We speak more through our bodies than our words. The posture we assume, the expression on our face, hand gestures, and our eye movement conveys far more than we would like to expose.
A subtle smile in a meeting can indicate a willingness to engage in a dialogue, while a stern look can instantly kill the conversation. Constantly checking the phone or looking at the watch can signal disengagement, while focusing on the other person signals interest.
Rolling our eyes expresses distrust or disgust in another person’s idea or behavior, while our eyes light up when we are genuinely curious about others. Keeping head down while walking in the hallway shows a lack of presence while acknowledging people passing by through a simple nod creates warmth. A firm handshake to begin an interview can exude confidence and power, while a limp handshake can reveal nervousness and weakness.
These non-verbal cues form a part of our body language that speaks even when we are silent, revealing how we are thinking and feeling in the moment.
Olivia Fox Cabane who has lectured at Stanford, Yale, Harvard, MIT, and the United Nations says:
In the scope of human evolution, language is a relatively recent invention. But we’ve been interacting well before this through nonverbal modes of communication. As a result, nonverbal communication is hardwired into our brains, much deeper than the more recent language-processing abilities. This is why nonverbal communication has a far greater impact.
She then points out ‘Without our realizing it, our bodies send out thousands of signals every minute. Just like our breath and heartbeat, these signals are part of the millions of bodily functions controlled not by our conscious mind but by our subconscious mind.’
Understanding the power of our body language and the role it plays in workplace communication and collaboration can bring us together by adopting positive communication styles as opposed to setting us apart through bridges of misunderstanding.
Importance of Body Language in Communication
Our body language plays a key role in impression management, the art of influencing how we are perceived by others.
A positive body language can show our enthusiasm to contribute, confidence in our abilities, being comfortable in taking on challenges, passion to drive results, and present to recognize future demands. It can open a world of new possibilities.
A negative body language can send strong signals of our resistance to contribute, doubt of our abilities, uneasiness to take on challenges, indifferent and uncaring attitude towards outcomes, and disconnected from reality to be able to handle future potential. It can close doors to success and growth.
Maya Angelou said, ‘People may not remember what you said, but they will remember how you made them feel.’
Since our emotions drive a large part of our decision-making, guess who will get the attention when a new project or a position opens up — a person who exhibited confidence in their body language or someone who looked like a nervous wreck?
Intelligence and brilliance are not enough to be successful at work. Our self-presentation skills far supersede our verbal communication.
The way you carry yourself is a source of personal power — the kind of power that is the key to presence. It’s the key that allows you to unlock yourself—your abilities, your creativity, your courage, and even your generosity. It doesn’t give you skills or talents you don’t have; it helps you to share the ones you do have. It doesn’t make you smarter or better informed; it makes you more resilient and open. It doesn’t change who you are; it allows you to be who you are. — Amy Cuddy
What happens when what we say is not in alignment with what we believe? We can lie through our words, but our bodies will reveal the truth. The non-verbal cues that we send through our body speak stronger than words.
Consider this. Someone approaches you with advice on a new strategy. Instead of expressing your true opinion, you simply nod in agreement. But, the tension around your eyes, the tone of your voice, and many other non-verbal cues can make the other person uncomfortable and leave them feeling unsure of your advice with the decision to never trust you again.
The idea is not to be inauthentic through your body language but to be aware of its implications.
Research shows that we form impressions about others within a few minutes of meeting them and then our confirmation bias guides us in picking data that confirms our point of view. Anything that strengthens our belief system is readily accepted and that which contradicts it is rejected.
Being aware of the role our body language plays in forming this impression can help us twist the outcome of an interview in our favor.
For someone in a leadership position, body language is extremely important since people in an organization mimic not only the way leaders talk but also pick on their non-verbal cues.
A leader with positive body language appears approachable, open to feedback and shows a willingness to change while a leader with negative body language appears inaccessible, closed to feedback, and arrogant to adapt and change with the future demands.
Amy Cuddy asks, ‘Our non-verbals govern how others think and feel about us, but do our non-verbals govern how we think and feel about ourselves?’
Absolutely. Mastering the art of non-verbal communication not only leads to better communication with others, but it benefits us too. Presenting our best self forward by adopting positive body language enables us to be the creator of our future as opposed to being a victim of other’s perceptions. It leads to more opportunities for growth with higher chances of success.
4 Body Language Mistakes and How to Fix Them
1. Mind Is Not Attuned to The Body
When our mind is not in congruence with our body, we may try to portray a state which is in conflict with our inner self by controlling our posture and expression on our face, but sooner or later this incongruence will show up in our body language.
A positive body language cannot keep up with the negative mental state — what goes up in our mind will show up in our body. Without our realization, these ‘microexpressions’ will be noticeable to the people around us.
Our body language expresses our mental state whether we like it or not. Our facial expressions, voice posture, and all the other components of body language reflect our mental and emotional condition every second. Because we don’t control this flow consciously, whatever is in our head will show up in our body language — Olivia Fox Cabane
How to Align Our Mind and Body:
Research shows that our mind cannot distinguish imagination from reality. So, whatever our mind believes, our body will project.
We can bring out the desired body language by catching ourselves in those moments of negative mental states — disagreement, insecurity, angst, frustration, anxiety, criticism, and self-doubt, and choosing to get into a positive one.
- When you need to project confidence, seek inspiration.
- When you feel angst due to a disagreement, ask yourself ‘What can I learn from the other person?’ and ‘How are my biases causing me to be closed-minded?’
- When all you can see is negativity, choose to ask ‘What’s the one positive thing I can think about this situation.’
- When self-doubt consumes you, tell yourself ‘I need to let go of my fears to create a better version of myself.’
- When you exaggerate a negative outcome, ask yourself ‘What’s the worst that can happen?’ and ‘Is it really that bad or am I making up stories?’
Adopting a positive frame of reference and moving from a problem to a solution mindset can help us shift gears from a negative internal state to a positive one.
2. We Do Not Make a Commitment to Be Present
‘Being present—paying attention to what’s going on rather than being caught up in your thoughts — can yield immense rewards. When you exhibit presence, those around you feel listened to, respected, and valued,’ explains Olivia Fox Cabane.
When we are not engaged in a conversation, consumed in our own thoughts, and pretend to listen, it clearly shows up in the non-verbal signals we send to the other person.
We may start fidgeting with our phone or laptop showing signs of distraction, look here and there instead of making eye contact signaling we are not interested in what they have to say and may even shift too many times in our position out of discomfort.
Without our awareness, our body language will convey disrespect and distrust to the other person.
How to Be Present:
You must commit to a conversation, even the brief ones, or walk away. If you’re too distracted, admit that to both yourself and the other person. Be present or be gone. — Celeste Headlee
It’s more polite to walk away from a conversation that doesn’t interest you than pretend to be present.
Once you decide to participate, you first need to convince and tell yourself that you want to be present. Say ‘I choose to be present,’ and then adopt body language that aligns with it — look at the other person with enthusiasm, lean just a little to build interest, and try to grasp what the other person intends to say.
You may occasionally drift away, but by choosing to be mentally present, you can bring your mind back to the conversation. Active listening though difficult is the most effective form of non-verbal communication that requires continuous practice and training of the mind.
3. We Ignore Context
When we talk to someone, their perception of us is based on the context of the meeting, their expectations, and their own personal and cultural filters.
Without recognizing that people operate within a certain context, we may send non-verbal signals that conflict with their values, contradicts their mental state, or even violates their sense of self.
How to Apply Context:
When engaged in a difficult conversation, without empathizing with how the other person might be feeling in the moment, we may appear cold, unemotional, and downright rude. By adopting kindness and warmth in our body language, we can convey the right message without necessarily making them feel bad.
