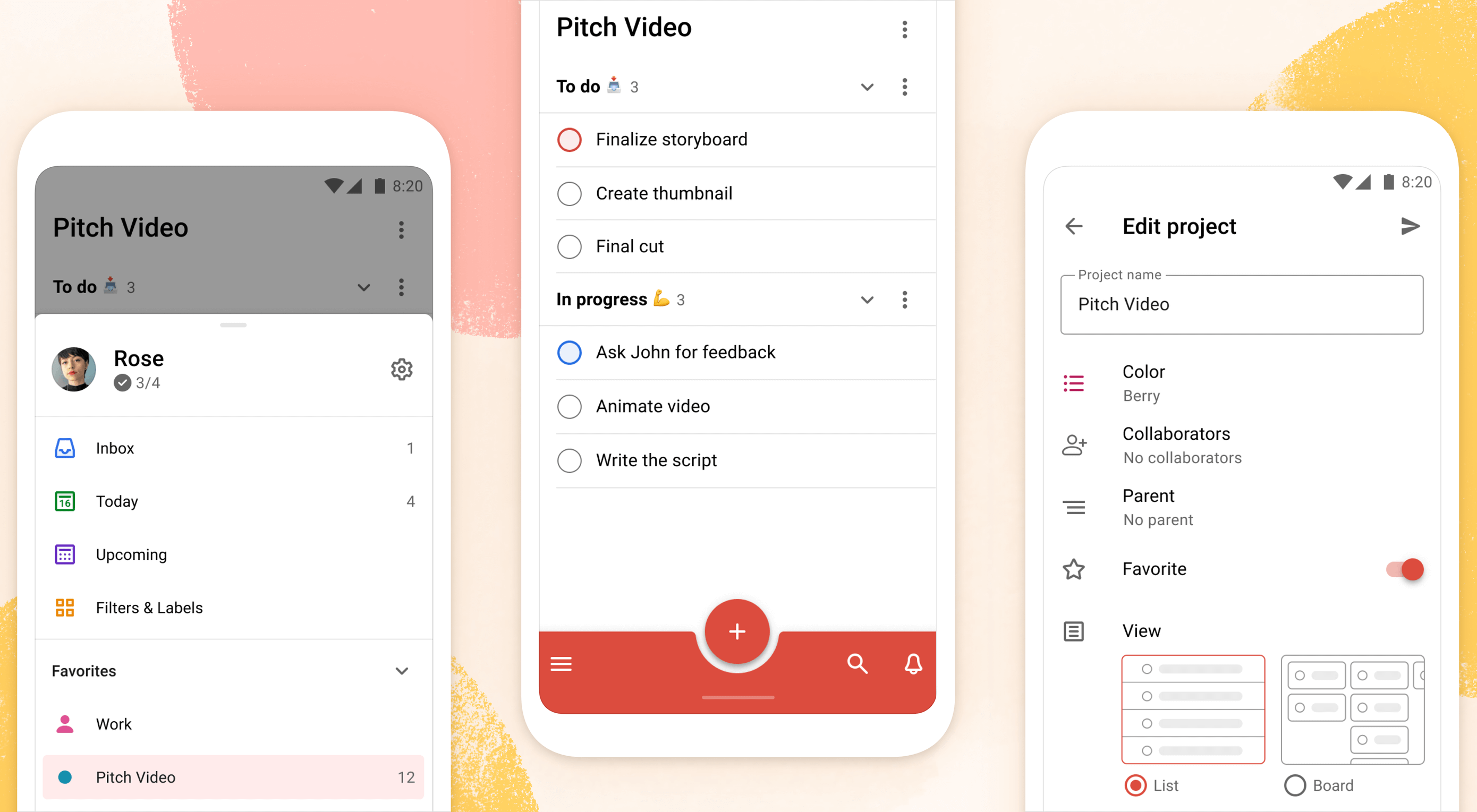
 Todoist is a to-do list app that 25 million people rely on every day to keep their lives organized. As part of the Doist design team’s goals for 2021, we aimed to redesign the Todoist Android app to take advantage of the latest Google Material Design guidelines.
Todoist is a to-do list app that 25 million people rely on every day to keep their lives organized. As part of the Doist design team’s goals for 2021, we aimed to redesign the Todoist Android app to take advantage of the latest Google Material Design guidelines.
In this post, we cover the design decisions and processes behind redesigning the Todoist Android app for Material Design. We explore the Design and Android team’s collaboration practices that brought the app update to life, which resulted in winning the Material Design Award 2021 in the large screen category. Let’s get started!
Opportunity
When we started the project, our design implementation on Android was ready for a major overhaul. The last milestone redesign on Android was initiated after the release of the first Material Design guidelines in 2016. Since then the team successfully worked on continuous improvements to the Android app, but we saw the opportunity to improve Todoist on Android on a more holistic level.
We set out to clean up instances of older UI components, colors, and text styles and update them with the latest Material Design components. We observed that some interactions and navigational patterns had become inconsistent with what users were expecting on newer Android devices and were eager to modernize this experience. With new hardware and software changes in mind, we set out to make the experience on larger phones and tablets even better, so Todoist could take full advantage of the latest generation of devices. Material 2 and 3 provided an incredible new framework to rethink the current app experience. With this in mind, we set out to challenge what a modern Android app should look like and innovate on top of the default user experience.
Solution
The team set itself the goal of redesigning our Todoist Android app and aspiring to make it the best-designed productivity app on Android. The project was ambitious and scheduled to take several months to complete. We set ourselves the following targets while working on the project:
- Review the current implementation and older design specs.
- Study the latest Material Design Guidelines and assess what is relevant for our project.
- Research great Material Design apps and case studies and learn from their execution.
- Define the new Todoist Android app design language and document the changes.
- Design and development work together to assess the proposed solution and implementation.
- Test an early version of the new app internally to gather feedback and make adjustments.
- Invite beta testers to the new app to gather feedback and make adjustments.
- Refine the app and address core issues before launching to the public.
Review

The project was kicked off by reviewing the current Todoist Android app implementation, noting down what areas needed to be fixed and what was up to date. While reviewing, we took screenshots of the app implementation for reference. This way we could easily see the current state of the app and compare it to the new design proposals that would be created. Once the review process was finalized, we had a comprehensive overview of the current state of the app and the layout, component, and styling changes we wanted to make.
Study

We continued the project by studying the latest Material Design Guidelines, assessing the components and practices that were most relevant to Todoist.
When the project kicked off in February 2021, Material 2 was the most recent version of their design system. Since Material 2 had already been released for quite some time, we anticipated that design changes to Material would be announced soon at the Google I/O event in May 2021. Rather than wait, because we expected the changes to be iterative, we pushed ahead with our work.
We identified 25 components and UI patterns that we wanted to change across the app. The changes included buttons, forms, menus, sheets, navigation drawer, app bar, system bars, text and color styles, and more. We started by creating a table view in a Dropbox Paper document with the component changes and references links to Google’s Material Design Guidelines.
This components list was a starting point for discussion to plan the scope and complexity of the changes. Close async discussions between the design and development team in Twist and Dropbox Paper comments helped us make decisions about scope and complexity early on and set a solid foundation for the project.
Research

