Web design clients come from a wide variety of backgrounds. One day, you’ll be designing a portfolio website for a voiceover artist, the next you’ll be creating a comprehensive ecommerce site for a leading retailer. In an ideal world, you’ll get to a point where you eventually specialize in a niche. However, you’ll need to master both avenues first.
Web design clients come from a wide variety of backgrounds. One day, you’ll be designing a portfolio website for a voiceover artist, the next you’ll be creating a comprehensive ecommerce site for a leading retailer. In an ideal world, you’ll get to a point where you eventually specialize in a niche. However, you’ll need to master both avenues first.
The more time you spend in this industry, the more you’ll learn that every client comes with their own unique requirements and challenges to consider. However, there’s a particularly huge divide between the kind of web design projects you do for B2B clients, and the ones you do for B2C customers.
Both B2B (Business to Business) and B2C (Business to Consumer) websites need to be clear, concise, and aesthetically pleasing. They should always have a strong focus on user experience, and they need to work consistently across devices. However, being aware of the difference between B2B and B2C projects will help you to deliver better results to your customers.
Defining the Differences Between B2B and B2C Sites
Some web design trends remain consistent in any environment.
Whether you’re creating a site for a hairdresser, or a leading SaaS company, you’ll need to deliver responsive design, intuitive navigation, and excellent site security.
Your process is unlikely to differ from B2B to B2C much in terms of project milestones, phases, prototyping and wire-framing. The differences that arise between B2B and B2C projects often come in the approach you take to building certain elements.
Let’s take a closer look at the things you might need to consider:
1. The Target Audience
In any design project, it’s always important to keep the end customer in mind. Knowing your client’s target audience will help you to create both an image and a tone of voice that appeals to the right people.
B2B Websites
With B2B websites, you’ll be speaking to a range of highly-educated individuals who already have a general knowledge of your service. The aim here will be to show the end-user how you can help them achieve better results. For instance, m.io highlights “syncing communication” so you can “effortlessly chat” with your team.
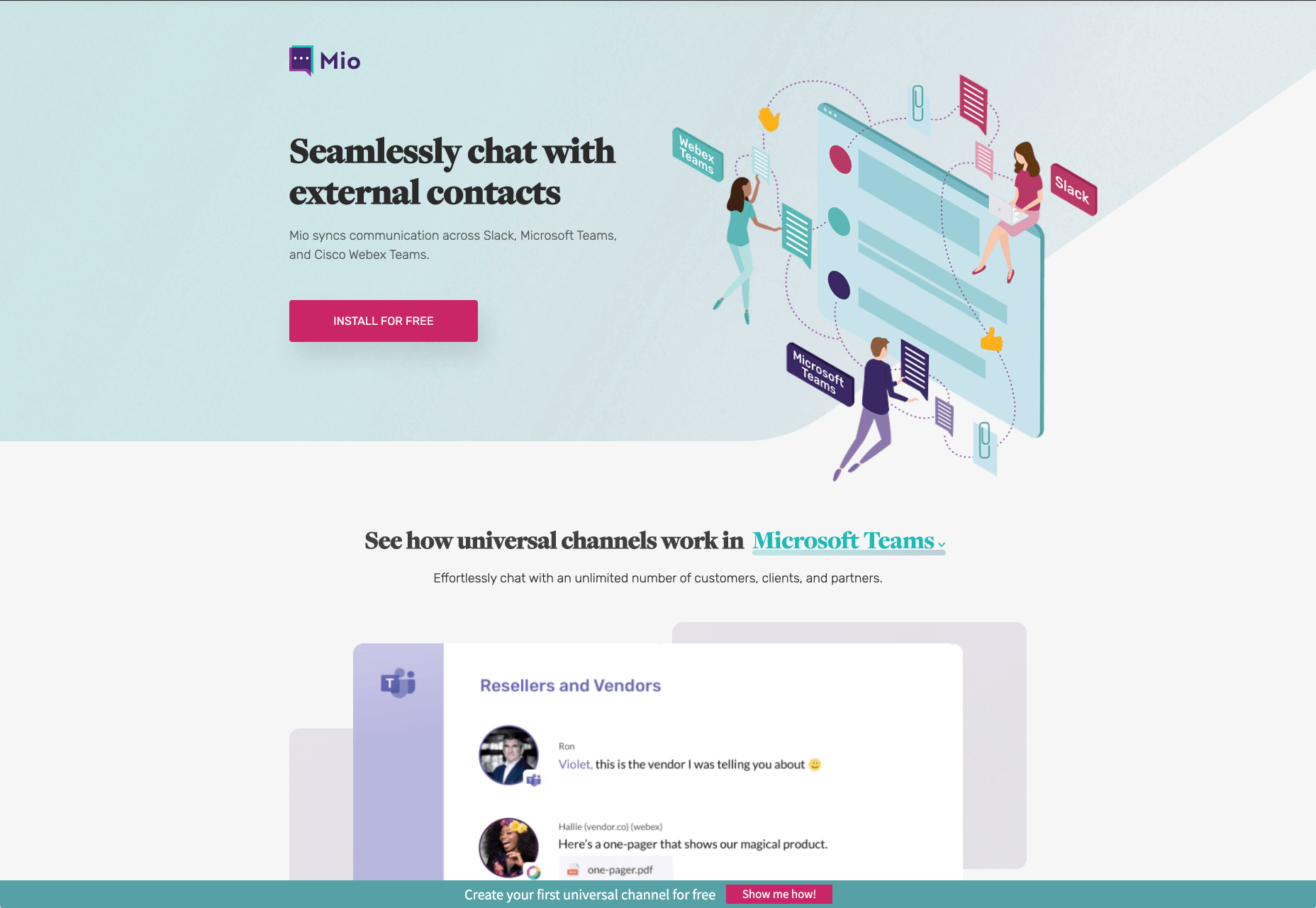
The language and content of the website is all about highlighting the key benefits of the products, and the kind of outcomes that they can deliver. The Nielsen Norman Group reports that there’s often a lot of discussion between decision-makers when they’re checking out a B2B website.
Designers need to work harder at convincing B2B buyers that they’re making the right decision. This is particularly true when you’re selling something like a software subscription that requires a lot of long—term investment.
B2C Websites
On the other hand, while B2B customers make decisions based on logic, information, and well-explained benefits, B2C customers are more influenced by emotion. They want quick solutions to their problems, and the opportunity to purchase from a brand that “understands” them.
Look at the Firebox website, for instance. It instantly highlights an ongoing sale at the top of the homepage, addressing any concerns a customer might have about price. That combined with a quirky layout full of authentic photos and bright colors means that customers are more inclined to take action.
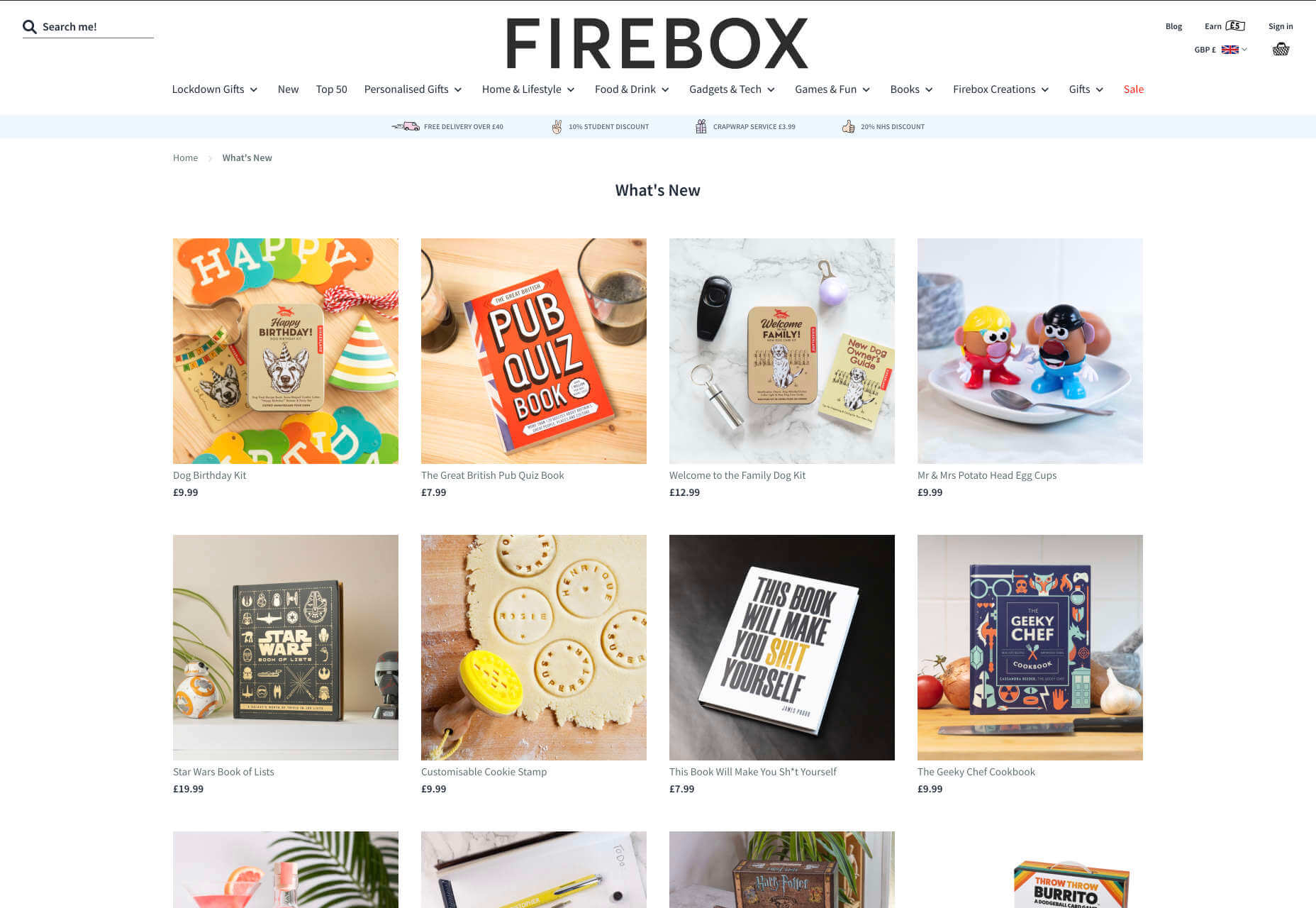
2. The Purpose
Another factor that can vary from B2C to B2B websites, is the motive behind a customer’s purchase. Knowing what’s pushing a target audience to interact with a brand will help you to create a website that appeals to specific goals.
