 WordPress powers nearly 40% of all websites, thanks to its commitment to making publication possible for everyone, for free. Combined with premium plugins and themes, it’s possibly the ultimate tool for building attractive, unique, and feature-rich websites without any coding or design experience.
WordPress powers nearly 40% of all websites, thanks to its commitment to making publication possible for everyone, for free. Combined with premium plugins and themes, it’s possibly the ultimate tool for building attractive, unique, and feature-rich websites without any coding or design experience.
However, you do pay the price for this experience, with WordPress and its third-party products not always being built for performance – whether it’s page loading times or SEO.
Image optimization is a particularly big concern. Images are one, if not the largest, contributors to page weight, and it’s growing significantly by the year. So, while images are crucial for beautifying your website pages, they are also one of the biggest factors slowing it down.
In terms of image optimization, WordPress+Elementor brings very little to the table. WordPress core now comes with both responsive syntax and lazy-loading. Elementor itself also only comes with responsive syntax out-of-the-box. However, these are baseline techniques for image optimization that will deliver the bare minimum of improvements.
This means that, while Elementor makes it easy to design sweet-looking WordPress pages (with tonnes of creatively utilized images), you will probably pay the price when it comes to performance. But don’t worry. We will show you how to dramatically improve web performance by over 30 points on scoring tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insight.
Why Optimize Your Elementor Images with ImageEngine?
In general, image CDNs use various techniques to get image payloads as small as possible and deliver image content faster, all while minimizing the visual impact. ImageEngine is no different in that regard.
Firstly, ImageEngine, when used in auto mode, will apply all of the following optimizations that web performance tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insight recommend. For example:
- Properly size images – ImageEngine automatically resizes images for optimal size-to-quality ratios depending on the screen size of the user device. ImageEngine supports Retina devices.
- Efficiently encode images – Applies different rates of compression depending on the PPI of the user devices. For example, ImageEngine adapts and more aggressively compresses on higher PPI devices without losing visual quality.
- Next-gen format conversion – Automatically converts images to the optimal next-gen format according to the browser, device, or OS. ImageEngine can convert images to WebP or JPEG-2000 as well as GIFs to MP4 or WebP. AVIF is also available in a manual directive mode.
- Strip unnecessary metadata
While these features are standard for most image CDNs, ImageEngine is unique for its use of WURFL device detection. This gives ImageEngine much deeper insight into the user device accessing a website page and, by extension, its images. Using the screen size, resolution, PPI, etc., ImageEngine can make more intelligent decisions regarding how to reduce image payloads while maintaining visual quality.
This is why ImageEngine brands itself as an “intelligent, device-aware” image CDN and why it can reduce image payloads by as much as 80% (if not more).
ImageEngine also provides a proprietary CDN service to accelerate image delivery. The CDN consists of 20 globally positioned PoPs with the device-aware logic built-in. This allows you to deliver image content faster in different regions while also serving images straight from the cache with a ~98% hit ratio.
ImageEngine also supports Chrome’s save data setting. If someone has a slow connection or has activated this setting, ImageEngine will automatically compress image payloads even more, to provide a better user experience on slower connections.
How to Use ImageEngine with WordPress and Elementor
If you’re using WordPress and Elementor, then chances are you want to spend as little time on development and other technicalities as possible. Luckily, ImageEngine is a highly streamlined tool that requires little to no effort to integrate or maintain with a WordPress site.
Assuming you already have a WordPress website with Elementor, here are the step-by-step instructions to use ImageEngine:
- Go to ImageEngine.io and sign up for a 30-day free trial.
- Provide ImageEngine with the URL of the website you want to optimize.
- Create an account (or sign up with your existing Google, GitHub, or ScientiaMobile account).
- Provide ImageEngine with the current origin where your images are served from. If you upload images to your WordPress website as usual, then that means providing your WordPress website address again.
- Finally, ImageEngine will generate an ImageEngine delivery address for you from where your optimized images will be served. This typically takes the form of: {randomstring}.cdn.imgeng.in. You can change the delivery address to something more meaningful from the dashboard, such as myimages.cdn.imgeng.in.
Now, to set up ImageEngine on your WordPress website:
- Go to the WordPress dashboard and head to Plugins -> Add New.
- Search for the “Image CDN” plugin by ImageEngine. When you find it, install and activate the plugin.
