The best free online coding websites for beginners are hubs of education and insight, designed to take your knowledge and career to the next level.
The best free online coding websites for beginners are hubs of education and insight, designed to take your knowledge and career to the next level.
For years, technical careers have been gaining more attention among innovative individuals. In a digital world, people capable of speaking computer language often have the widest selection of job opportunities. However, before you can start leveraging the blossoming job market, you need to hone your skills. That’s where free coding websites come in.
A free online coding website is an environment where you can develop your understanding of various kinds of code, update your programming prowess, and even earn certifications. Today, we’re going to be looking at some of the most impressive coding websites on the market.
Coding Careers: Opportunities in 2021 and Beyond
Before we leap into our overview of the best free coding websites, let’s examine why it’s so important to invest in your coding role. Looking at the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, we see that coders earn an average of $89,190 per year.
Elsewhere, CompTIA notes that technology hiring has accelerated since the end of 2020, with up to 391,000 new positions opening in the US during December.
Though coding careers have been popular for some time now, they have particularly high value following the pandemic, as companies worldwide adapt to the changes associated with remote workforces, digital customer service, and ecommerce. The pandemic has made us more reliant on technology than ever before, as a result:
- Coding skills are in high demand: Coding skills are essential for the newly digital world. Studies find that the pandemic has accelerated digital transformation by around 7 years. Companies need coding professionals to stay ahead of the curve.
- Coding knowledge is becoming more versatile: Companies are looking for coding skills in more than just programmers. They want their data analysts, IT workers, artists, designers, and other professionals to have these talents too.
- People with coding talent can earn more: Jobs requiring coding skills tend to pay more than those that don’t. This reveals the growing need for coding knowledge in the digital ecosystem.
Coding skills provide an avenue to tech professionals for higher-income jobs, and these careers are growing faster on average than other job opportunities.
The Best Websites for Learning to Code
Learning to code or developing your existing coding skills can help you to unlock a host of new opportunities. Today, you can learn coding online for free, just by visiting the right websites.
Even a basic knowledge of coding can drive a range of results, such as helping to support the better management of websites, reducing reliance on outside developers, and opening the door to app development. So whether you want to start a new career or upgrade your existing knowledge, these sites will help:
BitDegree
BitDegree is a wonderful website for anyone interested in web development, coding, data science, and programming. There are various courses to choose from, depending on the career path you want to take. For instance, you can learn about the AWS cloud or start your journey into gaming development. For coding, BitDegree covers languages like:
- CSS
- HTML
- PHP
- SQL
- JavaScript
- jQuery
The best thing about BitDegree is how it makes learning so fun. There are gamified courses and sections where you can really dive into the essentials of coding. In addition, the online coding course collection often features hundreds of discounted options for people on a budget.

CodeAcademy
One of the most popular sites for learning how to code for free, CodeAcademy is home to over 24 million students who have built their skills. The interactive learning approach lets you apply what you’ve learned immediately. Over 300 million hours of free coding content are available to check out at your leisure. Like most coding platforms, you can learn languages such as:
- CSS
- JavaScript
- HTML
- PHP
- jQuery
- Python
- PHP
- Ruby
CodeAcademy is particularly effective for beginners because you get instant feedback after submitting your coding efforts. When you make mistakes, you’ll find out exactly where you went wrong, allowing you to avoid similar mistakes in the future.

Codewars
Codewars by Qualified is definitely one of the most versatile free platforms for learning how to code. There are dozens of languages you can learn – too many to list right here. Options range from C++ and C# to Ruby, Python, Lean, Java, PHP, Scala, and countless others.
Codewars teaches you your programming language in-depth by selecting challenges designed to put your mind to the test. The goal for each challenge is to help you sharpen your knowledge over time, with tasks that get progressively more difficult over time.
The cool thing about Codewars is it allows you to see how you respond to challenges compared to how other coders have tackled the same issues.

Code.Org
Designed for a younger community of would-be coders, Code.org is an engaging and highly accessible introduction to coding. With around 60 million students worldwide, the Code.org platform gives you access to a wide range of different learning opportunities intended to suit different needs and learning levels.
The Code.org environment is built on a desire to bring coding into the standard curriculum. You can dive into full one-hour tutorials, or you can experiment with a more structured approach to learning, which is ideal for people with different learning styles. There’s also a huge catalog of courses extending from basic coding for younger kids all the way to University-level education.