B2B Websites
B2B websites often aim to solve expensive and time-consuming problems for companies. To sell a decision-maker on the validity of a solution, it’s important to thoroughly explain what the solution is, how it works, and how it addressees a specific pain point.
Look at the Zoom website for instance, they don’t just tell people that they offer video conferencing, they address the practical applications of the platform:
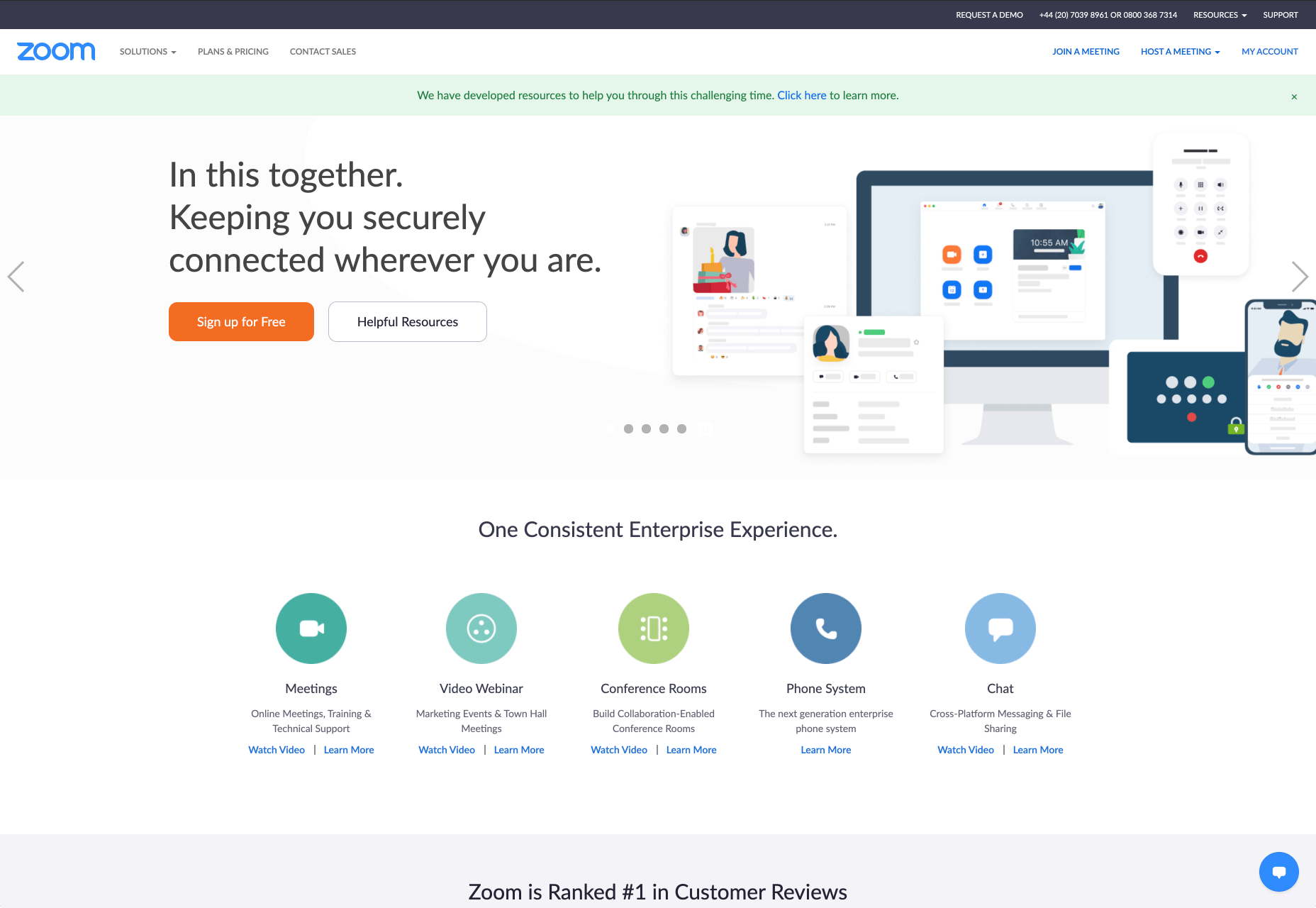
B2C Websites
Consumers are a lot easier to appeal to in terms of emotional impact, because many of them come to a website looking to fulfill an urgent need. Because of this, many web designers can take advantage of things like urgency and demand to encourage conversions. For instance, look at this website from TravelZoo. It takes advantage of a customer’s desire to get away:
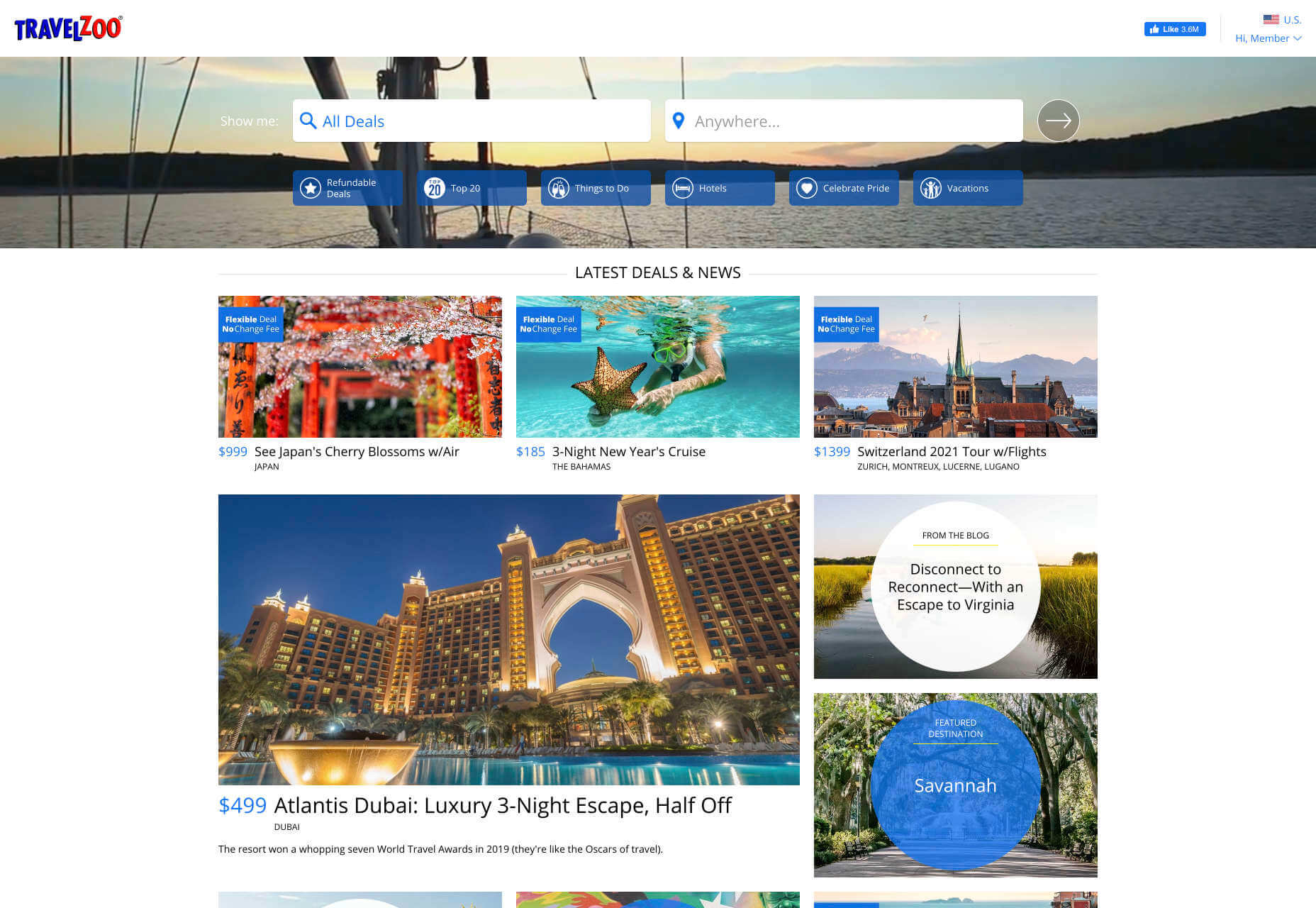
A B2B website needs to focus on providing information that helps companies to make more confident decisions. What’s more, with B2B sites, decisions are often made by several stakeholders, while B2C sites ask a single person to make a choice. A B2C website needs to address immediate concerns and connect with customers on an emotional level. B2C buyers still want to do their research on products or services, but the turnaround is much quicker, and often requires less information.
3. The Design Elements (Visual Appearance)
Just as the focus of your website design and the audience that you’re creating the experience for can differ from B2B to B2C websites, the visual elements of the design might change too.
B2B Websites
In most cases, B2B websites are all about presenting a highly professional and respectable image. You’ll notice a lot of safe and clear choices when it comes to typography and imagery. It’s unusual to see a B2B website that takes risks with things like illustrations and animations.
Look at the Green Geeks website for instance. Everything is laid out to encourage clarity and understanding. Information is easy to find, and there are no other issues that might distract a customer.