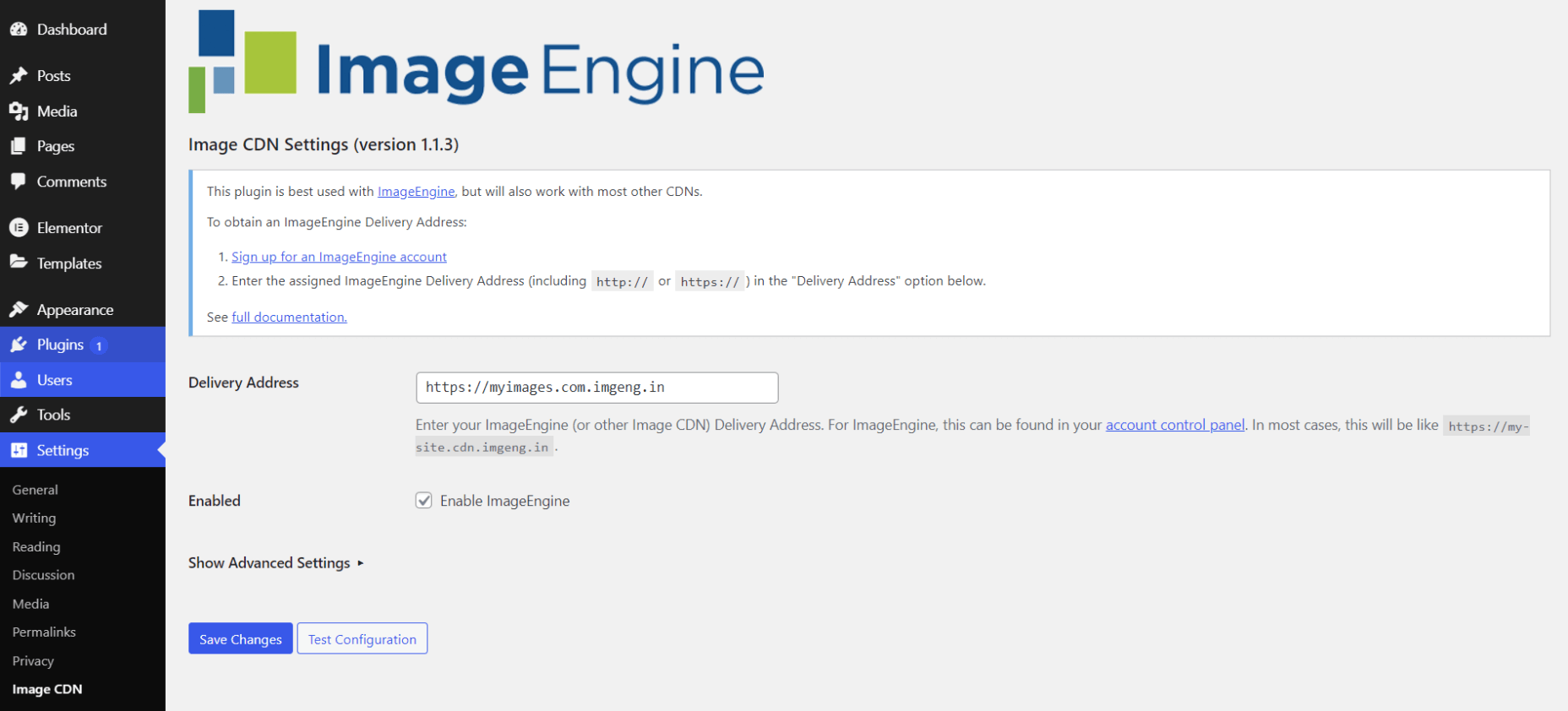
- Go to Settings -> Image CDN. OK, so this is the ImageEngine plugin dashboard. To configure it, all you need to do is:
a. Copy the delivery address you got from ImageEngine above and paste it in the “Delivery Address” field.
b. Tick the “Enable ImageEngine” box.
That’s literally it. All images that you use on your WordPress/Elementor pages should now be served via the ImageEngine CDN already optimized.
ImageEngine is largely a “set-it-and-forget-it” tool. It will provide the best results in auto mode with no user input. However, you can override some of ImageEngine’s settings from the dashboard or by using URL directives to manipulate images.
For example, you can resize an image to 300 px width and convert it to WebP by changing the src attribute like this:
<img src="https://myimages.cdn.imgeng.in/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/banner-logo.png?imgeng=/w_300/f_webp">
However, use this only when necessary, as doing so will limit ImageEngine’s adaptability under different conditions.
What Improvement Can You Expect?
Let’s see what results you can expect from using an image CDN to improve your page loading times.
For this, I created two identical WordPress pages using the Elementor theme. The one page purely relied on WordPress and Elementor, while I installed and set up ImageEngine for the other. The page had some galleries as well as full-size images:
The pages used many high-quality images, as you might expect to find on a professional photography gallery, photography blog, stock photo website, large e-commerce site, etc. I then ran page performance tests using Chrome’s built-in Lighthouse audit tool, choosing scores representing the average results I got for each page.