When someone is passed up for a promotion, showing an attitude of indifference without understanding the value it holds in their life can make them resent you. Body language that shows presence and concern by giving them an opportunity to express their feelings can build better relationships.
When a co-worker is grieving a personal loss, you may appear too intrusive in your body language when all they need is space to let the feelings subside. It could be a personal preference or a cultural nuance, but without understanding their context you may actually do more harm than good.
When dealing with difficult people, your body language may switch to a fight-or-flight response. But, if you take a moment to analyze the situation without being at the effect of a fundamental attribution error, you may understand the rationale behind their behavior.
Every situation is unique. We need to project the right body language for each person by taking their context and personal filters into account.
4. We Tell a Conflicting Story
We may believe that we are highly approachable, but others may find us unapproachable. We may also think that we are open-minded, while others may find us biased. We may assume that we provide a psychologically safe environment to our people, but our employees may be terrified to make mistakes.
Now, it’s easy to say that ‘it’s just them, not me. I have already communicated to them multiple times.’ But really, is that the true story? Your intention may be far from the reality of your situation.
Just after we observe what others do and just before we feel some emotion about it, we tell ourselves a story. We add meaning to the action we observed. We make a guess at the motive driving the behavior. Why were they doing that? We also add judgment — is that good or bad? And then, based on these thoughts or stories, our body responds with an emotion. — Kerry Patterson
