Are you a creative person looking for the perfect career path to take? If so, there are not many more creative professions than that of a web designer.
Are you a creative person looking for the perfect career path to take? If so, there are not many more creative professions than that of a web designer.
However, becoming a web designer can be challenging, especially if you do not know where to start. For example, do you need to attend college to become a web designer? And what kind of computer and software do you need to own to be successful as a web designer?
This guide aims to answer all these questions and show you the steps you need to follow to build a career in web design.
Web Designer: Main Skills and Responsibilities
Generally speaking, a web designer is a professional who creates, manages, and maintains content for the web. Nothing is left out from designing pages and visual elements via programming languages and creating user-friendly websites.
Web Designer (Hard and Soft) Skills:
- UX, UI, and visual design knowledge (web fonts, colors, etc.)
- Management of design software (e.g., Adobe Photoshop)
- Coding knowledge (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, etc.)
- Time management
- Communication skills
- Problem-solving and teamwork skills
- Research skills
Web Designer Responsibilities:
- Plan and create web pages
- Design appealing layouts
- Use codes to create user-friendly pages
- Ability to meet deadlines
- Listen and advise clients
- Able to work as part of a team and effectively solve occurring problems
- Analyze the client’s niche, explore new web design opportunities/ innovative digital marketing approaches
If you feel overwhelmed reading this table, don’t be! You do not have to master all of the above skills. No one expects you to either. Becoming a top-notch web designer takes some dedication, but ultimately it’s nothing more than a series of steps. Let’s dive deeper into them.
Becoming a Web Designer: 7 Essential Steps
1. Gaining the Knowledge Needed: Theory and Certifications
Let’s start with the most common question, “Do I need to go to college to become a web designer?” Research shows that more than 65% of web designers are self-taught (fully or partially). Of course, that does not mean you can jump into design from the start.
Instead, we recommend that you learn some essential web design elements and how to use them in your future projects. This includes UX (user experience), UI (user interface), protocols, and patterns. The same goes for technical knowledge like programming languages, frameworks, and design software.
2. Developing Certain Skills
So, there are numerous aspects you can explore regarding technical skills. To be specific, your first steps in web design include developing the following skills:
- Theory and certifications: Learning the theory to understand how the web and the market work
- Web design tools: Finding the web design tools you need to start designing (.e.g Webflow, Sketch, Figma). This will allow you to learn how to prototype web design mock-ups.
- Graphic design tools: Becoming familiar with software like Photoshop, Illustrator, etc.
- Programming languages: Especially if you think of becoming a freelance web designer, you should at least learn how to use fundamental languages (HTML, JavaScript, CSS).
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Learning how to optimize your web pages to rank on search engines is crucial.
3. Mastering Web Design Software
What software do you need as a beginner to start creating web designs? There are numerous apps that will help you gradually enter the fascinating world of web design.
When it comes to CMS platforms, WordPress is by far the most popular in the market. The good thing about WordPress is that it is very beginner-friendly and comes with thousands of pre-built themes and plugins that you can use when creating a website.
But the same is true for InVision Studio. Unlike WordPress, InVision Studio is specifically designed to help web designers prototype and design a website. Finally, when it comes to graphic design software, we recommend you start with Photoshop (for creating visual samples and prints) and Sketch (for UI designs).
4. Learning How Much Computing Power you Need
Although online CMS platforms like WordPress do not require special hardware, that’s not true for web design and graphic design software. To be precise, both InVision Studio and Photoshop have quite demanding system requirements.
Still, a mid-range desktop or an entry-level gaming laptop can easily handle such applications. You need a reliable CPU, 8 GB RAM, and a dedicated graphics card.
I find working with two screens perfect when it comes to prototyping. You do not need to spend thousands of dollars to buy a laptop or desktop for web design.
5. Practice, Practice, and Practice
As with any other profession, practice makes perfect in web design. Therefore, the good idea is to get involved with personal web design projects before you start seeking clients or applying for job offers. This way, you can gradually acquire the technical skills you need.
Also, by working on some personal projects first, you can build a professional portfolio.
6. Creating a Professional Portfolio
If you want to draw attention to your talent, you should have a comprehensive portfolio as a web designer. This way, potential customers to trust you by having a look at your work and previous experience.
When creating a portfolio, make sure to showcase all aspects of your work and make it user-friendly. In other words, think of your online portfolio representing your talent and treat it accordingly.
7. Choosing the Web Designer Type That Best Suits Your Needs and Preferences
Last but not least, before working as a web designer, you should know that there are three main types of web designers: Freelance web designers, Agency web designers, and In-house web designers.
If you prefer to be self-employed and believe that you have the required soft skills, freelancing is probably the best path.
On the other hand, working for an agency or a company is usually easier (especially for beginners) and will provide you with a stable income. But, in the end, it all depends on your needs and preferences.
Wrap Up
Being a web designer can be an exciting career. As long as you have the necessary dedication and willingness, nothing will stand in your way.
Learning different aspects of the profession and mastering specific software will only make you better. All you need to do is respond positively to (and ask for) incoming feedback and practice!
Featured image via Pexels.
The post How To Take Your First Steps in Web Design first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.