For thoroughness, I tested both the mobile and desktop performance. However, I focused on the mobile results as these showcase more of the image CDN’s responsive capabilities. Mobile traffic also accounts for the majority share of internet traffic and seems to be the focus for search engines going forward.
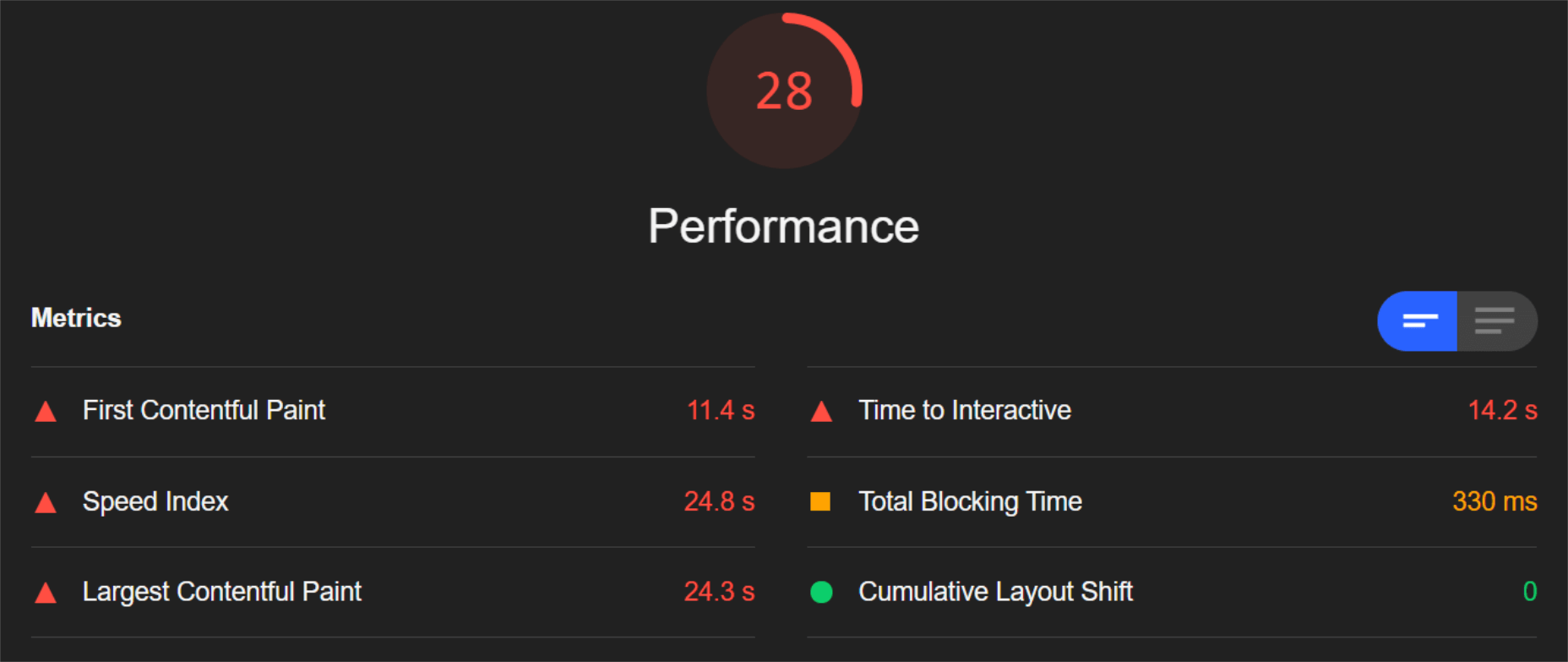
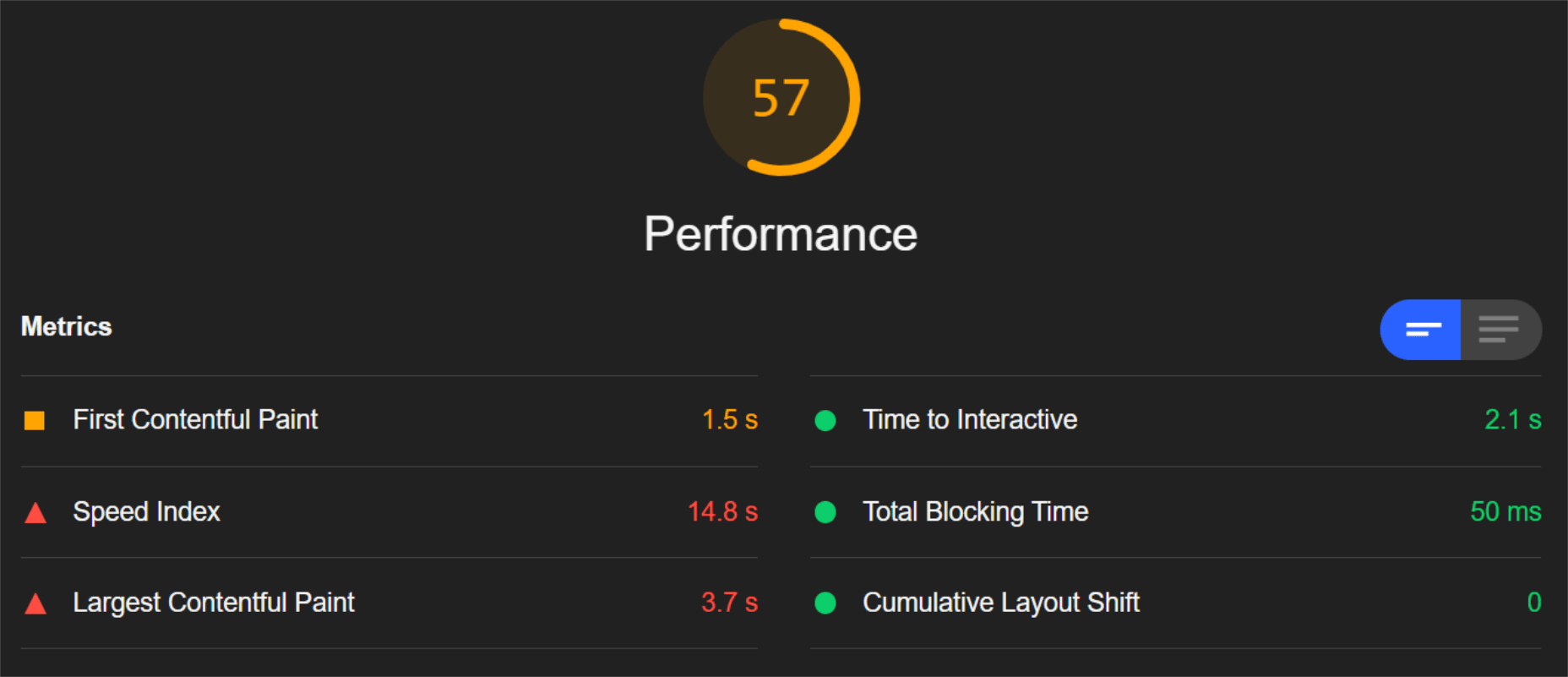
So, first of all, let’s see the mobile score for the page without ImageEngine:
As you can see, there was definitely a struggle to deliver the huge amount of image content. Google has shown that 53% of mobile users abandon a page that takes more than 3s