In the initial Material Design study, we also researched inspiring Material Design apps, Material studies, Play Store apps, and Google Workspace apps to learn from their execution.
We started out by studying the Material Design Award Winners 2020 and tested out the products that were showcased. The showcased winners struck a good balance between implementing the Material Design Guidelines while maintaining their own product’s brand within the system. This balance between Google’s guidelines and the Todoist brand was also key for us to get right and so we strived to find this mix across the work we created and implemented in the project.
Along with the MDA winners, we researched the Material Studies that Google produced to showcase what apps could look like with branding and Material Design guidelines applied. It was a great reference to see how far components could be customized while maintaining the core platform principles. The Reply case study in particular offered valuable insight to us as its content type and layout came closest to Todoist. It showcased how components like the app bar, navigation drawer, and large screen layouts worked while being customized.
We continued our research by searching the Google Play store for inspiring app examples. Google Tasks, Press, Periodic Table, and Kayak stood out to us as the level of polish and quality of the apps were on par with the experience we were aspiring to create.
Sometime later in the project when Material You was released (more on that later), we stumbled upon the Google Workspace apps blog post which previewed Material 3 changes that Google was introducing to their own products. It offered a great glimpse at what was to come before the Material 3 Design Guidelines were officially released. This post sparked new internal discussions and further design explorations that we considered for future Todoist Android updates.
Design Spec

As we started to define the new Todoist Android app design language and document the changes, we opted to create a design framework, focusing on creating components rather than designing every screen in the app. This allowed us to consistently apply the design system in the app. We did so by using the previously defined component list that we created during the review and study process.
Core screens from different areas of the app were chosen to demonstrate how the components could be applied. We chose to mock up the Todoist project view, navigation drawer menu, project view edit screen, settings, and project detail view, among others. These screens gave us a good overview of how buttons, forms, drawers, lists, and other components would work together and in different states; selected, pressed, disabled, etc.

During the project, we were transitioning our Doist design system to Figma and started creating our first components in the new Doist Product Android Library. We started by using some components from the Material Design UI kit – Components library from the official Google Figma resource file and added them to our Doist design system. We then continued to build up the Product Android Library file with our Todoist-specific components such as task list & board views, detail views, sheets, colors, typography, etc.

We continued by documenting color and typography changes that were based on the Material Design guidelines. The design team opted to implement a new Design Token framework that would share the same values between our design system and the development implementation. The development team would output the values they had in the current implementation and the design team would analyze which values were needed and which could be merged, changed, or deleted. This informed the new Design Token color and typography system which we then documented and discussed with the team to implement. Later in the project, we were happy to see a similar token system introduced by Material 3 in the latest guidelines which validated our thinking and principles behind the new design system.
The design documentation expanded to hold other edge-case mockups that could sit alongside the design system. We documented different responsive screen experiences between phones and tablets against the previous implementation. Additional sections were created to document the motion that should be used for certain components and screens by referencing existing Material Design guidelines examples or prototyping custom motion in Principle and After Effects. The design spec also touched on haptic feedback that should appear on touch targets, how dark mode should work across the new components, documenting Todoist themes within the new design language, and more.
Design Implementation

At Doist, the benefit of the squad is that cross-team collaboration is built into the make-up of the team. Designers, developers, support, and product managers work together in a squad to deliver the project. This close collaboration from the start is key to bridging the gap between scope, estimations, design, development, and delivery. The squad discussed their findings on a daily basis and came up with the best plan of action together.
Designers started by creating components in Figma and shared them with developers in Dropbox Paper. We used screenshots to document the current implementation next to the new designs and linked to the default Google Material Design components. This allowed the team to compare all references in one place. Developers shared their feedback, adjustments would be brainstormed together as the designs were iterated.
Designers on the project would share their work in progress on a weekly basis with the rest of the design team in a design review Twist thread. Here details about the designs were discussed, alternatives mocked up and bigger picture plans made. Design reviews brought up topics like FAB (Floating Action Button) placement, theme options, accent color usage on components, consistency with other platforms, navigation options, and shadow elevation. After thorough discussions and alternative mockups were presented, the design team aimed to find the right balance between Material Design and Todoist brand guidelines. The development team, also part of the design reviews, gave their feedback on the solution and raised technical complexities early on.
Eventually, the design was stabilized and consistencies updated across components and mockups. The design spec was kept up to date so the development team could always review the latest designs in Figma.
Testing
As soon as the development process started, the Android team provided early screenshots and videos in Twist threads while they were implementing the design spec. This practice allowed us to review the app implementation early and often. Designers could review the development work and share feedback in Twist, which resulted in getting the implementation to a high quality. Alongside Twist discussions, the team set up a Todoist project to track ongoing issues and fix bugs. Designers logged new issues, developers would solve them and share the new implementation for designers to review.

When the team had the first stable version of the Android app, we shared it internally at Doist to get more insight and feedback. Other Doisters could access the redesign via a feature flag that could be turned on in the app settings and test the new version for however long they wanted. The feature flag system allowed people to give us early feedback on the design decisions we made and report bugs. Feedback was submitted by the wider team through a dedicated Twist thread and designers and developers could discuss how best to address the feedback during the active project implementation.
After we refined the app implementation further and addressed early feedback we opened up the app update to our beta users. Here users had access to the new Android redesign and were able to give us feedback. Our support team gathered feedback and shared it with us in a dedicated Twist thread. The squad aimed to analyze every comment and looked for patterns where we could make tweaks and improvements to the user experience.

As part of these tweaks, we made changes to how the bottom bar and navigation drawer worked. Some users reported frustrations with the way the new bottom navigation and menu drawer worked. In its first implementation, the drawer was half raised when opened and had to be swiped up to be raised again to see the full content list. This was an issue for some users as it was slower to get to the content below the list. So we decided to fully raise the drawer by default when opening. We also made it easier to open the navigation drawer by sliding up from the bottom app bar. This was a small shortcut but it enabled users to get to their content faster.
Material You
While we were in the testing phase and about to wrap up the project, Google unveiled Material You, and sometime later the Material 3 Guidelines were published. With the newly announced resources, we went back to study the latest guidelines and references we could find to see where the Todoist Android app redesign fits in and which adjustments we might need to make now or in the future.

Dynamic Color was a big new feature that was announced as part of the Material You update. As Todoist supports many different themes the Material You Dynamic Color feature seemed like a good fit for our product. We decided to prioritize this feature and implement Dynamic Color light and dark themes as part of our Todoist theme settings options.
To implement Dynamic Color, the development team started off by creating a demo prototype that utilized the Dynamic Color system and showcased how we could select from a range of color choices that the system defined based on the wallpaper choice. From there, we tried to incorporate system behavior in our design mockups. We designed a range of different color mockups and components to see which ones could fit with which components. We then came up with a color system that worked for the Todoist app and the new themes. These new Dynamic Color themes would sit alongside our current theme options in the Todoist app settings. From here users could choose between Dynamic Color Light and Dark themes.

Along with Dynamic Color, the team also created a customizable bottom app bar, allowing users to set up the app in a way that’s most convenient to their workflow. The location of the Dynamic Add Button can be changed to the center, left, or right corner of the screen. The order of the Menu, Search, and Notification buttons can be rearranged to best fit the ergonomics of the user’s dominant (left or right) hand and optimize their navigation patterns.
Launch
As critical beta feedback was addressed and stability tweaks were made, the squad felt ready to release the new Todoist Android app to the public. The team logged the issues that could not immediately be addressed for future reviews and updates.
The design and marketing team readied the launch by creating What’s New banner artwork and copy that are displayed within the app when launching the update. The Doist marketing team also created release notes and shared the app update announcements on our social channels. The brand and product design team worked together to create custom image assets and copy that summarised the project work in a simple and beautiful way.
What’s Next: Material 3
After a successful launch of the redesigned Todoist for Android app, Google contacted Doist to announce that Todoist was selected as the Material Design Award 2021 winner in the Large Screen category. The team was excited to be recognized for their hard work and it felt like we achieved the goal we had set out to accomplish.
Internally, designers and developers continued to study and discuss the Material 3 updates. The design team started exploring mockups and design changes inspired by Material 3 and Google’s Workspace app updates. Some of our current Todoist explorations include changing the FAB styling, updating the app bar, further removing elevation shadows, and more. Here is a preview of what a future Todoist update could look like.