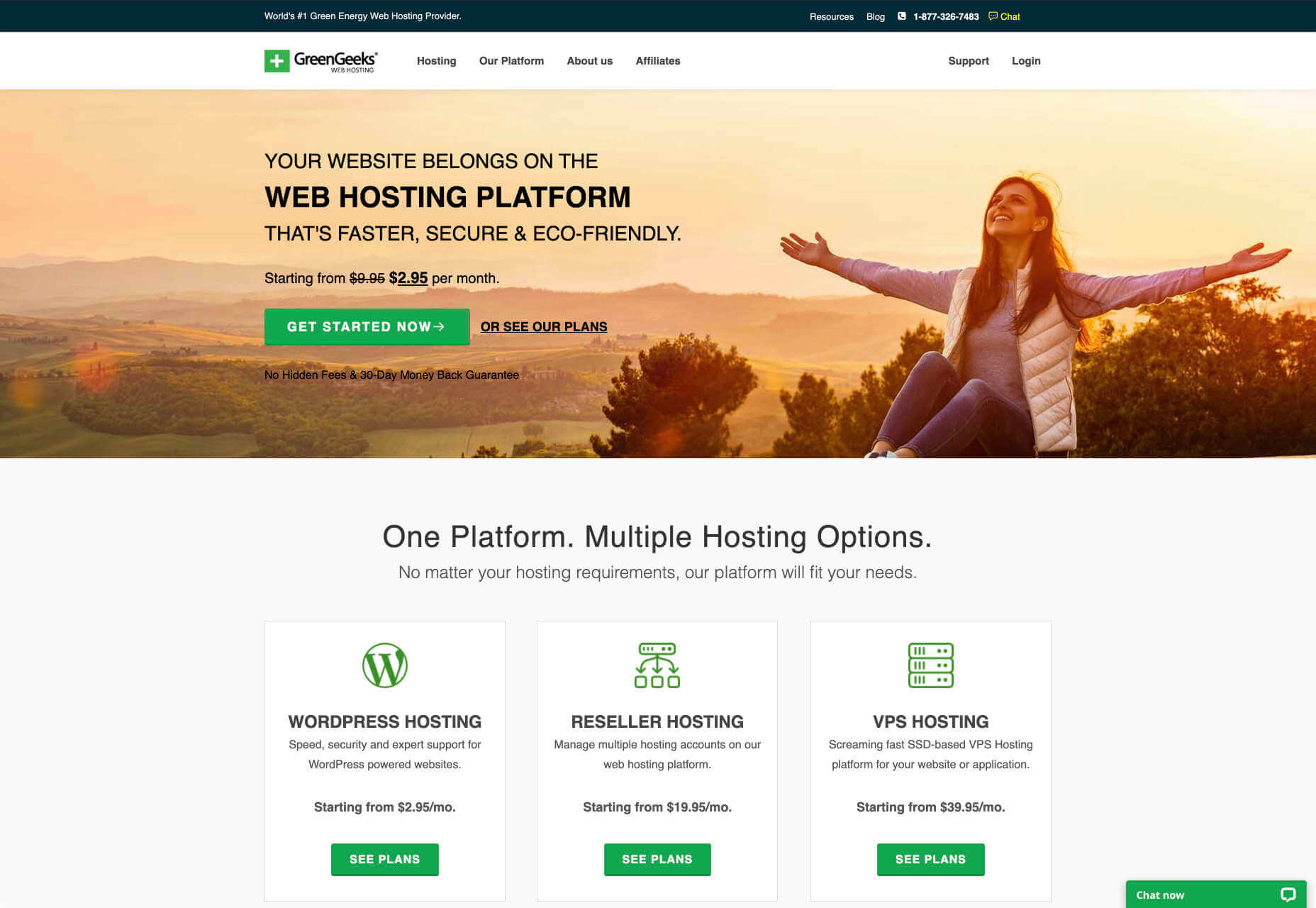
B2C Websites
On the other hand, B2C websites can be a little more daring. With so many different options to choose from, and most customers buying out of a sense of urgency or sudden demand, designers are under pressure to capture attention quick. This means that it’s much more likely to see large pieces of eye-catching imagery on B2C sites, with very little text.
Movement, like slideshows and animations often play more of a role here. Additionally, there’s a good chance that you’ll be able to experiment more aggressively with color. Take a look at the Yotel website, for instance. There’s very little textual information here, but the appeal of the website is conveyed through sliding images:

4. Website Content
The way that information is conveyed on a B2B website is very different to the messages portrayed on a B2C site. Usually, everything from the language, to the amount of content that you use for these projects will differ drastically.
B2B Websites
When designing for a B2B website, you’ll need to be careful with content, as you’ll be speaking to a very mixed audience. If your site caters to different industries, you’ll need to ensure that you show authority, without using too much jargon. Some companies even create different pages on their site for specific customers. The aspin.co.uk website covers the benefits from a company, sale and integration perspective:
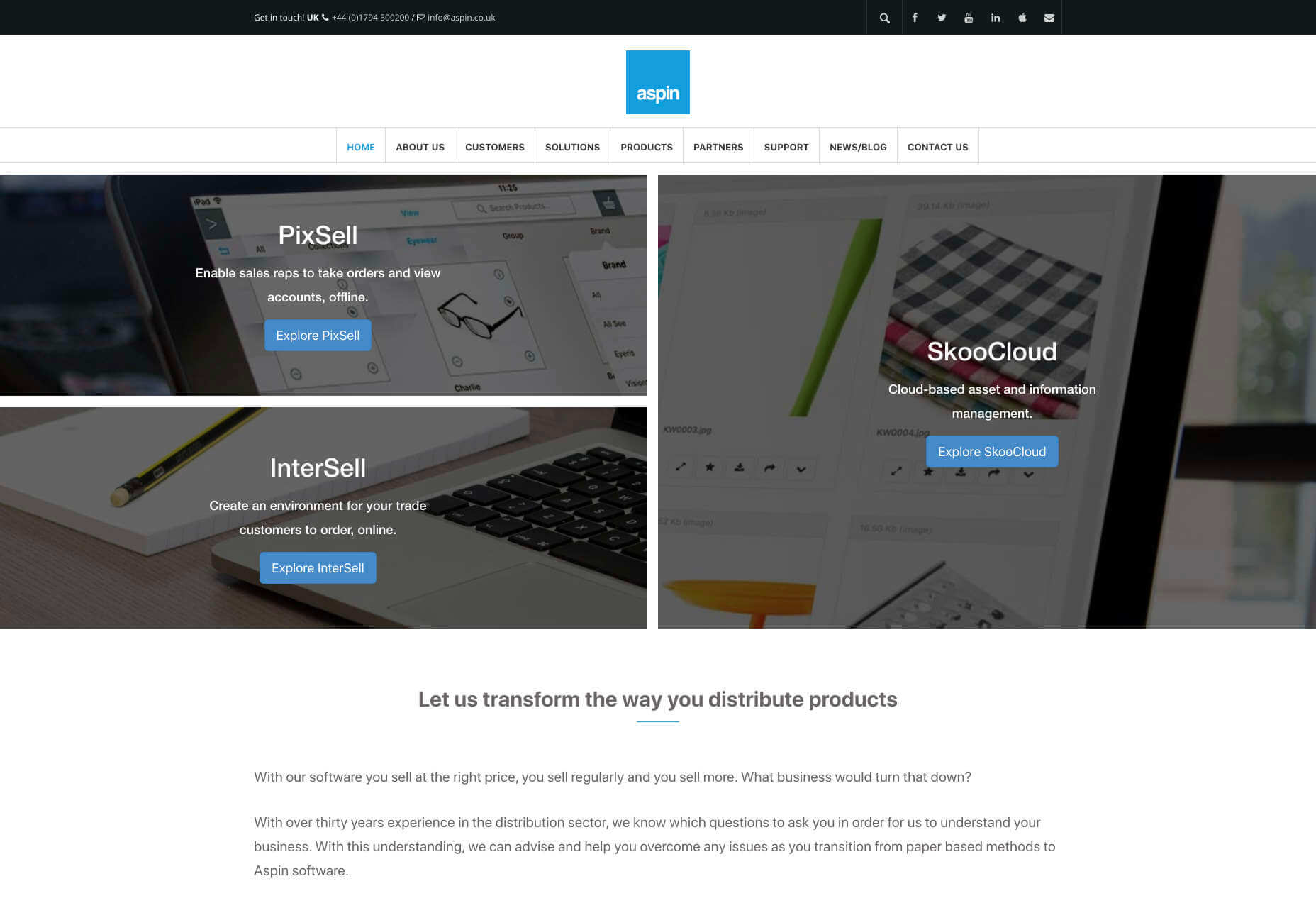
Rather than try to talk to all business owners about their differing communication pains, G-Suite anticipates its audience and creates pages for each.