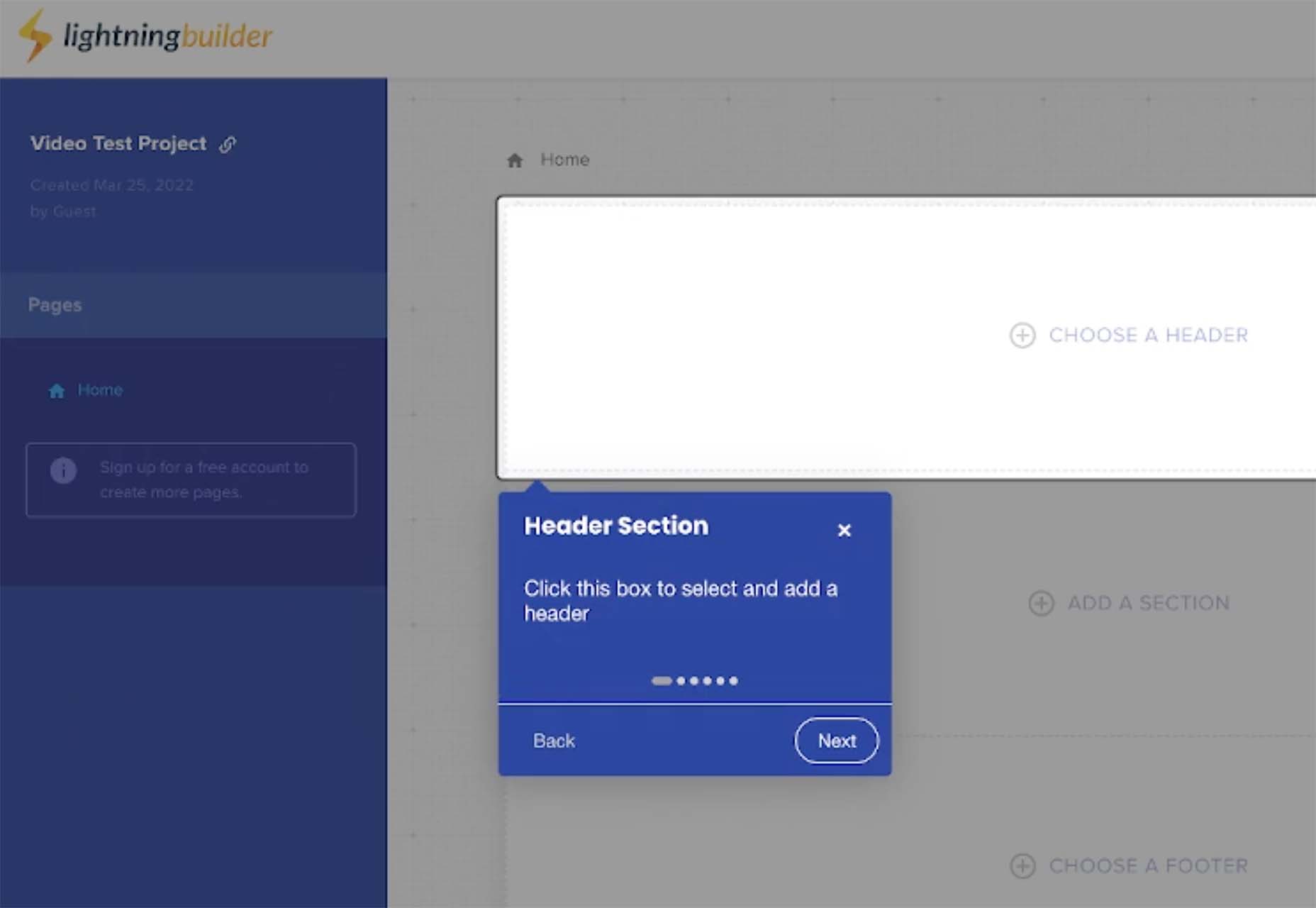
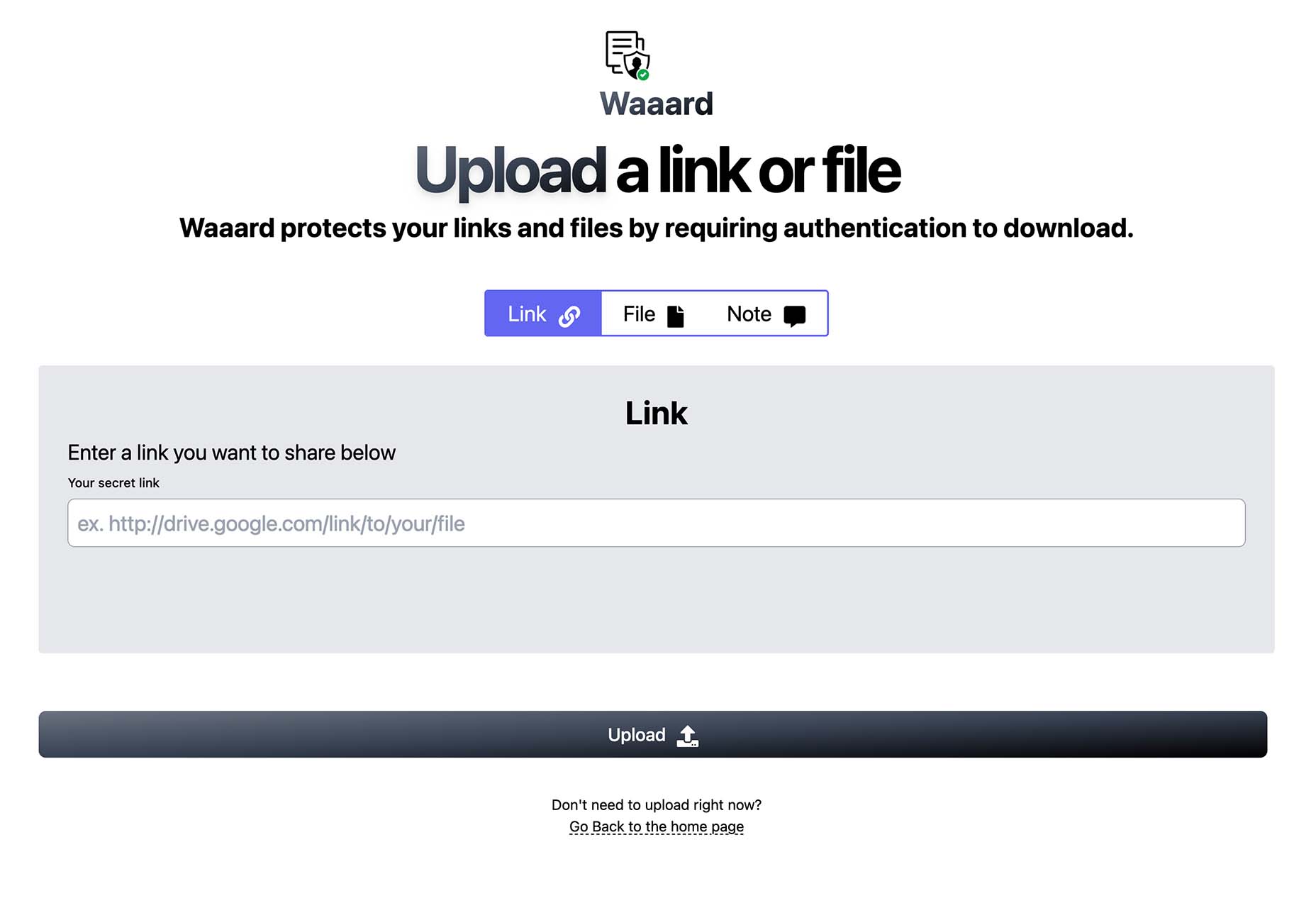
 Bored with the same old design tools? There are plenty of new toys to experiment with, from fun divots to functional design tools that could become your new go-to’s.