We hope these insights into Doist’s design process and collaboration practices have sparked your interest. Thank you for reading and stay tuned for future design updates!
Takeaways
- Study the Material guidelines, Material Design winners, Material studies, and Google Workspace apps to make informed design decisions when designing your next product or app update.
- Evaluate which Material Design components and practices are right for you and implement them into your product.
- Carefully balance the Material Design guidelines with your brand guidelines to create a unique and consistent experience between your product and the platform it lives on.
- Collaborate with your Android developers early and often to ship app updates efficiently and increase the design implementation quality.
- Use design components and build a design system along with practical mockups to create an efficient design spec.
- Consider how the latest Android features fit into your product and which have the most impact on your users before deciding to implement them.
- Test and review builds with your internal team and external beta users to get valuable feedback and make adjustments before releasing them to the public.
- Create announcement artwork to showcase your latest app or feature update along with a clear description to share in-app and on social media.
The post Case Study: Redesigning Todoist for Android first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.

 Bored with the same old design tools? There are plenty of new toys to experiment with, from fun divots to functional design tools that could become your new go-to’s.
Bored with the same old design tools? There are plenty of new toys to experiment with, from fun divots to functional design tools that could become your new go-to’s.




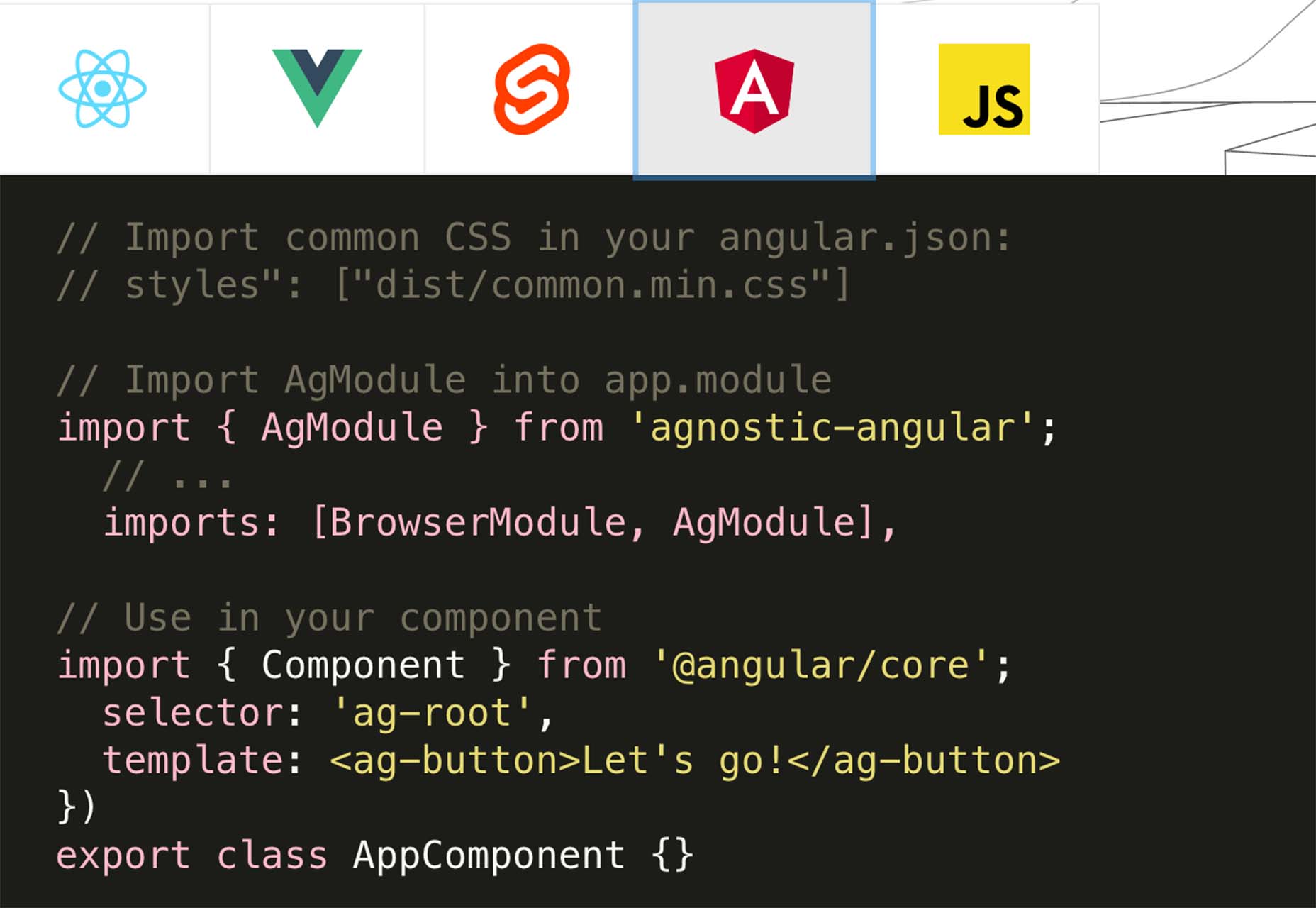







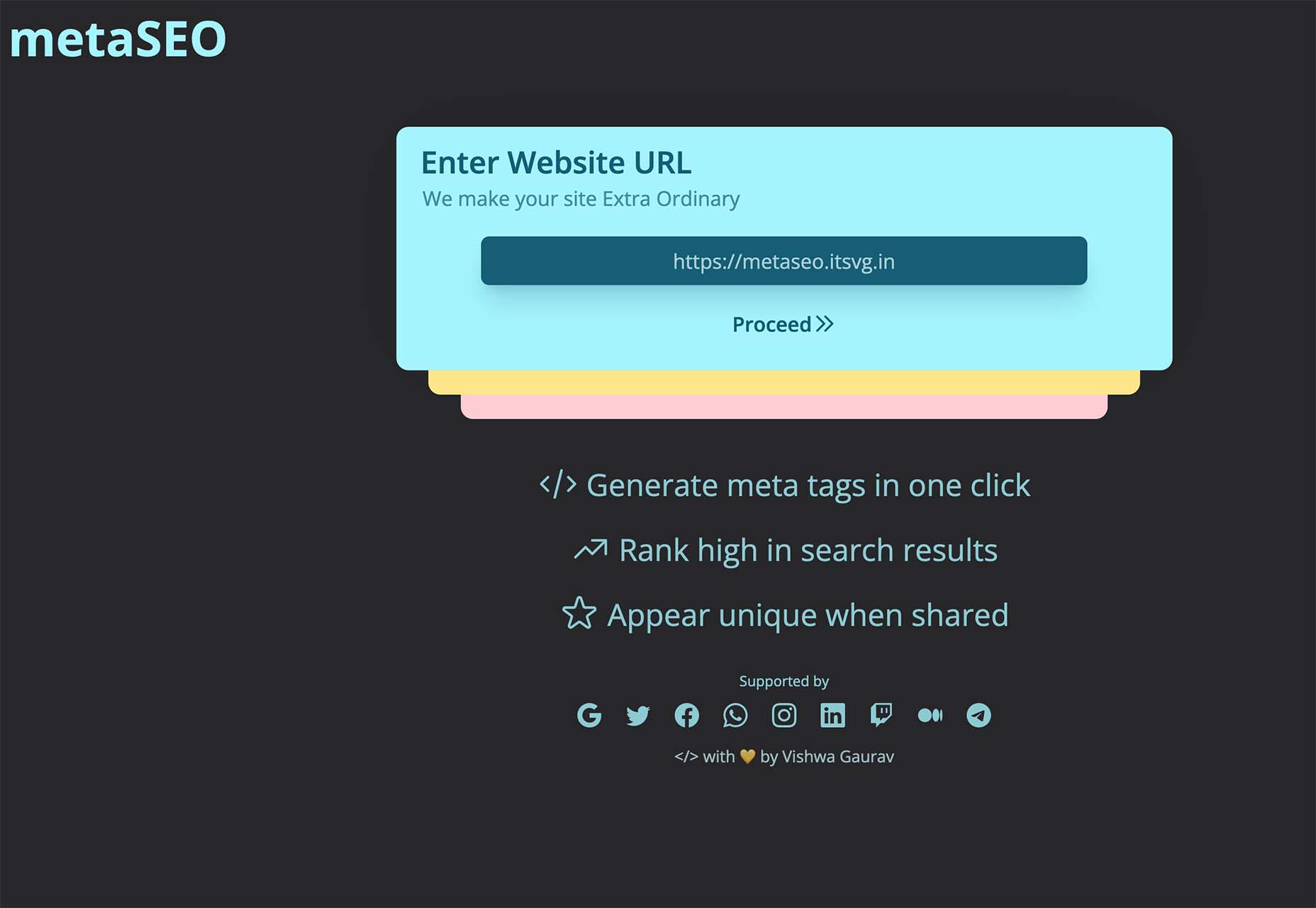
 Whether you are a CSS expert or a front-end beginner, using the right CSS framework is crucial for your daily tasks. There are numerous frameworks whose ultimate goal is the same: helping developers target multiple screens, in the simplest possible way.
Whether you are a CSS expert or a front-end beginner, using the right CSS framework is crucial for your daily tasks. There are numerous frameworks whose ultimate goal is the same: helping developers target multiple screens, in the simplest possible way.