Free Code Camp
A diverse option in our free coding website list, Free Code Camp is all about developing your coding knowledge while simultaneously networking with other like-minded people in the industry. The solution allows you to learn coding by participating in challenges – which is ideal if you want to put your skills to the test as soon as possible.
To help you jump in, you’ll have access to a range of courses and tutorials designed to help you understand and overcome each challenge. You can even code for non-profits on the platform and build tradeable projects in languages like:
- HTML5
- Javascript
- Node.JS
- CSS3
- React.JS
- Databases
- Git
If you’re a little nervous about the concept of coding alone, you’ll have a full community to work within the Free Code Camp. You might even meet someone you can work with in the years ahead.

Code Conquest
Code Conquest is less of a course website and more of a comprehensive guide for beginners diving into the world of code. This amazing platform will help you understand all of the basics of coding in no time – even if you’re brand-new to the landscape. You can find out what coding is all about, learn which languages are best to learn for your needs, and more.
The website is full of resources for all kinds of coders, including comprehensive tutorials, reviews, a knowledge center, training packs, and more. You can even choose from a range of languages like:
- CSS
- HTML
- PHP
- jQuery
- Ruby
- JavaScript
- Python
- MySQL
To help you figure out where you should get started, the Code Conquest website also gives you recommendations on which tutorials to take next.

W3Schools
One of the better-known free websites for coding on the market today, W3Schools is an environment packed full of example codes, resources, tutorials, exercises, and libraries to help you learn how to code. The site is one of the largest in the world for developers.
To begin coding with W3 Schools, you’ll need to choose the programming language that’s right for you, then either jump into the program immediately or select from a range of learning options. The site comes with a handy quiz to help you define your knowledge level.
Languages range from CSS to SQL, JavaScript, HTML, Python, Java, C++, and many more.

Code Avengers
Code Avengers offers a fun and interactive approach to learning how to program and code. There are various course options to teach you how to create everything from games and apps to entire websites. The good thing about the Code Avengers website is you don’t need a lot of spare time to start learning. Each course takes around 12 hours to complete.
You can choose from languages like HTML, CSS, Python, jQuery, JavaScript, and more, and connect with a wide selection of similar coding enthusiasts, just like you. The biggest downside is that the free trial only lasts for seven days before you’ll need to pay to use the full program.

The Code Player
A simple and effective website for learning how to code and building your existing skills. There are tons of videos and demos to walk you through the process of learning how to code from scratch. All you need to do is click on one of the things you want to learn how to do, like creating a simple web page, and the site will give you a video walkthrough.
Though a little simple compared to other coding resources, the Code Player still has a lot of great video guidance to help beginners jump into various languages. For example, you can learn about CSS and HTML or check out various tools to help you make a more effective website.

CodeGym
If you’re particularly interested in learning about Java, the CodeGym is probably the website for you. This online Java programming course teaches you the basics of Java by allowing you to dive into various tasks. You can get involved with various exercises depending on your existing skill level and play around with games designed to teach you more about the coding landscape.
This website is fantastic for people in all stages of the coding journey. Whenever you suggest a solution to a challenge, the website will give you immediate feedback to learn from. There are more than 500 hours of Java coding exercises and educational resources to explore.

The Odin Project
One of the better-known free coding websites on the market, the Odin Project aims to take the headaches and frustration out of learning web development. If you’re a beginner looking to develop a career in coding, then the Odin Project will give you all the pieces of the puzzle required to decide exactly where you want to go and build the appropriate skills.
This site offers a full-stack curriculum of coding education options, with tons of challenges, tasks, and exercises to help you put your newly gained knowledge to the test. You’ll learn how to program in languages like CSS and HTML, explore the basics of JavaScript and Ruby, and even get tips on how to get hired when your skills are maxed out.

Plural Sight
Previously known as Code School, Plural Sight is a fantastic online learning platform that allows you to build your knowledge through a range of paid and free courses. The comprehensive platform is organized into a wide selection of different learning paths. You can choose how you want to develop your skills based on your chosen language and your existing skillset.
You choose an education path created by professional instructors to achieve specific outcomes, and Plural Sight gives you all the material you need. You can also practice what you’ve learned during the course in your browser and get immediate feedback on what you need to work on. There’s even a gamification aspect that allows you to earn points for every course level you complete.

MIT Open Courseware
Imagine how amazing it would be to get accepted to MIT to learn your new coding skills? What if you didn’t have to go through the headache of an official application. If you have a computer and internet access, you can explore MIT’s course material easily through the MIT Open Courseware website. This dedicated website gives you an insight into all of the courses and materials learned by students at MIT.
You can browse through all the courses available in the programming landscape and filter through results based on things like course features. For instance, you might specifically look for courses with their own online textbook, lecture notes, and videos. It’s a great way to get an insight into how one of the most reputable universities in the world offers coding education.

