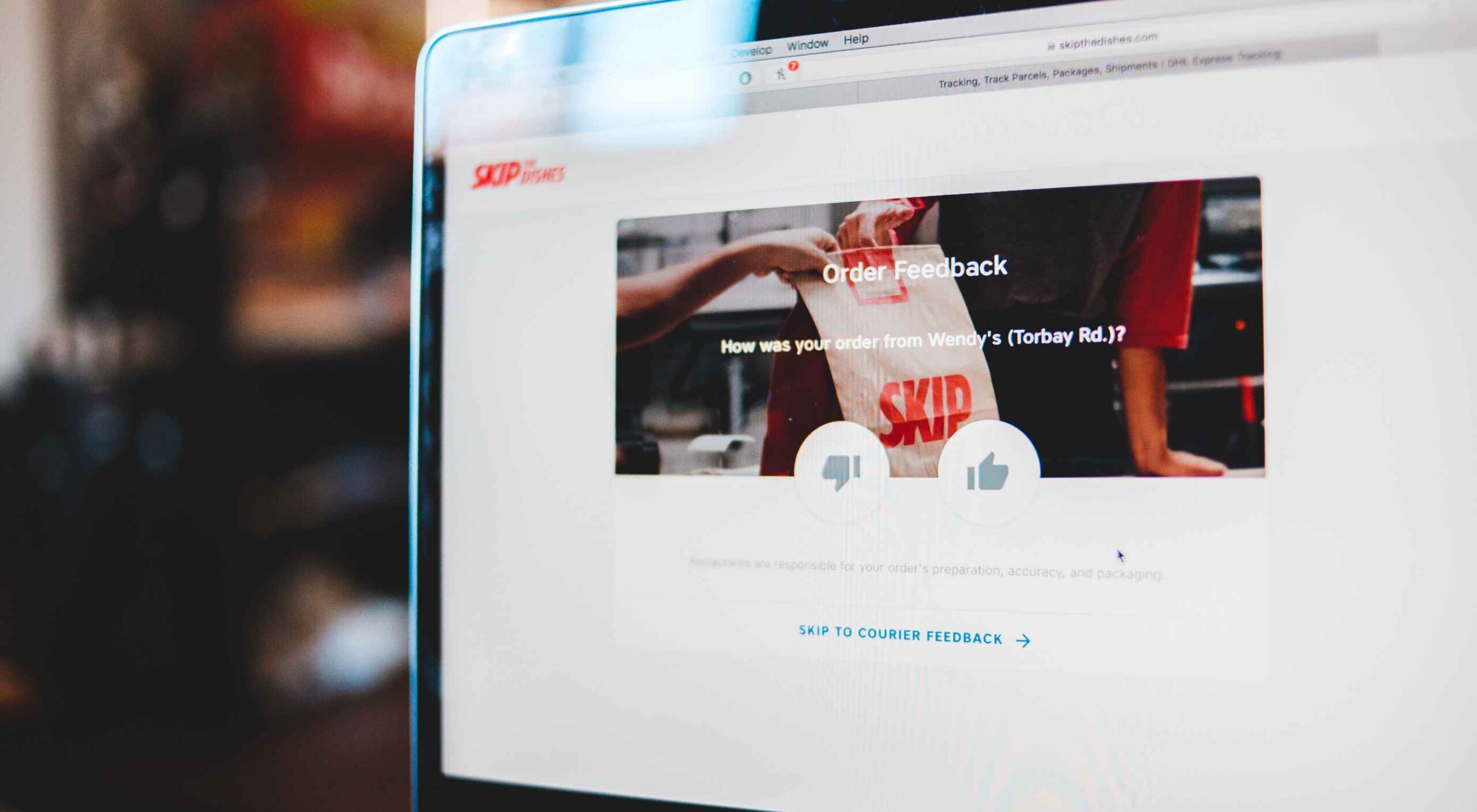
 Feedback is one of the most valuable resources for any business. Informative messages from your customers can tell you a lot about your company. They’re a way to check that your service strategies are paying off and a chance to learn which parts of your product need an upgrade.
Feedback is one of the most valuable resources for any business. Informative messages from your customers can tell you a lot about your company. They’re a way to check that your service strategies are paying off and a chance to learn which parts of your product need an upgrade.
Reviews and testimonials can also help you better understand your audience and the kind of solutions they’re looking for with your brand.
Solid feedback is also how you improve your chances of gaining more customers in the long term. Brands with superior customer service generate about 5.7 times more revenue than their competitors.
Of course, before you can begin tackling challenges like pulling trends from feedback or using your reviews to upgrade your business, you have one essential task to consider: How are you going to collect the valuable information your customers have to share?
There are a lot of options to choose from. You can reach out to clients individually with email messages or set up a feedback form on your website. You could even consider working with a review site to give your audience more options.
Today, we will look at the steps you can take to collect customer feedback the right way.
Unlocking the Benefits of Customer Feedback
Customer feedback is the information and input shared by your community. It provides a behind-the-scenes view of people’s interactions with your team and shows you where you need to focus on beginning driving new opportunities.
Customer feedback becomes a guiding compass for your organization when used correctly. It shows you what you’re getting right and wrong from your customer’s perspective. Positive feedback can even become part of your marketing campaigns. User-generated content in the form of reviews and testimonials makes for excellent tools to encourage new people to purchase your products.
Case studies and in-depth reviews from your clients can also help generate trust among potential customers, so you’re more likely to earn crucial sales.
Only around 3% of customers say that they find marketers and salespeople “trustworthy.” This means that no matter how good your marketing messages might be, you’re only going to be able to accomplish so much with the claims you make about your brand. Ultimately, your clients will turn to other customers like them to determine who they should buy from.
On average, buyers read around seven reviews before they’ll even consider trusting a business.
The good news is that around two-thirds of customers will share their personal information with a brand. Clients are happy to provide feedback in the right circumstances. It’s your job to ensure that the process is as easy as possible for your customers.
So, how do you get customer reviews?
1. Design an Effective Feedback Survey
The most obvious way to encourage feedback from your customers is to ask for it. Unfortunately, designing a good customer survey isn’t always as simple as it seems.
On the one hand, you’re keen to gather as much information as possible from your customer, which could mean that you want to ask many questions. On the other hand, asking too many questions could easily scare your audience away.
To improve your audience’s chances of actually sharing information, keep the feedback requests as simple as possible.

One or two questions at a time should be enough to give you some helpful information about customer preferences and expectations. When choosing what to include in your survey, remember:
- Only ask essential questions: If the answer to a question isn’t going to help you achieve your goals, don’t ask it. You don’t need to know someone’s age if you want to know if they had a good experience with your service reps. Keep it relevant.