to load. So, clearly, this page has major concerns when it comes to user experience and retaining traffic.
The desktop version fared much better, although it still left much to be desired:
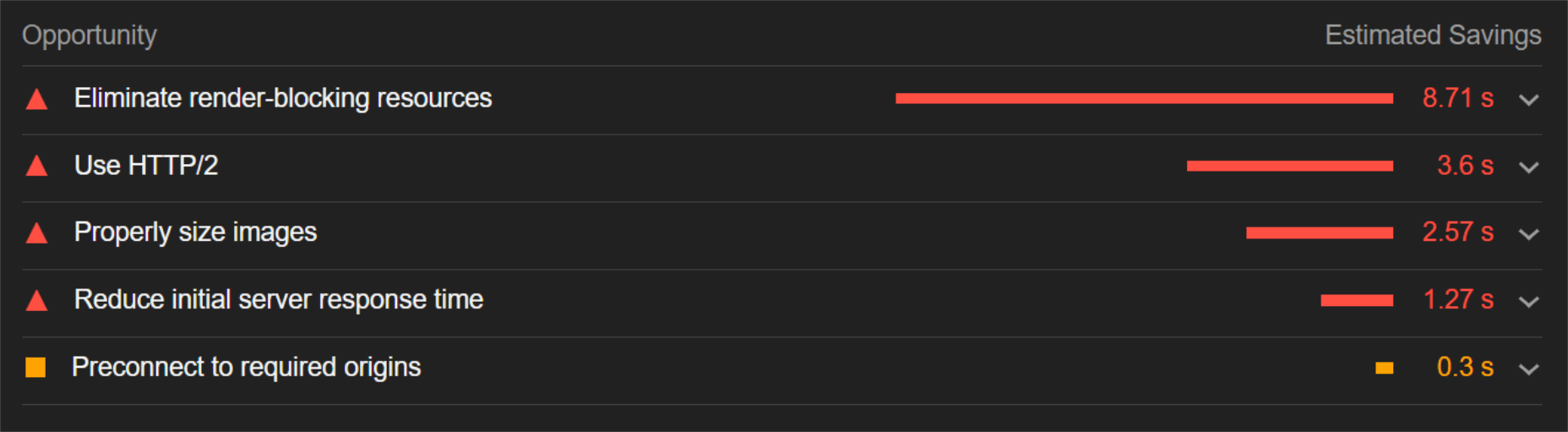
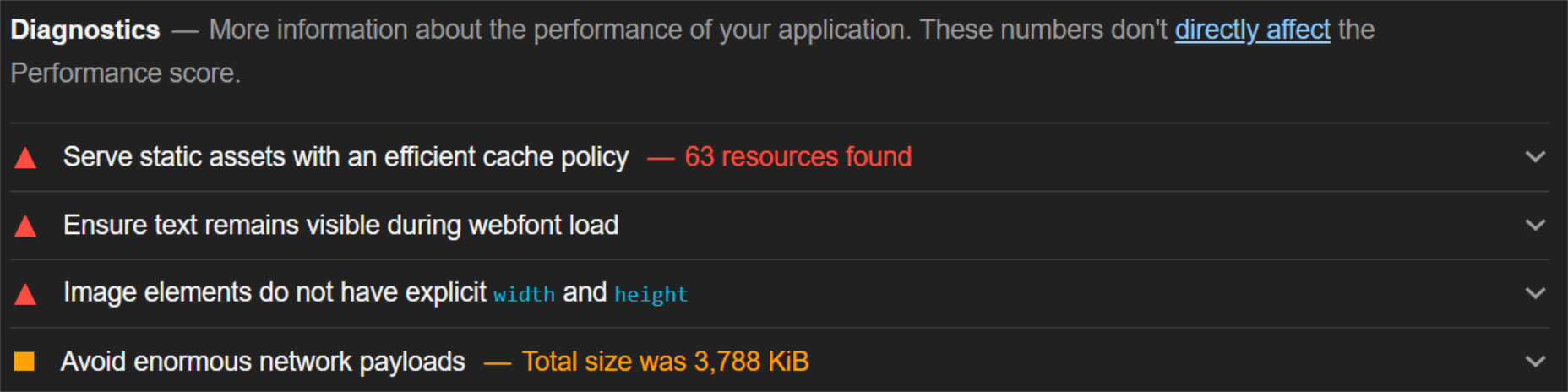
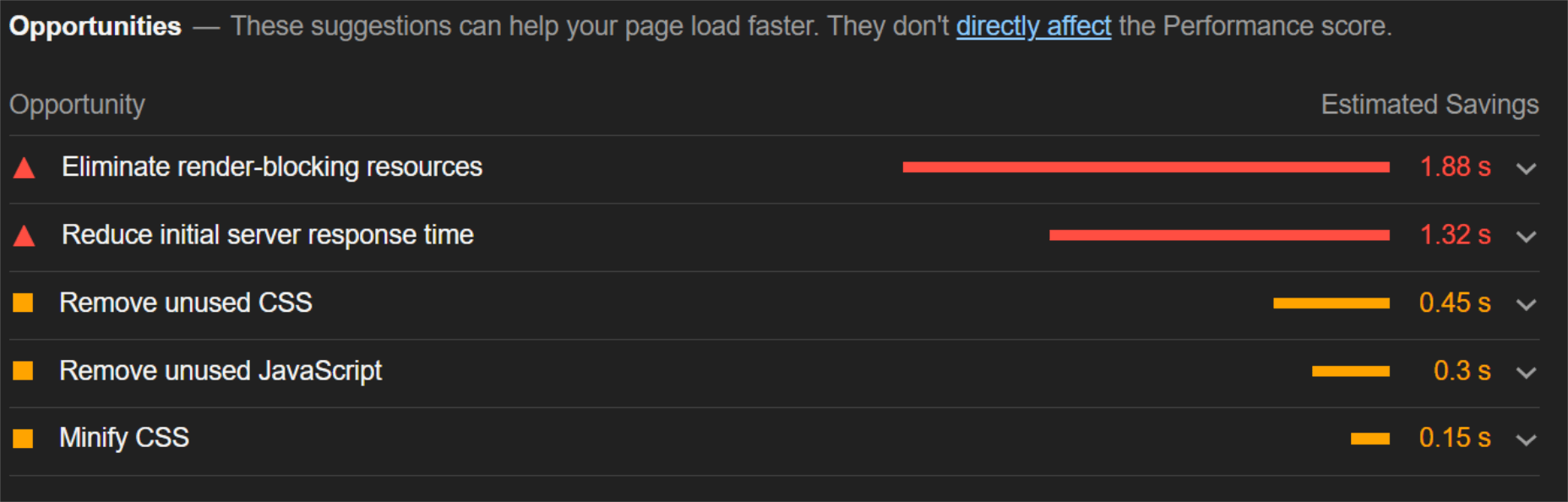