Web Fundamentals
We’ve already looked at a website offering coding resources specifically for Java, now let’s take a look at one designed for HTML5. Launched about 11 years ago as HTML5 Rocks, the Web Fundamentals website is packed full of tutorials, resources, and insights into the most recent updates to HTML5. This open-source environment allows developers and programmers to really get active with their skills.
You can play around with some of the code already available on the website, and explore tutorials authored by a range of amazing individuals. Although these courses are very comprehensive, it’s worth noting that they might not be the perfect choice for true beginners, as the tutorials can be more complex than most.

Dash General Assembly
If you’re keen to learn the essentials of coding in some of the most popular languages, like CSS, JavaScript, and HTML, then Dash General Assembly is the site for you. This website offers fun and free courses which will guide you through the basics of web development. You even get interactive tasks and challenges you can leverage within your browser, with no downloads required.
Users learn how to do a range of amazing things with this website, including how to code HTML5, build a beautiful website, and balance your layouts for aesthetic appeal and usability. You can even design dynamic interfaces where you can add aminations and effects. Dash General Assembly is a fantastic tool for anyone keen to get started in the world of coding.

Codeasy.net
Finally, Codeasy.net promises beginners a fast and simple way to start learning how to code, while having plenty of fun. This exciting website immerses you within a digital story which takes you on an adventure through the basics of coding. You’ll need to learn real-life coding skills to navigate your way through the rest of the story, which means you can develop your C# knowledge as you go.
