For instance, say you wanted to rank for eCommerce SEO. There are tons of related words that connect to that primary search term. Rather than making dozens of different pages that try to rank for distinct phrases, you can cover a lot of other ideas at once with a larger, more detailed piece of content.
If a topic is too big to cover everything on a single page, then you might decide to create something called “pillar” content out of your main terms. This involves using one main page where you discuss all of the topics you will cover. Then, you design several smaller sub-pages that link back to that central pillar.
Once again, this helps the search engines to navigate your website and index your pages while assisting the customers in finding the correct information. At the same time, you combine more pages on a website and remove anything that might be detracting from your site’s authority or not offering enough value.
4. Improving Website SERP Listings
It’s easy to forget as a developer that a customer’s first experience with a website won’t always happen on that site’s homepage. Usually, when your customers are looking for solutions to a problem, they’ll find your website on the search engine results instead.
This means that you need to ensure that you make the right impression here:
There are a few ways that developers can ensure the search engine listings they create for their clients are up to scratch. For instance, a reasonable title tag for each page that includes appropriate keywords is excellent for SEO and UX. A title tag lets your customers know they’re in the right place and helps them find the information they need.
Remember, around eight out of ten users on search engines say that they’ll click a title if it’s compelling.
Another component you have control over as a developer or designer is the “rich snippet.” Rich snippets are the informative chunks of content that Google adds to a search listing to help it stand out. You can use rich snippet plugins on a website to tell Google what kind of extra information you want to include on a page.
For instance, you might want a company’s ratings to show up on your search results, so customers can see how trustworthy they are:
5. Local Business Rankings
When you’re creating a website for a company, it’s easy to forget about local rankings. We see the digital world as a way of reaching countless people worldwide. Local orders are easier to overlook when you have a global scope to work with.
However, as a developer, you can boost a company’s chances of attracting the right local audience and boosting its credibility. For instance, you can start by ensuring that the correct directory information appears on your client’s website and social media profiles.
Another option is to create dedicated location pages for each area the company serves. This will make it easier for clients to find the contact details they need for their specific location.
At the same time, pages that have been carefully optimized to rank for specific locations will earn more attention, specifically from search engines. The more of the search engine landscape your client can cover, the more chances they have to attract new customers and leads.
Combing SEO and UX
In a world where experience is crucial for every business, it’s no wonder that UX and SEO are blending more closely together. There are a lot of areas where SEO and UX work in harmony together if you know where to find them. Improving your client’s SEO ranking with UX doesn’t just mean ensuring that their pages load quickly anymore.
Simple strategies, like making sure a call-to-action button is clickable on a mobile page, can simultaneously boost a website’s UX potential and SEO performance. At the same time, adding images and alt text to a website provides search engines with more information while adding context to your content.
The key to success is understanding how SEO and UX work together. If you look at SEO and UX as part of the same comprehensive strategy to give end-users a better online experience, achieving the right design goals is much easier.
Of course, just like any strategy, it’s also worth making sure that you take the time to track the results of your UX and SEO campaigns. Examine which systems help you, and examine customers from an SEO perspective with design and development strategies.
Features image by gstudioimagen on Freepik
The post 5 Ways That UX Developers Influence SEO first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.

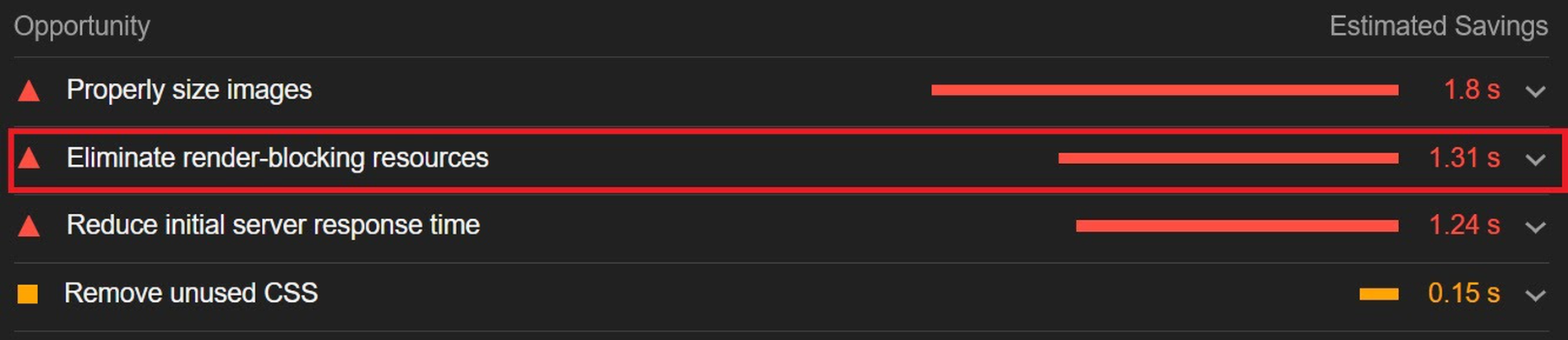
 Users expect websites to load quickly. As a result, companies like Amazon and Target spend millions of dollars optimizing their sites to make them load as fast as possible because there is a direct correlation between site speed and conversions.
Users expect websites to load quickly. As a result, companies like Amazon and Target spend millions of dollars optimizing their sites to make them load as fast as possible because there is a direct correlation between site speed and conversions.
 Many websites today use some type of traditional Content Delivery Network (CDN), which means improvements in website load times, decreases in bandwidth, and better redundancy and security. But not everything is optimized, specifically when it comes to images, and image CDNs can help with that!
Many websites today use some type of traditional Content Delivery Network (CDN), which means improvements in website load times, decreases in bandwidth, and better redundancy and security. But not everything is optimized, specifically when it comes to images, and image CDNs can help with that! 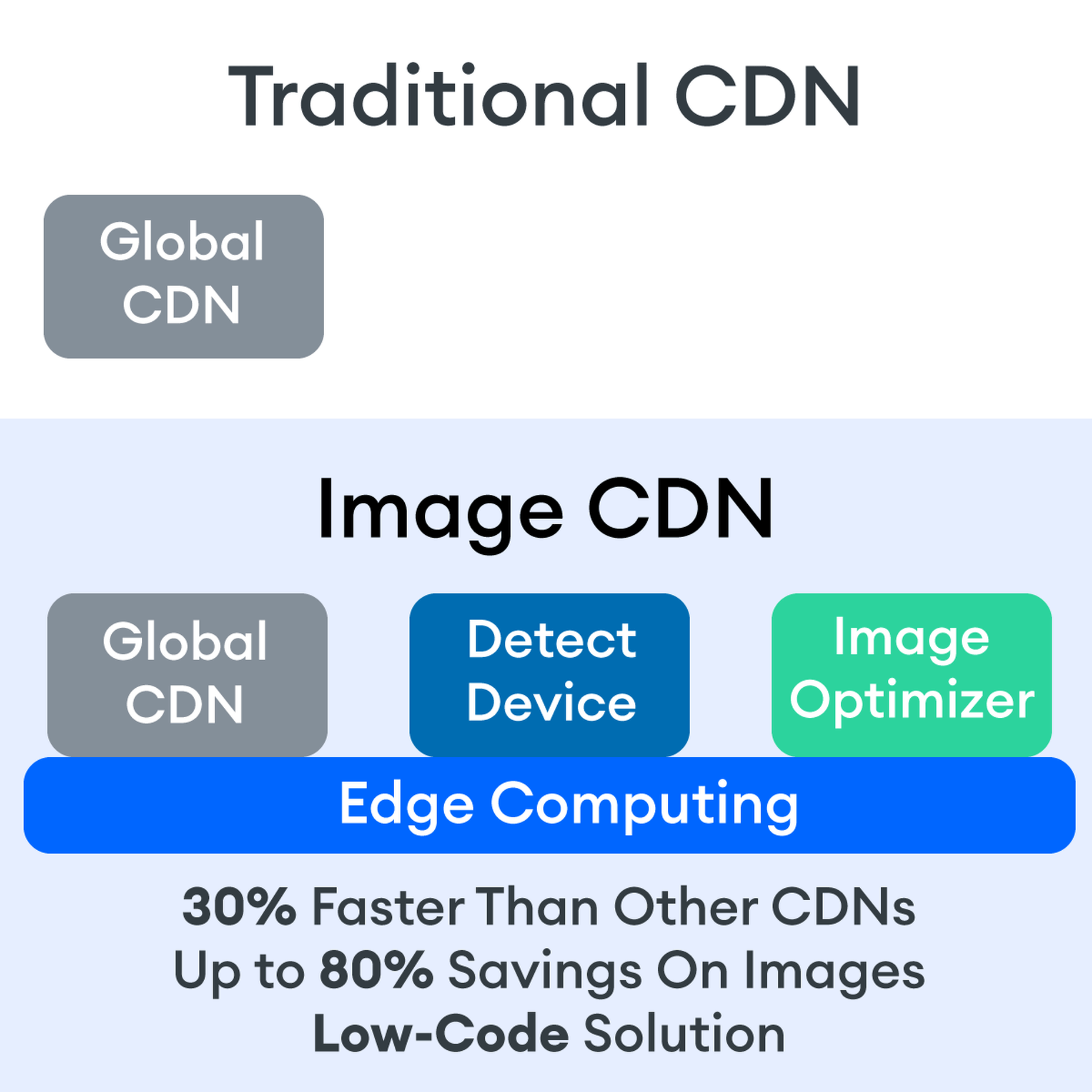
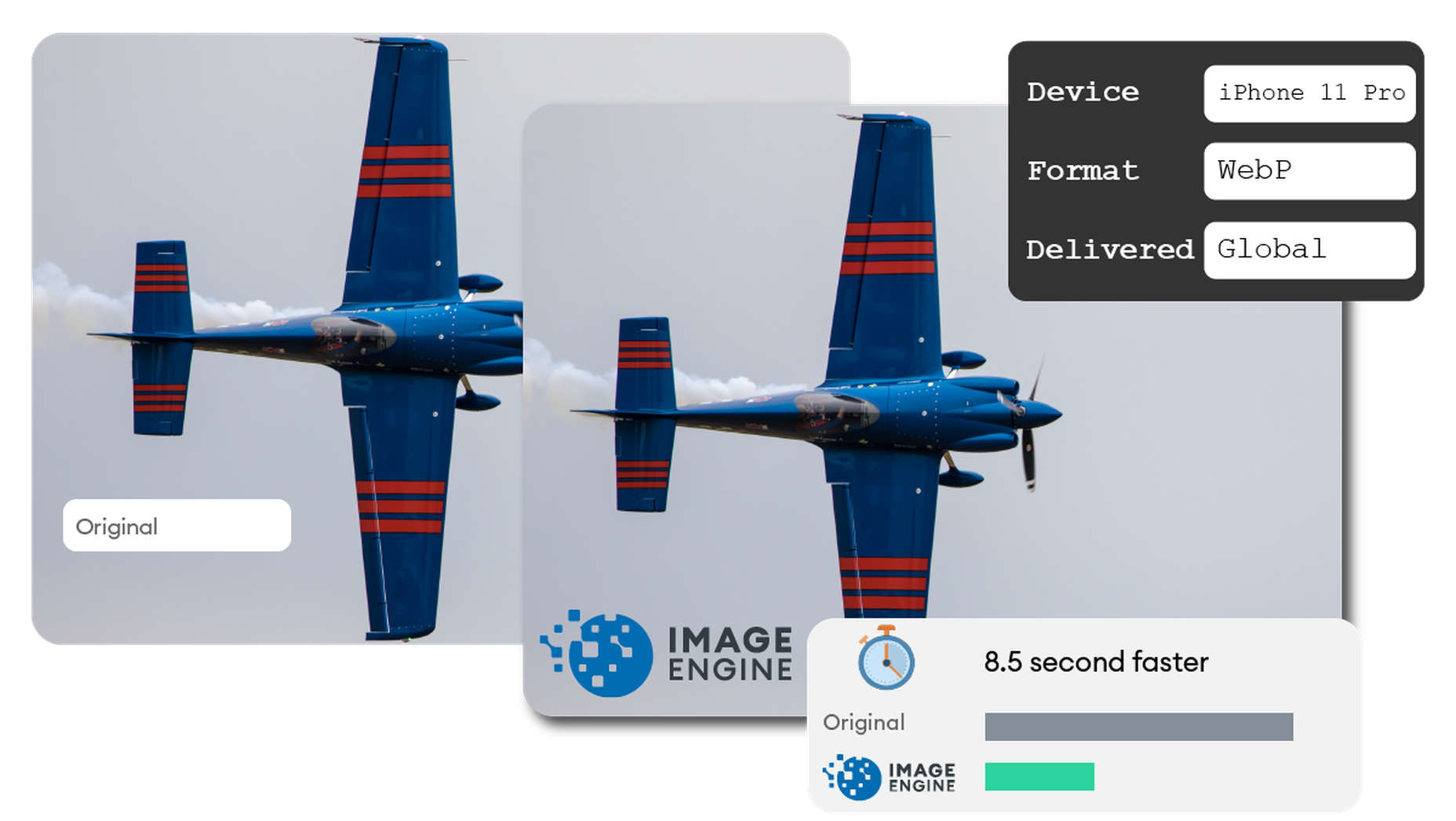
 1, 2, 3 – That’s exactly how long it takes you to start losing visitors if you have a slow-loading website.
1, 2, 3 – That’s exactly how long it takes you to start losing visitors if you have a slow-loading website.