When our body language doesn’t match our words, people pick up on our non-verbal signals — the sign of contempt on our face when someone makes a mistake, pacing back and forth when conveying bad news, showing nervousness by fidgeting when asking for feedback, rolling eyes when we disagree, making hand gestures that signal blame and so on.
So, while you may communicate one thing with your words, your body may speak the opposite. And when people get confusing signals, they tend to go with what they observed and not what they heard.
How to Tell the Right Story:
Bring your body language in sync with the message you wish to convey. People find it easy to trust a person when their body language reflects their words.
When asking for feedback, look the person in the eye and don’t be distracted. When someone makes a mistake, show curiosity in your face to enable them to learn from their mistakes. When telling people to feel comfortable to approach you, make open arm-hand gestures. When communicating bad news, be intense but show confidence in your ability to make things right by looking at people with passion and hope.
People spend a lot of time perfecting their speech without verifying what their speech is conveying through their body. When it comes to making the right impression, don’t just speak through your words, make your body language count too.
Summary
Master the art of non-verbal communication in the workplace by:
- Tuning to a positive state of mind: Be self-aware of your negative mental states and choose to get into a positive one.
- Committing to being present: Practice active listening and engage fully in the conversation instead of being simply present.
- Taking context into account: Connect with the other person by taking their values, mental state, and sense of self into account.
- Telling the right story: Bring your body in sync with the message you wish to convey.
Previously published here.
Source de l’article sur DZONE



 Advertising knows you better than your friends, better than your family, perhaps even better than your partner.
Advertising knows you better than your friends, better than your family, perhaps even better than your partner.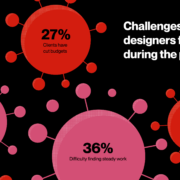
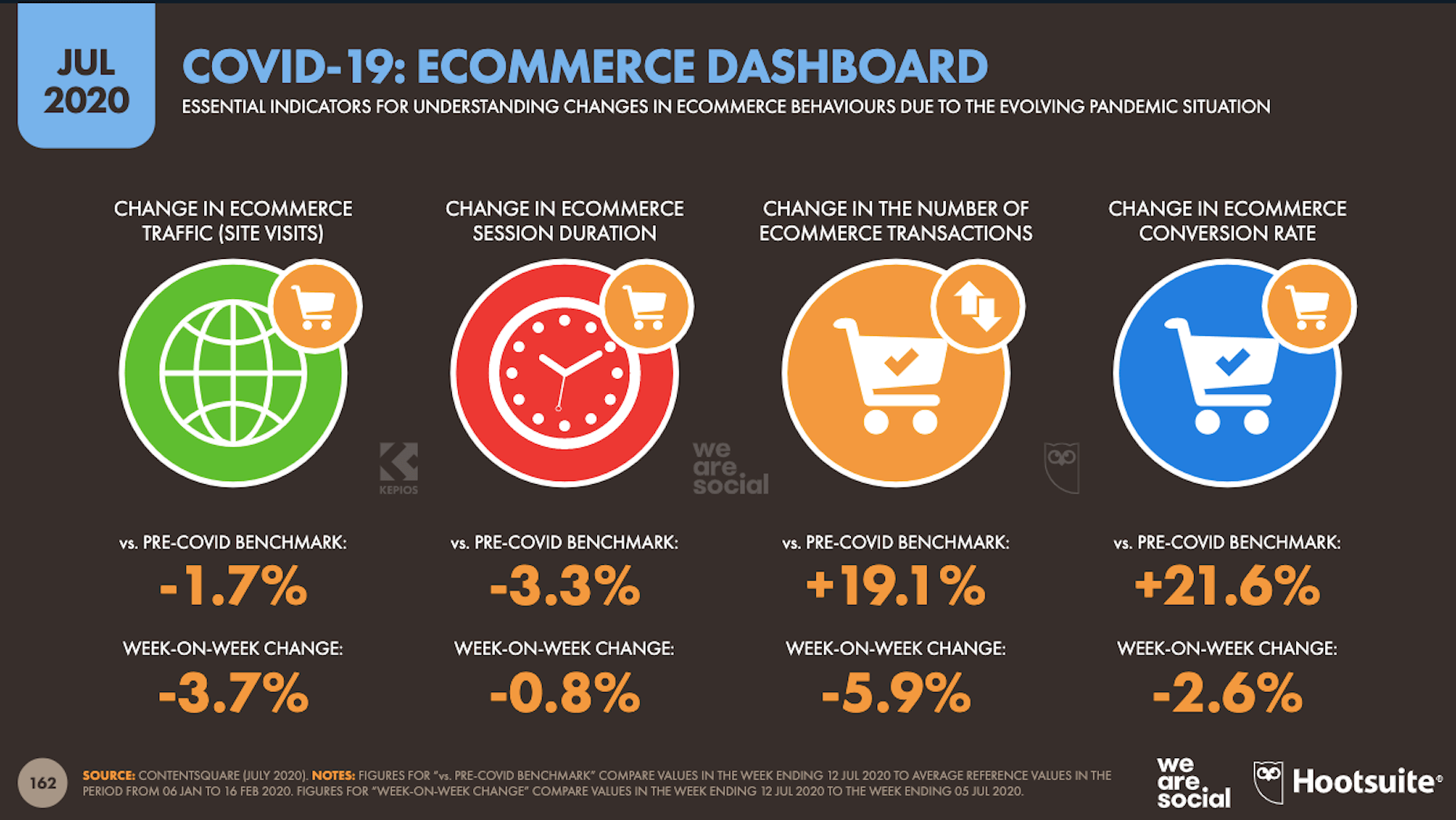
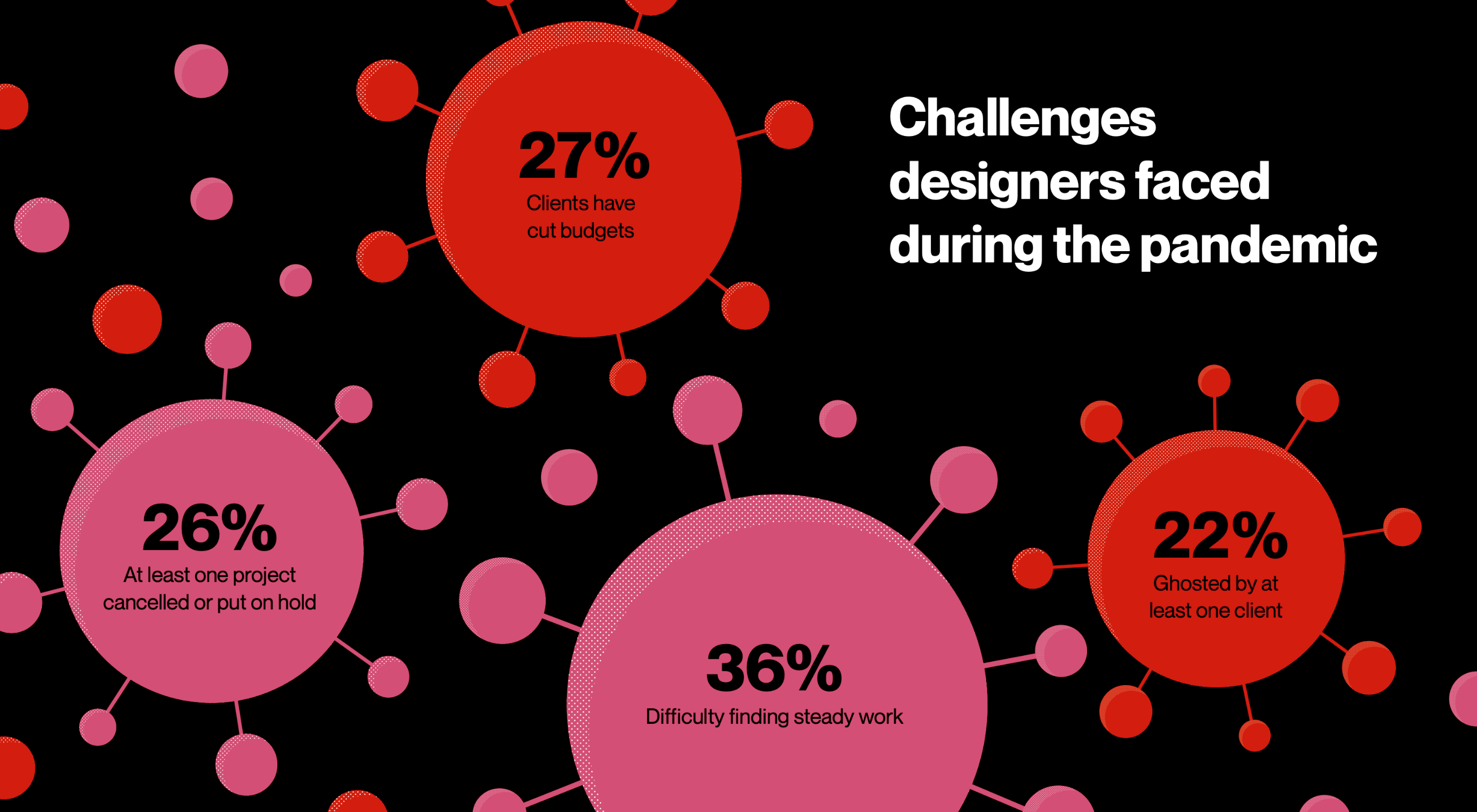 2020 has been an interesting year, to say the least. And although I’m sure many of you can’t wait until the calendar flips ahead to 2021, it doesn’t look as though we’re going to be able to say goodbye to 2020 so easily. Many of the changes we’ve had to make this year are now expected to stay with us — a least for the following year.
2020 has been an interesting year, to say the least. And although I’m sure many of you can’t wait until the calendar flips ahead to 2021, it doesn’t look as though we’re going to be able to say goodbye to 2020 so easily. Many of the changes we’ve had to make this year are now expected to stay with us — a least for the following year.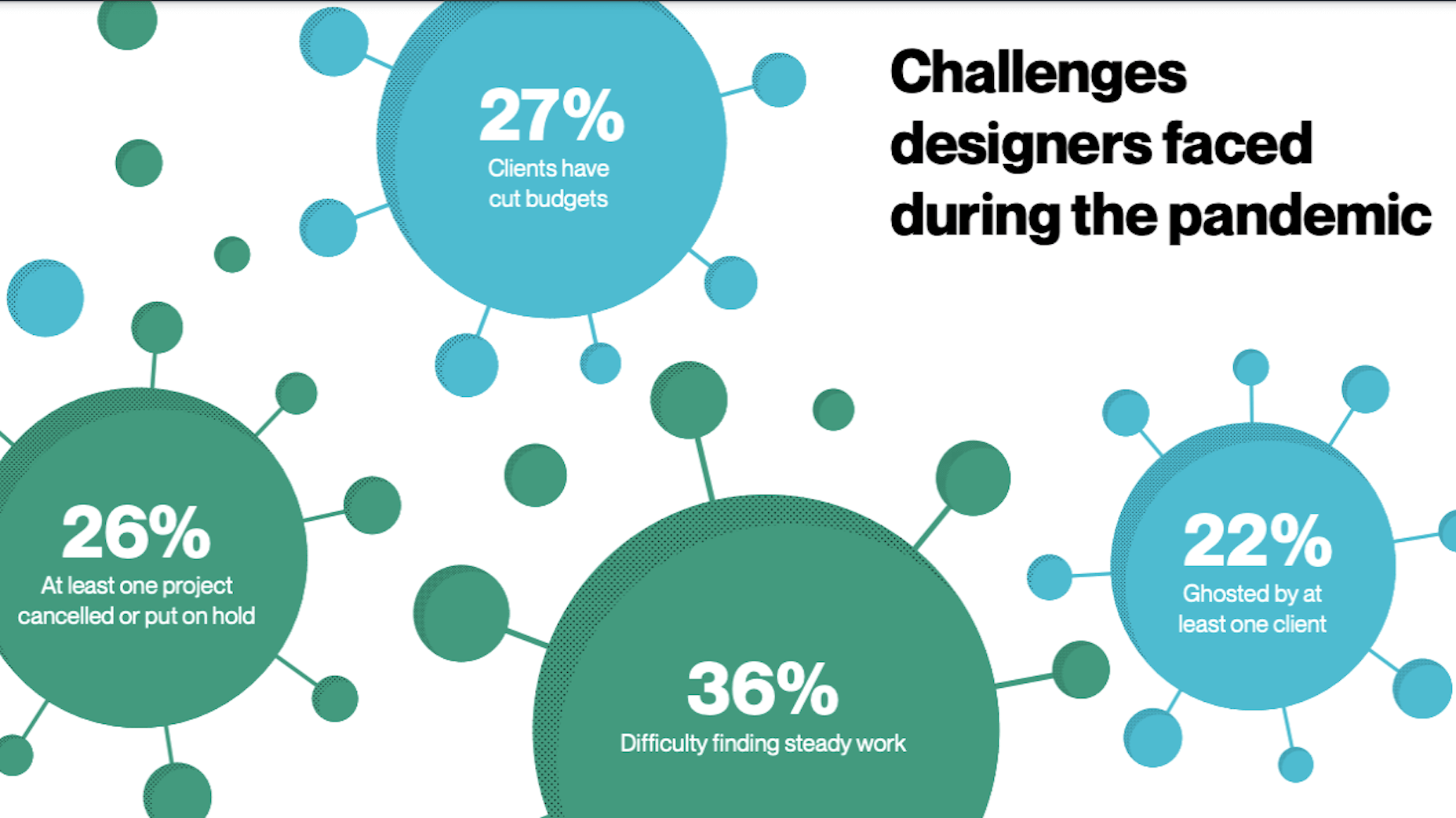
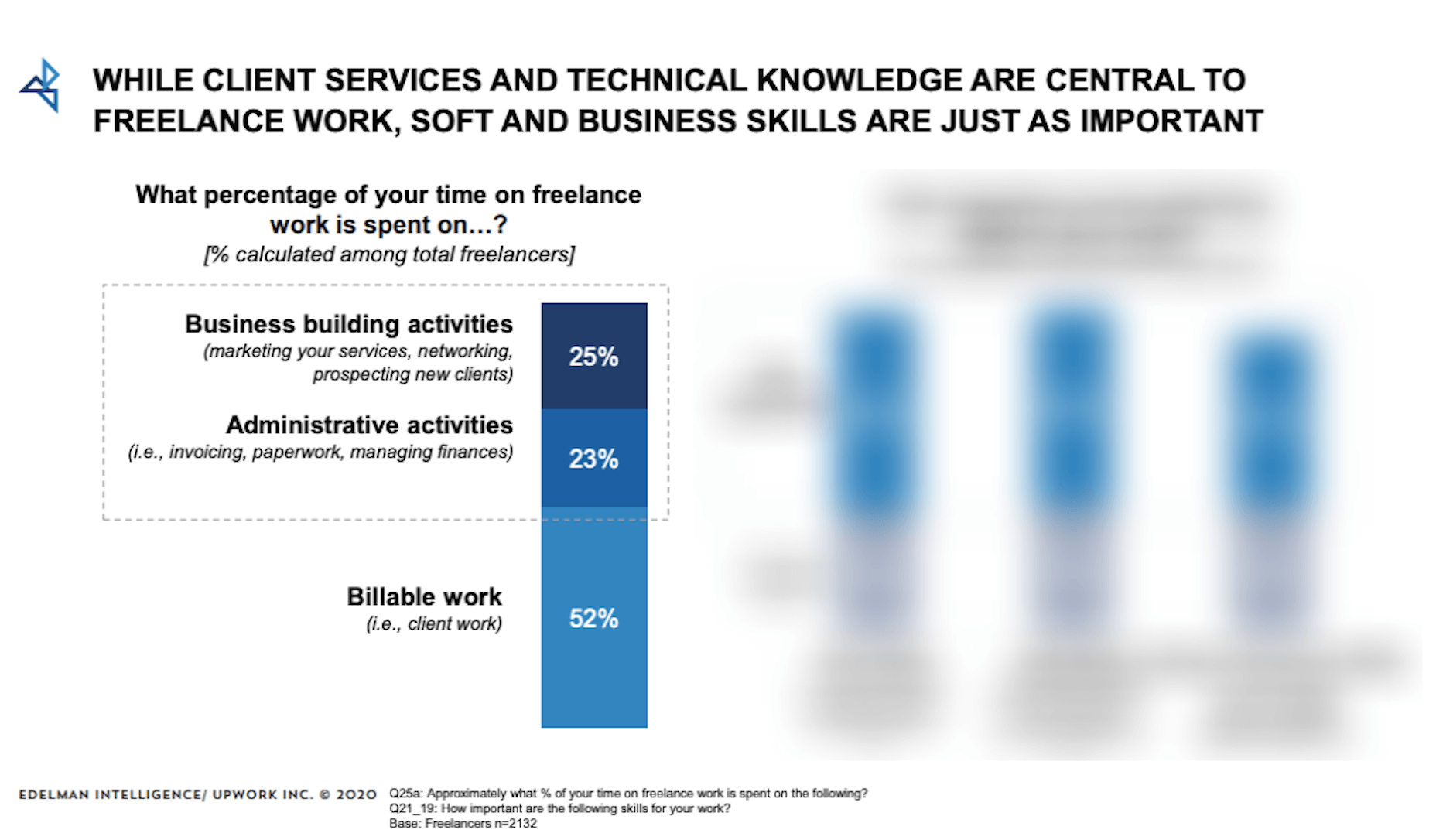
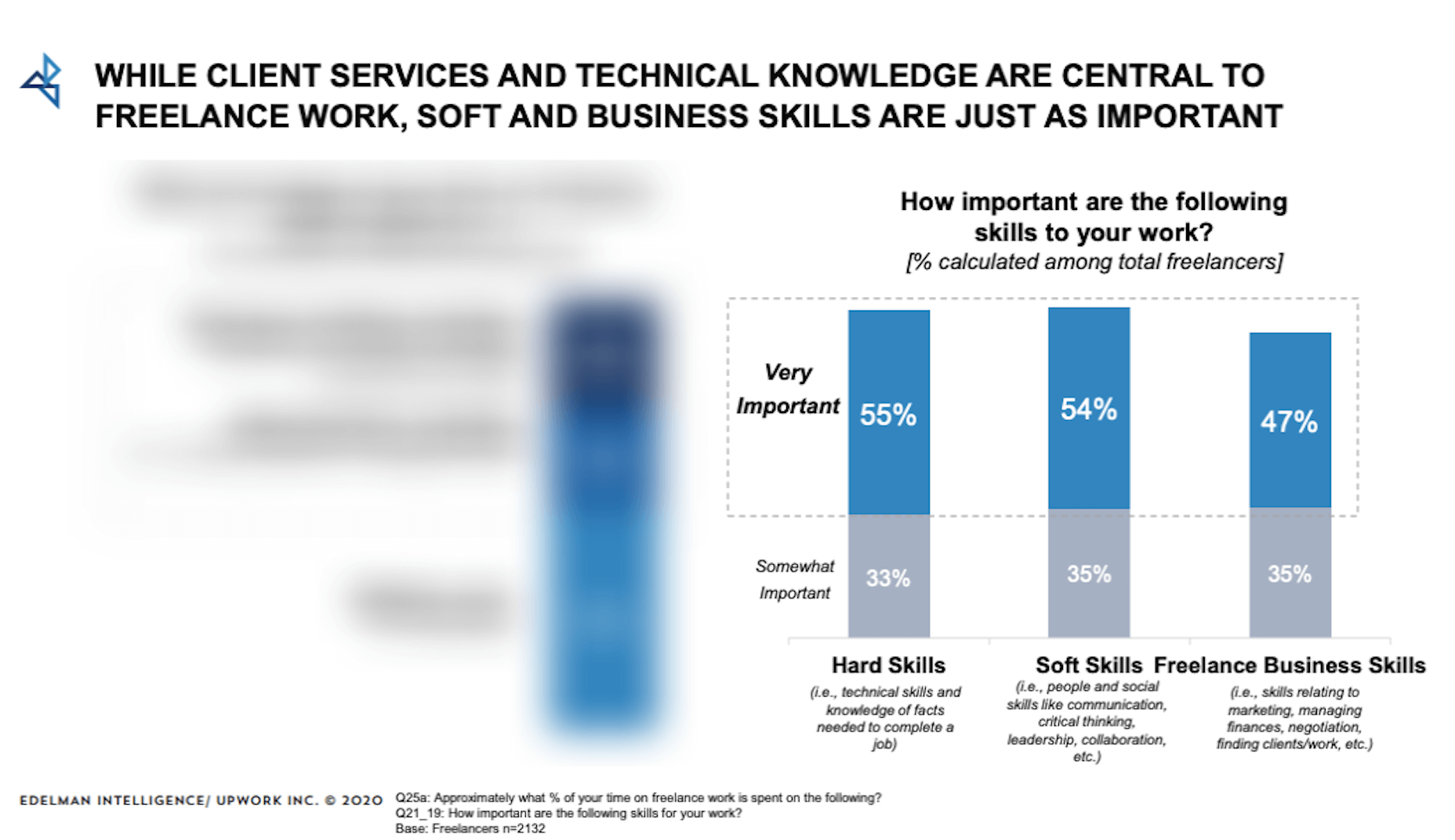

 How can your customer reach you? If a client arrives on your website after searching on Google, what can they do to take the next step in a relationship with your brand, without buying anything?