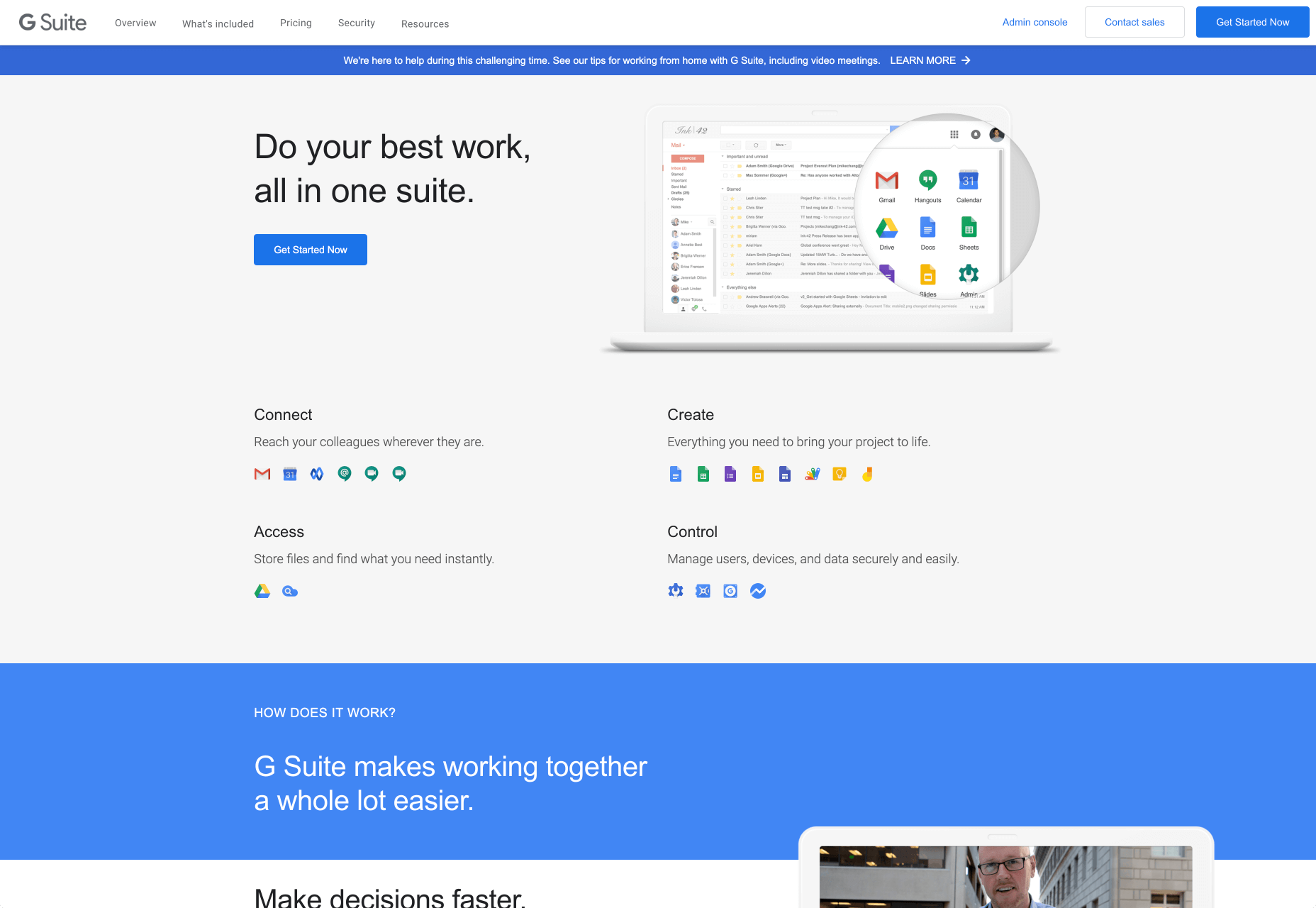
B2C Websites
Alternatively, B2C websites can make things a little simpler. For instance, on glossybox.co.uk, there’s no need to provide a ton of information for different types of shopper, designers can appeal to one audience, i.e. the “beauty addict”:
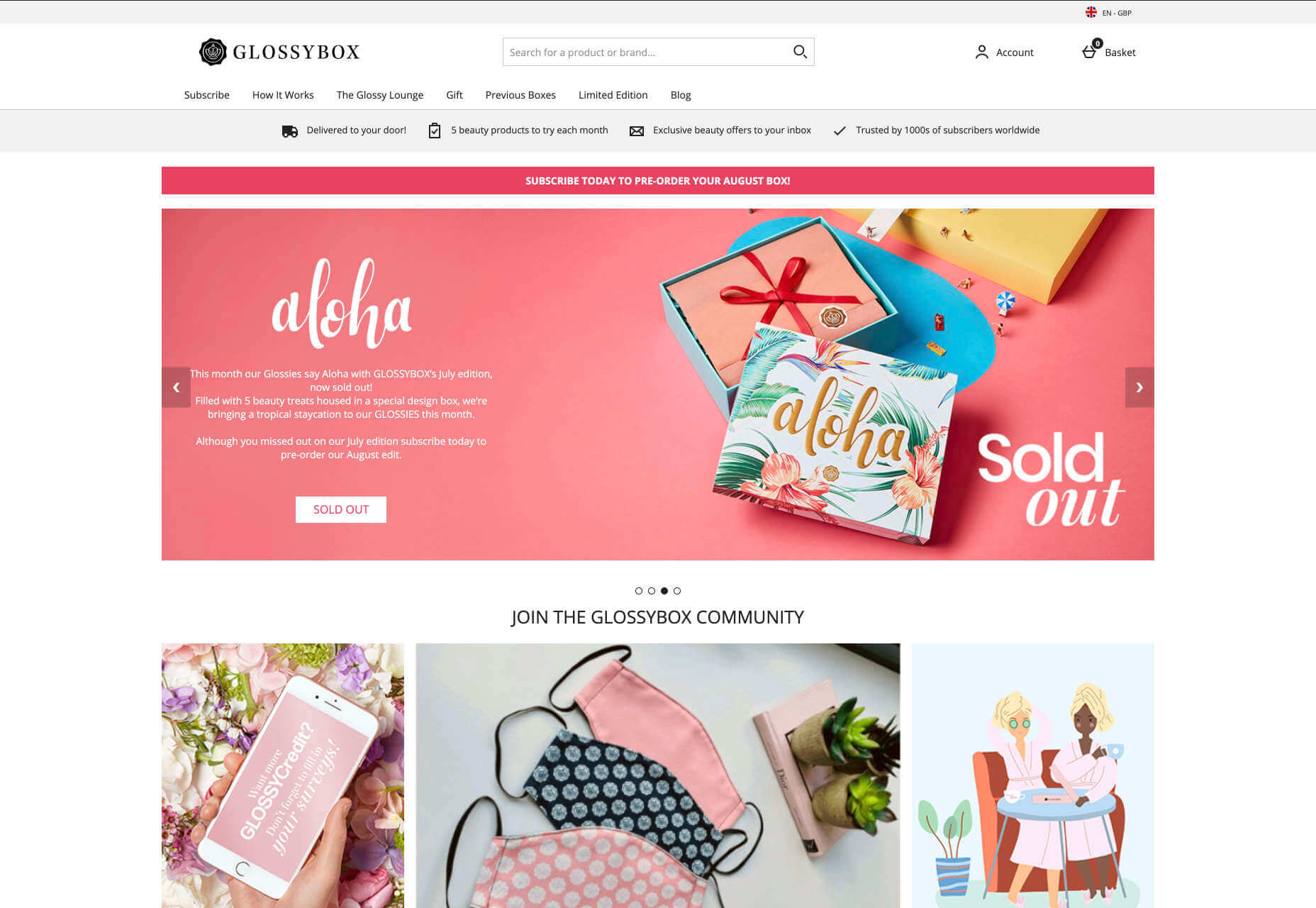
In both B2B and B2C websites, the aim of the content should always be to answer any questions that the end user might have.
5. CTA Buttons
Call to Action buttons are often a crucial part of the web design journey. However, it’s sometimes difficult to determine where they should be placed, or how many buttons you need.
B2B Websites
Because the decision to buy something won’t always happen immediately with a B2B website, these kinds of sites often use a variety of CTAs. For instance, you might have a “Request a Quote” button at the top of a page, as well as a Sign in button.
On the Klaviyo site, for instance, you can request a demo, sign up or log in:
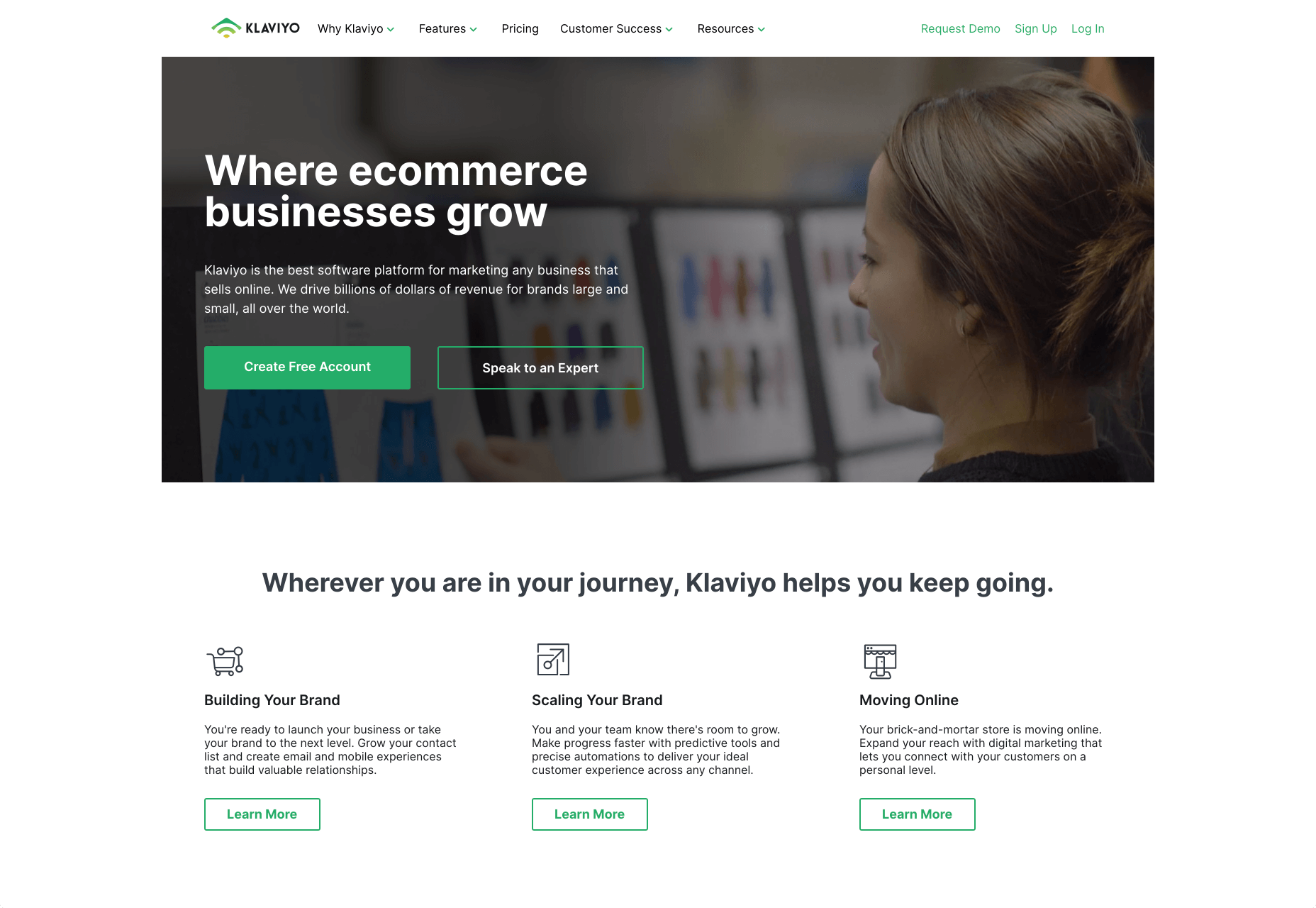
You can place CTAs lower on the page with B2B websites too, as it’s more likely that your customers will be scrolling through the site to collect more information before they decide to buy.