This is one of the more unique tools for learning how to code that we’ve found so far. It’s a great way to discover the basics of C# without being bogged down in boring lectures. Remember, though, this website is intended for complete beginners, so you might find it a little basic if you already know some of the coding essentials.

Free Websites for Learning to Code
Free coding websites are an excellent way to develop your skills and unlock new opportunities in the world of coding. If you’re keen to jump into a new career as a programmer or coding developer, make sure you check out some of the options above. There’s no doubt you’ll find a site capable of giving you the boost you need.
Featured image via Unsplash.
Source
The post 16 Free Websites for Learning to Code in 2021 first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.

Source de l’article sur Webdesignerdepot
 Websites as we know them are going to change very soon. The days of text, images, and basic interactions in a 2D browser window have served us well, but virtual, augmented, and mixed reality experiences are getting better all the time. Developers and designers need to think beyond the browser window and prepare for an immersive future.
Websites as we know them are going to change very soon. The days of text, images, and basic interactions in a 2D browser window have served us well, but virtual, augmented, and mixed reality experiences are getting better all the time. Developers and designers need to think beyond the browser window and prepare for an immersive future.
 As a UX designer, you get to work on creative, rewarding, even life-changing projects. It’s an industry with flexible working and countless opportunities. All this, and you get paid well too.
As a UX designer, you get to work on creative, rewarding, even life-changing projects. It’s an industry with flexible working and countless opportunities. All this, and you get paid well too.
 Not so long ago, customers only had a couple of ways to interact with brands.
Not so long ago, customers only had a couple of ways to interact with brands. 
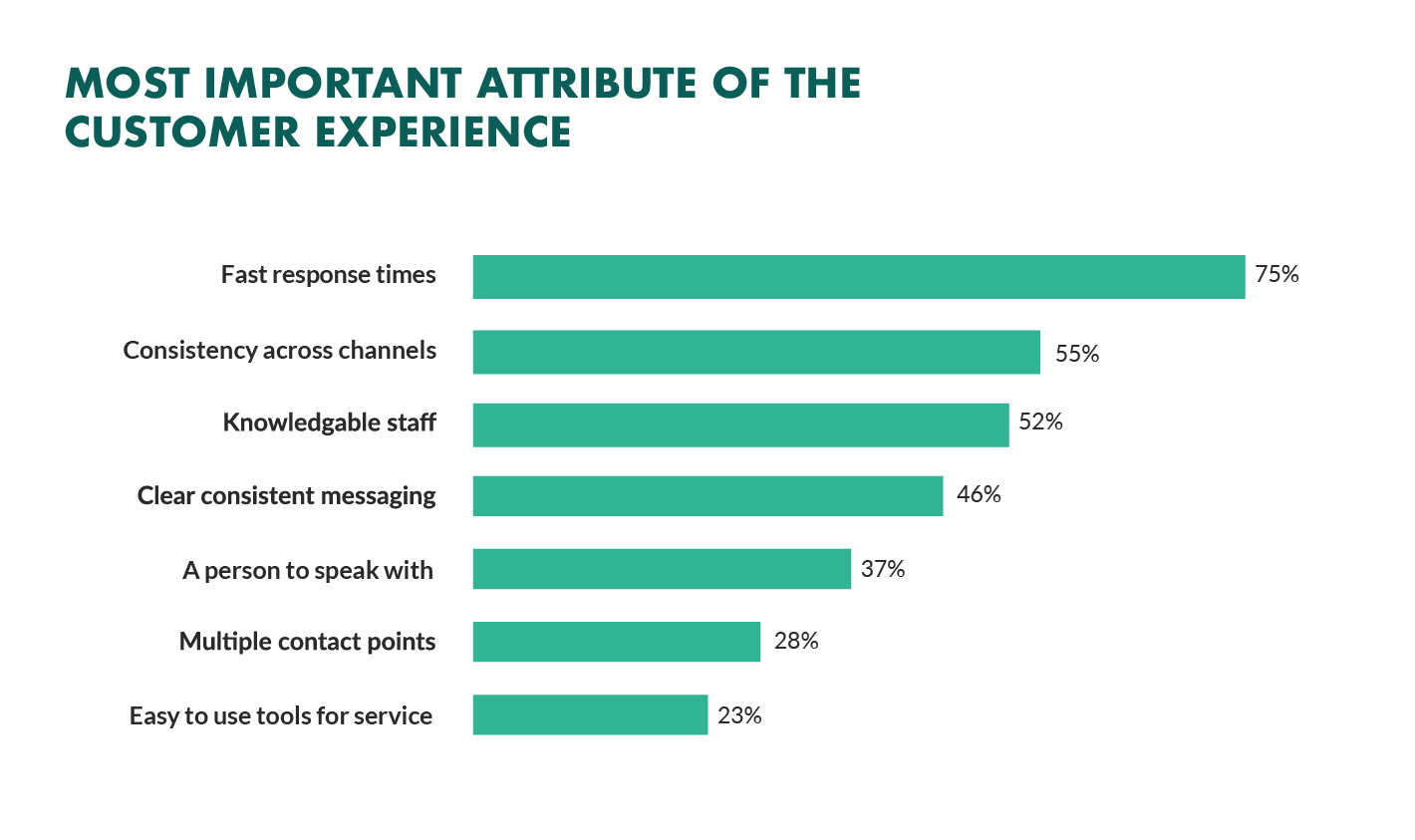

 We all want a little more fun and games in our lives. So, why not add some gamification to your next interactive content campaign?
We all want a little more fun and games in our lives. So, why not add some gamification to your next interactive content campaign?




 The best free online coding websites for beginners are hubs of education and insight, designed to take your knowledge and career to the next level.
The best free online coding websites for beginners are hubs of education and insight, designed to take your knowledge and career to the next level.
















 On June 29th,
On June 29th, 

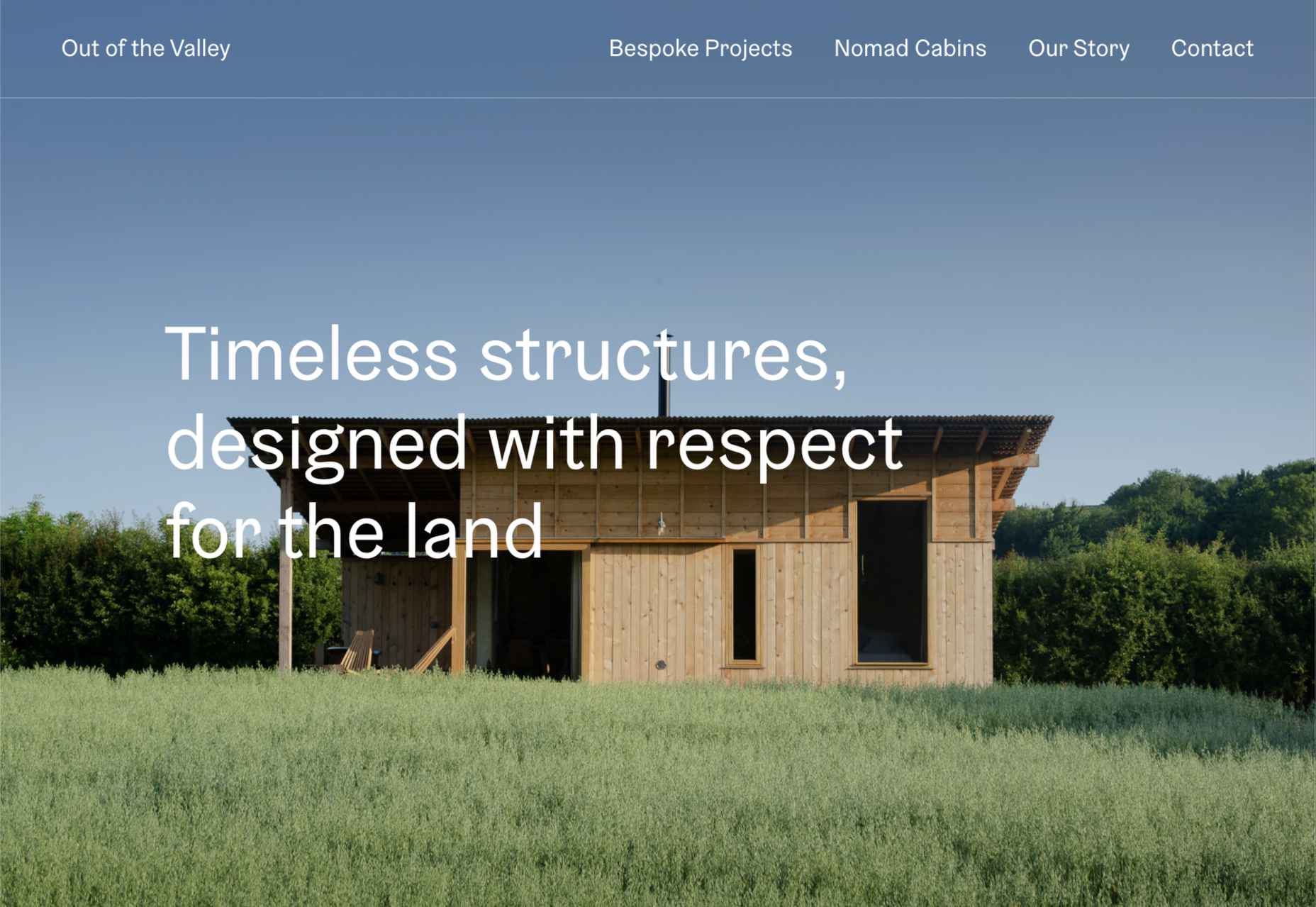
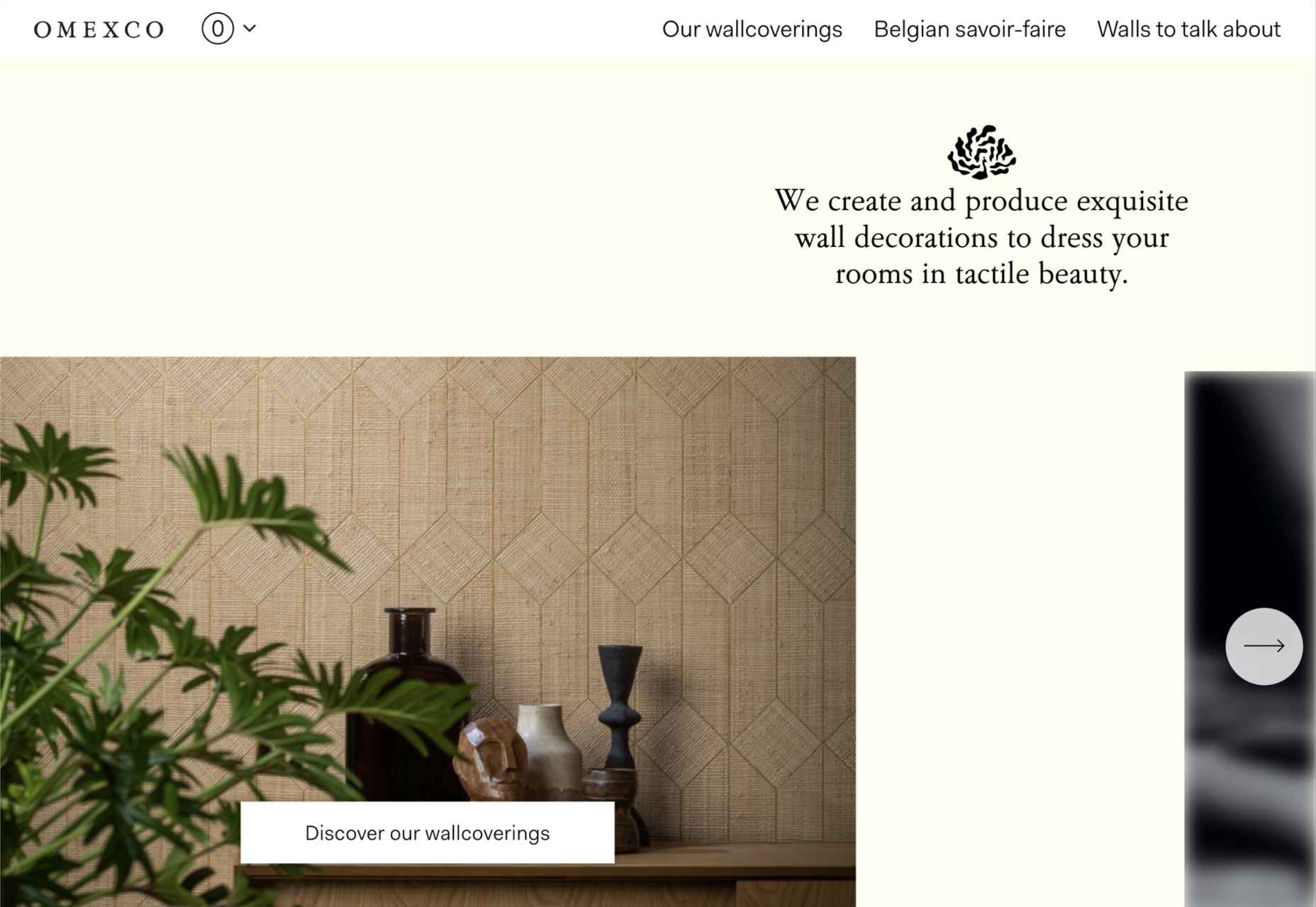
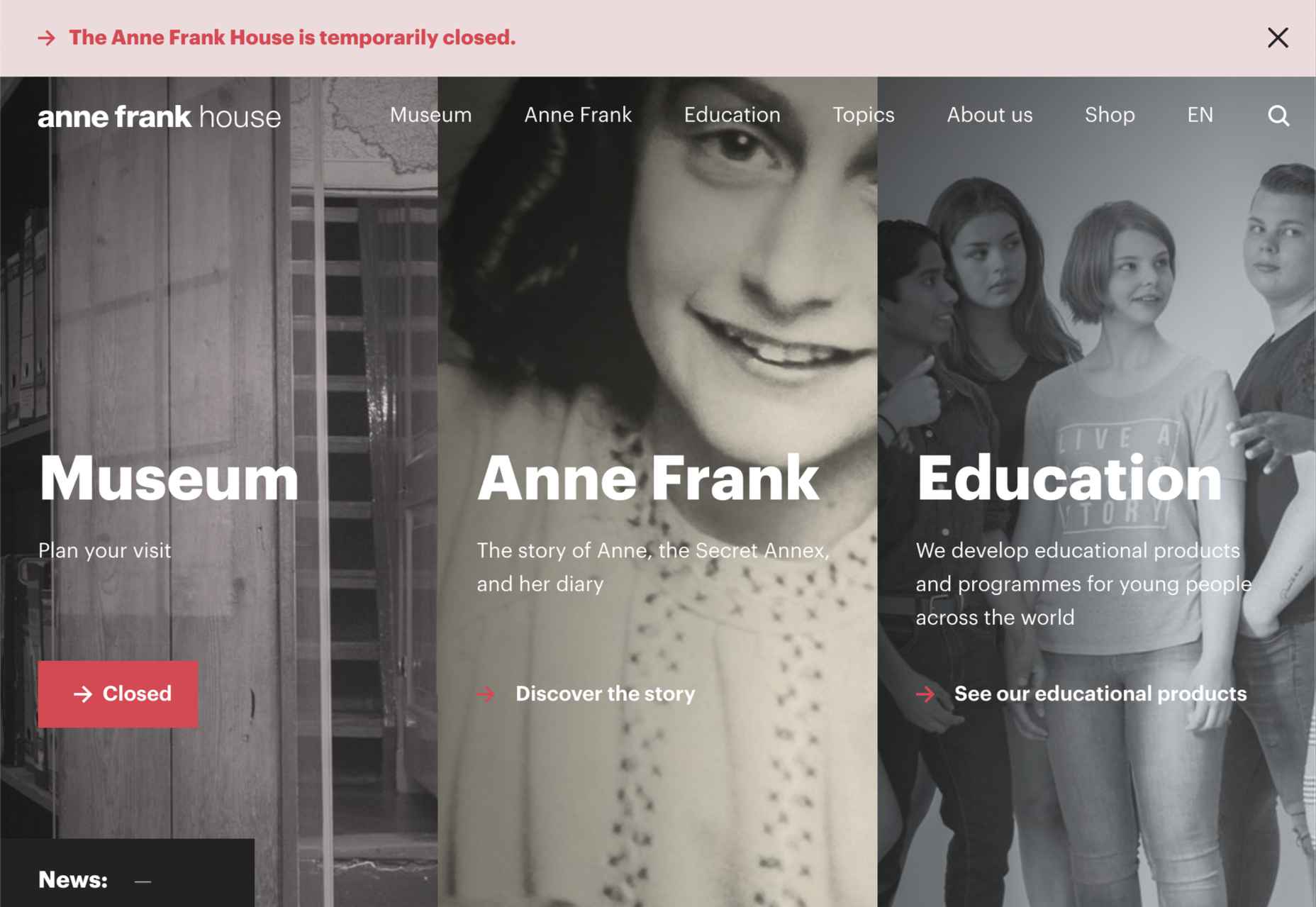