How can your customer reach you? If a client arrives on your website after searching on Google, what can they do to take the next step in a relationship with your brand, without buying anything?

 There are so many things to think about when first starting a business. What will your business offer? How will this differ from existing solutions? Who will benefit most from your offering? And why are you so passionate about this?
There are so many things to think about when first starting a business. What will your business offer? How will this differ from existing solutions? Who will benefit most from your offering? And why are you so passionate about this?


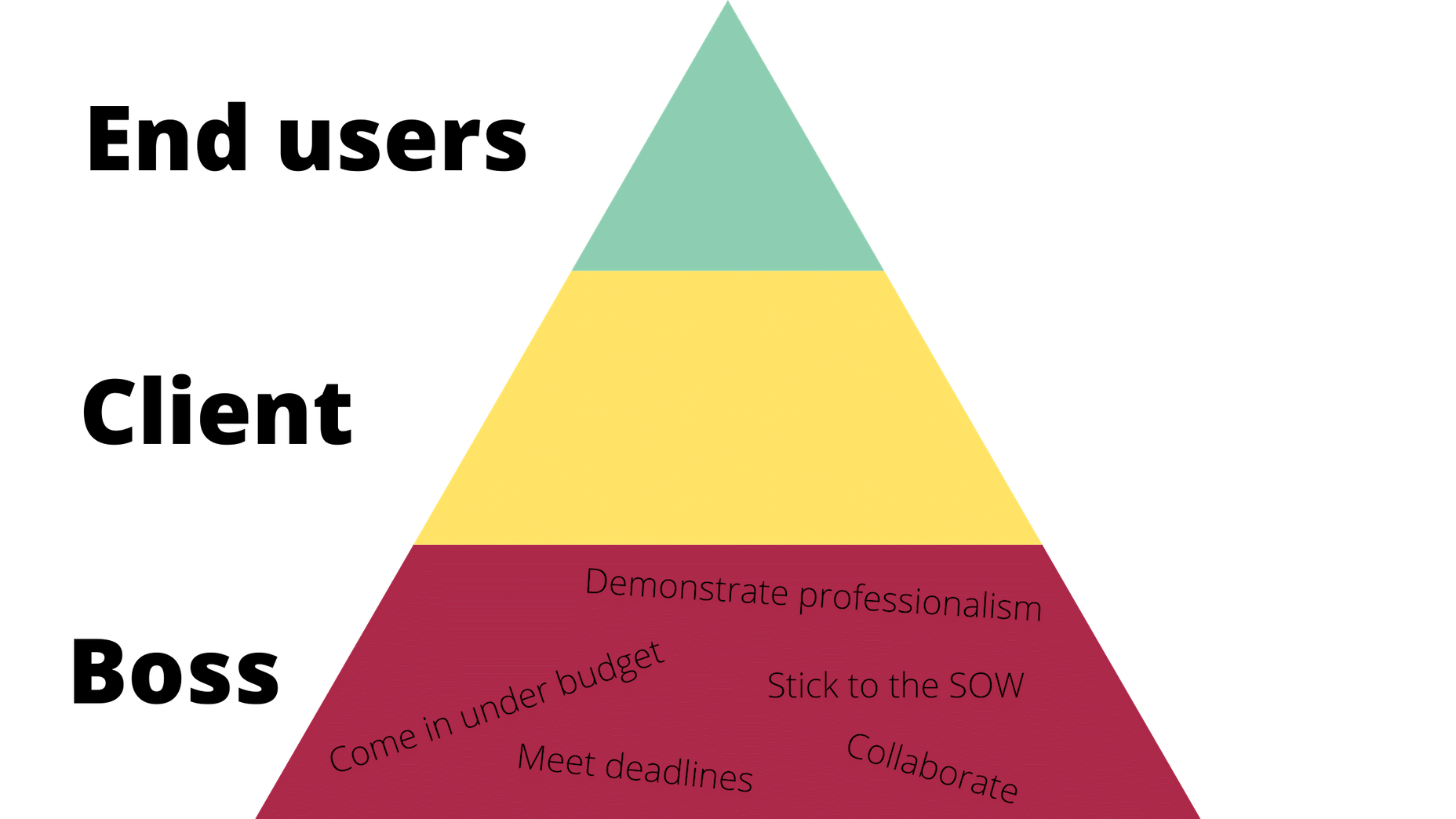
 It would be way too easy to answer this question with: “Whoever pays your bills.” And, honestly, I don’t think you can be a very successful web designer if you’re only driven by what the person paying you tells you to do.
