 A career as a web designer can be extremely lucrative. The average web designer in the US makes around $50-55,000 per year, equating to an hourly rate of around $25. Of course, not every designer will automatically get a full-time, high-paying job as soon as they earn their web design credentials.
A career as a web designer can be extremely lucrative. The average web designer in the US makes around $50-55,000 per year, equating to an hourly rate of around $25. Of course, not every designer will automatically get a full-time, high-paying job as soon as they earn their web design credentials.
Sometimes, you might need to generate a little extra cash, perhaps to supplement your part-time income or keep the lights on while you’re taking some new courses. You can even use your web design skills to earn some extra money on the side while working a standard 9-to-5.
Today, we will be looking at some of the most effective ways to make extra cash on your web design skills.
1. Freelance
Starting with the simplest option, working as a freelancer is one of the best ways to start making cash with your design skills. There are dozens of websites out there to help freelancers find clients these days. Some of the best options include:
- Toptal: For web developers, designers, and software experts;
- Upwork: For all kinds of design freelancing;
- 99Designs: Excellent for selling your designs whenever you like;
- Dribbble: Display your work and find new clients;
- Behance: Sell everything from animations to videos;
- Envato Studio: Sell packages for web design.
As a freelancer, you’ll be able to choose which hours you want to work, and which projects to work on. You can make money from all kinds of design skills this way, from making pages for a website to designing widgets and applications.
However, you’ll also be responsible for tracking down potential leads, building your portfolio, and managing your own taxes, so keep this in mind.
2. Sell Design Assets
As a web design professional, you’ll end up with a lot of assets over the years. Whether you’re working freelance or full-time, not every asset you create is going to be picked up by your customers. Sometimes, you’ll end up with unused content sitting on your computer.
Fortunately, you can leverage these assets for some extra cash. You can sell things like icons, backgrounds, UI assets, and more. You can even sell themes on sites like ThemeForest if you’ve built something your clients weren’t happy with.
There’s a market out there for just about every asset, from icons and PSD templates to documents, fonts, UI assets, backgrounds, and brushes. You might even build your own website where you can sell assets in the future.
3. Design and Sell NFTs
Feel like getting in on the cutting-edge of a new marketplace? NFTs are probably one of the hottest topics in the digital world today. As concepts like Web 3.0 and the metaverse gain traction, NFTs will only become more valuable.
Countless companies and innovators are looking for people to design their NFTs for them these days. If you don’t mind dedicating some of your free time to creating digital graphics, you’re in for a significant amount of earning potential.
If you learn enough about the NFT landscape and blockchain, you could even create your own NFTs. However, this would probably require a lot of time and research. You can learn more about the NFT design and art landscape here.
4. Become a Consultant
Don’t have time to build endless new websites right now? No problem, just help other people build their sites instead. Consultants are people in any industry with expertise and insights they can share to support other people. As a web design consultant, you can offer your expertise to other upcoming freelance designers or business leaders.
You’ll need to invest some time into building your personal brand as a consultant. This means developing your social media pages (like LinkedIn) and creating a portfolio. It also helps to have an air of thought leadership. This usually means you’ll need to share at least some content online.
Consulting can be an excellent way to share your skills with other people without having to do all the work of building a design course.
5. Teach Web Design
On the other hand, if you like the idea of being a teacher, you can make money almost passively with web design courses and webinars these days. While you do have the option of selling one-on-one education to students, this will usually take up a lot of your time.
If your focus right now is on a side hustle to increase your earnings, it’s often much easier to use a site like Udemy or Skillshare. The great thing about teaching web design these days, it’s much easier than you might expect. The majority of solutions on the web allow you to drip content to your clients automatically. This means you only have to create the content once.
You can create a handful of videos, quizzes, and downloadable assets, and make money off your educational resources while you sleep.
6. Create a Web Design Blog
Blogging is still a surprisingly lucrative way to make money. If you have a creative streak and you know how to write about web design in a way other people can understand, you can turn this into an excellent side hustle.
Start by building your own website using your design skills, then start publishing regular blogs with the content you know your customers would be interested in. It’s a good idea to cover a range of topics, from Photoshop, to how to design widgets and more. You can even share reviews of various web design tools and add affiliate links to earn money that way.
Make sure you use SEO strategies to improve your chances of customers actually seeing your blog and promote your content as often as you can across social media. Once you have your blog, you can make money from it by:
- Working as an affiliate and promoting design products;
- Showing banner ads or sponsored posts on your website;
- Selling digital products through your blog (like themes).
If you decide to take the affiliate route, here are some excellent programs to consider.