- Make the questions thoughtful: Yes or no questions are great for collecting quick information. However, if you want more valuable feedback, leave your queries open-ended, and give customers room to explain themselves.
- Use rating scales: If your customer doesn’t have time to respond to a question in your survey with a complete answer, a rating scale can give you some helpful insights with minimal effort from the client.
Ensure none of the questions on your survey are leading or loaded. Customers don’t want to feel like you’re answering questions for them. It might also be worth showing your audience how much you value their data with a quick response. Hilton Hotels always responds to any adverse reactions to surveys within days of receiving the information.
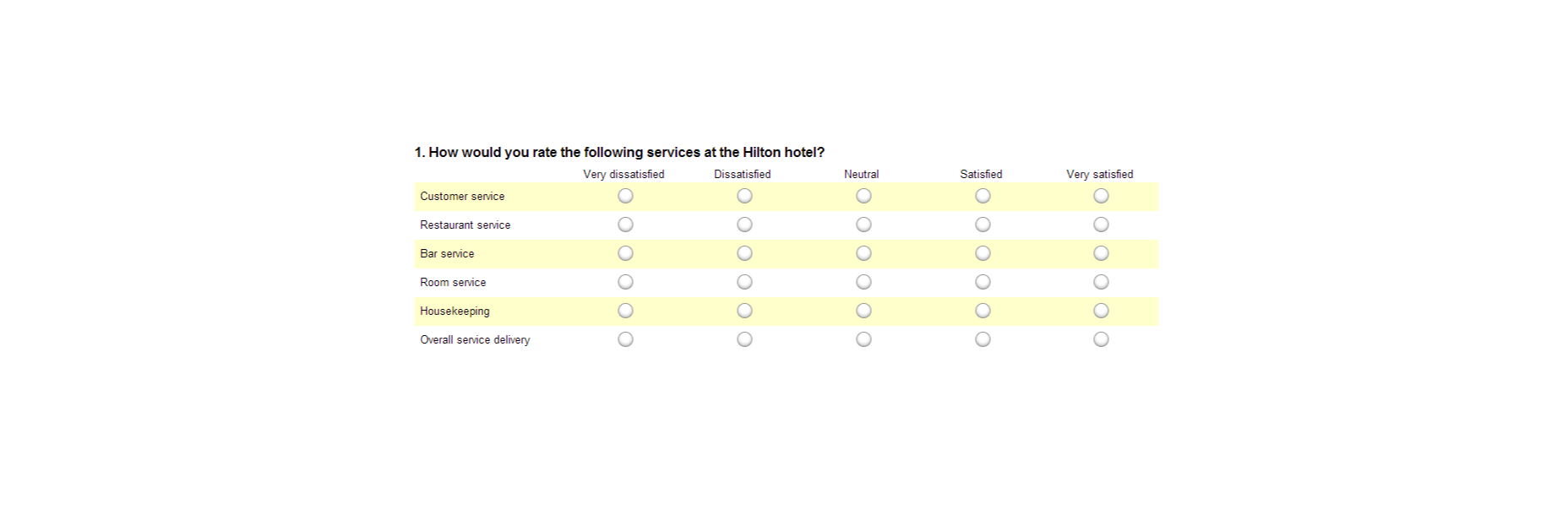
Customers can even see how their reviews contribute to the overall rating of the business.
2. Master Your Emails and Customer Contact Forms
Email is one of the easiest and most effective ways to gather customer feedback. Because this is a standard support channel for most businesses, there are plenty of opportunities to generate feedback.
The first step in using emails for feedback is to send a message thanking your customer for their recent interaction with you. If someone purchased a product from your company, immediately follow up to let them know you appreciate their custom. A couple of days after, when your customer has had a chance to use your product or service, that’s when you follow up with your feedback request.
Ideally, your email request should be as short and straightforward as possible, with a clear call to action that tells your customer what to do next. This example from Papier keeps things as detailed as possible.
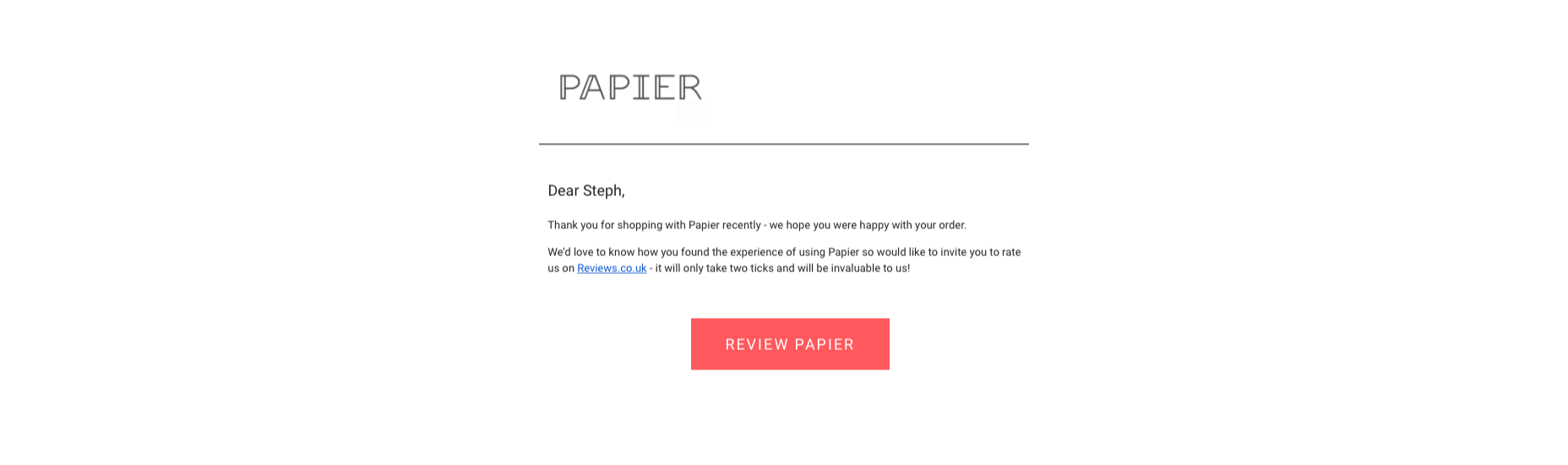
If you want to boost your chances of engagement, you can add elements to your email that might encourage a positive response, for instance:
- Remind them of what they bought: Remind your customer of the item they purchased with a picture and a bit of information. Highlight the key features and benefits of that product, so they have some inspiration on what to write about in their review.