 Experienced web designers are always on the lookout for tools or resources that will (1) introduce them to the latest design trends, (2) enable them to incorporate features and functionalities that will make their products more competitive, (3) allow them to improve their workflows or all the above.
Experienced web designers are always on the lookout for tools or resources that will (1) introduce them to the latest design trends, (2) enable them to incorporate features and functionalities that will make their products more competitive, (3) allow them to improve their workflows or all the above.









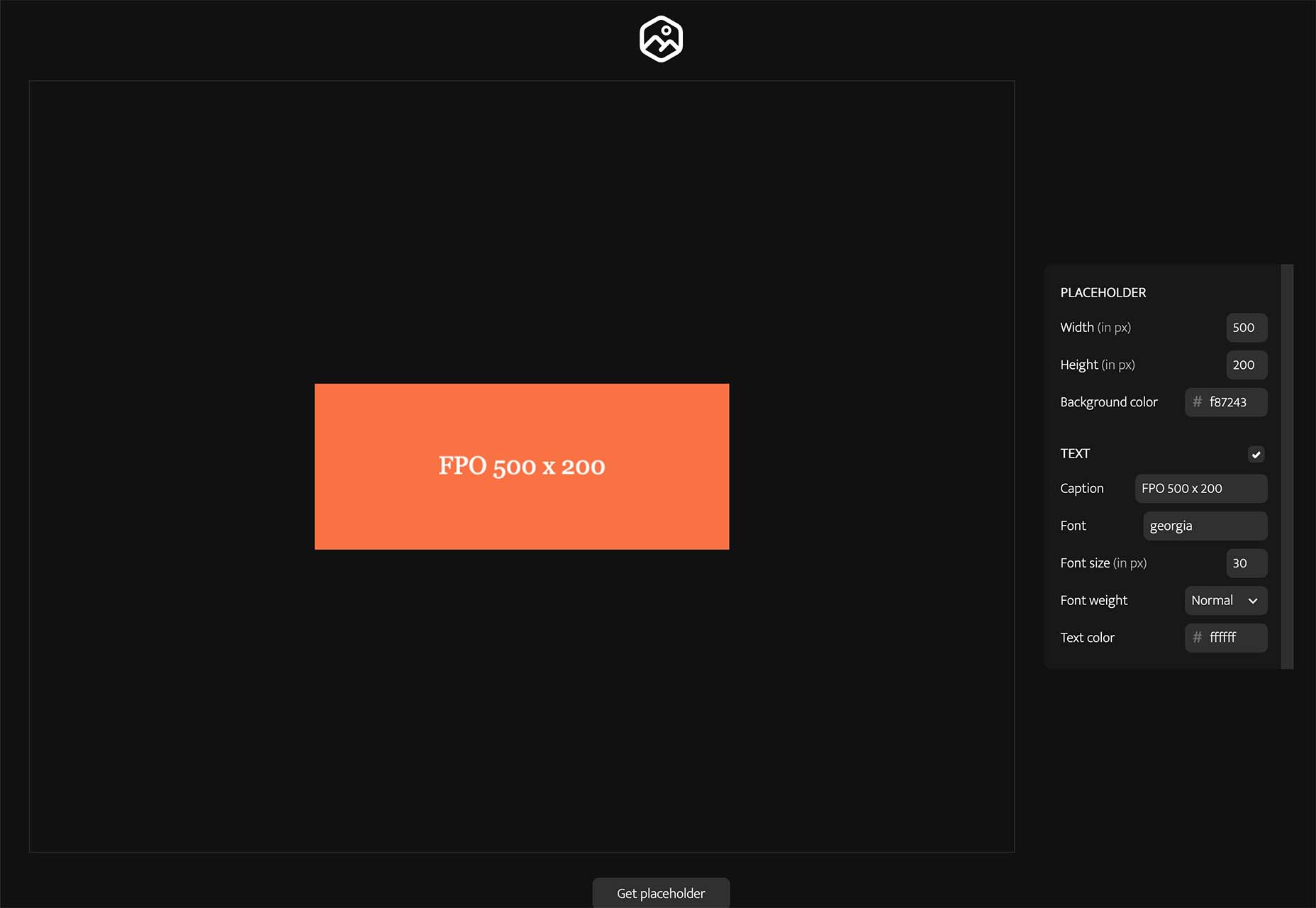
 We’re going to have some fun this month. There are so many new tools and resources out there for designers that make life easier, and others are simply enjoyable.
We’re going to have some fun this month. There are so many new tools and resources out there for designers that make life easier, and others are simply enjoyable.


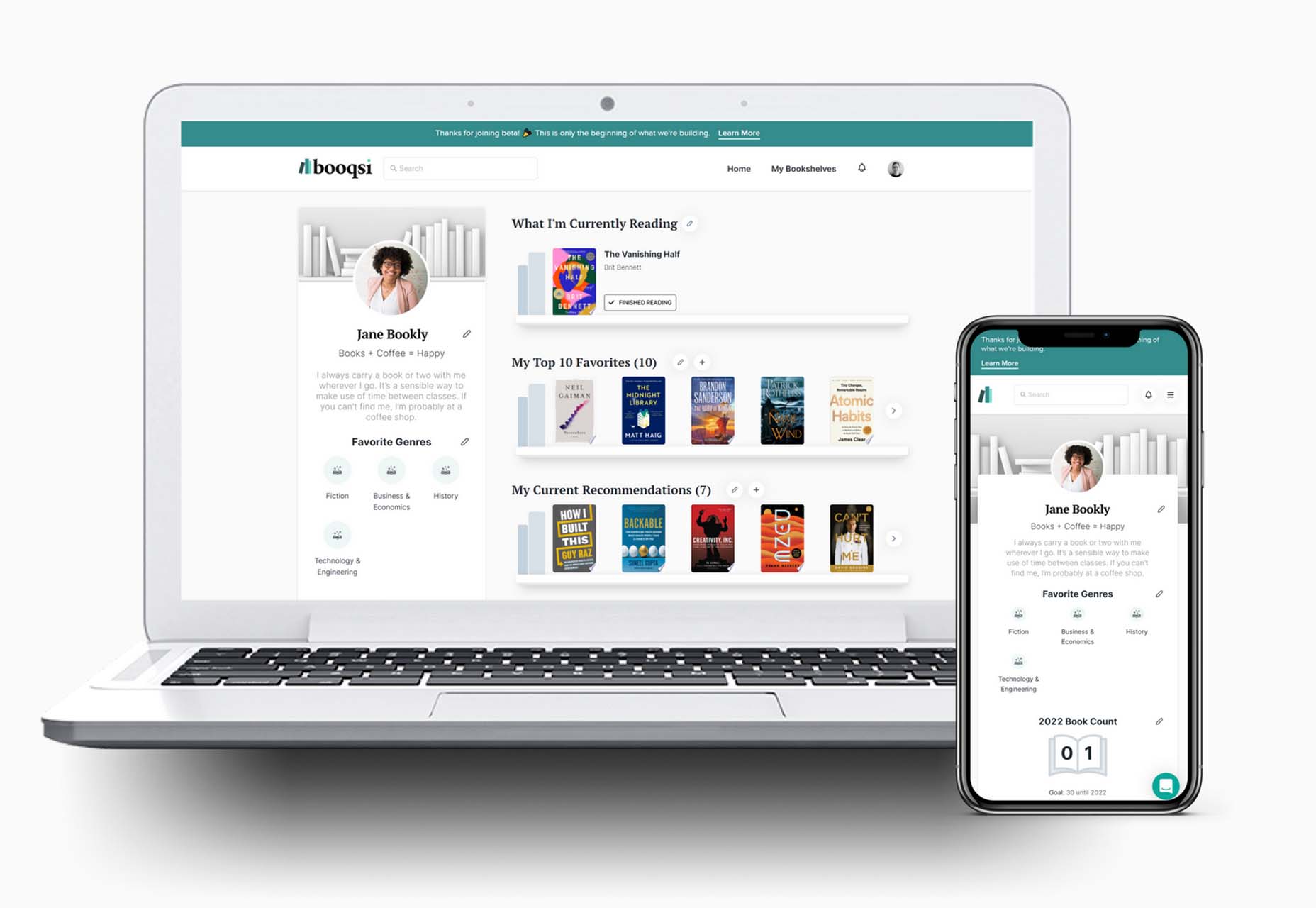





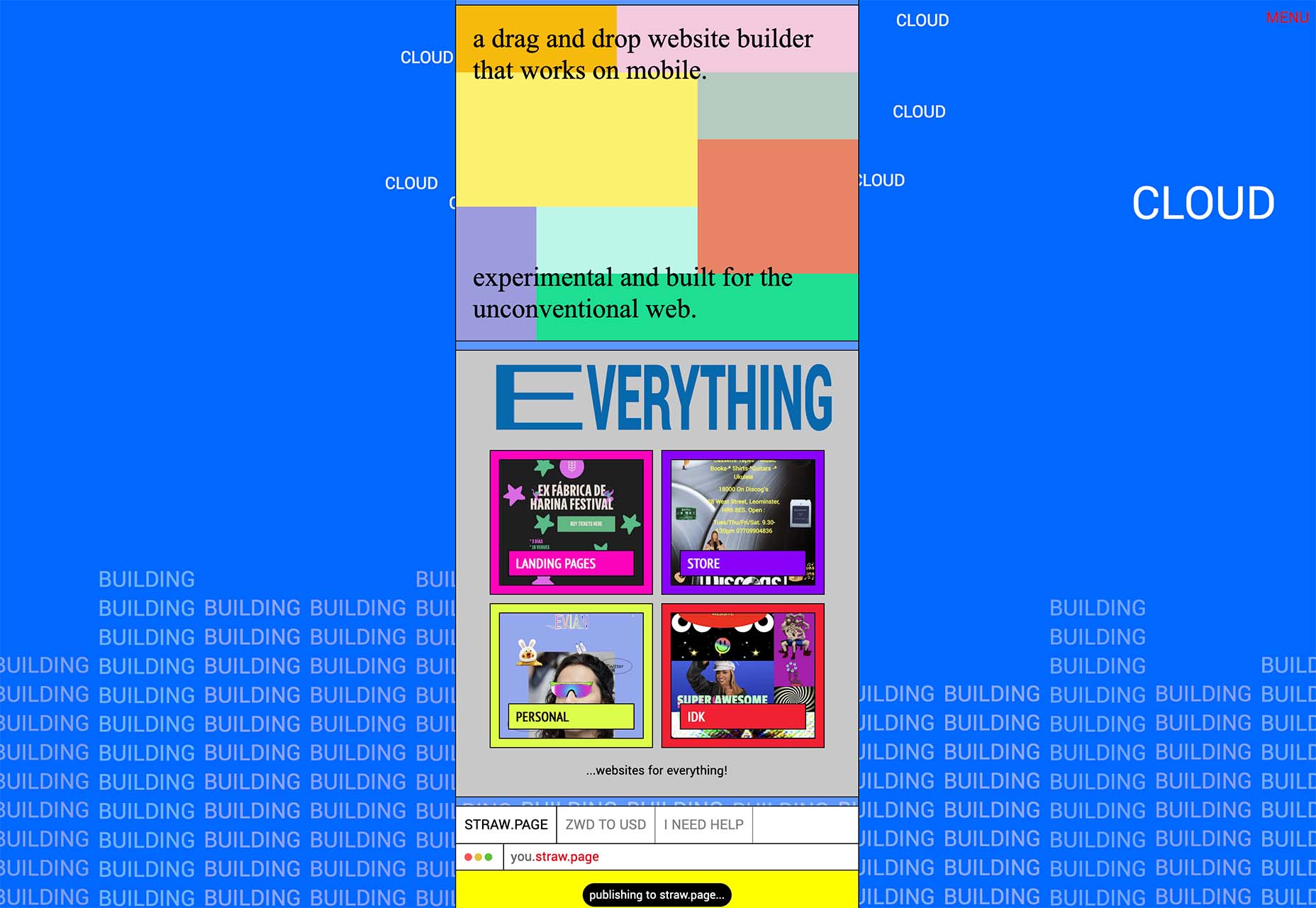
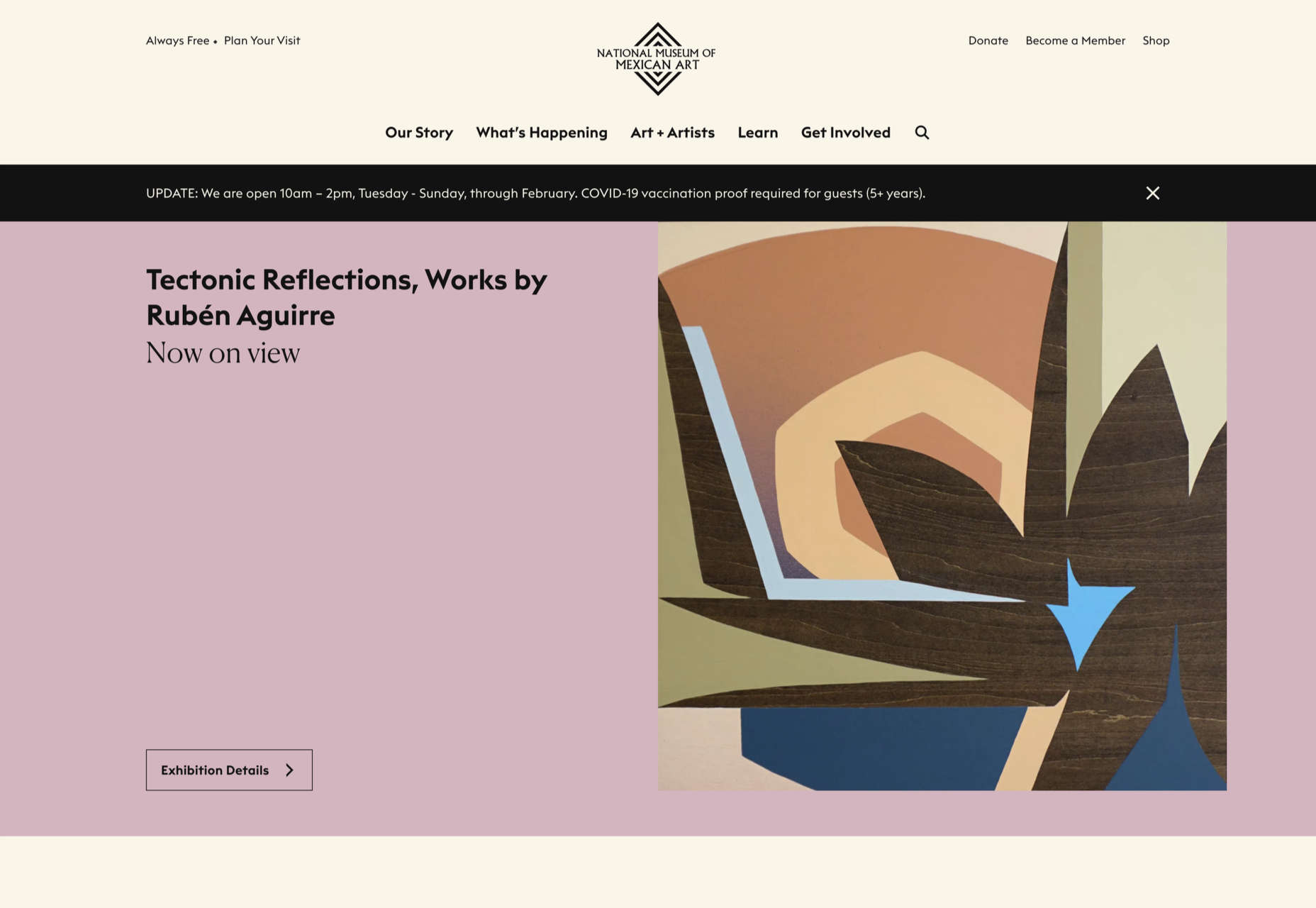
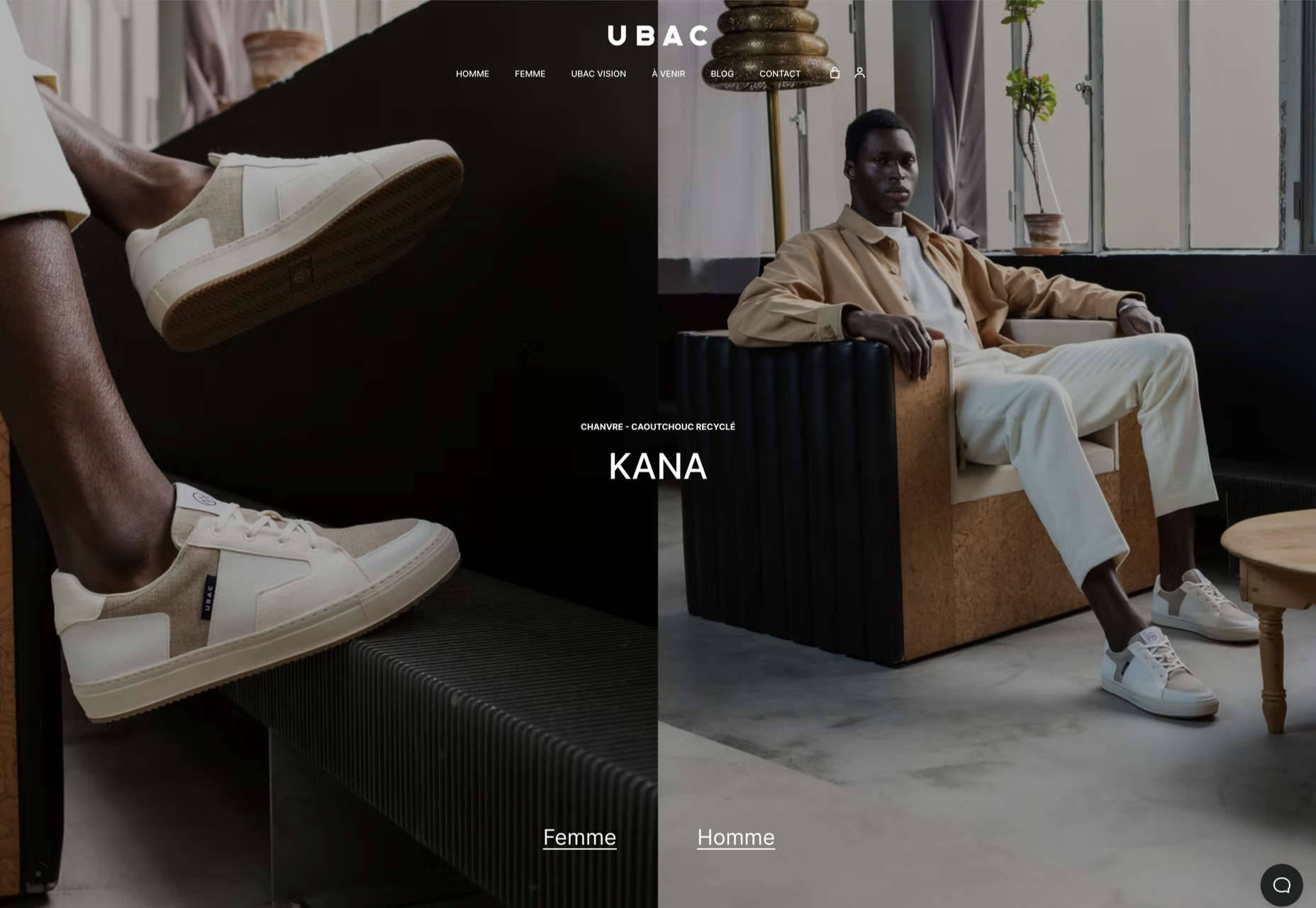
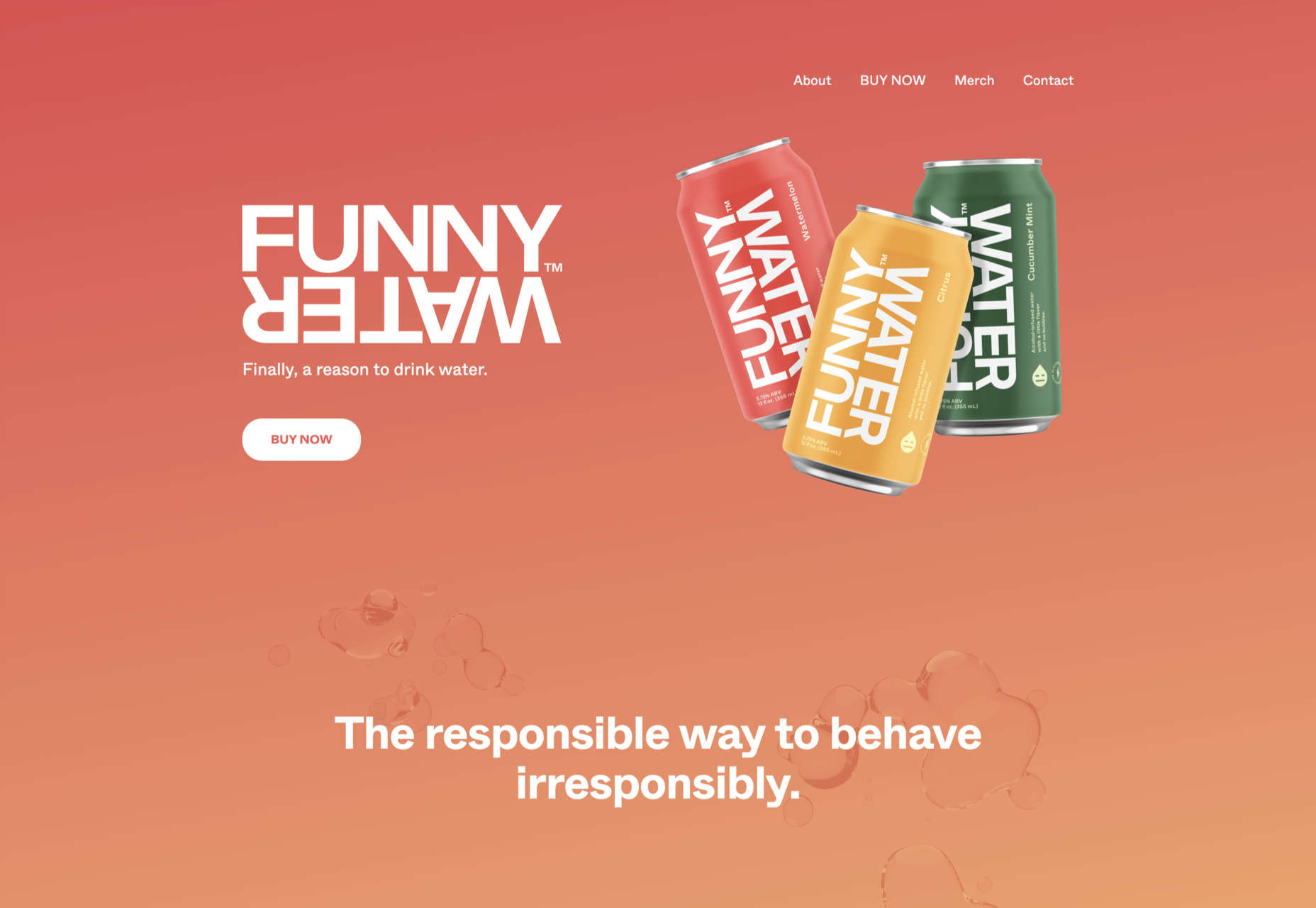
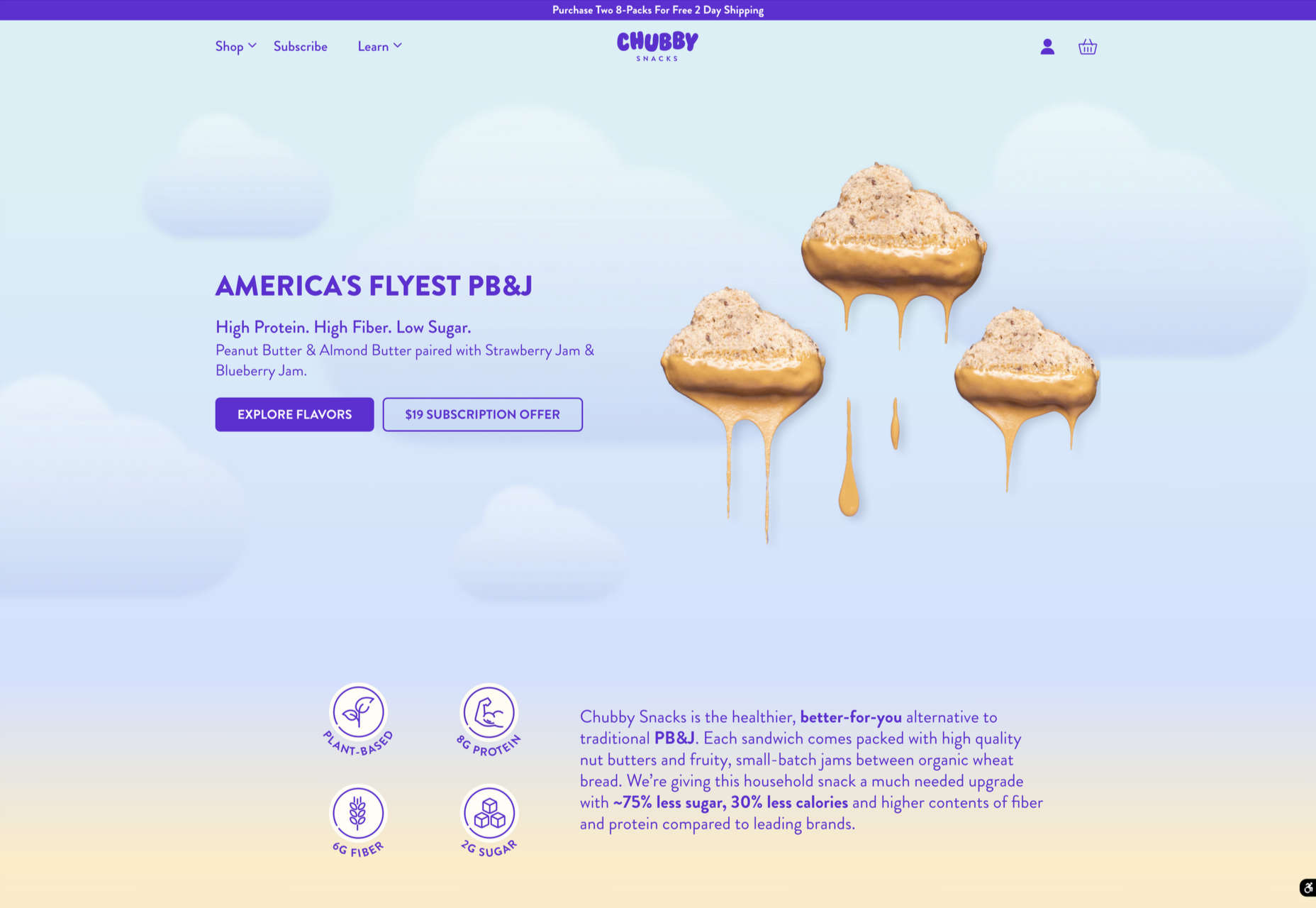
 Welcome to the latest edition of our top 20 sites of the month. In this February’s collection, the overall feel is lighthearted and optimistic, as we are seeing the positivity of a new year persisting across the web.
Welcome to the latest edition of our top 20 sites of the month. In this February’s collection, the overall feel is lighthearted and optimistic, as we are seeing the positivity of a new year persisting across the web.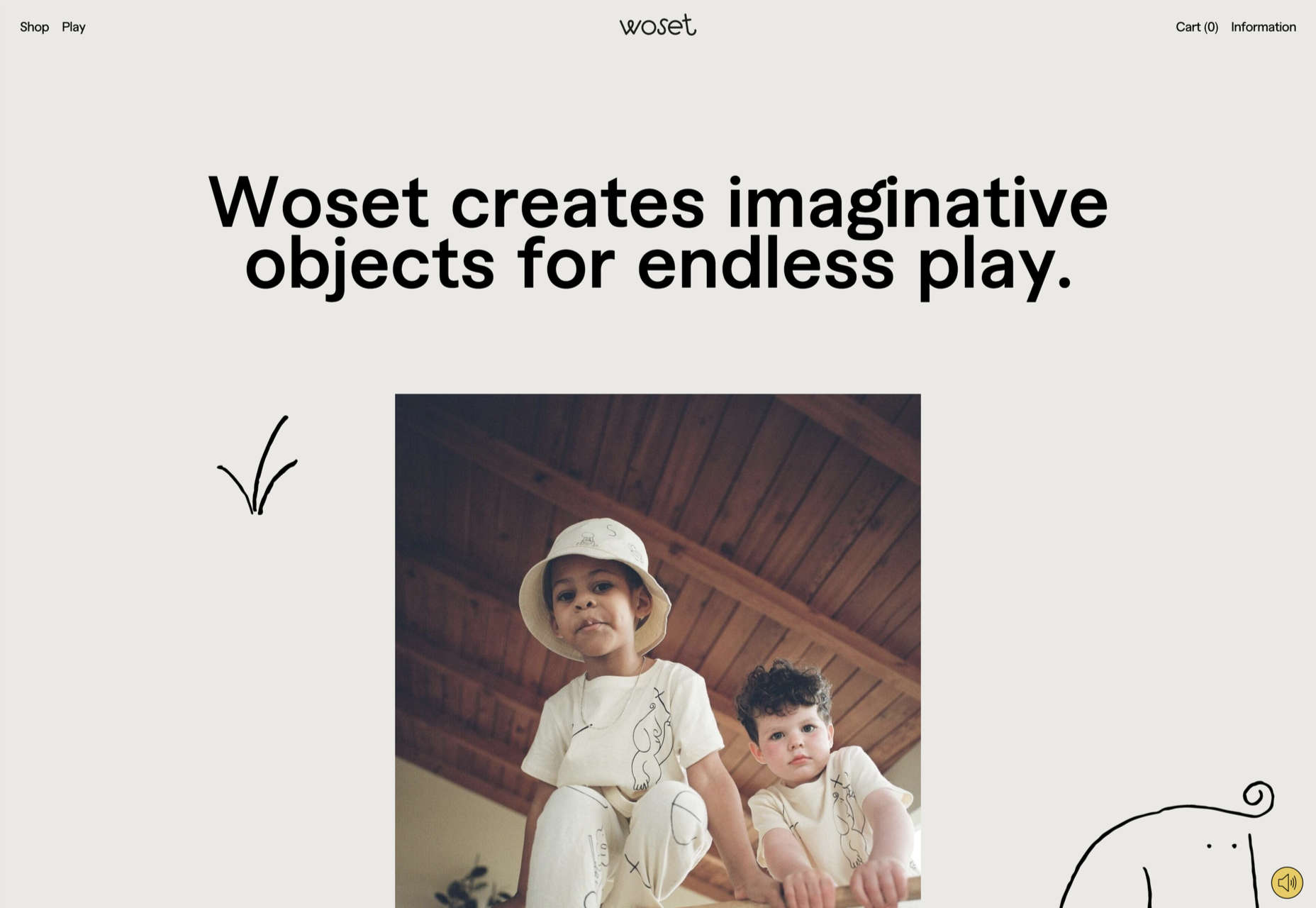