7. Contribute to other Websites
If you don’t have time to launch your own website and build a following for your blog, you can still make money from writing in other ways. Becoming a freelance web design writer means you can sell your blogs and content to other leading publications.
Many popular websites are constantly looking for new content to add to their blog. If you develop a strong relationship with some of these site owners, you could get yourself a regular gig.
Contributing to other sites as a writer helps you to develop your thought leadership. Many companies will even allow you to link back to your social media pages or profile.
At the same time, you get to earn some extra money writing about things you enjoy.
8. Sell Themes and Templates
A lot of web designers today rely on other themes and templates created for WordPress to help them build their websites. Access to themes and templates can make building a new website a much easier, straightforward process.
If you’ve got some excellent coding prowess, you can develop and sell a host of website themes and templates, and sell them wherever you choose. As mentioned above, there are a number of websites available for selling web design assets. Alternatively, you can sell your own packages and templates on your website, depending on your needs.
If you create a particularly valuable theme, you can actually earn a full-time passive income over time. Placing your themes and templates on marketplace sites will also get you a lot of attention from potential clients in the future.
9. Flip Websites
If you’ve ever seen one of those shows where someone buys a house, makes it look great, and then sells it for a higher price, you’ll understand the basic premise of flipping websites. The idea is to purchase an existing website for a low price (preferably with a good domain name), then fix it up to sell on a website selling directory.
If you want to earn a decent amount of money for your website, you’ll need to dedicate a decent amount of time to building traffic, improving the appearance of the site, and so on. However, it can be fun to take on these projects in your free time if you’re looking for a way to hone your skills.
You might learn some important lessons about how to make websites more profitable while you’re flipping your various sites, which could make you more appealing to customers in the long term.
10. Write a Book
Similar to flipping websites or producing an income from a high-traffic blog, writing a book isn’t something that’s going to give you a lot of extra income overnight. However, it can be an excellent source of passive income in time if you know how to use this strategy correctly.
If you have a specialist skill in web design, or you serve a specific niche, you can generate a lot of attention for an eBook or physical book sharing plenty of accurate and specific information. Remember, writing about web design, in general, will usually make it harder to earn money because there’s already a lot of competition out there.
Writing a book is a fantastic way to create a possible extra source of income as a side hustle, and it can also make you more credible if you decide to go full-time with your web design skills in the future. It’s definitely more impressive to present yourself to clients as a published author.
Remember to advertise your book whenever you can to improve your chances of additional sales.
Find Your Side Hustle
Web design skills are highly sought after in various parts of the digital world. If you’re willing to devote a little time and creativity to exploring the various avenues above, they can all deliver an excellent source of income to you and your potential business. All you need to do is figure out which side hustle makes the most sense for you.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all. In some cases, you might even be able to run multiple side hustles at the same time, particularly if you’re using strategies for passive income, like writing your own book or selling your own course.
Featured image via Unsplash.
Source
The post Side Hustles for Web Design Professionals: How to Make Some Extra Cash first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.
Source de l’article sur Webdesignerdepot
 There were mixed reactions on Thursday morning when Adobe announced it had acquired Figma.
There were mixed reactions on Thursday morning when Adobe announced it had acquired Figma.
 Last week,
Last week, 
 Moving from studying design into
Moving from studying design into 
 Are you a creative person looking for the perfect career path to take? If so, there are not many more creative professions than that of a web designer.
Are you a creative person looking for the perfect career path to take? If so, there are not many more creative professions than that of a web designer.
 A career as a web designer can be extremely lucrative. The average web designer in the US makes
A career as a web designer can be extremely lucrative. The average web designer in the US makes
 Designing for user experiences is what all designers do. UX is often thought of as the preserve of app or web designers; however, even a print designer laying out a magazine anticipates reader reaction to the scale of type, the placement of adverts, and the art direction of successive stories.
Designing for user experiences is what all designers do. UX is often thought of as the preserve of app or web designers; however, even a print designer laying out a magazine anticipates reader reaction to the scale of type, the placement of adverts, and the art direction of successive stories.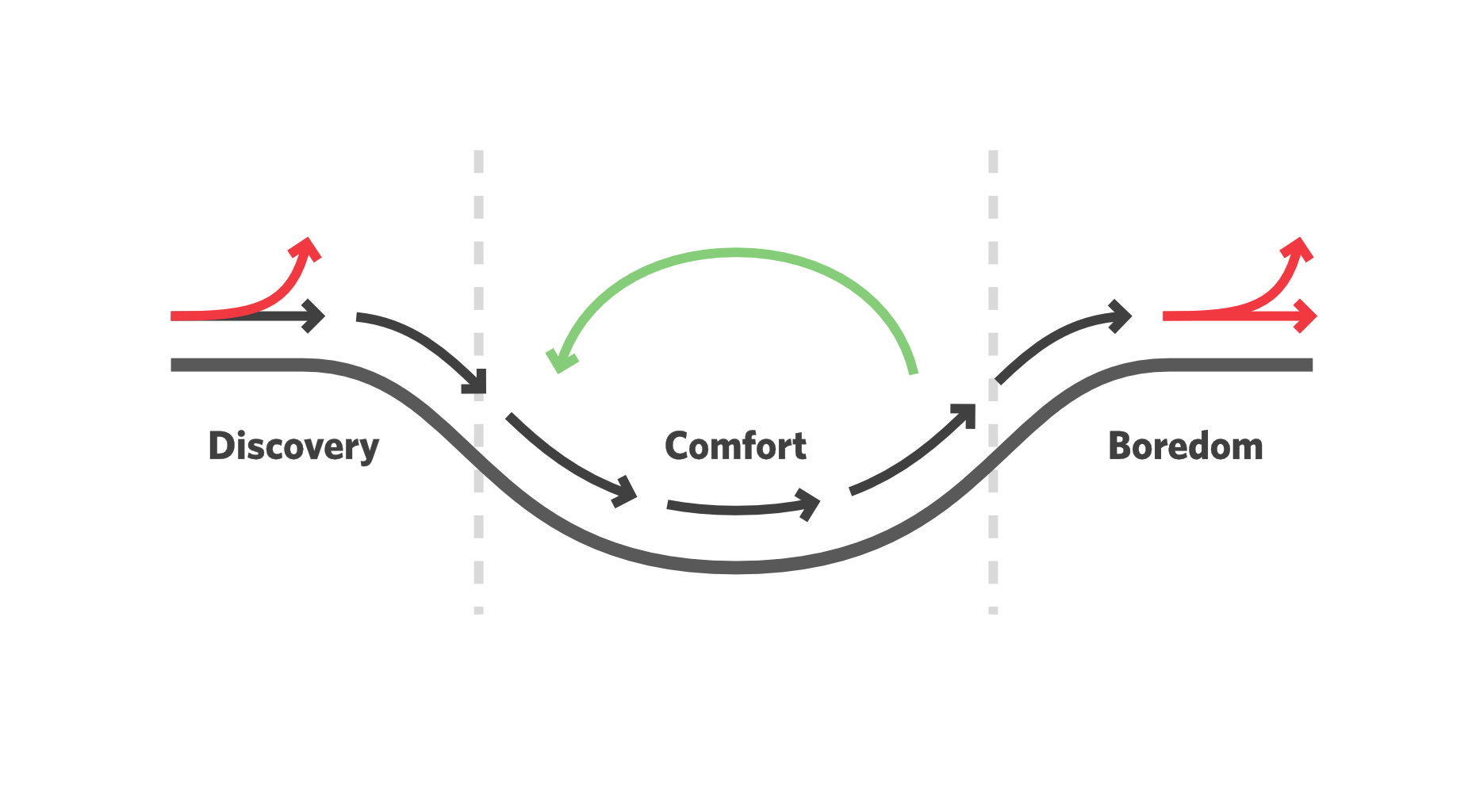

 Whether you are looking for comprehensive tutorials on UX design or professional courses on topics like logo design, video or photo editing, there’s the perfect YouTube channel for you as a designer.
Whether you are looking for comprehensive tutorials on UX design or professional courses on topics like logo design, video or photo editing, there’s the perfect YouTube channel for you as a designer.

 No one likes talking about money. Most of us got into web design because we loved it. But the fact is, we’ve all got bills to pay.
No one likes talking about money. Most of us got into web design because we loved it. But the fact is, we’ve all got bills to pay.
 For decades Artificial Intelligence has been a focus of best-selling science fiction authors and an antagonist for blockbuster Hollywood movies. But AI is no longer relegated to the realm of science fiction, it inhabits the world around us. From the biggest enterprise companies to plucky startups, businesses everywhere are building and deploying AI at incredible speed.
For decades Artificial Intelligence has been a focus of best-selling science fiction authors and an antagonist for blockbuster Hollywood movies. But AI is no longer relegated to the realm of science fiction, it inhabits the world around us. From the biggest enterprise companies to plucky startups, businesses everywhere are building and deploying AI at incredible speed. 
 Data junkies rejoice, this is the episode for you.
Data junkies rejoice, this is the episode for you. 