- Offer them a reward: If you want to boost your chances of your customers doing something for you, you need to offer something in return. This could be a discount on their next order, a chance of winning something, or even just free shipping on their next purchase.
- Personalize the message: Make your customer feel special by personalizing the message. Use their name and reference their previous interactions with your company. If they’ve been with your business for a while, mention that in the email.
Remember, many of your customers are likely to check their emails on the go. That means that giving feedback should be as simple as possible, regardless of the tech your customer is using. For instance, in this Zomato example, users can choose to drop an email to the company or send feedback straight from the app.
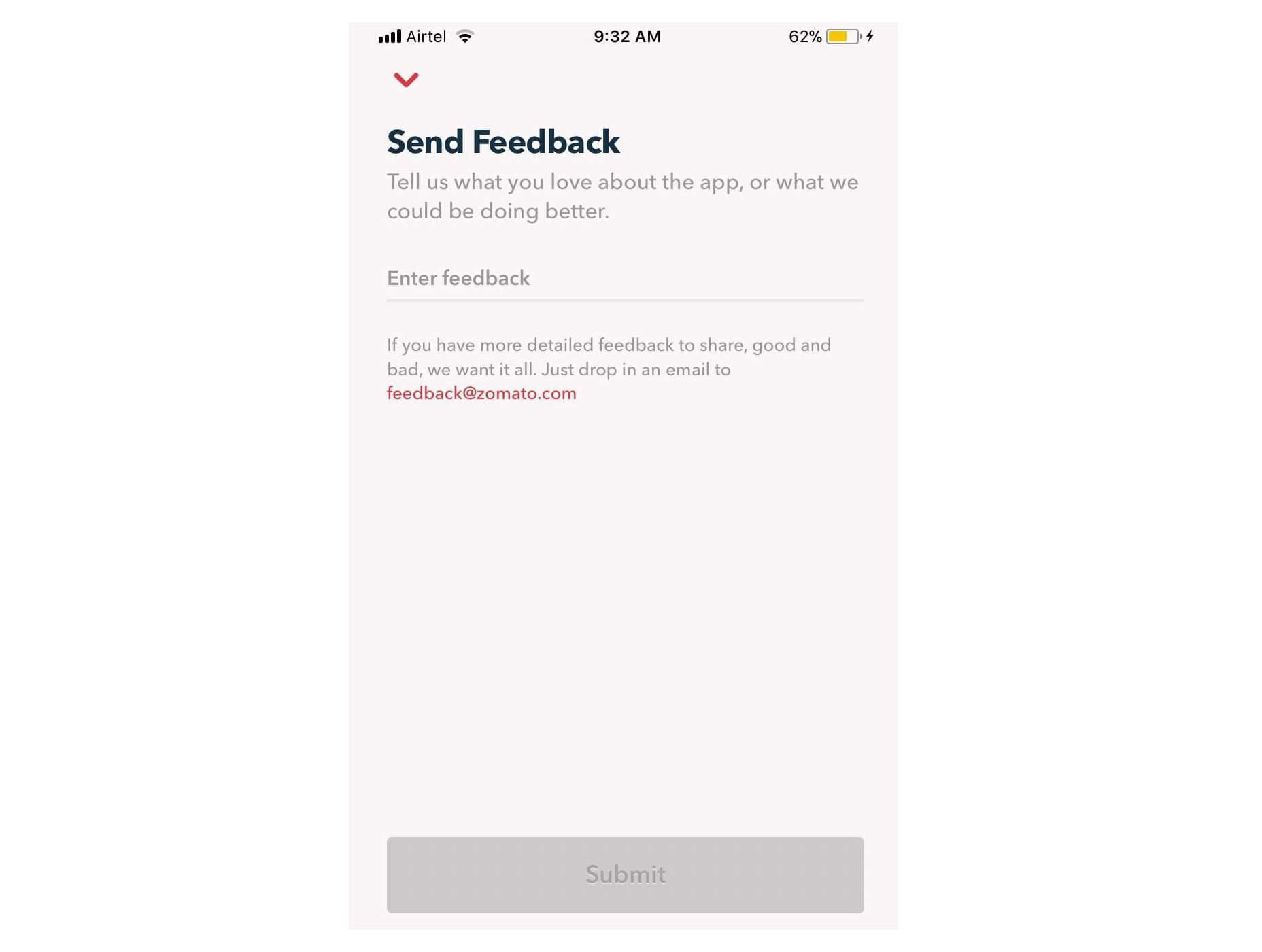
3. Create App Usability Tests
If you want some in-depth insights into your company, and your business processes, then a usability test could be the best way to generate valuable feedback. If you have your app, ask your customer to submit some information right there and then, after they’ve finished using the service. The great thing about this kind of input is it’s fresh.
Unlike other customer reviews that might come a day or two after your customer has used a product, usability tests allow you to get feedback at the moment. There’s a much better chance that you’re going to get some relevant and detailed responses here.
For instance, in this Skype lab feedback request, customers can tick boxes for any video or audio issues they had and leave a starred review.
If there’s extra information to share, the customer can tap on the comment box to elaborate. However, they don’t need to do this part unless they want to.