Bored with the same old design tools? There are plenty of new toys to experiment with, from fun divots to functional design tools that could become your new go-to’s.




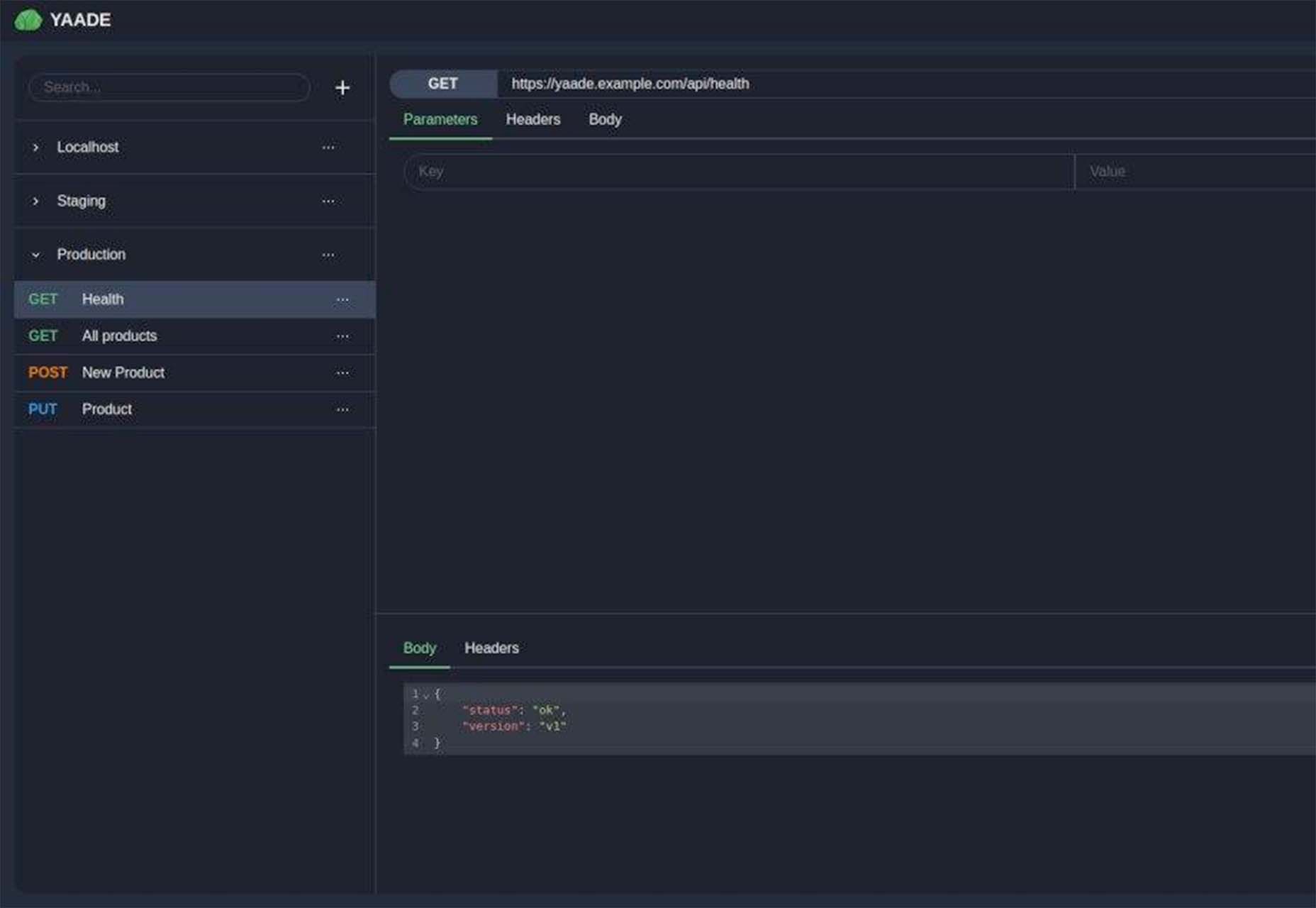
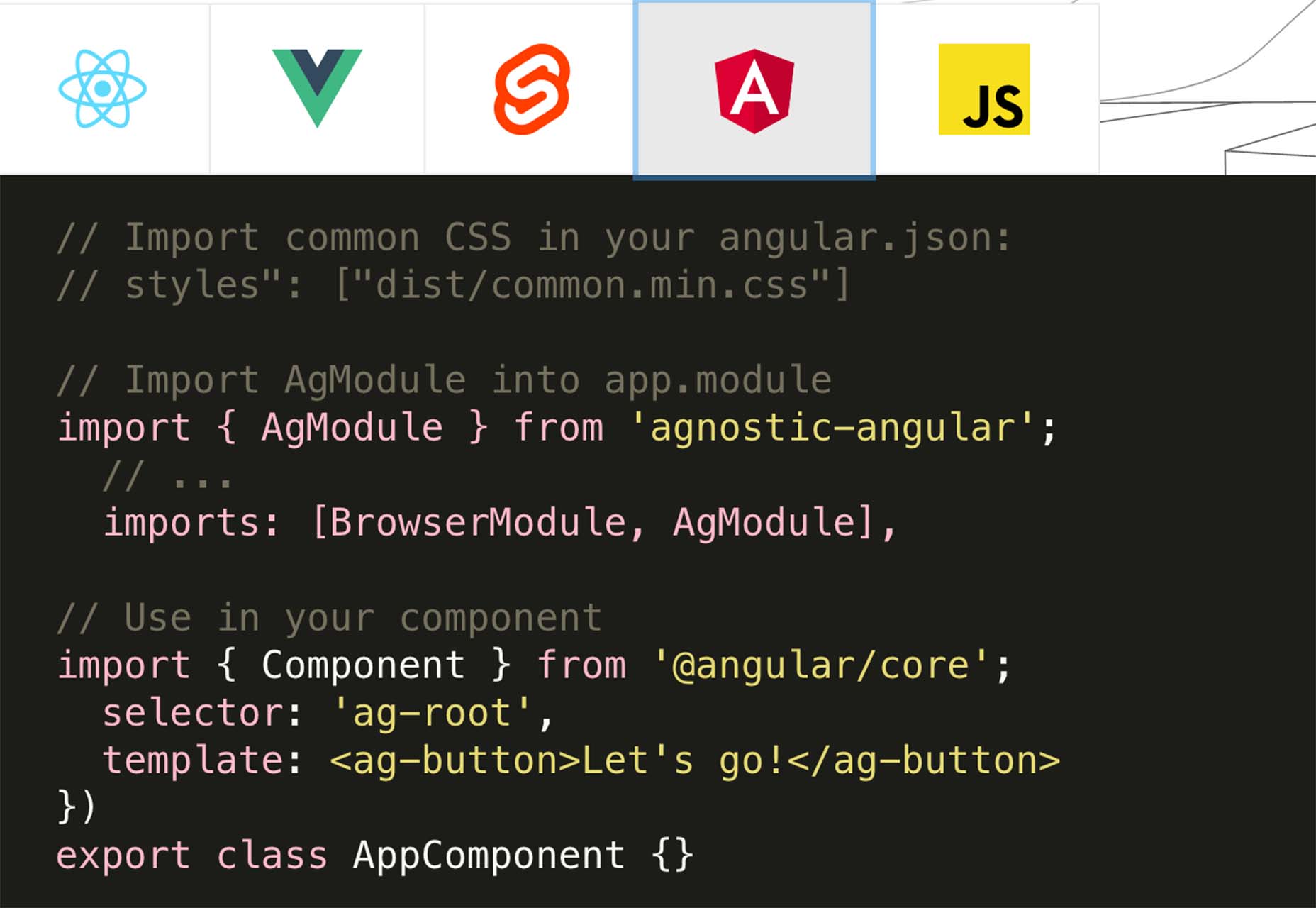







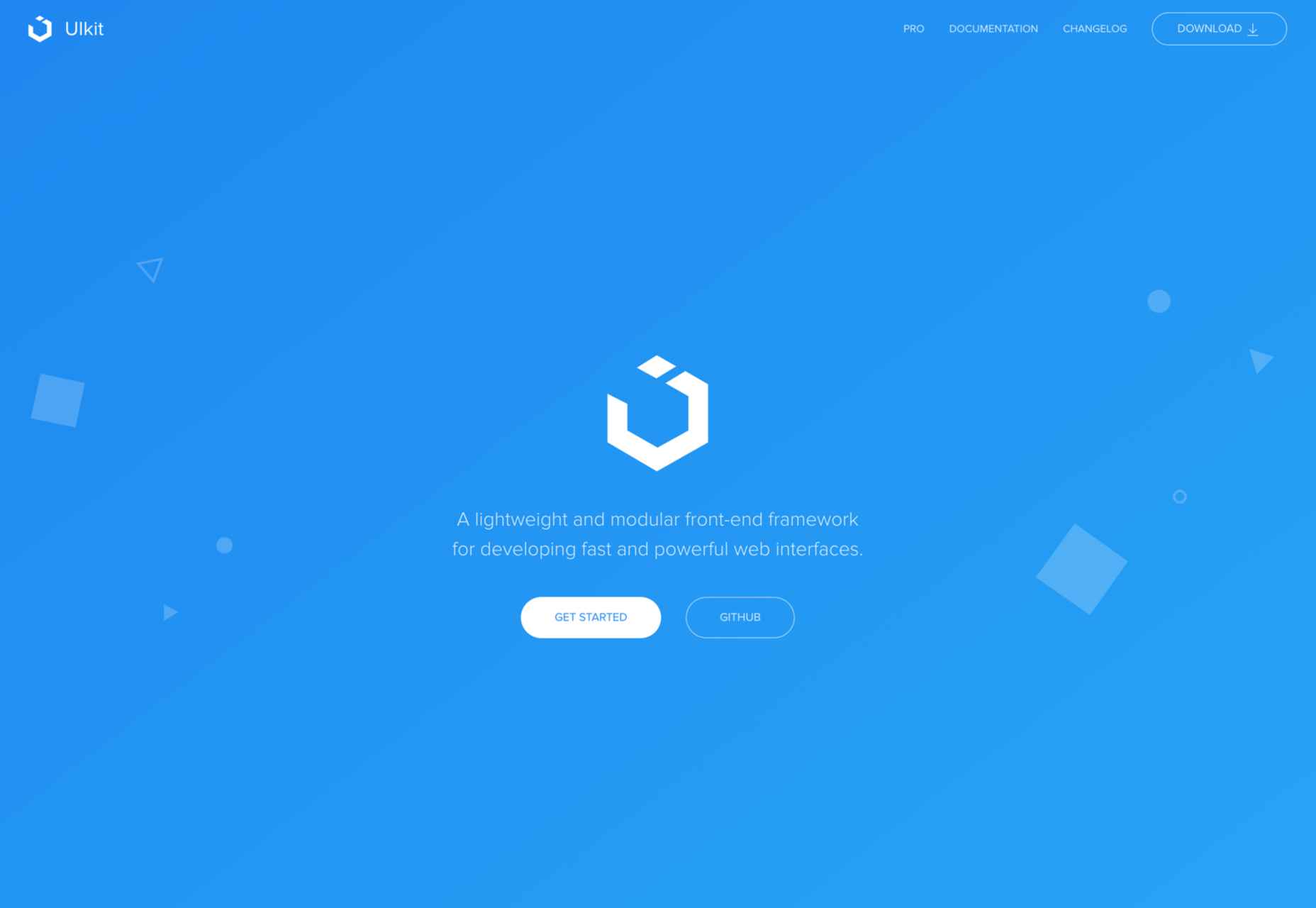
 Whether you are a CSS expert or a front-end beginner, using