 User Experience (UX) design and User Interface (UI) design are two terms people sometimes mistakenly use interchangeably. While aspects of each are interconnected, there are distinct differences between UI/UX design.
User Experience (UX) design and User Interface (UI) design are two terms people sometimes mistakenly use interchangeably. While aspects of each are interconnected, there are distinct differences between UI/UX design.
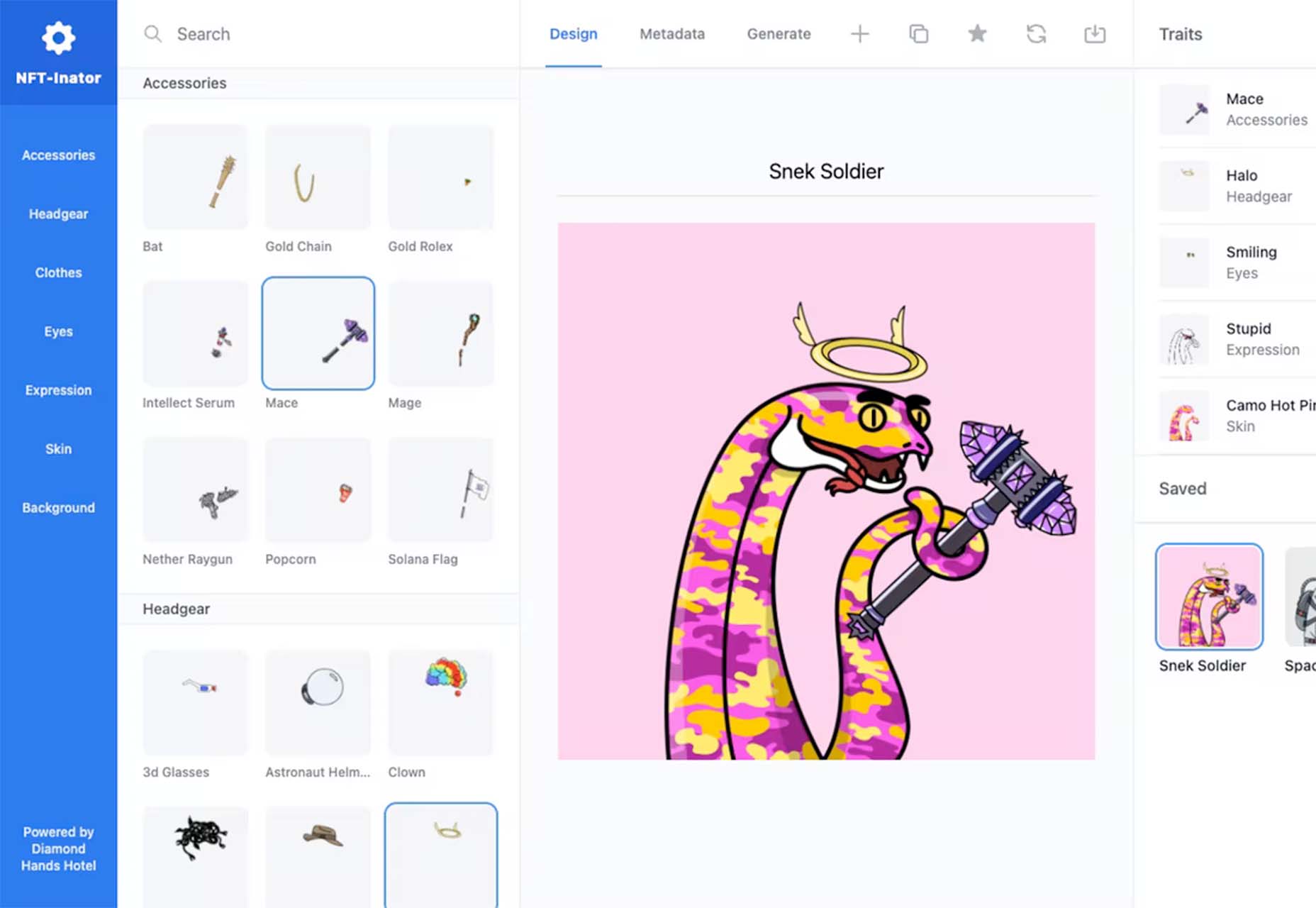
 One of the most talked-about digital elements of the new year leads our roundup of tools and resources this month – NFTs. The NFT landscape seems to be exploding right now and that includes tools for designers to get in on the game as well.
One of the most talked-about digital elements of the new year leads our roundup of tools and resources this month – NFTs. The NFT landscape seems to be exploding right now and that includes tools for designers to get in on the game as well.