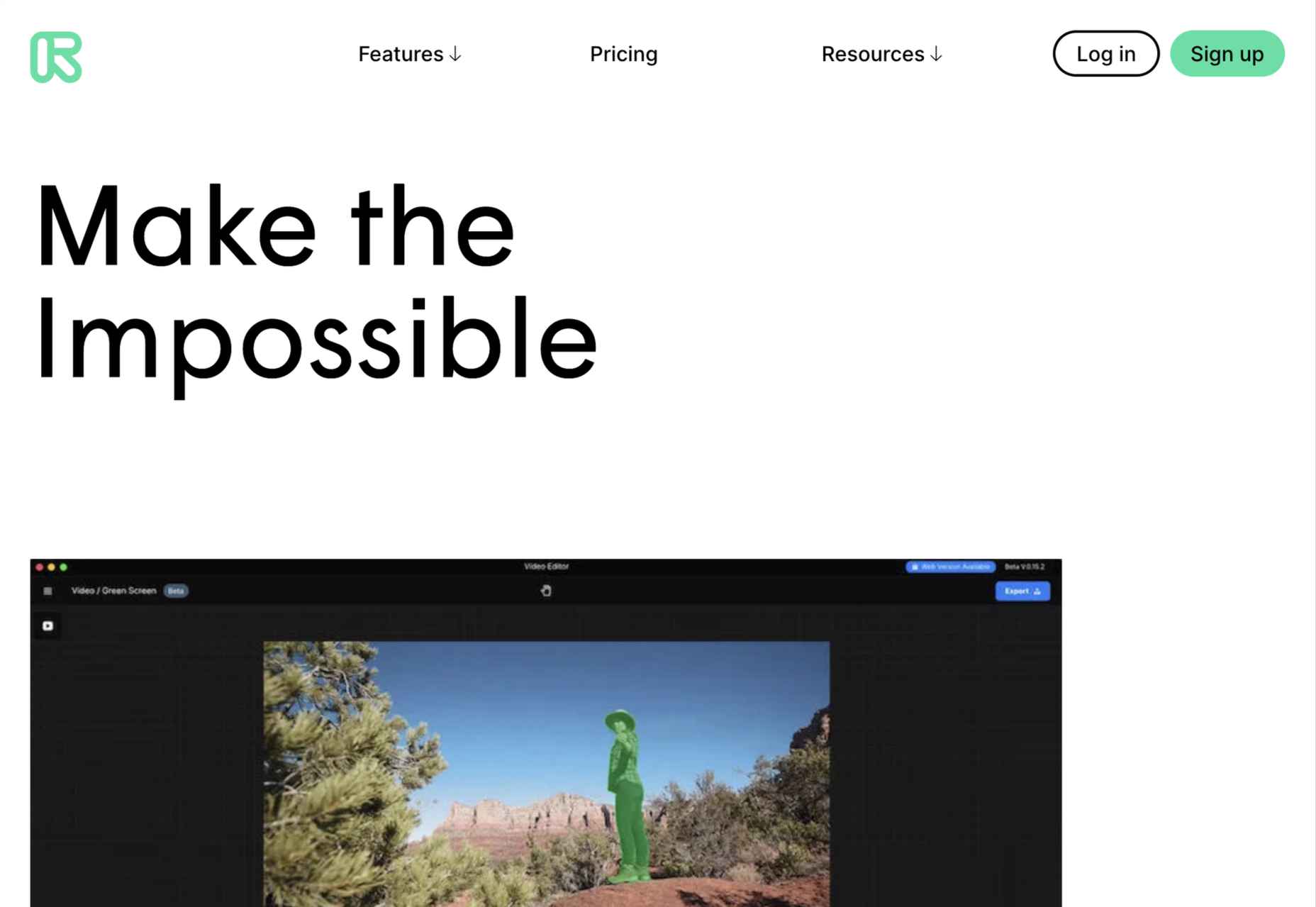
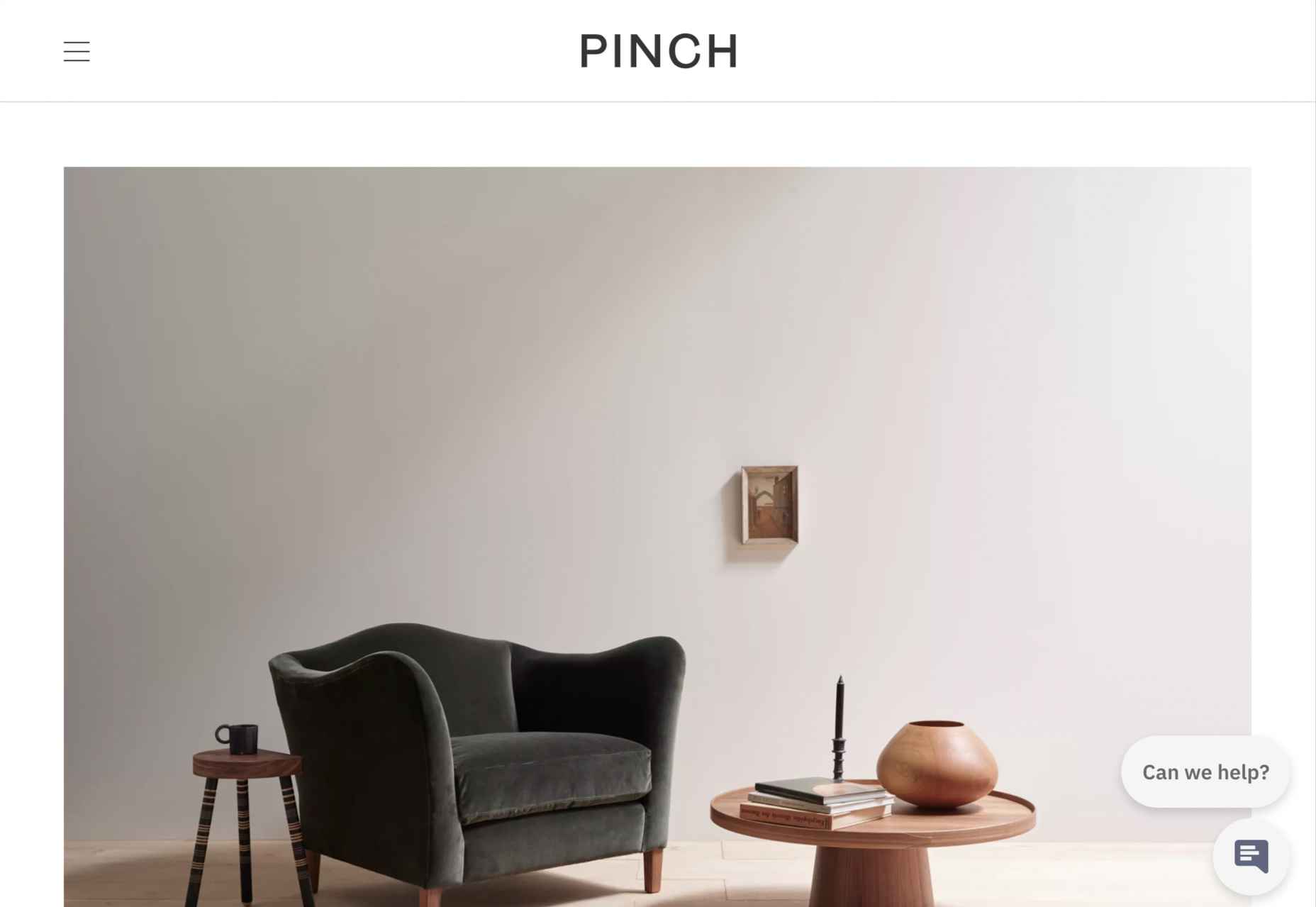
 This month’s collection contains a combination of big and bold, and clean and minimal. Although basic minimalism is still trendy, with lots of white space and greyscale type, we are seeing it softened with color. This is implemented differently, ranging from hints of off-whites in images to gentle pastels as section backgrounds.
This month’s collection contains a combination of big and bold, and clean and minimal. Although basic minimalism is still trendy, with lots of white space and greyscale type, we are seeing it softened with color. This is implemented differently, ranging from hints of off-whites in images to gentle pastels as section backgrounds.