the right CSS framework is crucial for your daily tasks. There are numerous frameworks whose ultimate goal is the same: helping developers target multiple screens, in the simplest possible way.
Whether you are a CSS expert or a front-end beginner, using the right CSS framework is crucial for your daily tasks. There are numerous frameworks whose ultimate goal is the same: helping developers target multiple screens, in the simplest possible way.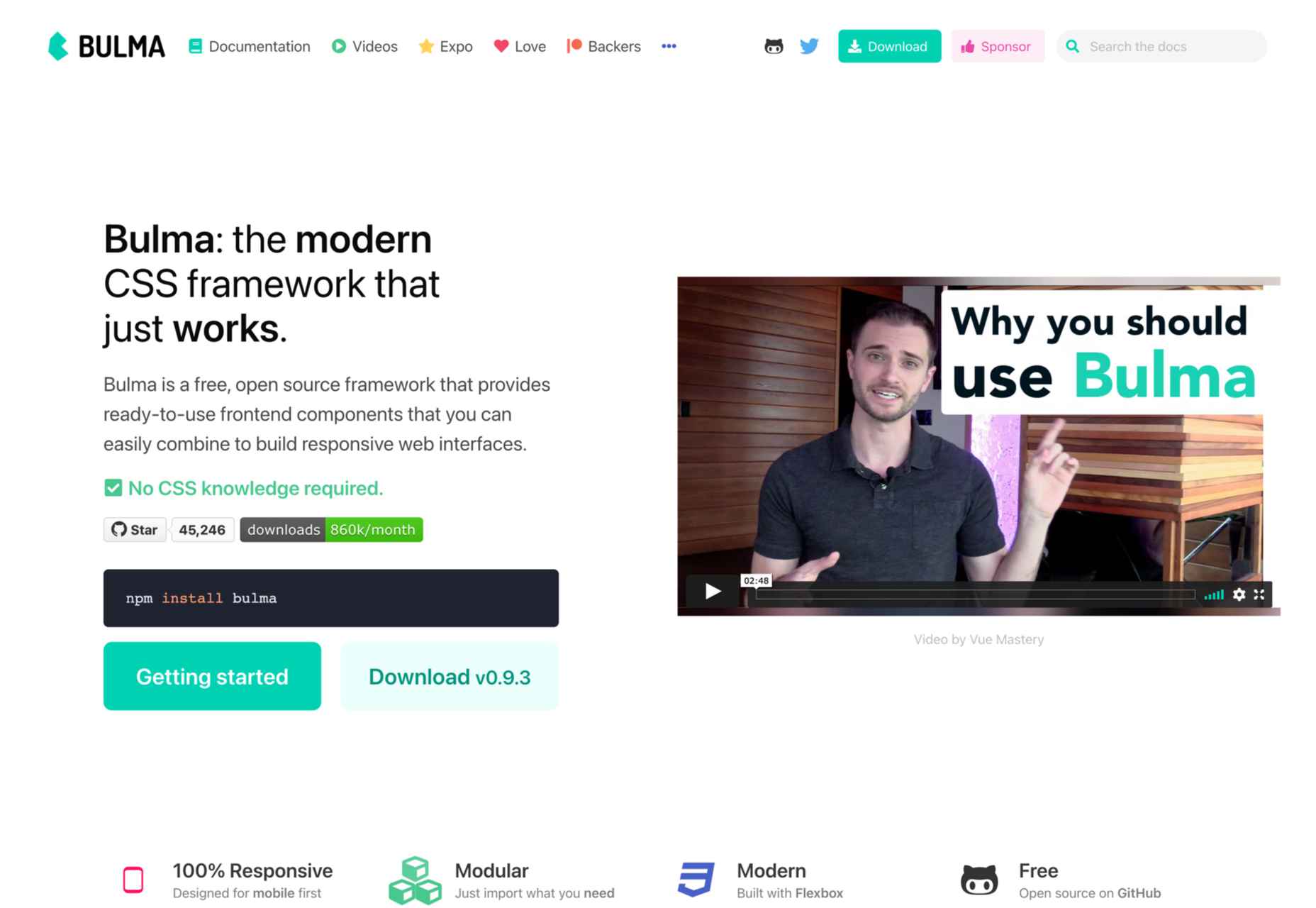


 Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site, Webdesigner News. Our colleagues sift through it, selecting the very best stories from the design, UX, tech, and development worlds and posting them live on the site.
Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site, Webdesigner News. Our colleagues sift through it, selecting the very best stories from the design, UX, tech, and development worlds and posting them live on the site.








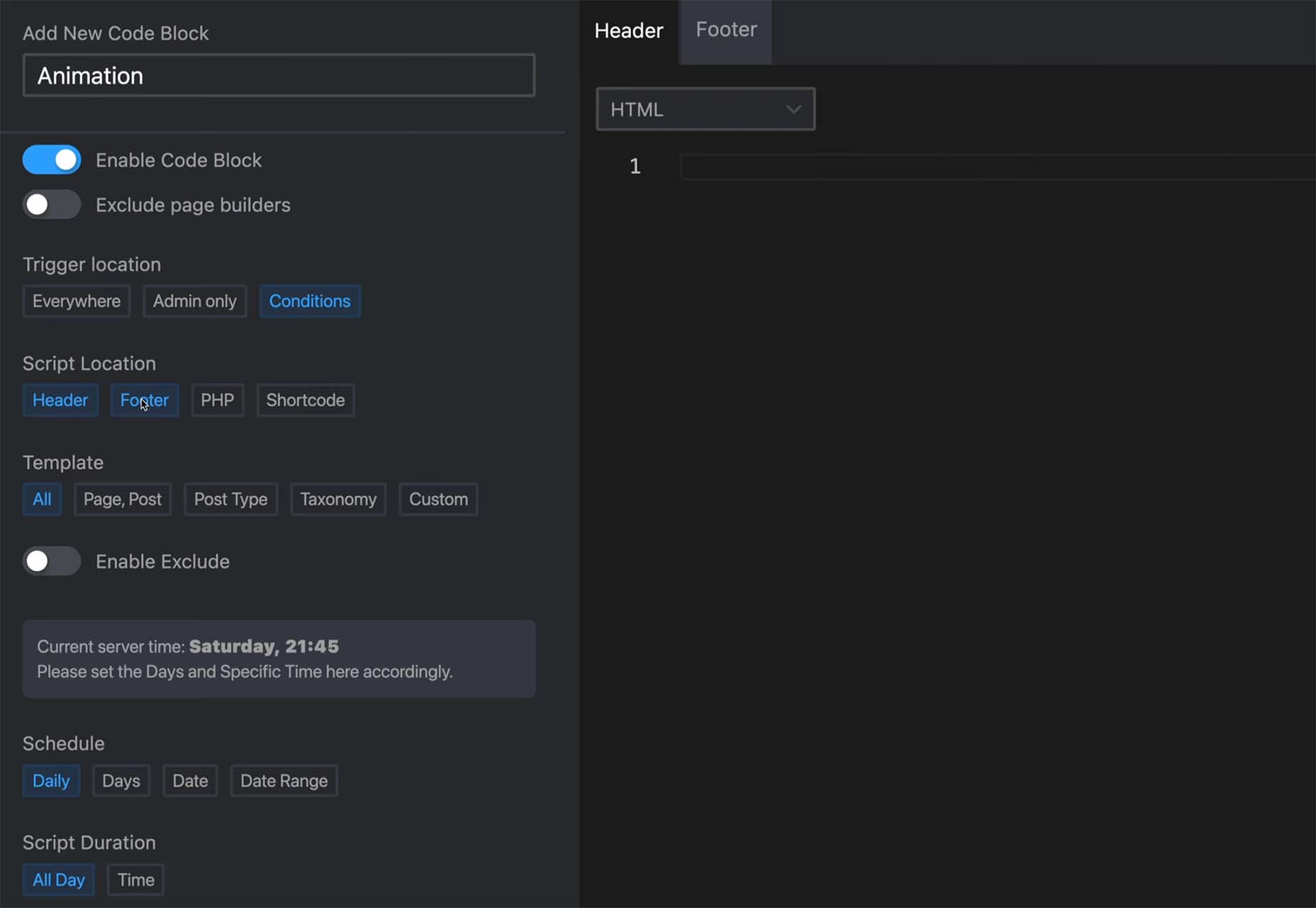
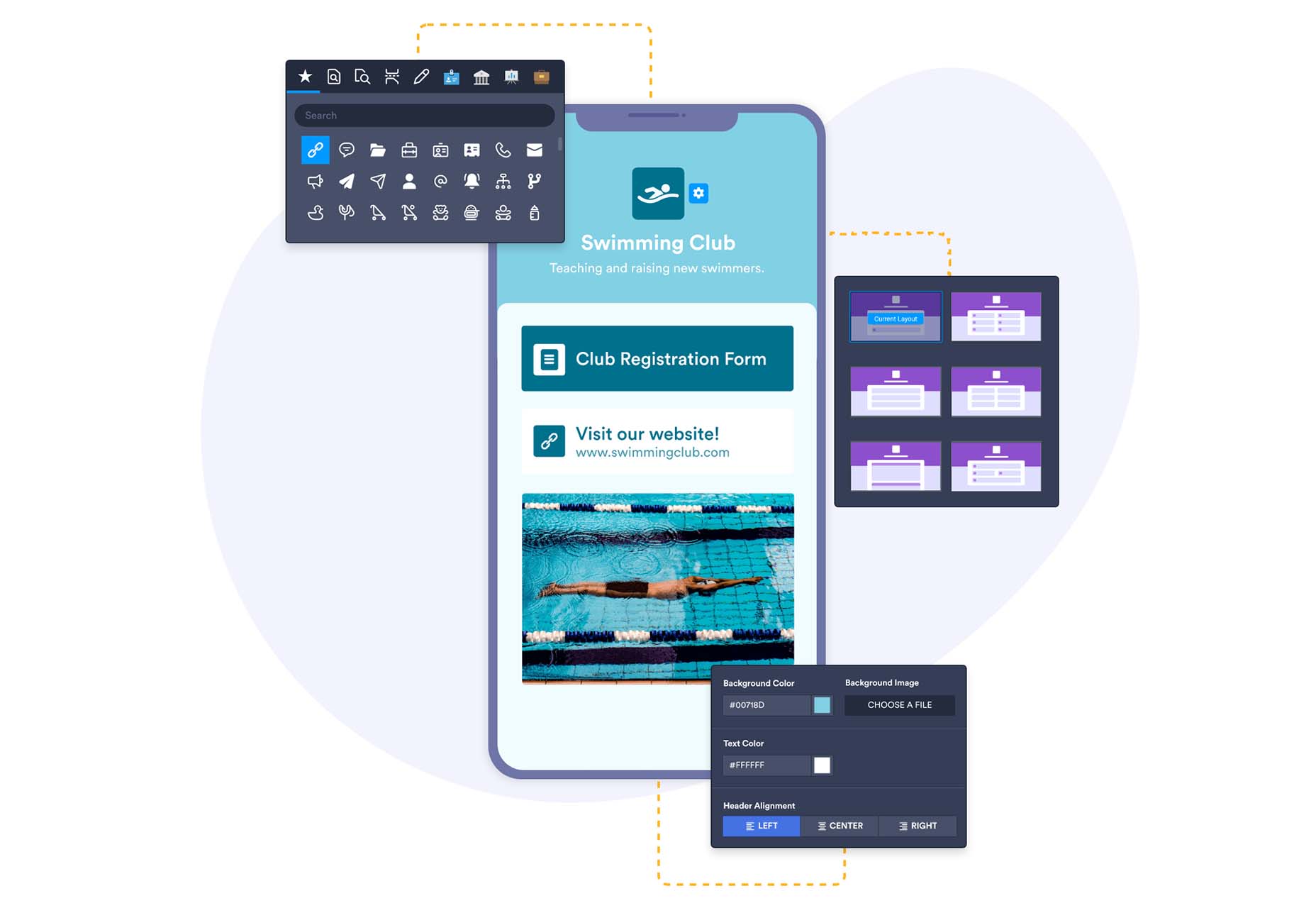
 It’s something every design team dreams about – a better design process and handoff procedure. Your design team is not alone if you are looking for a better solution.