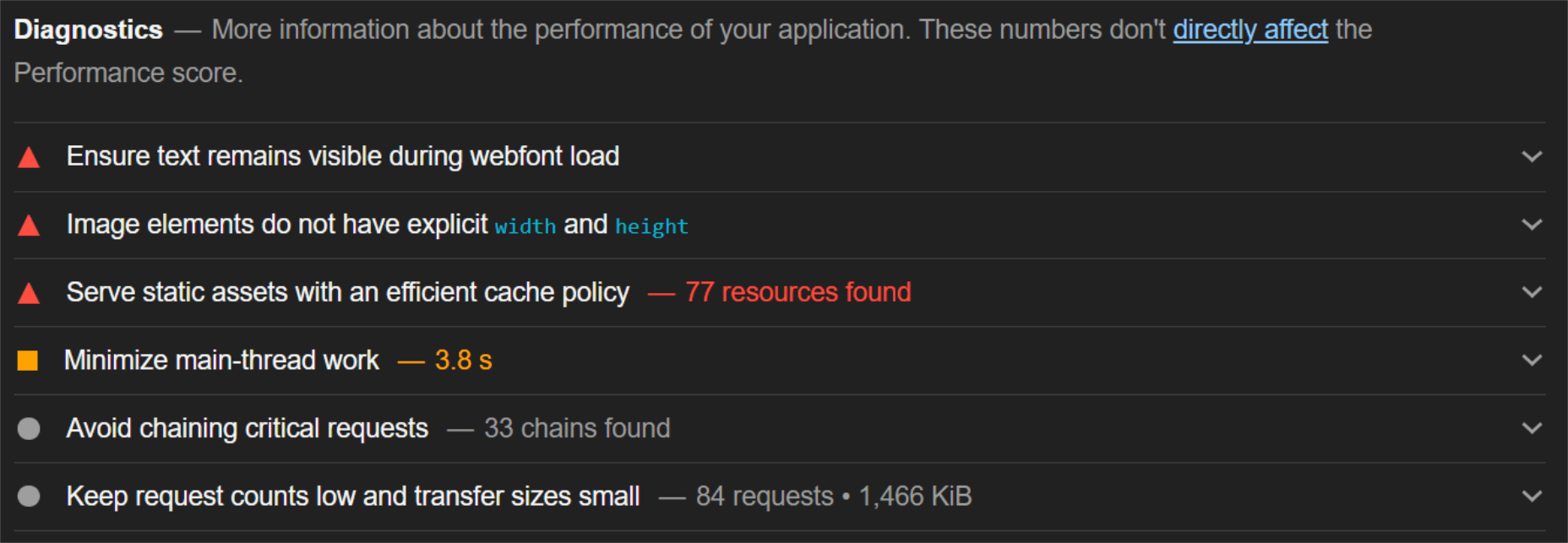
When digging into the reasons behind the slowdown, we can identify the following problems:
Most of the issues related somehow to the size and weight of the images. As you can see, Lighthouse identified a 3.8 MB payload while the total image payload of the entire page was close to 40 MB.
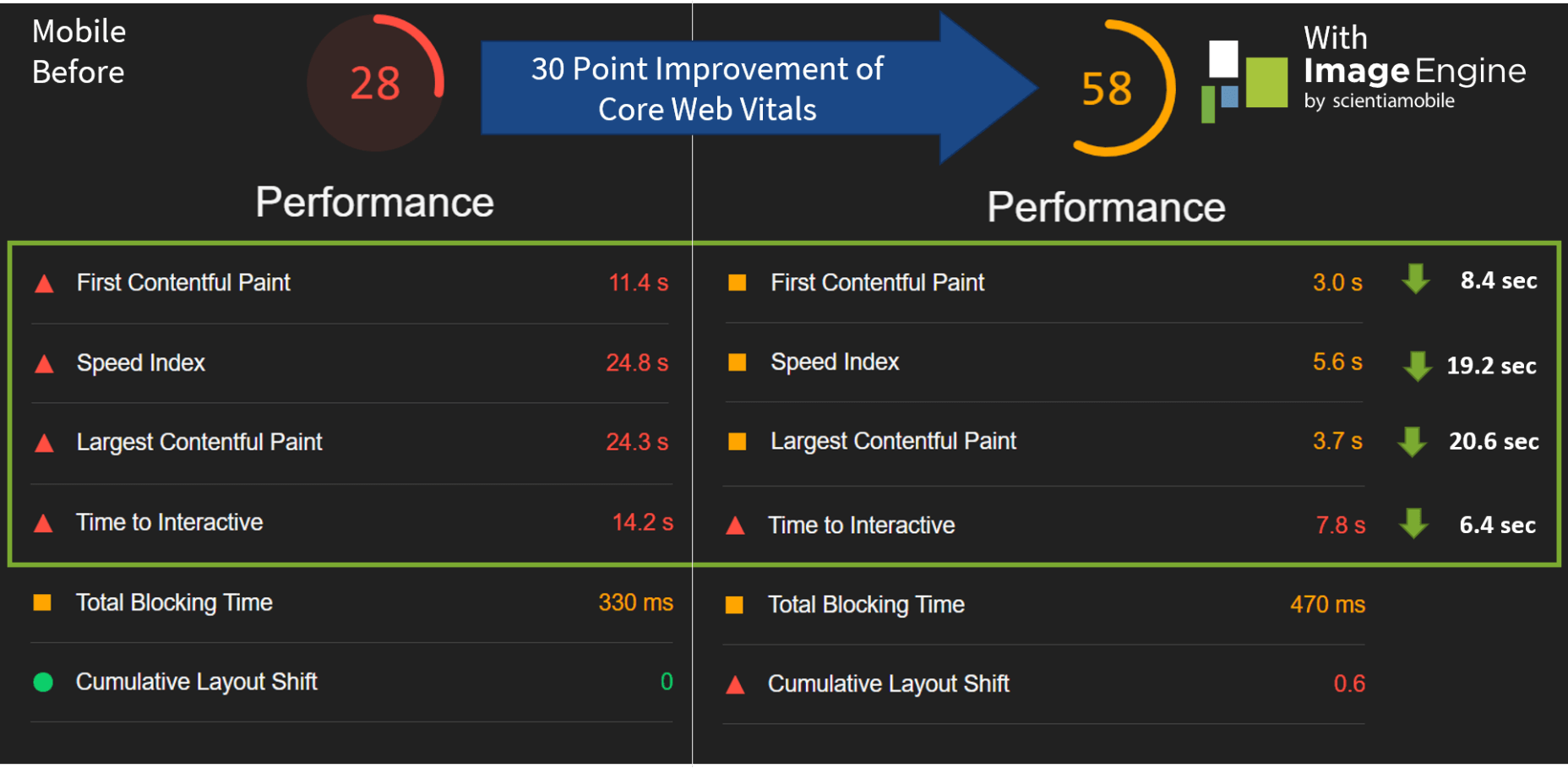
Now, let’s see what kind of improvement ImageEngine can make to these issues by looking at the mobile score first:
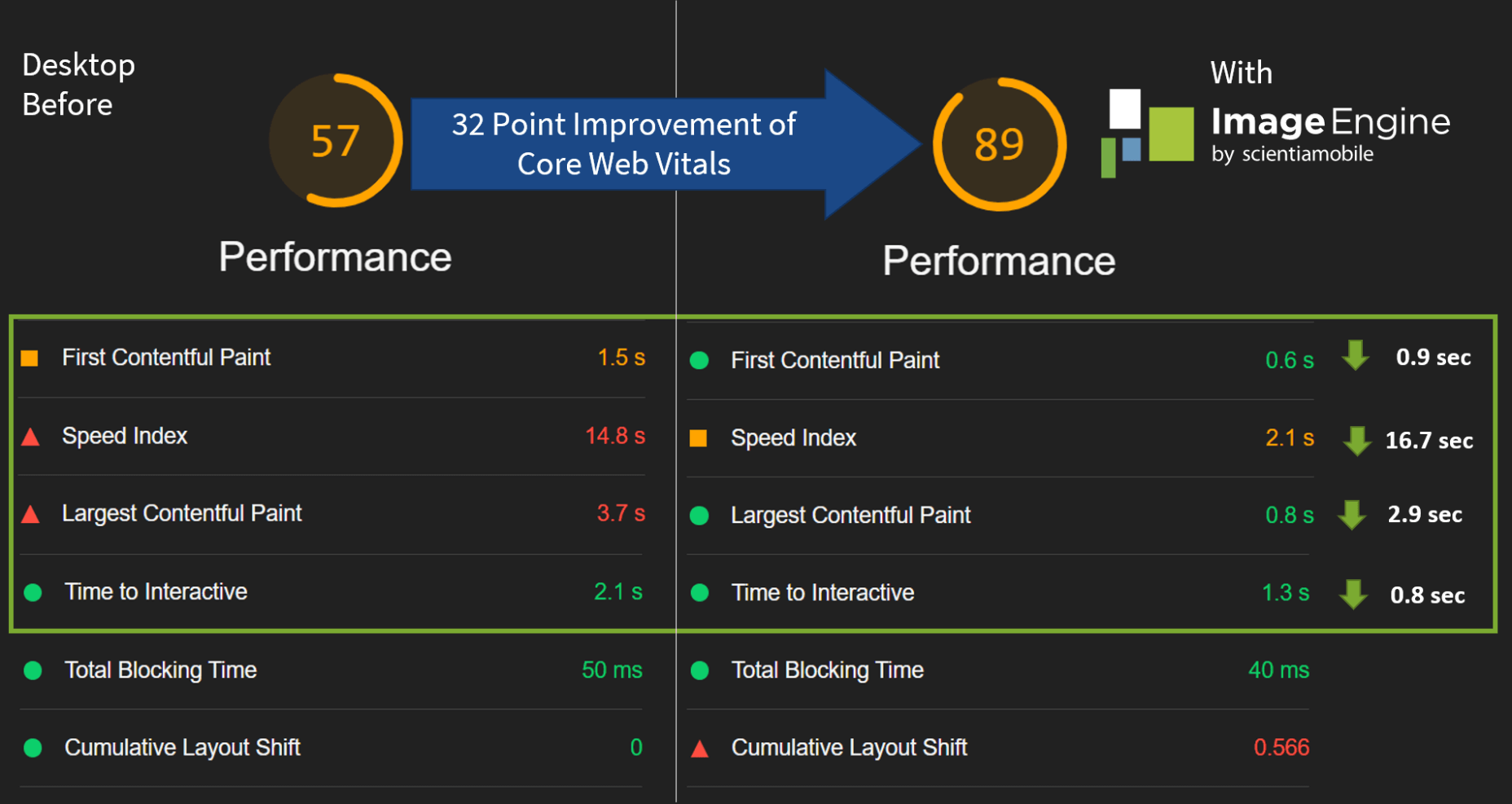
So, as you can see, a major improvement of 30 points over the standard WordPress/Elementor page. The time to load images was cut down by roughly 80% across the key core web vital metrics, such as FCP, LCP, and the overall Speed Index.
In fact, we just reached that critical 3s milestone for the FCP (the largest element on the visible area of the page when it initially loads), which creates the impression that the page has finished loading and will help you retain a lot of mobile traffic.
The desktop score was also much higher, and there was further improvement across the key performance metrics.
If we look at the performance problems still present, we see that images are almost completely removed as a concern. We also managed to bring down the initial 3.8 MB payload to around 1.46 MB, which is a ~62% reduction:
An unfortunate side effect of using WordPress and WordPress plugins is that you will almost inevitably face a performance hit due to all the additional JavaScript and CSS. This is part of the reason why we didn’t see even larger improvements. That’s the price you pay for the convenience of using these tools.
That being said, the more images you have on your pages, and the larger their sizes, the more significant the improvement will be.
It’s also worth noting that lazy-loaded images were loaded markedly faster with ImageEngine if you quickly scroll down the page, again making for an improved user experience.
Thanks to its intelligent image compression, there was also no visible loss in image quality, as you can see from this comparison:
Conclusion
So, as you can see, we can achieve significant performance improvements on image-heavy websites by using the ImageEngine image CDN, despite inherent performance issues using a CMS. This will translate to happier users, better search engine rankings, and an overall more successful website.
The best part is that ImageEngine stays true to the key principles of WordPress. You don’t have to worry about any of the nuts and bolts on the inside. And, ImageEngine will automatically adjust automation strategies as needed, future-proofing you against having to occasionally rework images for optimization.
The post Create Beautiful WordPress Pages with Optimized Images Using Elementor and ImageEngine first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.




 Ten years ago, people began talking about the “Independent Web.” Although we don’t commonly use the term anymore, that doesn’t mean that it’s not still as vital a topic of discussion today as it was a decade ago.
Ten years ago, people began talking about the “Independent Web.” Although we don’t commonly use the term anymore, that doesn’t mean that it’s not still as vital a topic of discussion today as it was a decade ago.