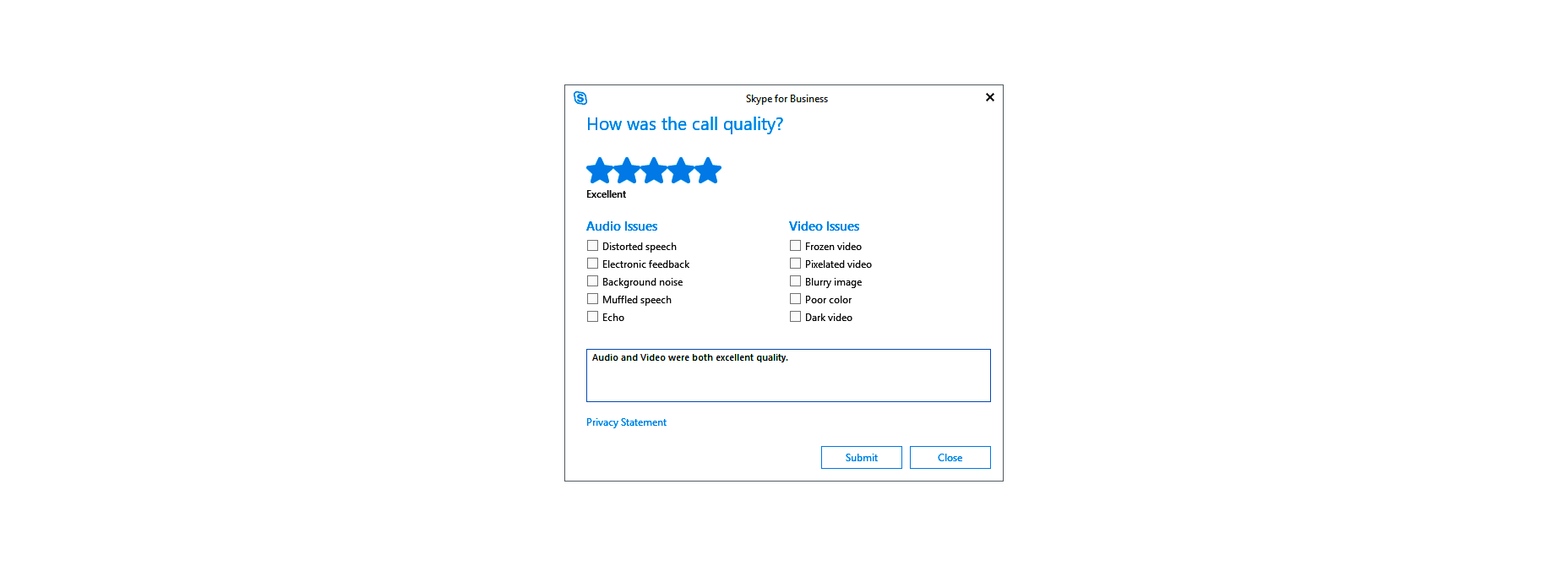
With usability tests, it’s a good idea to focus on a few key things that you want to learn about. For instance, Skype’s example above demonstrates that the company wants to check at least five user experience issues for both video and audio.
Giving your customers options that they can choose from reduces the amount of work they need to put into leaving a review. It also means that you can get actionable information on which parts of your app or site need the most improvement.
You can get the same kind of instant feedback on your website, too, mainly if you’re using a live chat app for customer service.
Live chat is quickly becoming an essential part of the customer experience environment because it’s fast, easy to use, and efficient. It’s also highly affordable for most companies, thanks to evolving technology. Set up your Live Chat app to immediately request a review from your customer when the interaction is over.
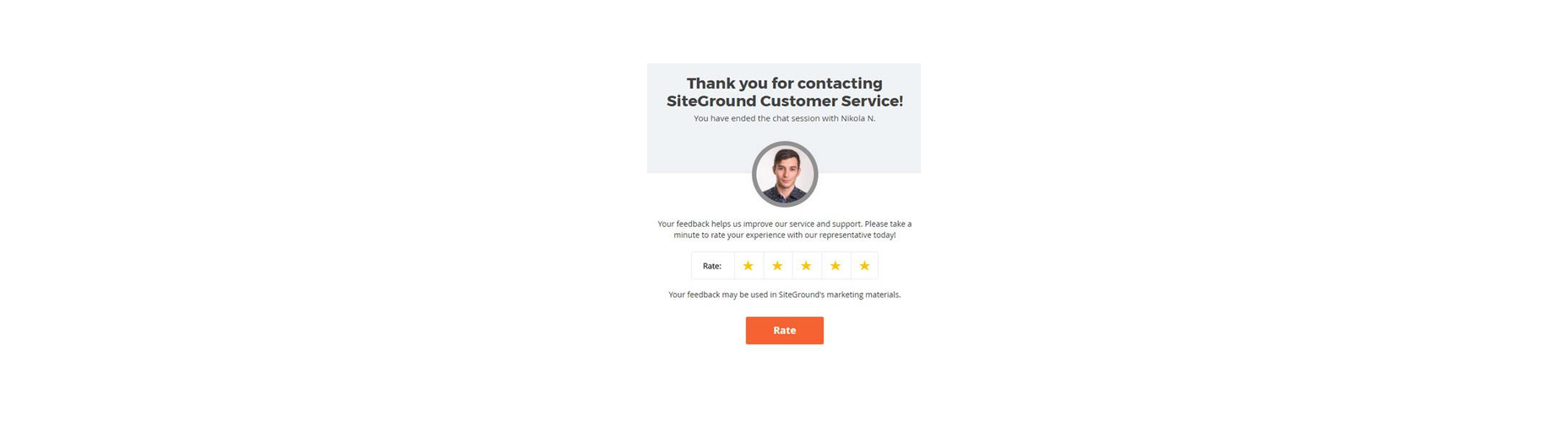
For instance, SiteGround asks customers to rate their service provider with a picture of the employee they spoke to. The image lets the customer see that they were talking to a real person, which improves the relationship with the company. The statement about feedback improving the customer service and support that SiteGround can offer shows the customer how valuable their reviews are.
4. Conduct Customer Interviews
Conducting a customer interview is a lot like sending out a survey. The main difference is that you ask the client to engage in a much more in-depth conversation. Usually, these interviews will be the initial research required for a published case study on a B2B website.
Reaching out to valuable and loyal customers can give you a fantastic source of in-depth information to learn from. You’ll need to make sure that you have a good relationship with the customer in question before you attempt this, however. Most one-time clients won’t want to get involved with a time-consuming interview.
Look at your CRM technology and find out who your most impressive VIP customers are. Reach out to them with a request for feedback, and make sure you offer something in return. For instance, tell them that you’d like to interview for a case study that you can display on your website. If they’re happy for you to do this, you can reward them with a discount on their next purchase or some gifts.
You could also follow up with a customer who recently contacted your team for an interview, like Ticket Arena does here. With this message, they promise the customer that their insights will make the customer experience better for future clients:
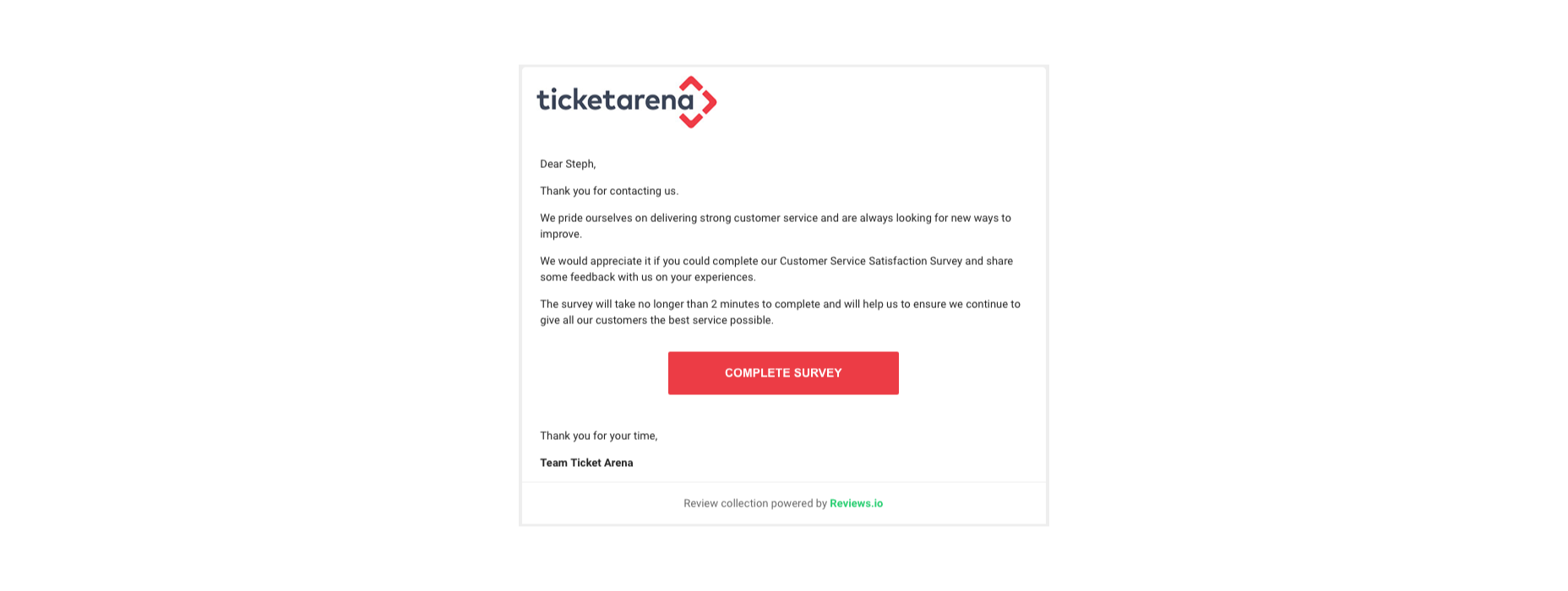
When requesting long-form qualitative feedback, remember to think through your questions carefully. In-depth stories from customers bring nuance and color to your quantitative data. They could even guide your business to making some crucial future decisions.
When talking to your customers:
- Start with an open-ended dialogue: Remember that open-ended questions are crucial to get as much detail as possible from your customers. These queries give your customers more flexibility to cover the details of their experiences.
- Get more specific as you go: Start with simple questions, then build on them as your conversation evolves. Use the things you learn from your customers to dive into topics that are relevant to them. For instance, if a customer mentions your live chat app, go into a deeper discussion about the channels they prefer to use.
- Practice active listening: Make sure that you’re open and receptive to the information you’re given. Actively listen to customers, even if you’re not in the same room, by acknowledging what they say and providing valuable responses.
5. Use Social Media
Sometimes, people are reluctant to give feedback for your business on your website because they’re not in the frame of mind. When customers come to your site, there’s a good chance they’re looking for information from you or want to check out a new product.
They’re probably not in the right mood to start sharing their opinions.
However, if you capture your customers on social media, there’s a good chance they’ll be feeling a lot more talkative. After all, social media platforms are where most customers discuss their issues with companies, talk about purchases with friends, and make their voices heard.
Simply paying attention to when people talk about your company on social media can give you a lot of helpful feedback. Social listening tools allow you to collect post information every time someone mentions your business name or product.
Alternatively, you can actively use the tools on social media to gather data from customers. For instance, Instagram has its own “poll” feature on Stories that allows companies to collect opinions.
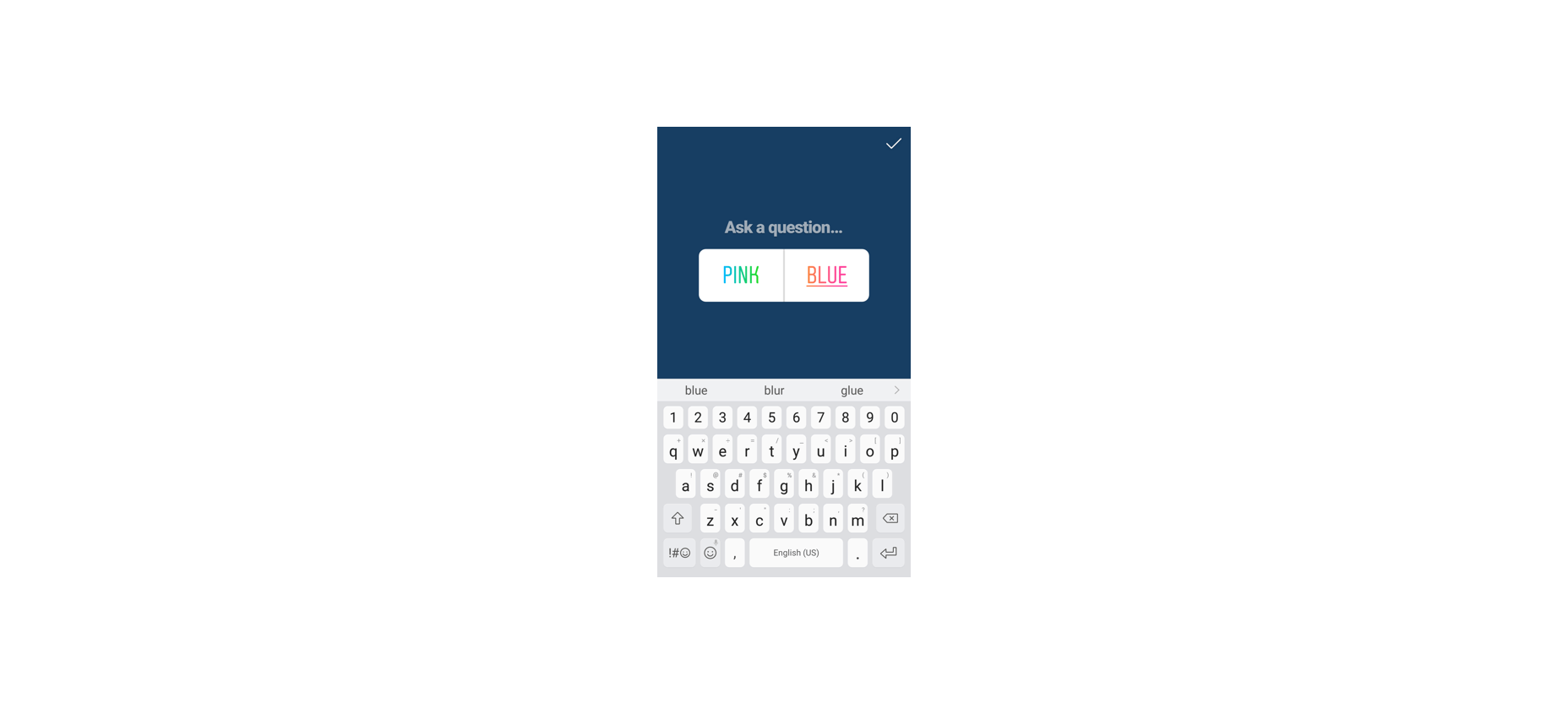
If you’re collecting feedback on social media, remember that you shouldn’t be asking any questions that are too complicated. Although people are more willing to share their opinions on social, they’re still looking for a relatively laid-back and casual experience.
Polls, where people can vote for their preferences with a single click, are more likely to garner engagement than a post asking people to tell you about the best purchasing experience they ever had with your brand.
If you do want to encourage more in-depth feedback, the best option is to promise a reward in return for your follower’s effort.
Make the experience fun by transforming it into a competition.
For instance, ask your customers to share their favorite story involving your brand for a chance to win an impressive prize. You can ask each customer to tag their response with a branded hashtag so that relevant answers are easier to find. You could even add users to tag their friends in their posts too, to increase brand reach while you collect feedback:
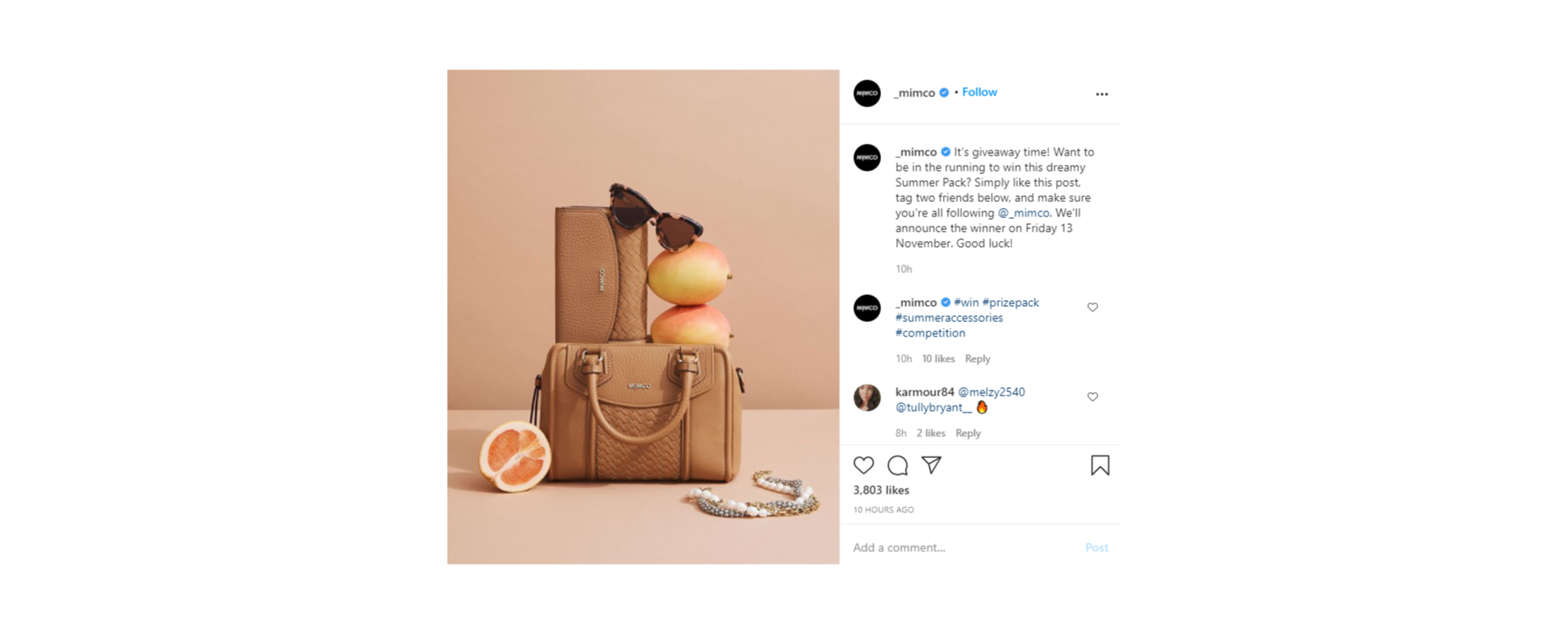
With gifts and rewards to incentivize them, people will be much more likely to interact with your brand and put effort into the reviews they leave. You could even gather some user-generated content to put into your subsequent ad campaigns.
6. Create a Dedicated Website Page
Finally, if you want to make it as simple as possible for people to leave feedback on your website and for you to collect all of that information into one space, then create a review page on your website. This can double up as social proof for people who need additional evidence to buy from your brand.
A review page could be as simple as a page on your website listing the latest comments that your customers have left. You can include a form at the bottom of the page where people can add their thoughts. Just make sure that you carefully review these posts before they’re submitted to your website if you want to prevent spam from getting through.
You could also create a case study or portfolio page that showcases the work you’ve done with other companies like Fabrik Brands does here:

At the bottom of each case study, give your customers a unique email address they can reach out to if they want to be featured as your following case study. Or include a contact form where people can get in touch to discuss their own experiences.
Having a dedicated review, case study, or testimonial page on your website could be enough to inspire more feedback from your customers. It’s also a fantastic way to demonstrate how credible your company is to potential buyers.
Still, Struggling? Take the Customer Out of the Equation
If, even with all the suggestions above, you still can’t seem to convince your audience to give you some decent feedback, then take them out of the equation. You can learn things about your audience without asking them for information. Google Analytics and other tools will give you valuable insights into which of your blog pages get the most engagement and how many people click on individual buttons throughout your site.
These fundamental insights might not be as good as valuable, contextual feedback from your audience, but they’re an excellent way to start figuring out how to invest in your future growth.
Remember, feedback of any kind – even if it’s just statistics and numbers – gives your business the ability to grow and make informed decisions.
Gather as much feedback as you can, and make sure you use it!
Featured image via Pexels.
Source
The post 6 Tips for Collecting Customer Feedback (The Right Way) first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.

Source de l’article sur Webdesignerdepot
 We’re going to have some fun this month. There are so many new tools and resources out there for designers that make life easier, and others are simply enjoyable.
We’re going to have some fun this month. There are so many new tools and resources out there for designers that make life easier, and others are simply enjoyable.