It’s something every design team dreams about – a better design process and handoff procedure. Your design team is not alone if you are looking for a better solution.
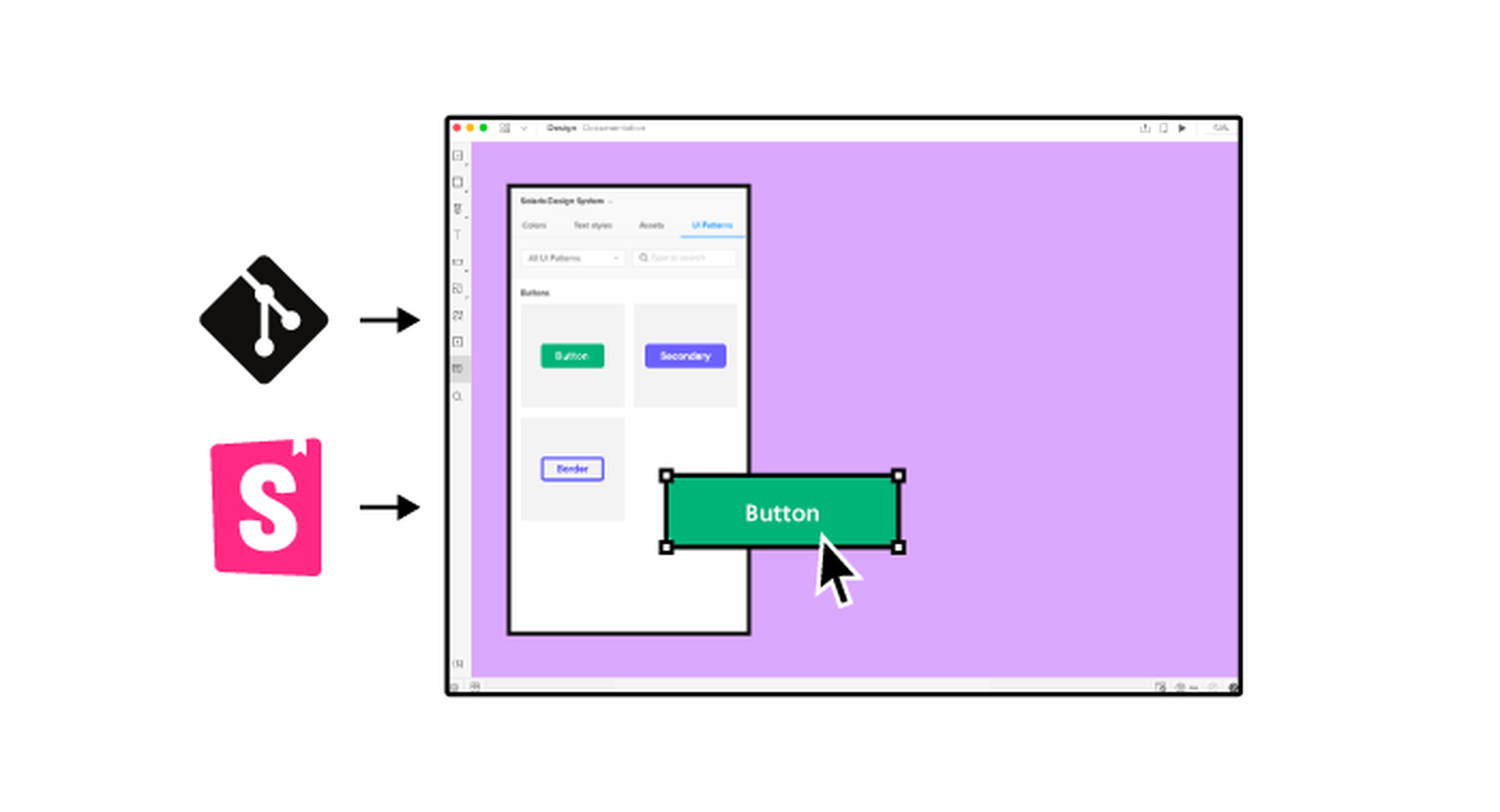




 Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site, Webdesigner News. Our colleagues sift through it, selecting the very best stories from the design, UX, tech, and development worlds and posting them live on the site.
Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site, Webdesigner News. Our colleagues sift through it, selecting the very best stories from the design, UX, tech, and development worlds and posting them live on the site.

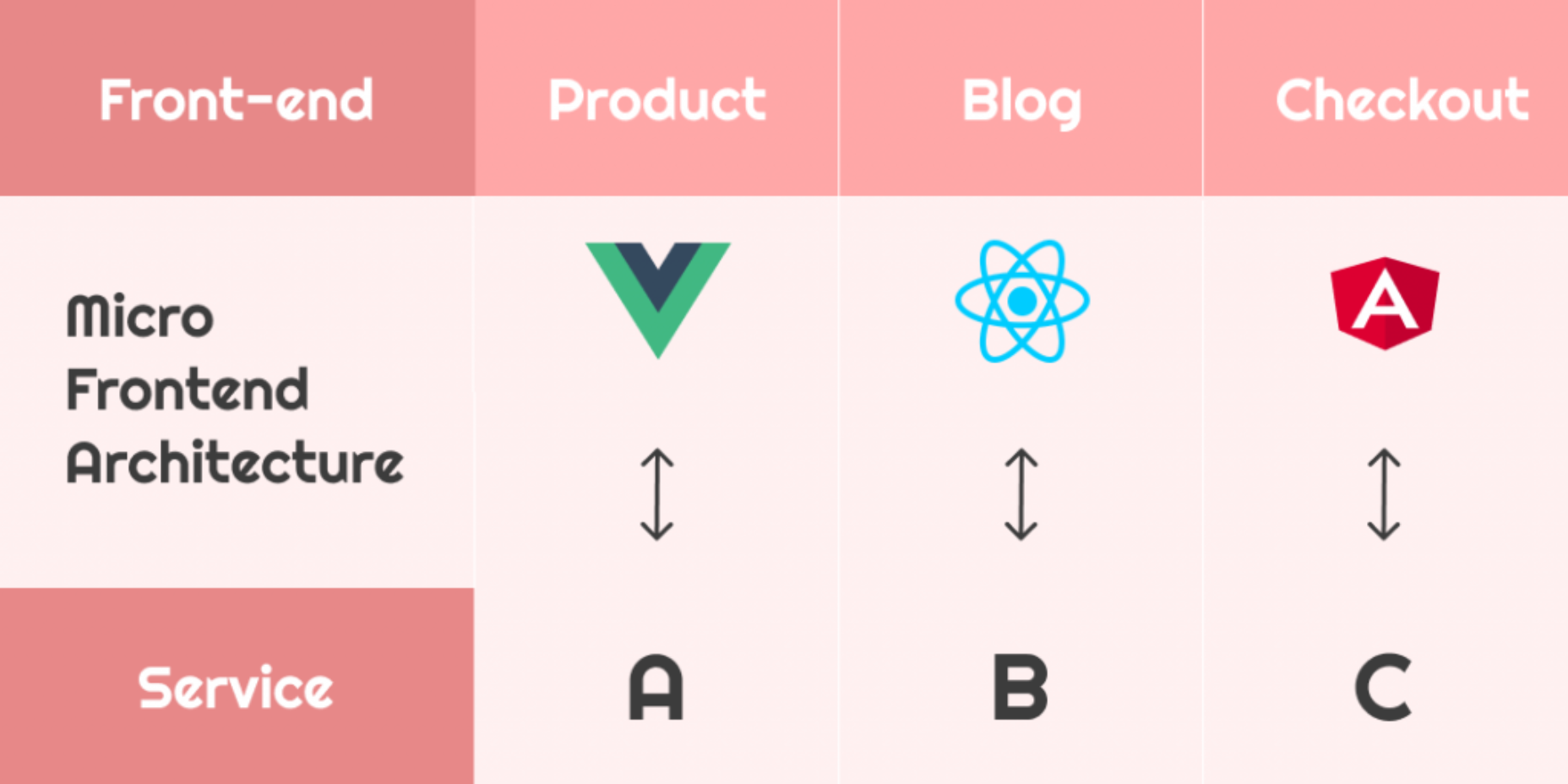






 Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site,
Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site,