B2C Websites
On the other hand, with B2C websites, you usually don’t need to give your visitors as many options. A single option to “Add to Cart”, or perhaps an extra choice to “Add to Favorites” is all your user will need. Customers need to instantly see what they need to do next as soon as they arrive on a page:
On the Evil Hair website, you immediately see how to add a product to your cart.
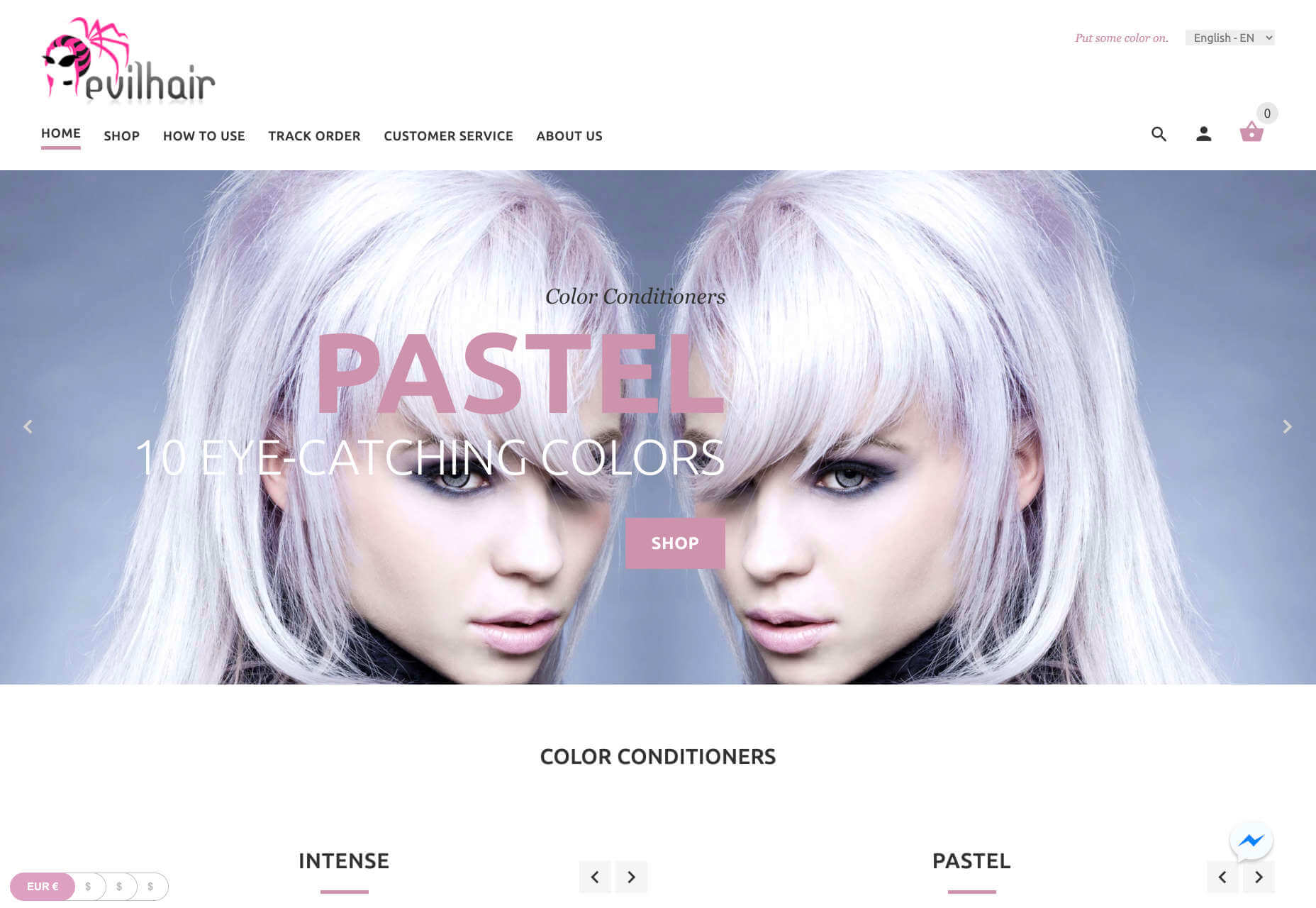
Remember, the sales process is a lot quicker with B2C customers. This means that you need your CTA buttons to be front and center as soon as someone clicks on a page.
6. Contact Forms
In a similar vein, the way that you design your contact forms will also depend on the end-user that the website wants to appeal to. There’s a very different process for getting in touch on a B2B website, compared to a B2C site.
B2B Websites
B2B websites often require longer contact forms, as clients need to collect additional information about a prospect’s position in a company, and what that company does. B2B companies need to share things like what they’re looking for in a service, and how many users they have, so a sales team knows what kind of demonstration to give.
As with any strategy for contact form design, you should always only include the fields that your client needs and no more. If you demand too much from any client, you could send them running in the opposite direction. Check out this straightforward option from Ironpaper, for instance:
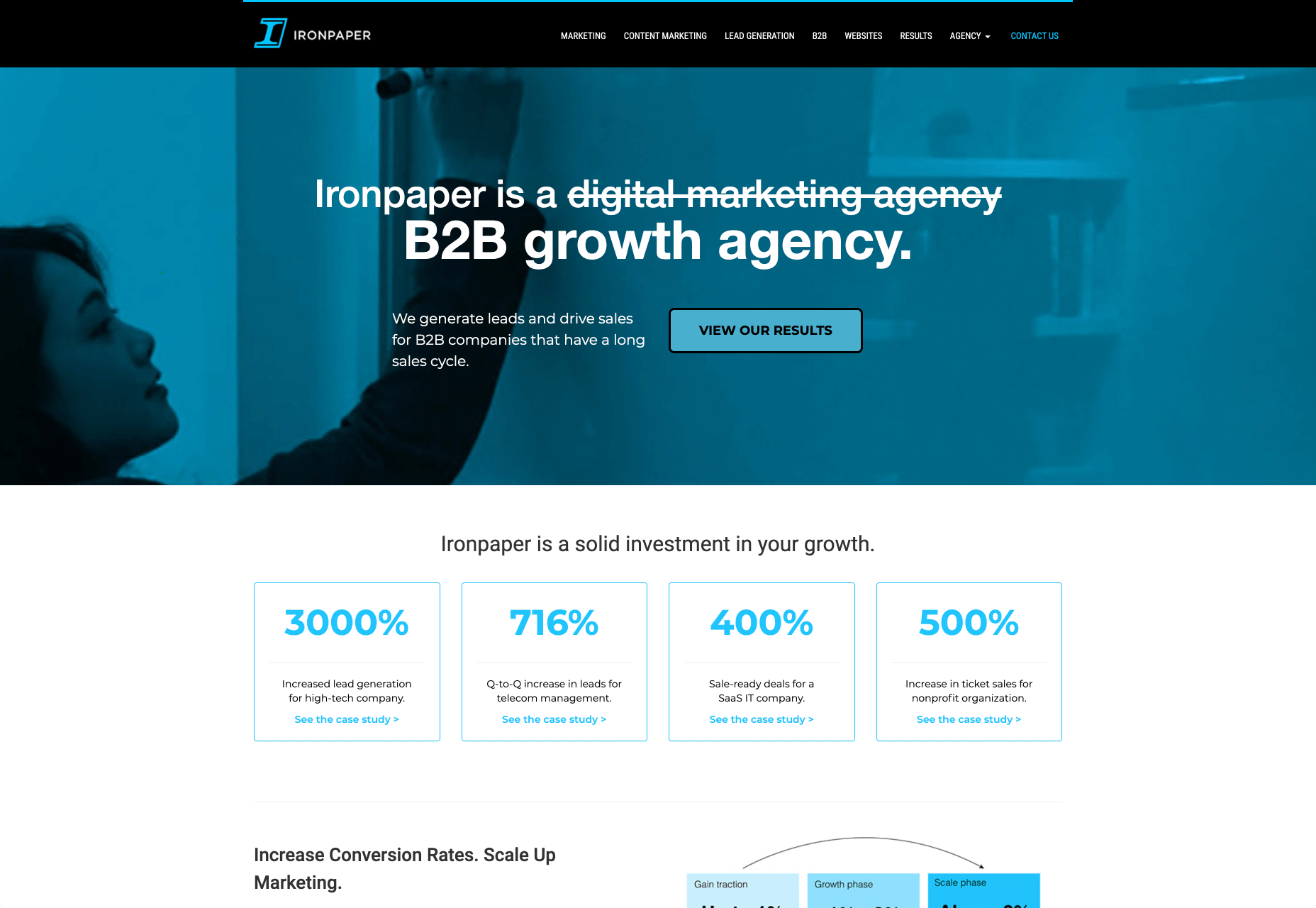
The form addresses as many relevant questions as possible without overwhelming the customer. Because the site handles things like design, it makes sense that they would ask for a link to the company’s existing website.
B2C Websites
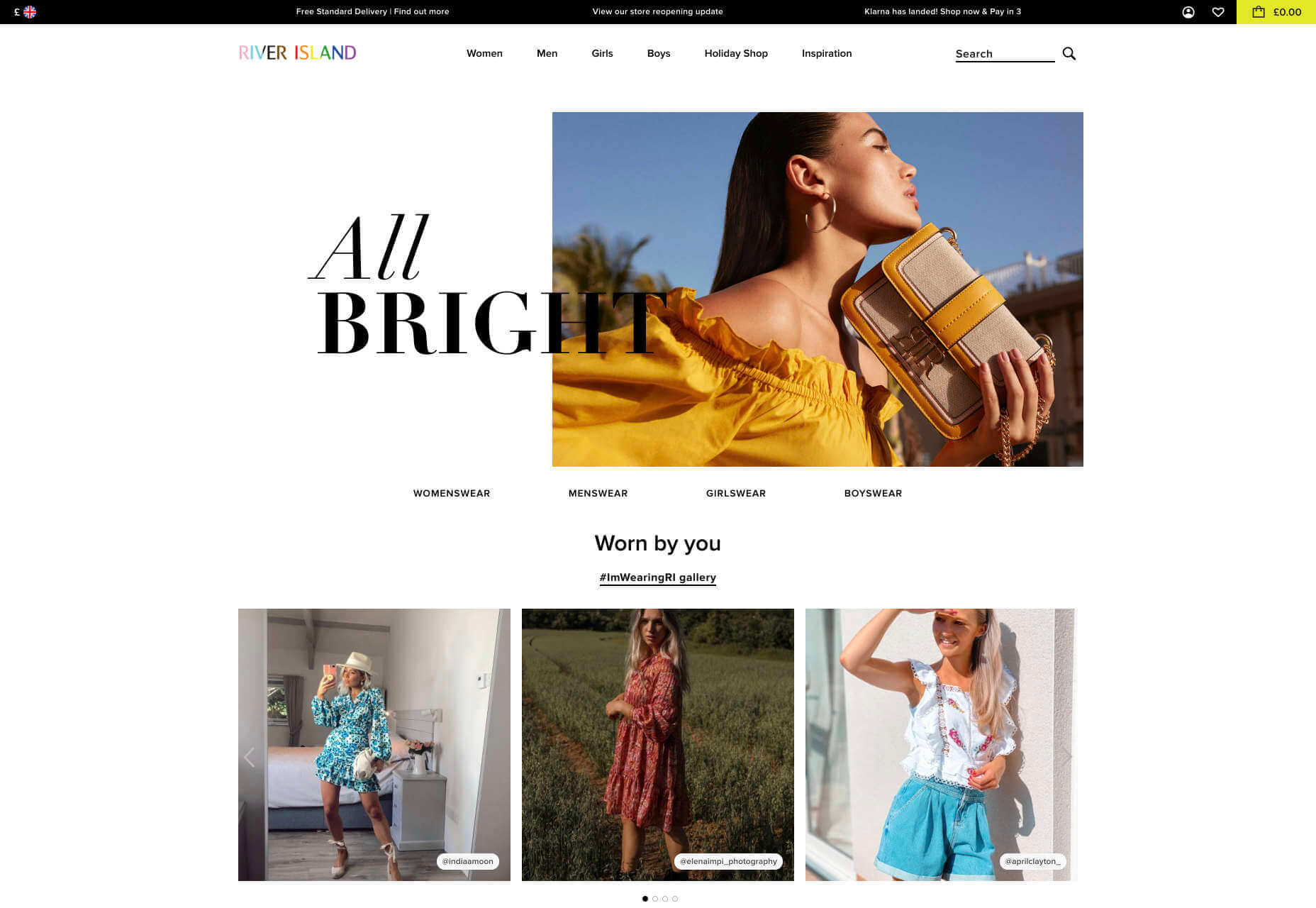
On a B2C website, there are very different approaches to contact forms. You may have a dedicated contact form on your website where people can get in touch if they have any questions. A FAQ page where customers can serve themselves is another great way to help your client stand out from the competition. Check out this option from River Island, for instance:
On the other hand, you might implement pop-up contact forms into a website if your client wants to collect emails for email marketing. In that case, it’s important to make sure that you’re only asking for the information you need, and nothing more.
The easier it is to sign up for a newsletter, the more likely it is that customers will do it. Being able to enter their name and email address and nothing else will make the signup seem less tasking.
7. Search Bars and Navigation
Whether you’re designing for B2B or B2C companies, navigation will always be a critical concern. End users need to find it easy to track down the information that they need about a company, whether they’re looking for a particular product or a blog.
B2B Websites
On a B2B website, the search bar often takes up a lot less prominence than it does on a B2C site. That’s because all of the information that a client needs, and the buttons they need to take their next steps, are already visible front-and-center.
As a designer, it will be your job to push as many people to convert as possible, by making the purchasing journey the most appealing path for visitors. For instance, on the Copper website, the “Try Free” buttons are much easier to see than “Continue with Google” or “Login”:
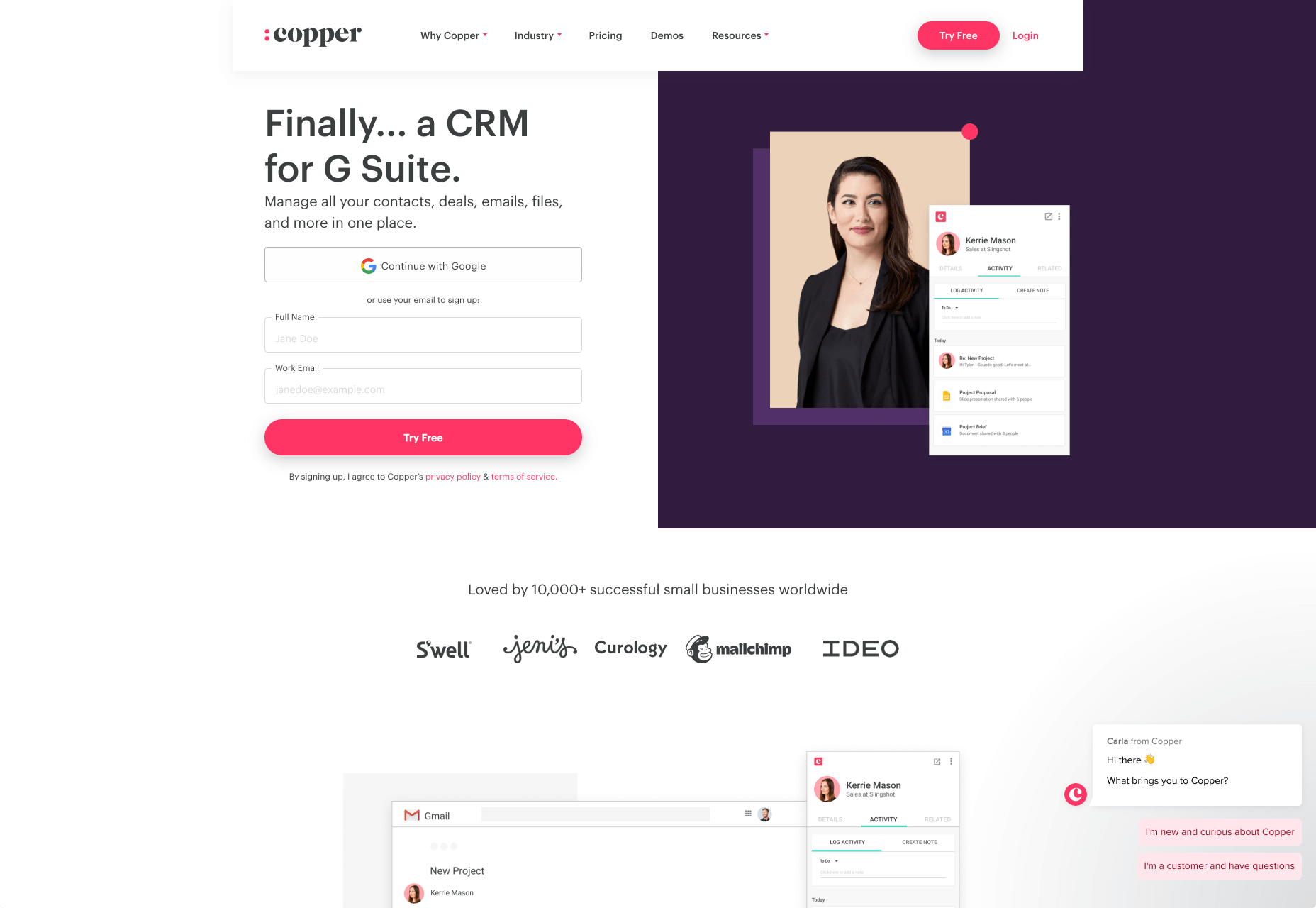
With B2B sites, the focus is on a very specific goal. Although navigation still needs to be available, it doesn’t need to be as obvious as it is on a B2C site.
B2C Websites
On the other hand, most B2C websites offer a wide range of products, and they’re perfectly happy for their customers to purchase anything, as long as they eventually convert. Because of this, they make navigation a much more significant part of the customer journey.
The search bar is often presented at the very top of the screen where customers can see it immediately. Additionally, there may be multiple pages within certain product categories, so that customers can browse through the items they’re most interested in. For instance, look at the homepage on the IWoot website:
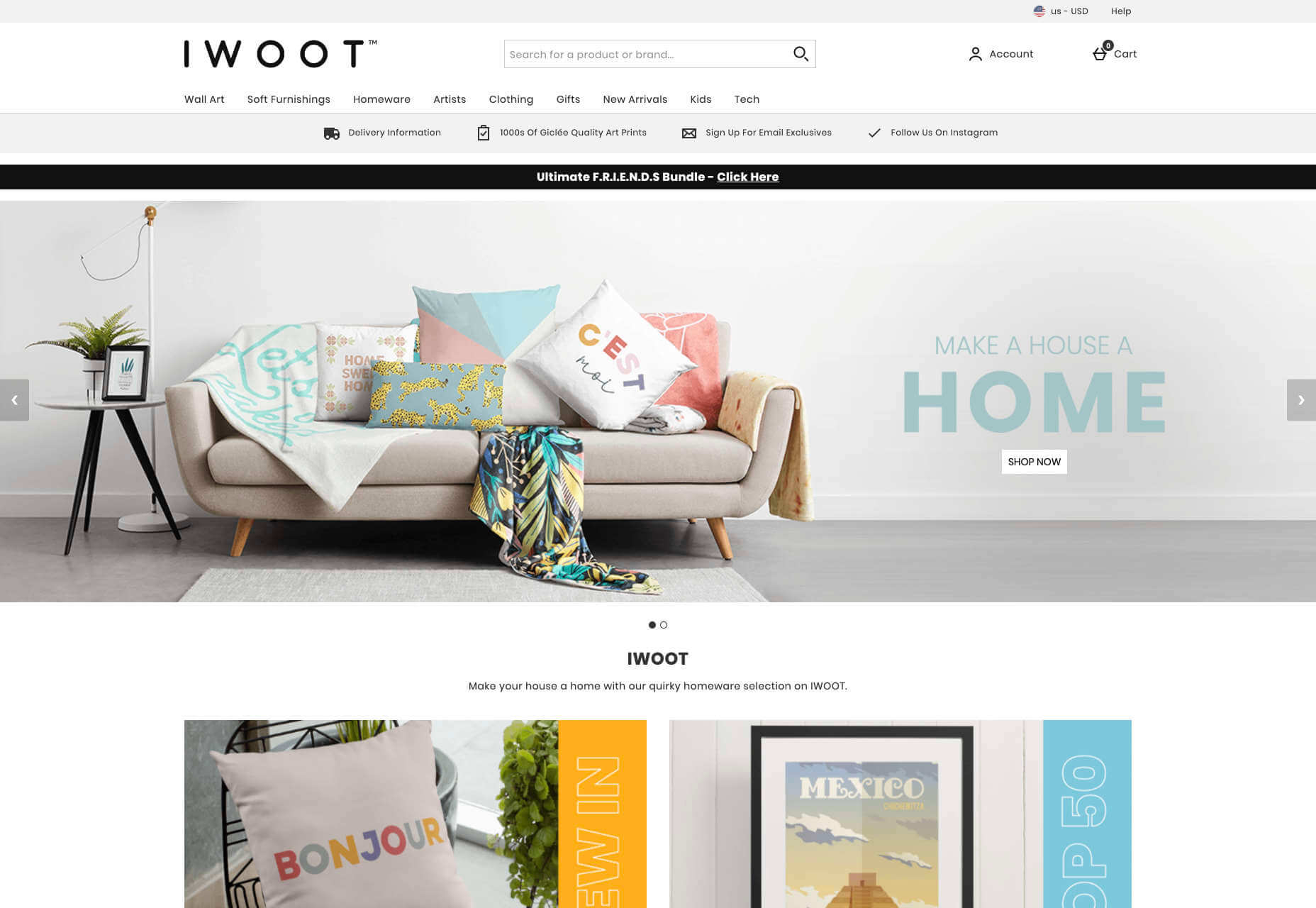
The navigation elements in B2C websites need to be a lot more obvious, because consumers are more likely to use them when they’re searching through their options.
8. Social Proof and Testimonials
Finally, social proof is one of the things that will work well for improving conversions on any kind of website. When your customers aren’t sure whether or not they should buy from you, a review or testimonial could be just the thing to push them over the edge.
B2B Websites
On a B2B website, the decision-making process takes a lot longer. Because of this, it’s worth including as much social proof as possible in every part of the website. Client testimonials, reviews and ratings, and even high-profile company logos make all the difference. Many B2B websites include a page dedicated to case studies highlighting the success of other brands.
Your client might even go as far as to ask for a page that highlights their awards and recognition or showcases comparison tables that pit their products against the competition.
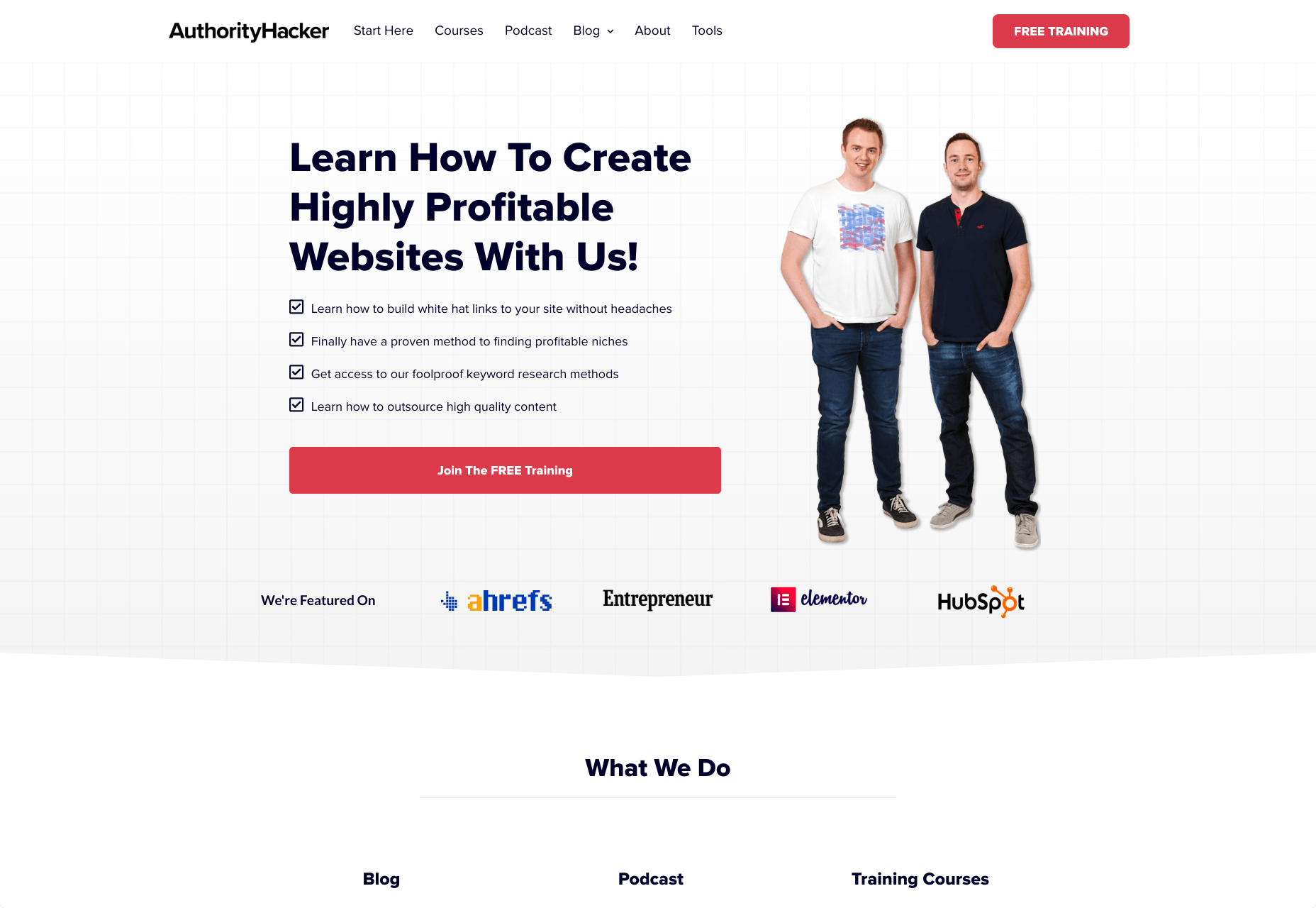
For instance, Authority Hacker has a “what the pros say about us” section as social proof:
B2C Websites
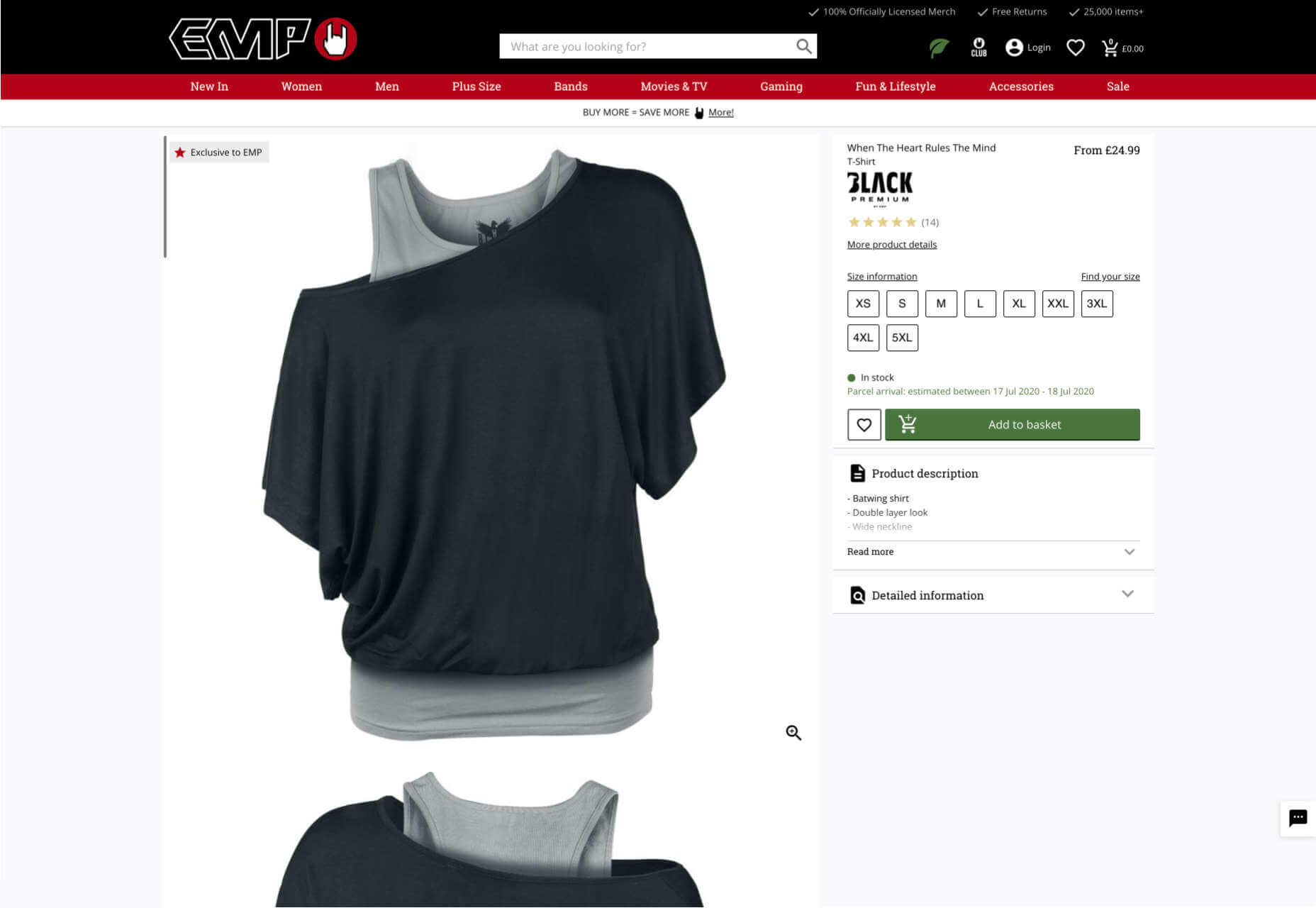
With a consumer website, you can include consumer ratings and reviews wherever you like. However, it’s most likely that you’ll want to have a place where customers can see the reviews of other clients on the product pages themselves. On the EMP website the company gives users the option to click on the star review section to jump to a different space on the page where testimonials are listed. This ensures that customers don’t have to scroll through a lot of excess information if they just want to add an item straight to their cart.
Designing for B2B vs B2C
In the world of web design, no two customers are ever the same. While you’ll need to adapt your processes to suit each customer you interact with, you can set your expectations in advance by learning the differences between B2B and B2C strategies.
Featured images by Chris Ross Harris and Mike Kononov.
Source
p img {display:inline-block; margin-right:10px;}
.alignleft {float:left;}
p.showcase {clear:both;}
body#browserfriendly p, body#podcast p, div#emailbody p{margin:0;}

Source de l’article sur
 Artificial Intelligence is the use of computers or machines that have been created to work and react like humans. Some of the computers that have AI, are designed to include speech recognition, and learn user behaviours so they can predict activities or decisions before they happen.
Artificial Intelligence is the use of computers or machines that have been created to work and react like humans. Some of the computers that have AI, are designed to include speech recognition, and learn user behaviours so they can predict activities or decisions before they happen.


 I think of a creative practice as a combination of an approach (a design philosophy) and a series of techniques (craft skills); a good tool facilitates a technique, which in turn supports an approach.
I think of a creative practice as a combination of an approach (a design philosophy) and a series of techniques (craft skills); a good tool facilitates a technique, which in turn supports an approach.





 Like it or not, we’re slowly edging towards a two-tier web: those sites that are secure, and…everything else.
Like it or not, we’re slowly edging towards a two-tier web: those sites that are secure, and…everything else.
 Web design clients come from a
Web design clients come from a 
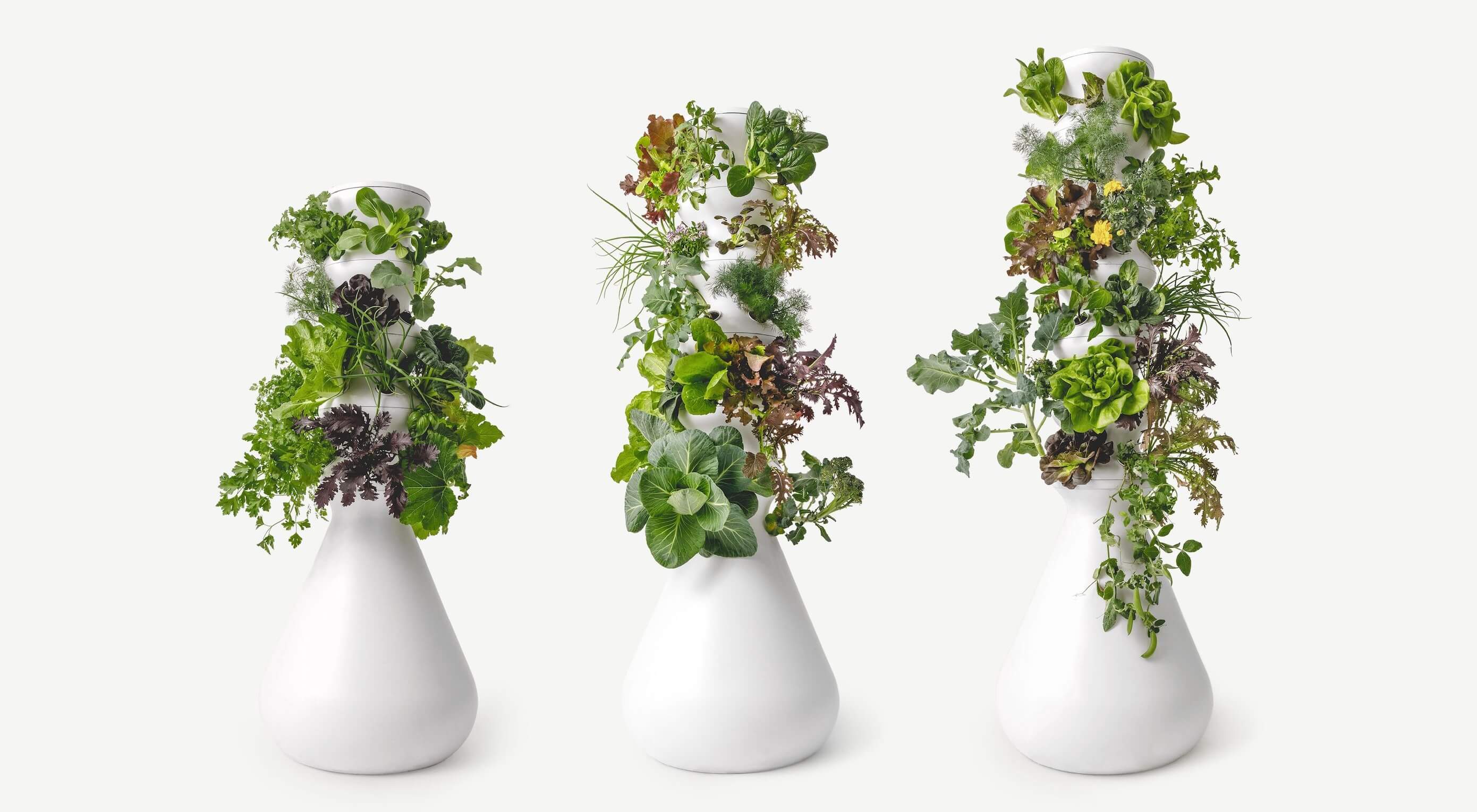

















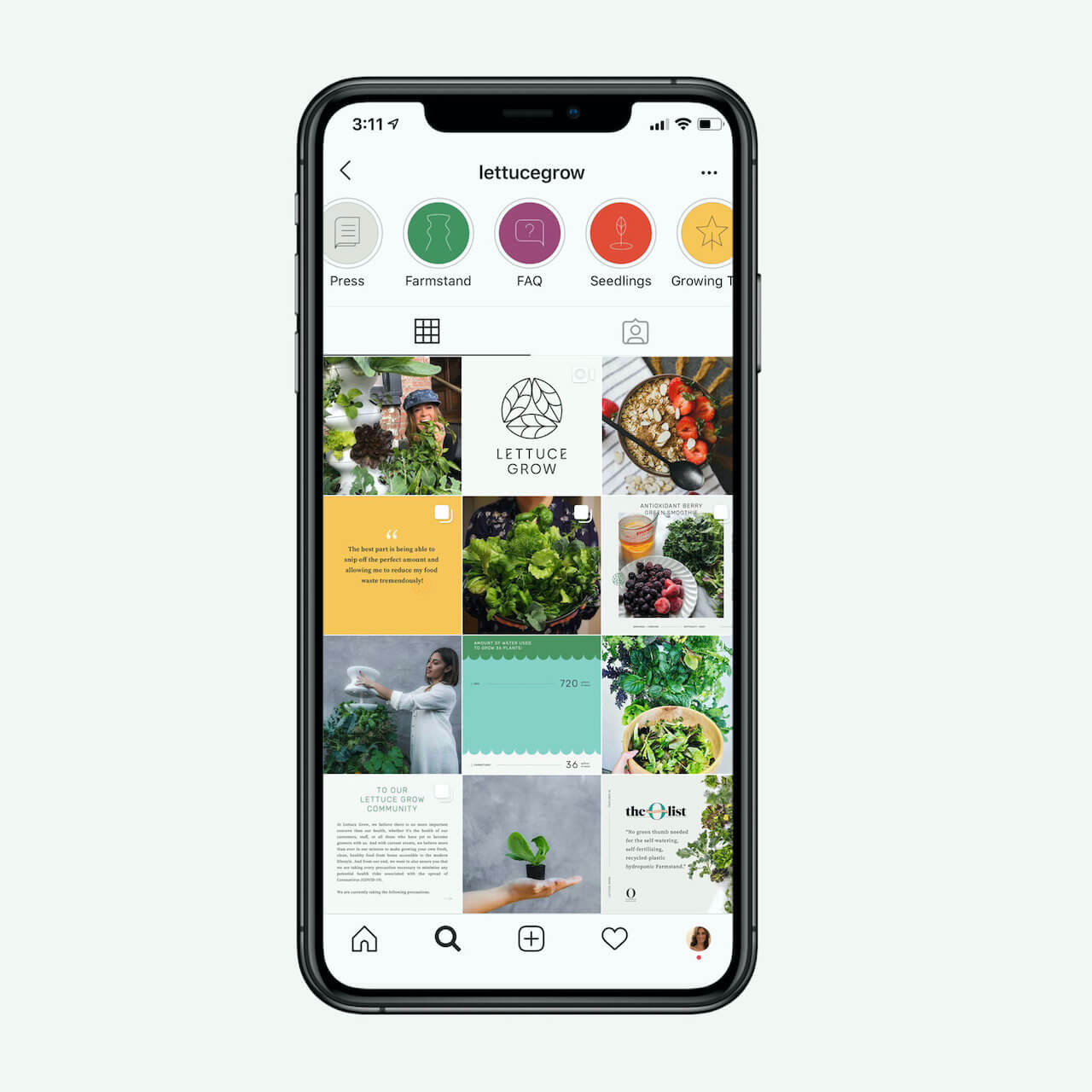
 A successful rebrand goes far beyond flashy graphics and high-res photos. It tells a story. It positions a product to fulfill the wants and needs of the consumer. Following the rebrand journey of Lettuce Grow, take a look at how visual elements can enforce the mission of your brand, engage your consumer and cultivate incredible results.
A successful rebrand goes far beyond flashy graphics and high-res photos. It tells a story. It positions a product to fulfill the wants and needs of the consumer. Following the rebrand journey of Lettuce Grow, take a look at how visual elements can enforce the mission of your brand, engage your consumer and cultivate incredible results.