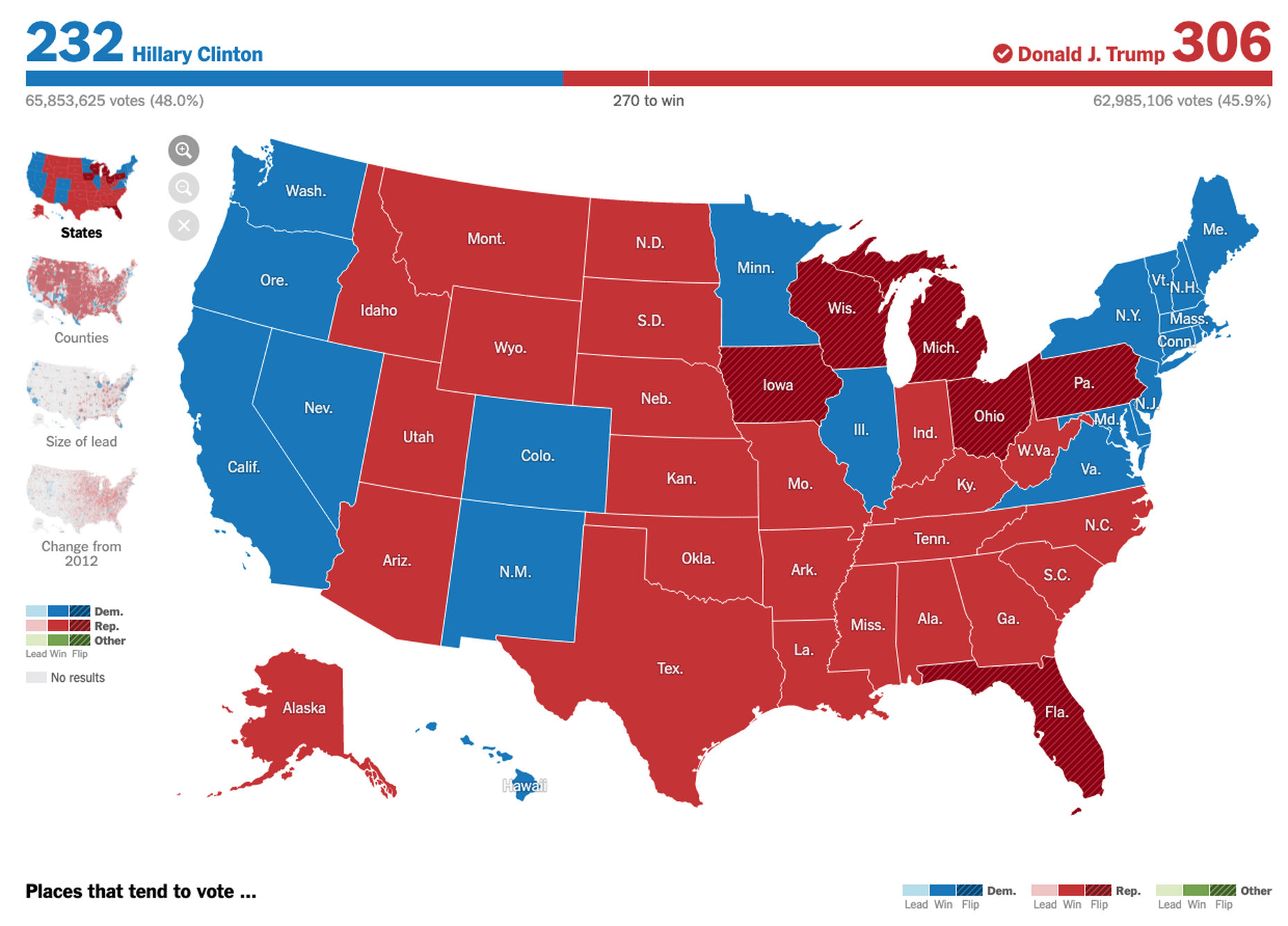
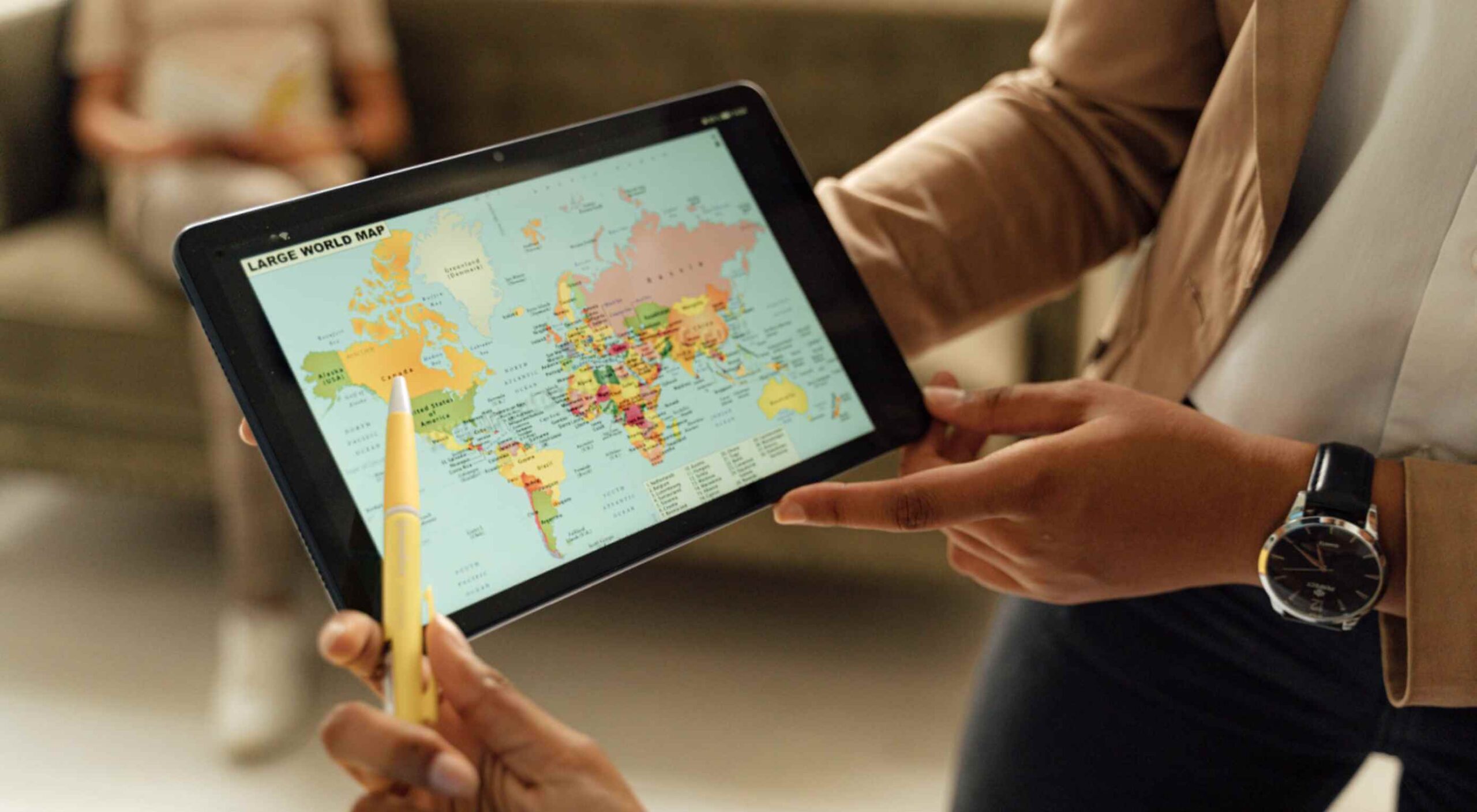 Maps are a fascinating method for delivering content. At their best, they can create an intuitive way of presenting information and interacting with it. This is the advantage that digital maps, through mobile apps and websites, have over print maps and images where no interactivity is possible.