It would be way too easy to answer this question with: “Whoever pays your bills.” And, honestly, I don’t think you can be a very successful web designer if you’re only driven by what the person paying you tells you to do.
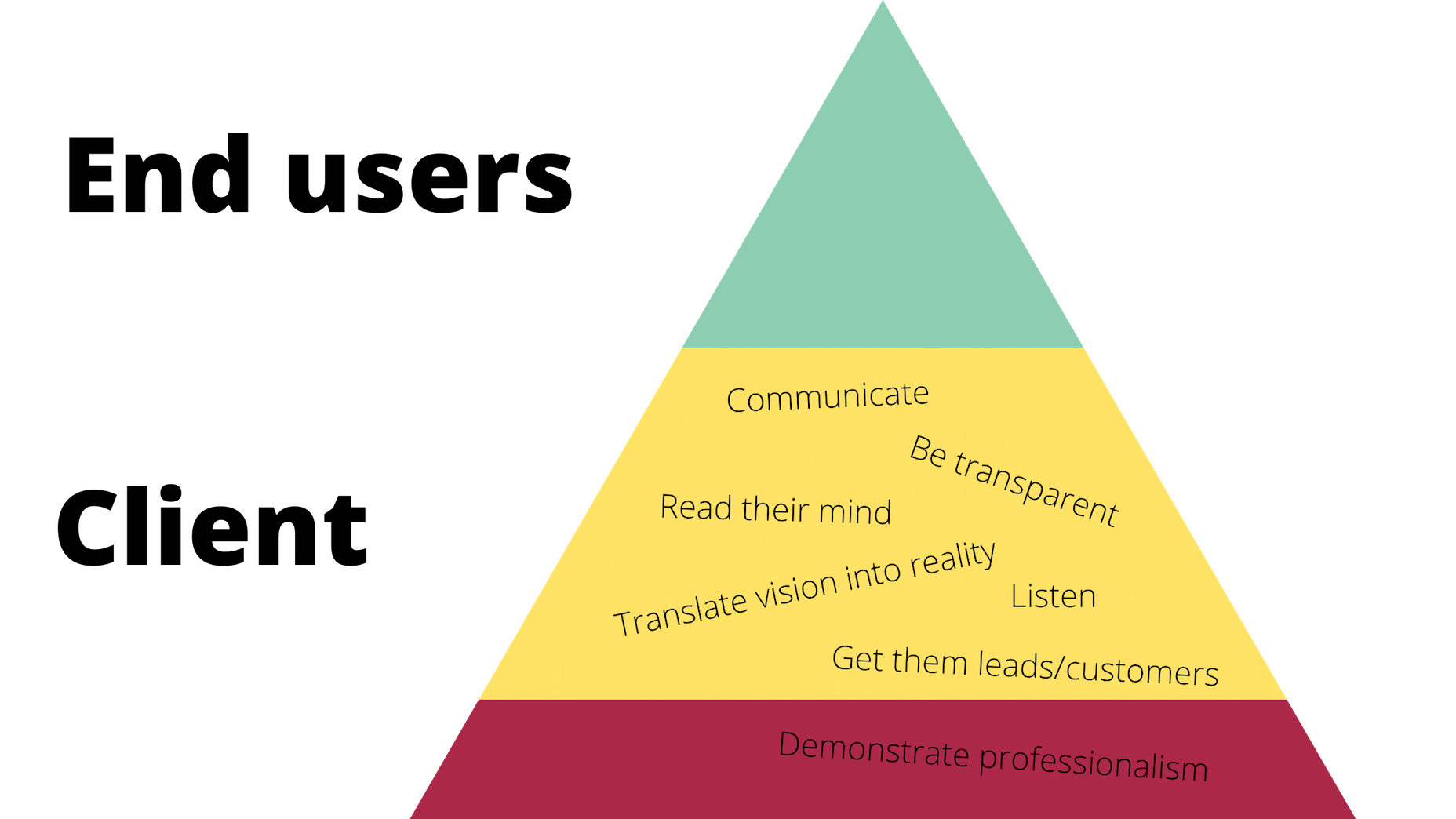
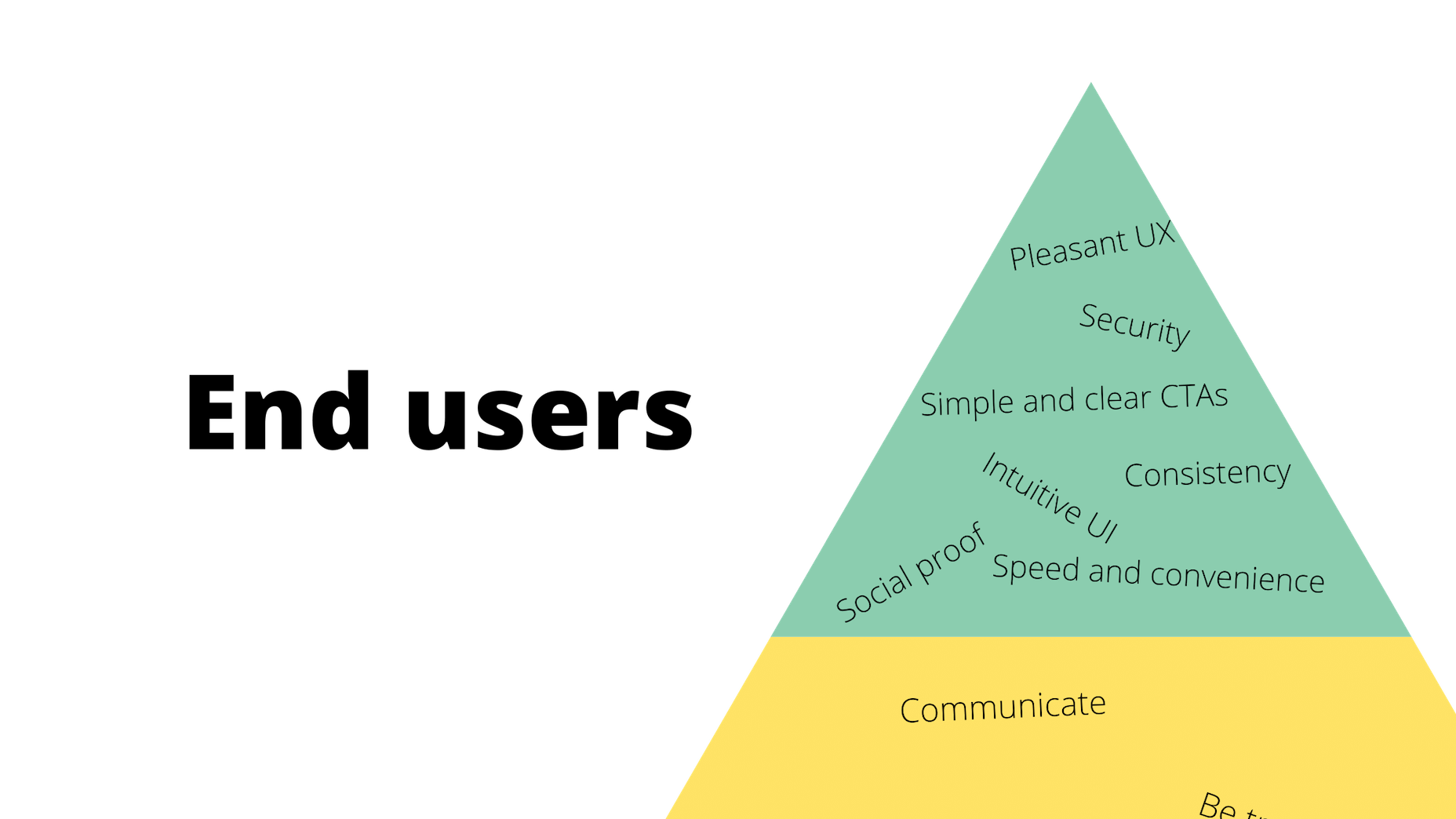

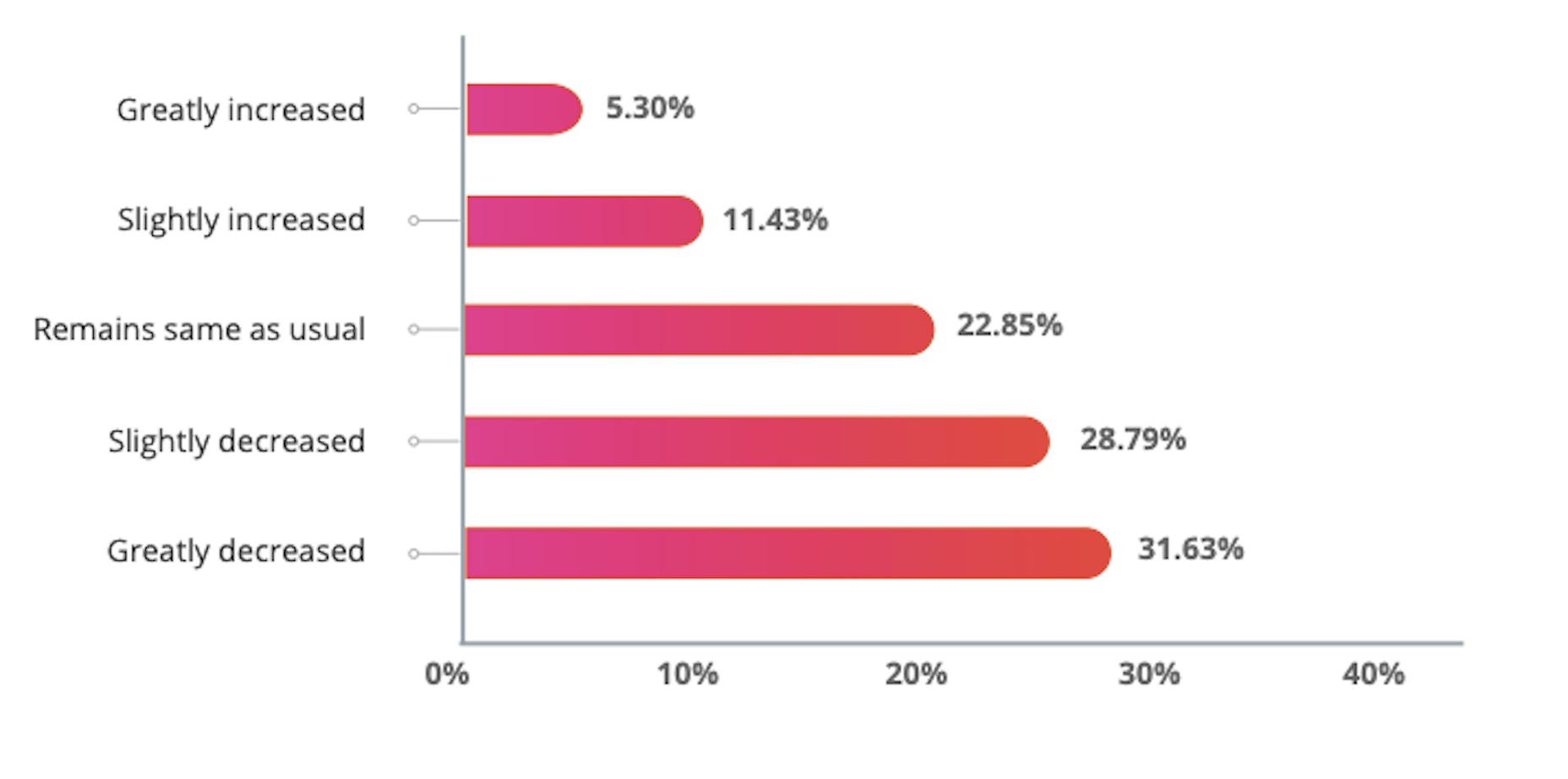
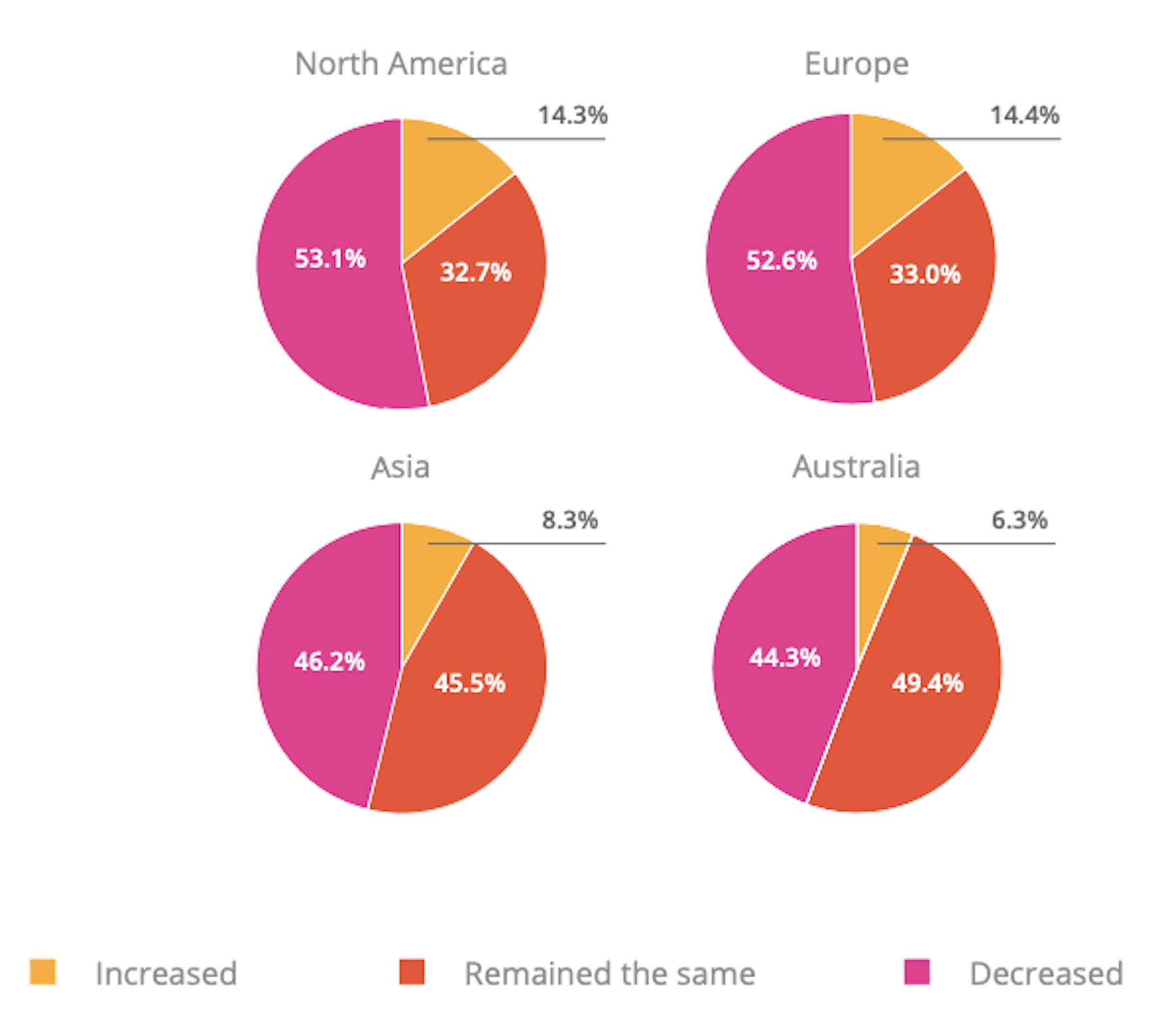
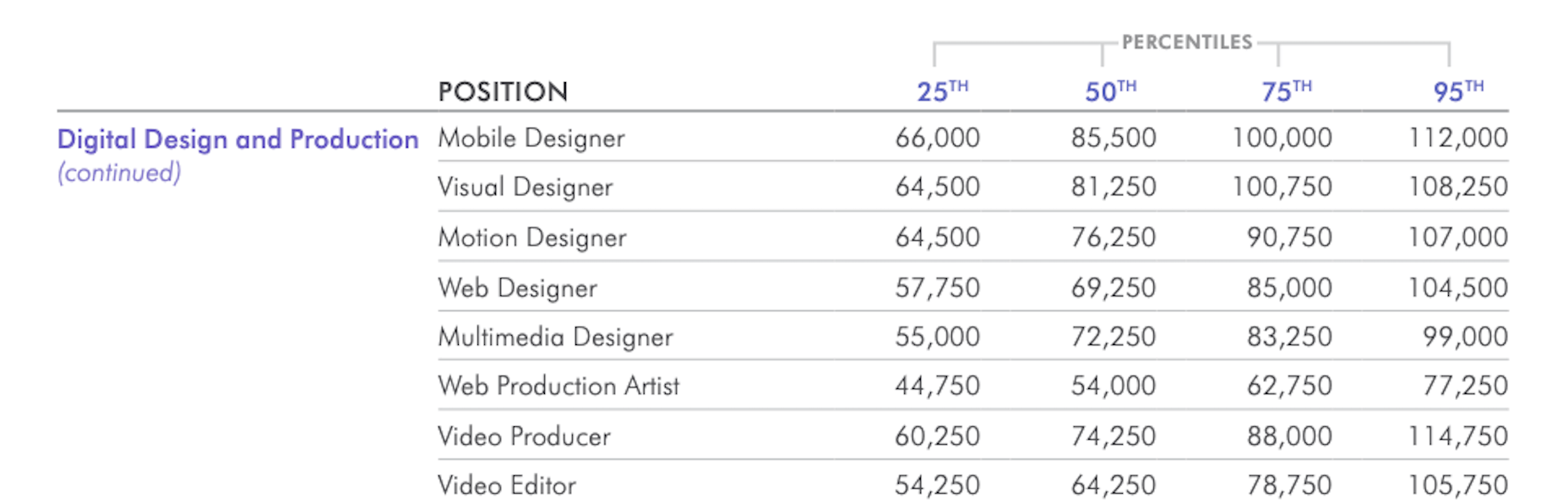
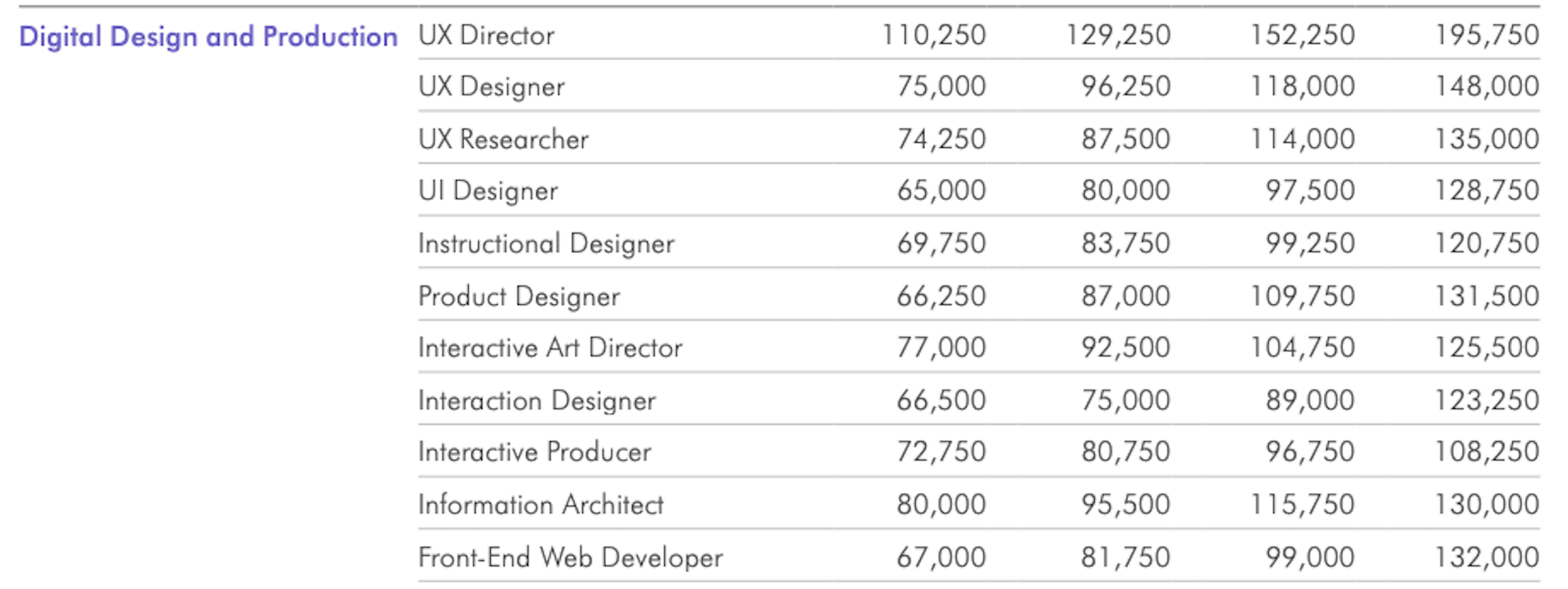