Maps are a fascinating method for delivering content. At their best, they can create an intuitive way of presenting information and interacting with it. This is the advantage that digital maps, through mobile apps and websites, have over print maps and images where no interactivity is possible.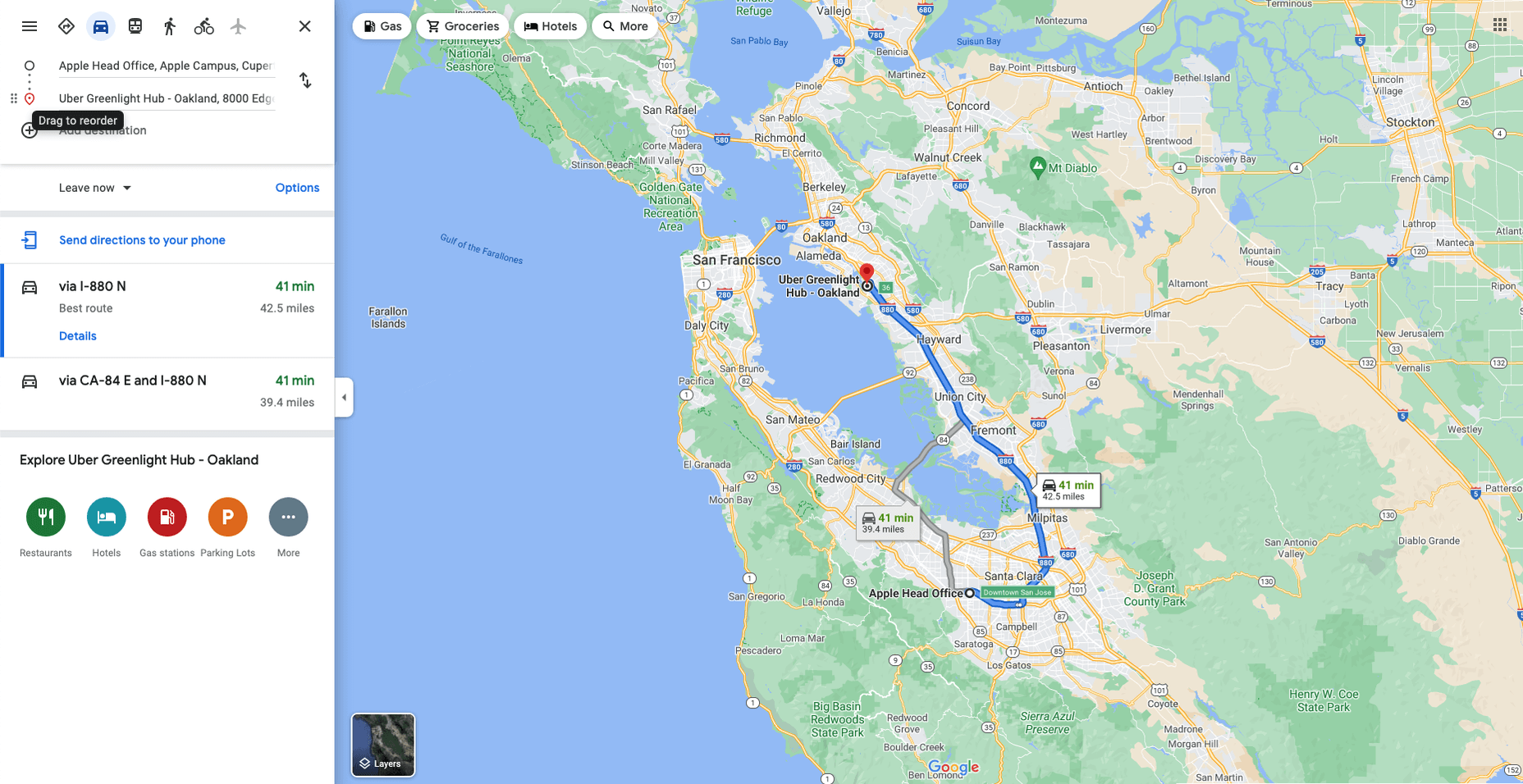


 The year’s winding down as everyone segues into a much-needed holiday R&R. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t some awesome new tools and resources for website design projects.
The year’s winding down as everyone segues into a much-needed holiday R&R. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t some awesome new tools and resources for website design projects.








 It’s normal to pull up sharp in front of a problem; after all, if there was a known solution, it wouldn’t be a problem. But knowing that it’s normal, doesn’t make encountering problems any less frustrating. So how do we avoid sitting in front of a UX problem for hours, achieving nothing?
It’s normal to pull up sharp in front of a problem; after all, if there was a known solution, it wouldn’t be a problem. But knowing that it’s normal, doesn’t make encountering problems any less frustrating. So how do we avoid sitting in front of a UX problem for hours, achieving nothing?

 Feedback is one of the most valuable resources for any business. Informative messages from your customers can tell you a lot about your company. They’re a way to check that your service strategies are paying off and a chance to learn which parts of your product need an upgrade.
Feedback is one of the most valuable resources for any business. Informative messages from your customers can tell you a lot about your company. They’re a way to check that your service strategies are paying off and a chance to learn which parts of your product need an upgrade.