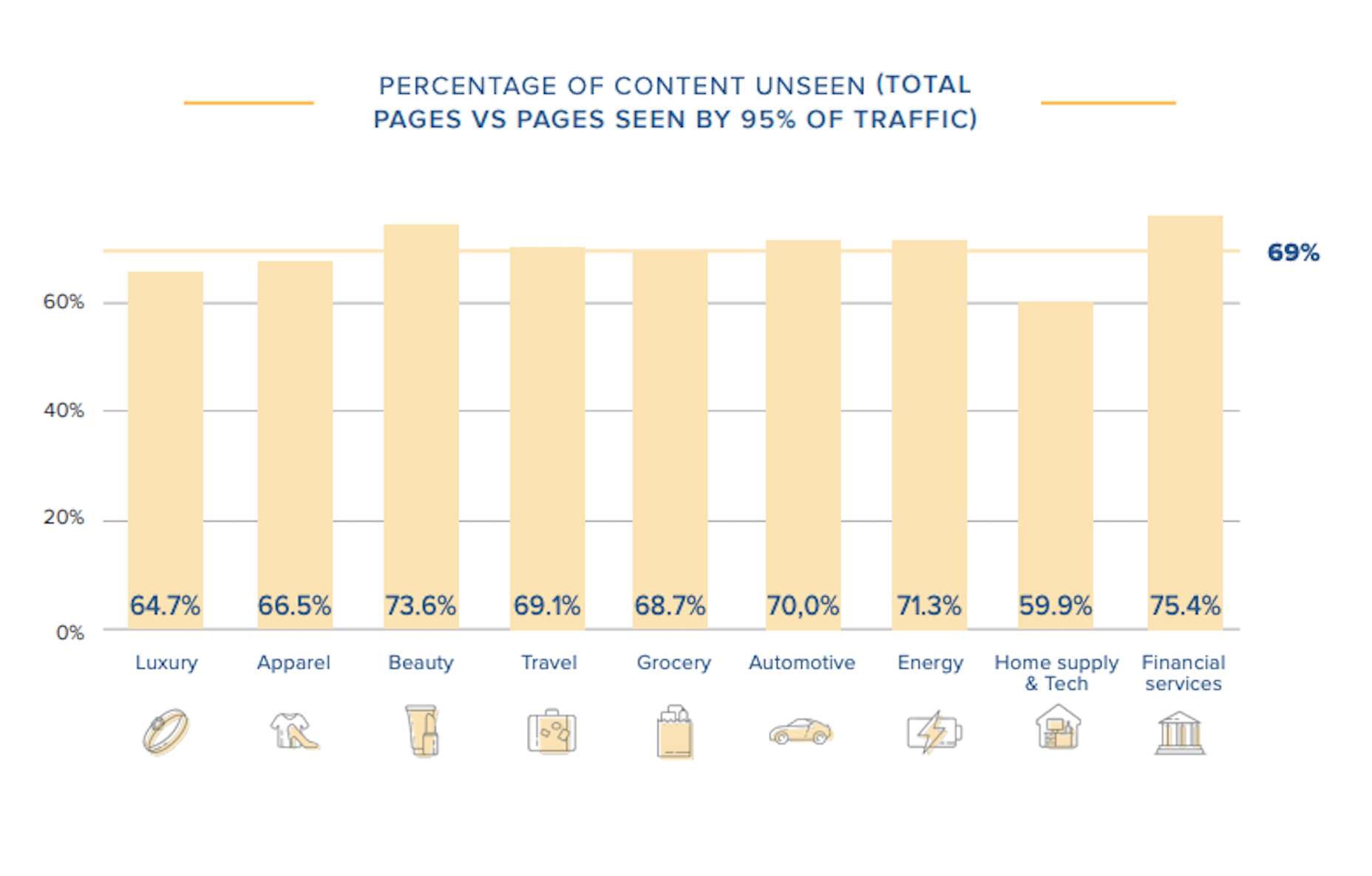
 In today’s look at the latest research for web designers, we’re going to look at studies and reports from Payoneer, Robert Half, Hootsuite, and Contentsquare to see what they have to say about things like:
In today’s look at the latest research for web designers, we’re going to look at studies and reports from Payoneer, Robert Half, Hootsuite, and Contentsquare to see what they have to say about things like: