 How can your customer reach you? If a client arrives on your website after searching on Google, what can they do to take the next step in a relationship with your brand, without buying anything?
How can your customer reach you? If a client arrives on your website after searching on Google, what can they do to take the next step in a relationship with your brand, without buying anything?
One of the primary aims of any website is to drive conversions. However, it usually takes between 5 and 8 touchpoints to generate a viable sales lead. People don’t want to convert straight away.
Since building a relationship with customers is crucial to success, it makes sense that the contact page would be an essential part of driving results. Unfortunately, a lot of website owners pay virtually no attention to that page. They ask their designer to create a page with their address and phone number on – and that’s it.
What many business owners don’t realize, is that the contact page is the door to deeper, more lucrative relationships with potential prospects. The design of this essential website element needs to be fantastic to drive results.
So, where do you start?
Defining a Well-Designed Contact Page
Let’s start with the basics, what makes a great contact page?
The complete answer to that question depends on the target audience. Some customers will want to see fun and friendly contact pages, complete with social media sharing buttons. Others will want to see a map that shows them exactly how to reach an office or business.
There are a few golden rules to keep in mind, of course. Contact pages should be:
- Easy to find: Don’t hide the link to the contact page on the website footer. Make it easy for customers to find out how they can get in touch.
- Simple: Don’t put too much content on this page or it will overwhelm your audience. Just let them know where they can go to get answers to various questions.
- Professional: Even if you have a friendly brand personality, your contact form still needs to be grammatically correct and well-designed to show a professional edge.
- Convenient: Make your phone number clickable so customers can use it on Skype. The same can apply for your email address. Provide easy access to social media profiles, and if you have a contact form – keep it short and sweet.
- Informative: Include all of your contact information in the same place. This may include your address, a map to your location, social media pages, email addresses, and even forums.
- Accurate: Ensure that the information on your contact page matches the information listed elsewhere. Check directories and Google my Business listings to be sure.
- Attractive: Yes, a contact page needs to look good too. Plenty of white space will make essential information stand out. A good layout will guide the eye through the page.
- Consistent: Make sure the contact form on your website matches the brand personality that appears on all of your other pages.
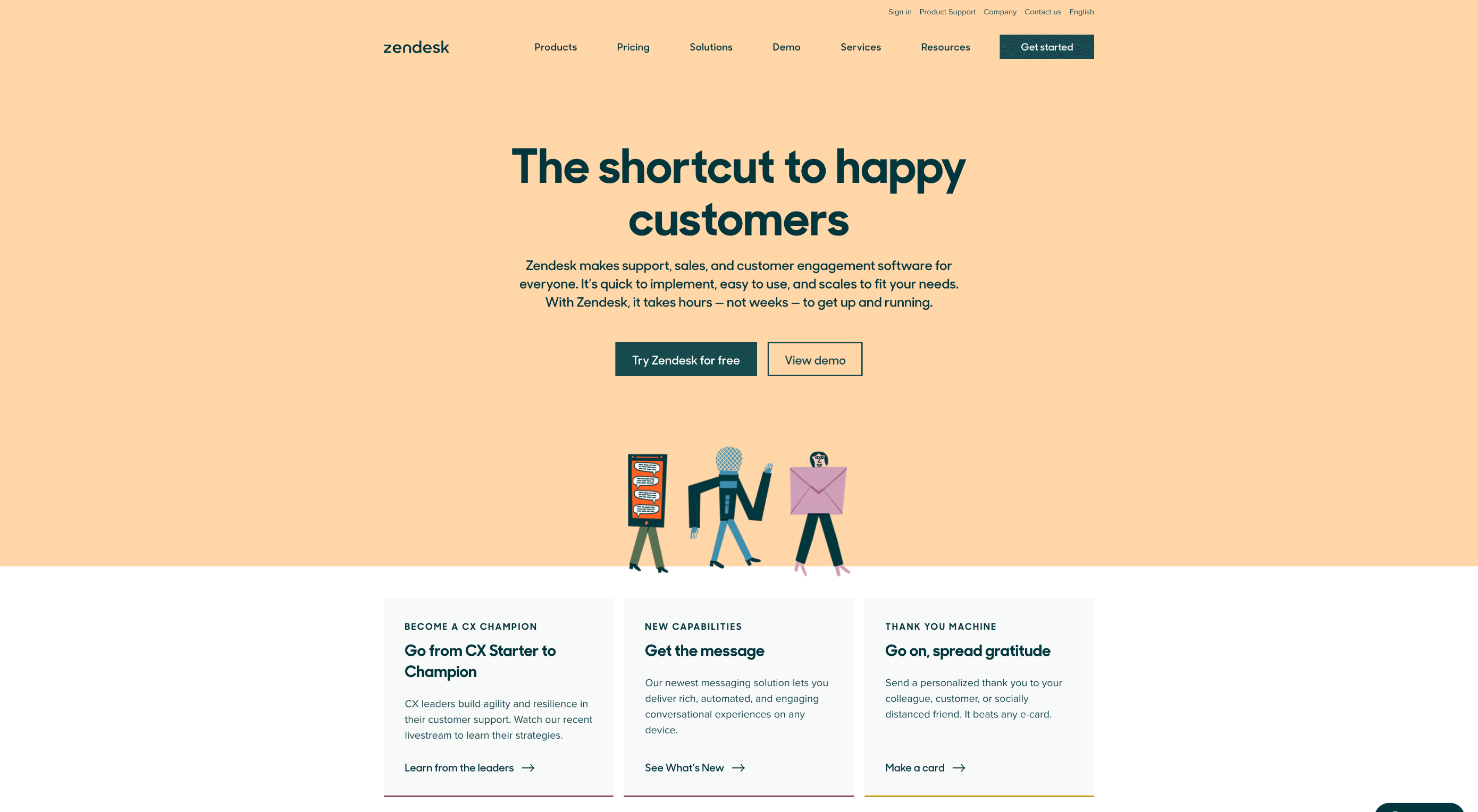
Take a look at the Tune Contact page:
It’s beautifully laid out, with clear information that’s easy to read. The company shows exactly why customers might want to get in touch and how they can reach out. As you scroll through the page, you’ll find additional office locations, email addresses for different teams (sales and support), and links to social media accounts too.
How to Drive Engagement on a Contact Us Page
A good contact page needs to look fantastic, showcase the company’s personality, and capture audience attention. However, there’s a big difference between a contact page that gets the job done, and one that convinces your audience they have to connect with you.
Here are some excellent ways to make your contact us page stand out.
Step 1: Using Color Correctly
Color and color psychology have a massive impact on user experience.
Studies constantly demonstrate the conversion powers of having the right shades on certain pages throughout your website. For instance, changing a CTA button from red to green can increase click-through rates by 27%.
However, every audience is different. The colors that drive engagement on a contact page for your company will depend on your target customer. A/B testing color palettes that match your brand personality is a good way to get started.
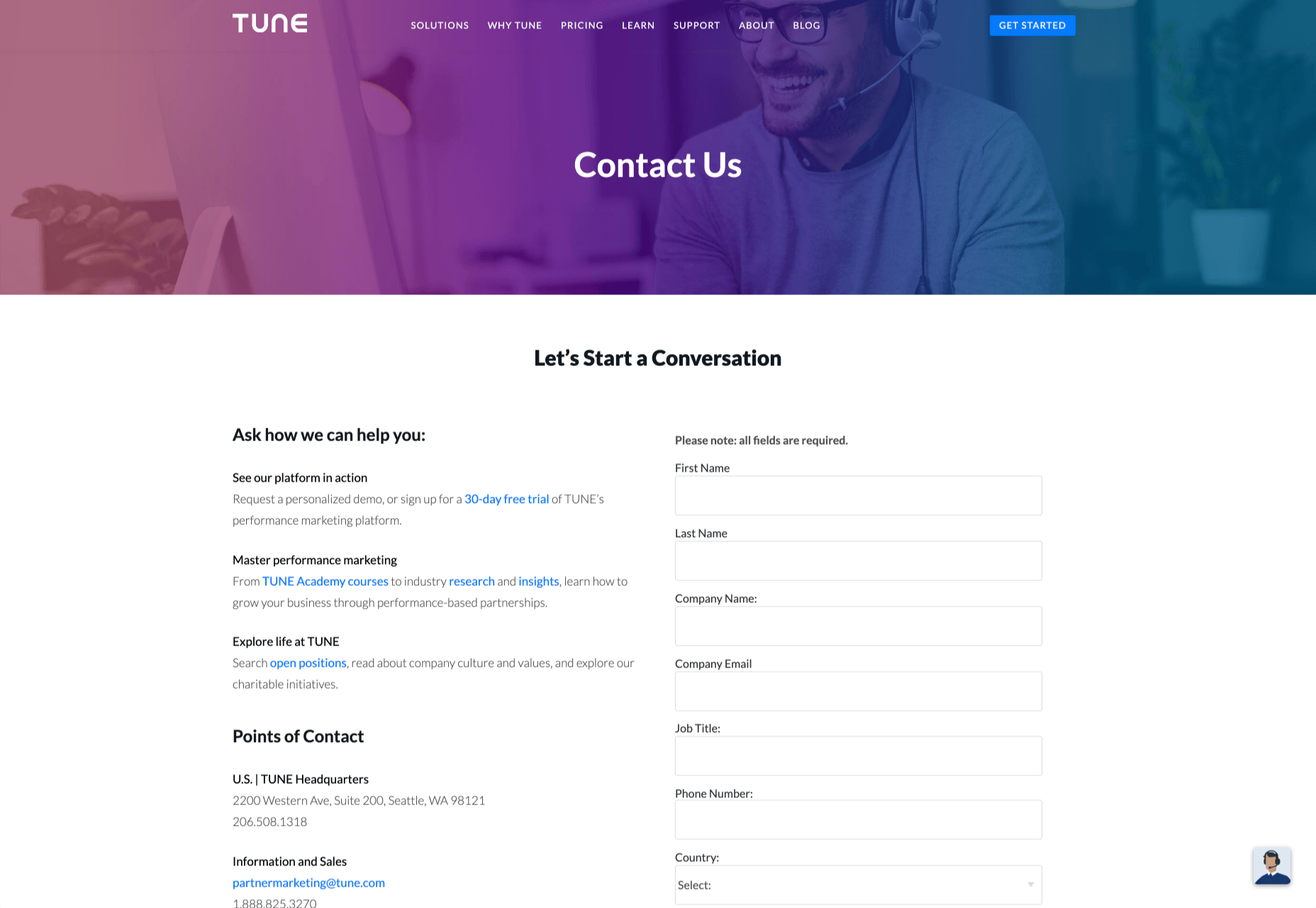
One interesting example of colors that make the right impact on a Contact Us page comes from Hubspot. Here, the brand maintains it’s brand color (orange), but it also introduces some new shades that convey trustworthiness and professionalism.
Blue is the most calming and credible color for any brand, The gradient that Hubspot uses here blends perfectly with its brand identity, allowing for a stunning contact page, with CTA buttons that still stand out.
Experiment with colors that can generate the right emotional response from your audience, but don’t ignore the golden rules of color in web design. You still need to showcase your brand identity, and you still need a way of making crucial information stand out.
Step 2: Humanizing the Customer Service Team
Some of the customers that arrive at a contact page are interested in your product or inspired by the potential of your service. Other customers will be looking for assistance because they’re frustrated with something or stressed out.
If you’ve ever had a problem with a product and wanted to reach out to the brand about it, you’ve probably noticed how annoying it is to find a blank contact page with nothing but an email address. The lack of effort and humanity in the contact page is enough to convince you that you probably won’t get a response.
But what if you add some happy smiling faces to the page?
Research indicates that brains are fine-tuned to recognize and appreciate human faces. Having a picture of your customer service team, or just any human being on your contact page makes you instantly more approachable. Your customers start to feel like they’re reaching out to a person – not an empty website.
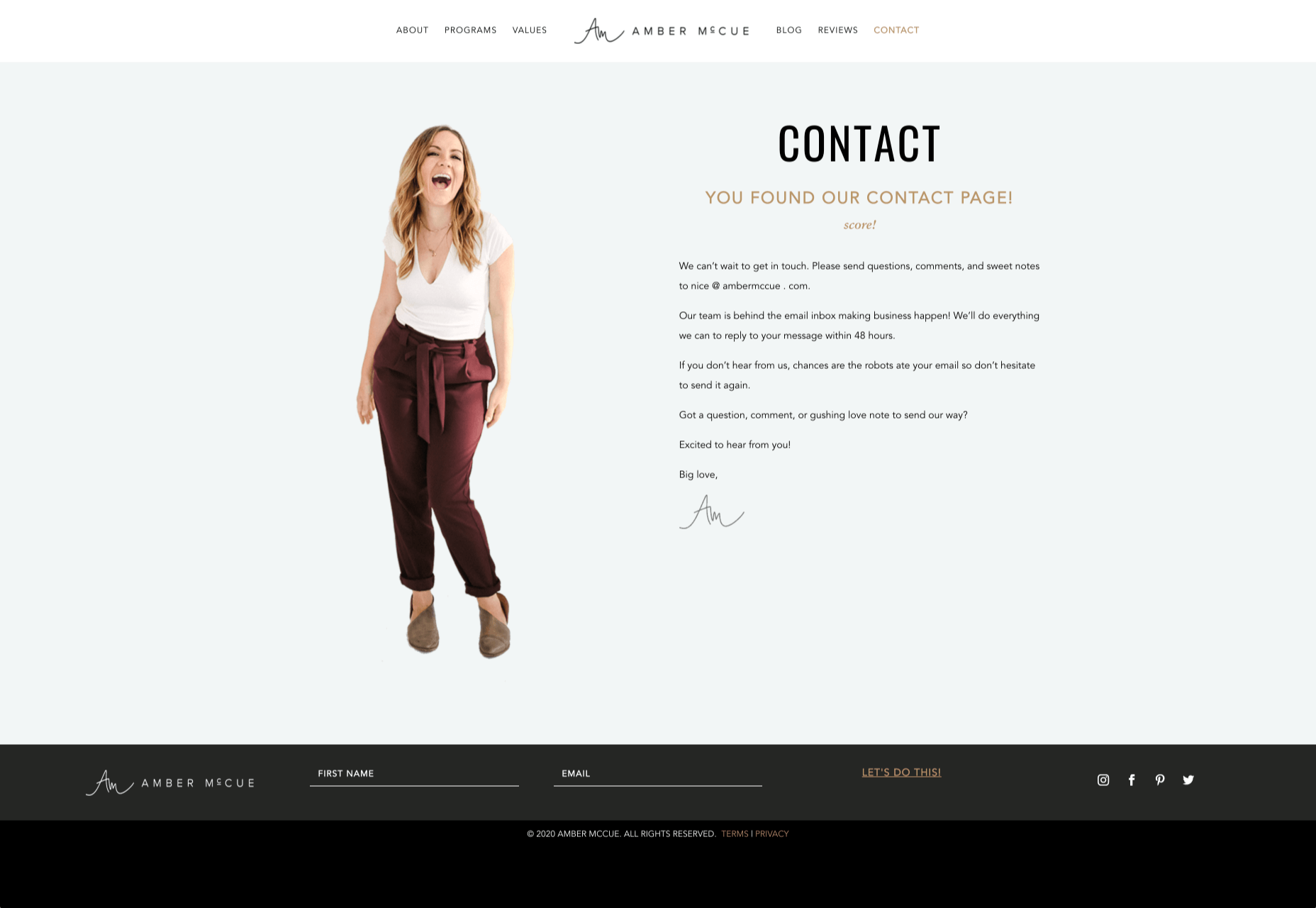
Look at how engaging and personalized this contact page from Amber McCue looks:
Although you can show any human face on your contact page and potentially get results, showing your actual agents will be more likely to drive positive results. It’s a great way to showcase the authenticity and humanity of your team.
Step 3: Making it Easy to Find
A surprisingly large amount of the time, companies shove their contact information into the footer of their website, forcing customers to spend forever looking for them. However, your audience might not want to spend an age searching for your details if they’re in a hurry to get answers.
Stowing a contact page in a footer is also a problem for those visiting your website via mobile, as they might not be able to see all your footer details and links as well.
A Contact Us page doesn’t have to be a massive part of your website navigation if you don’t want it to be. However, it should be one of the first things your audience can see. Putting the information on the header of your website, or even sticking it to the top of the page as your users scroll is very helpful.
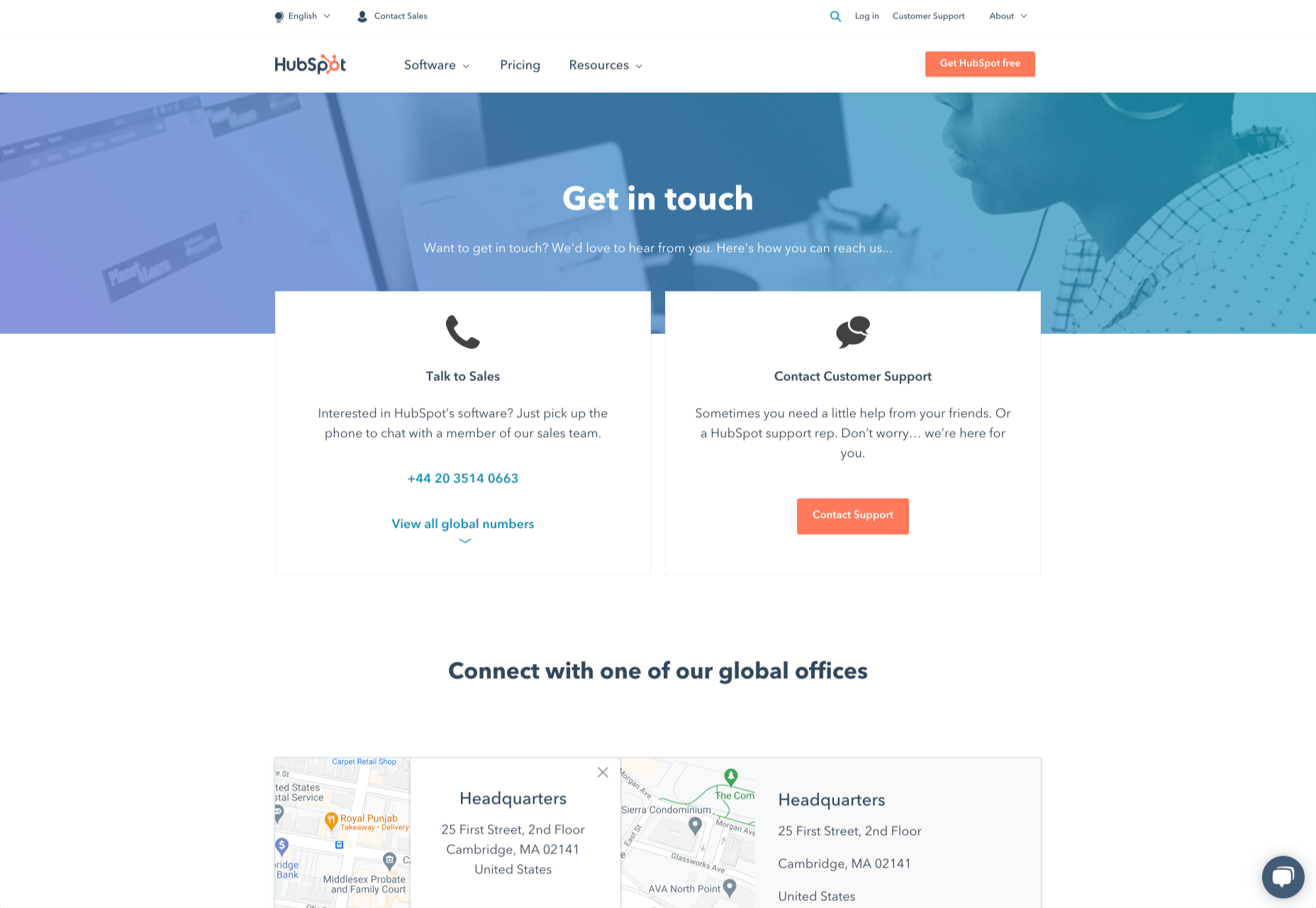
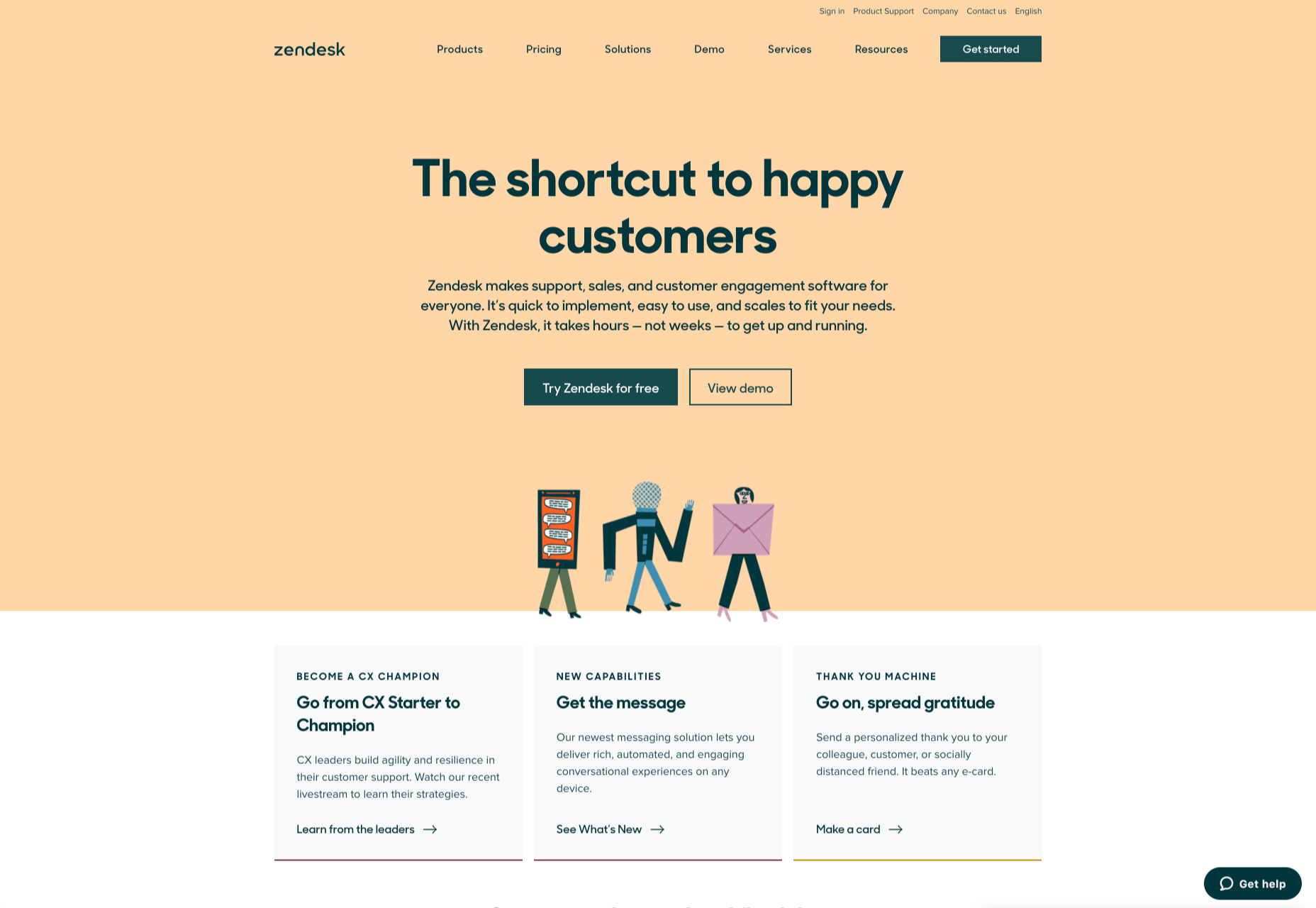
Zendesk makes it easy for customers to get in touch in multiple ways. First, the Contact section of the website is clear at the top of the page. Secondly, if you start scrolling through the Zendesk website, a “Get Help” button pops up, so you don’t have to scroll back to find assistance:
Remember, aside from making sure that your contact page appears in the right part of your website, it’s also worth ensuring that it’s easy to understand. Don’t use unusual terms like “Chat”, or “Chill with us”. Stick to tried-and-true options like Help, Contact, or Support.
Step 4: Making the Experience Relevant
There’s a reason why it’s practically impossible to find a one-size-fits-all contact page.
It’s because different customers need different things from your brand.
Some customers will be looking for the answer to a question; others will want to discuss something with your sales team. That’s why many companies are using adaptive contact pages that can change to suit the situation.
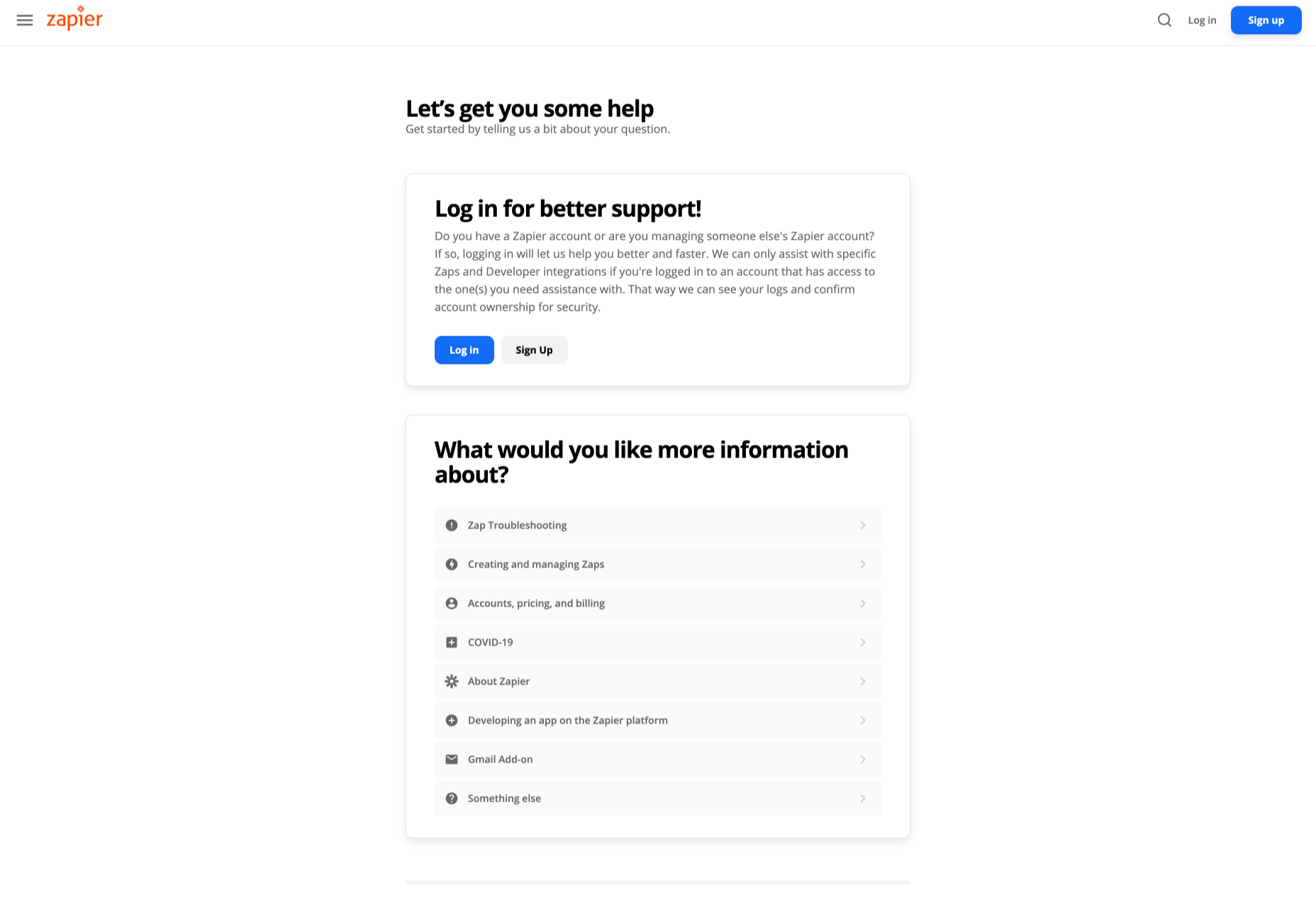
For instance, you may start by asking customers what they need help with. Zapier takes this approach with its Contact page:
By asking the client what they need straight away, Zapier can make sure that the visitor finds the right information, and the right number or email address for the appropriate agent. You can even scroll down the help page and look for something in the available help centre, using the search bar. Or you can click on View our experts to hire a Zapier pro.
Creating a dynamic and customized experience like this does a few things. First, it ensures that the customer will reach the right person to help them first-time around. This reduces the number of inappropriate calls your employees have to deal with, and the number of transfers.
Secondly, you deliver a better experience overall for your client, because they don’t have to repeat their issue to multiple people or start a massive email thread. They get the support they need immediately.
Dynamic contact pages can even save you some money and time. If clients decide to solve an issue themselves, using your resources, that’s great for your busy agents.
Step 5: Direct People to the Right Place
The central focus of your contact us page needs to be the available contact options. Centralizing the contact options on a page is an excellent way to make sure that they get the right amount of attention. Centralizing also means that your customers can spend less time searching for the contact details that they need, which is great for usability.
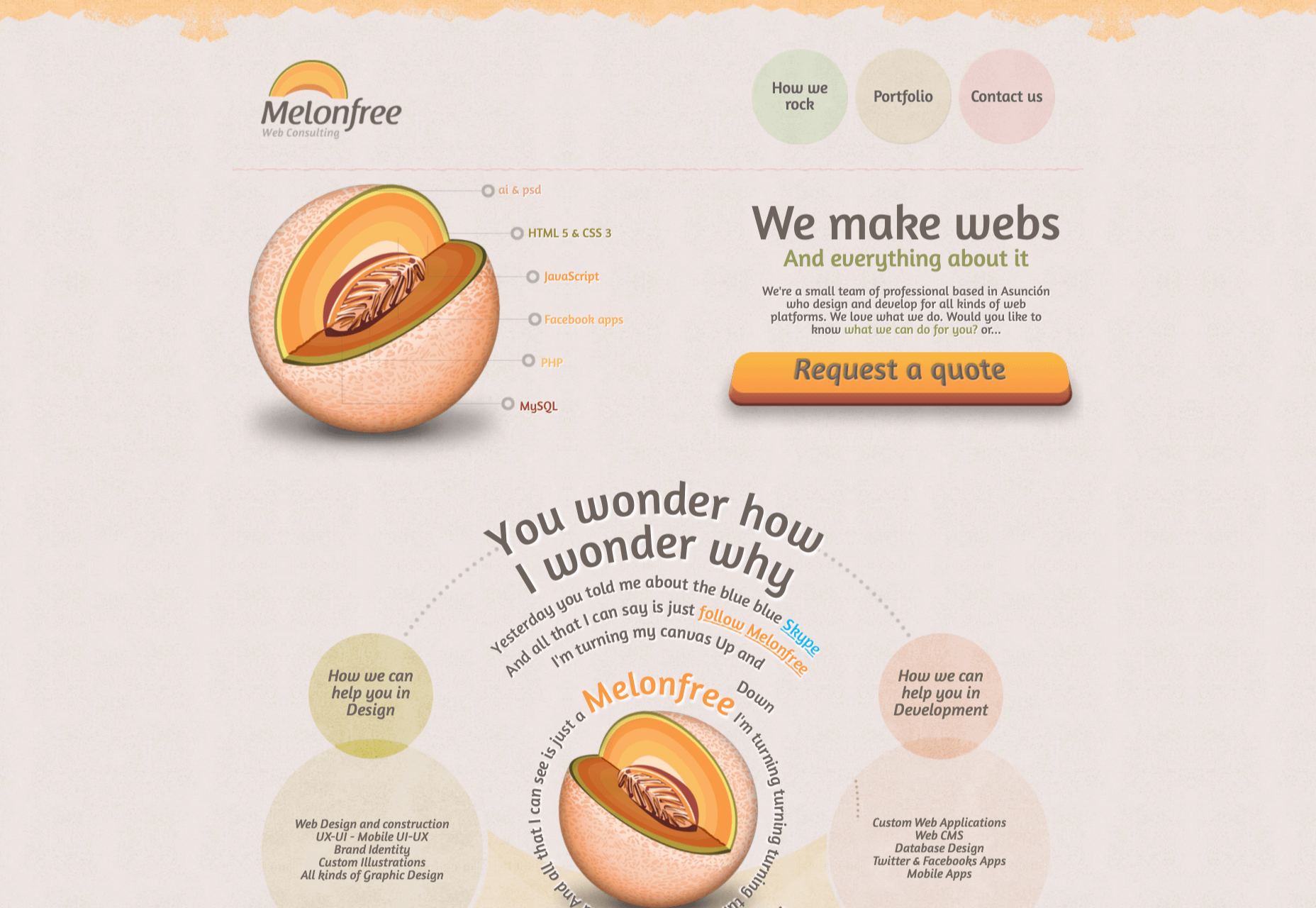
The Melonfree.com website uses a contact us form that’s centralized to immediately pull attention to the customer’s options for getting help.
Centralization isn’t the only way of using design principles to guide visitors on a contact page. According to Ray Hyman and Edmund Hick, increasing the number of choices on a page often increases the time it takes for people to make a decision.
When it comes to connecting with a brand, the right option for each customer will depend on the person and the situation they’re trying to overcome. For instance, a customer that needs to reset their password will probably be able to get the solution they need from an FAQ page.
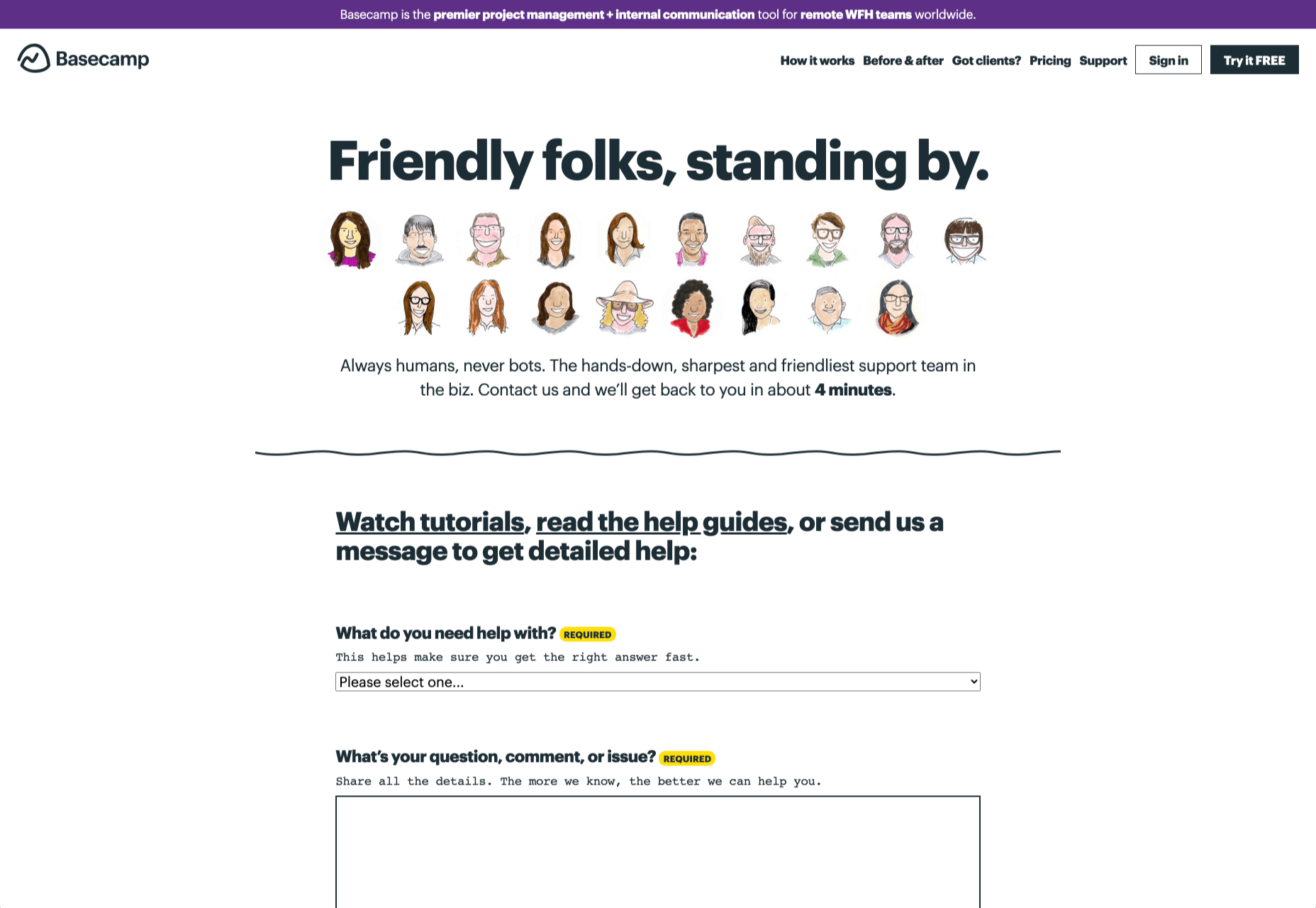
On the other hand, someone who needs help using a new feature might need the guidance of a professional. To help guide customers to the right solution, Basecamp gives customers a variety of steps to follow to get the right solution fast.
The main purpose of the contact page is to help customers get the right answer with an informative form. However, there are unobtrusive alternative options available too. If all you’re looking for is a way to help yourself fix a problem, you can click on the help guides link before you ever scroll down to the form.
Step 6: Support the Contact Team Too
The best contact us pages aren’t just a great way to improve customer experience. Well-designed solutions also help the customer service team to save time and stay productive.
One of the primary metrics that companies consider when evaluating the success of a service team, is the number of replies required before an issue is resolved. However, if the initial question from a customer doesn’t contain enough information, this number often increases.
Using the design of the contact form to access the right information helps with:
- Automatically routing people to the right team member: Companies can set up segmentation rules that automatically send certain emails to different employees based on keywords. You might have questions that go to the sales team, and separate queries that you direct straight to the customer service team.
- Show appropriate support options and FAQs: Remember to give the audience a chance to help themselves before they reach out for extra support. Links to an FAQ page or self-service options can really reduce the pressure on a team. Some companies even add automated chatbots to the mix to help with self-service.
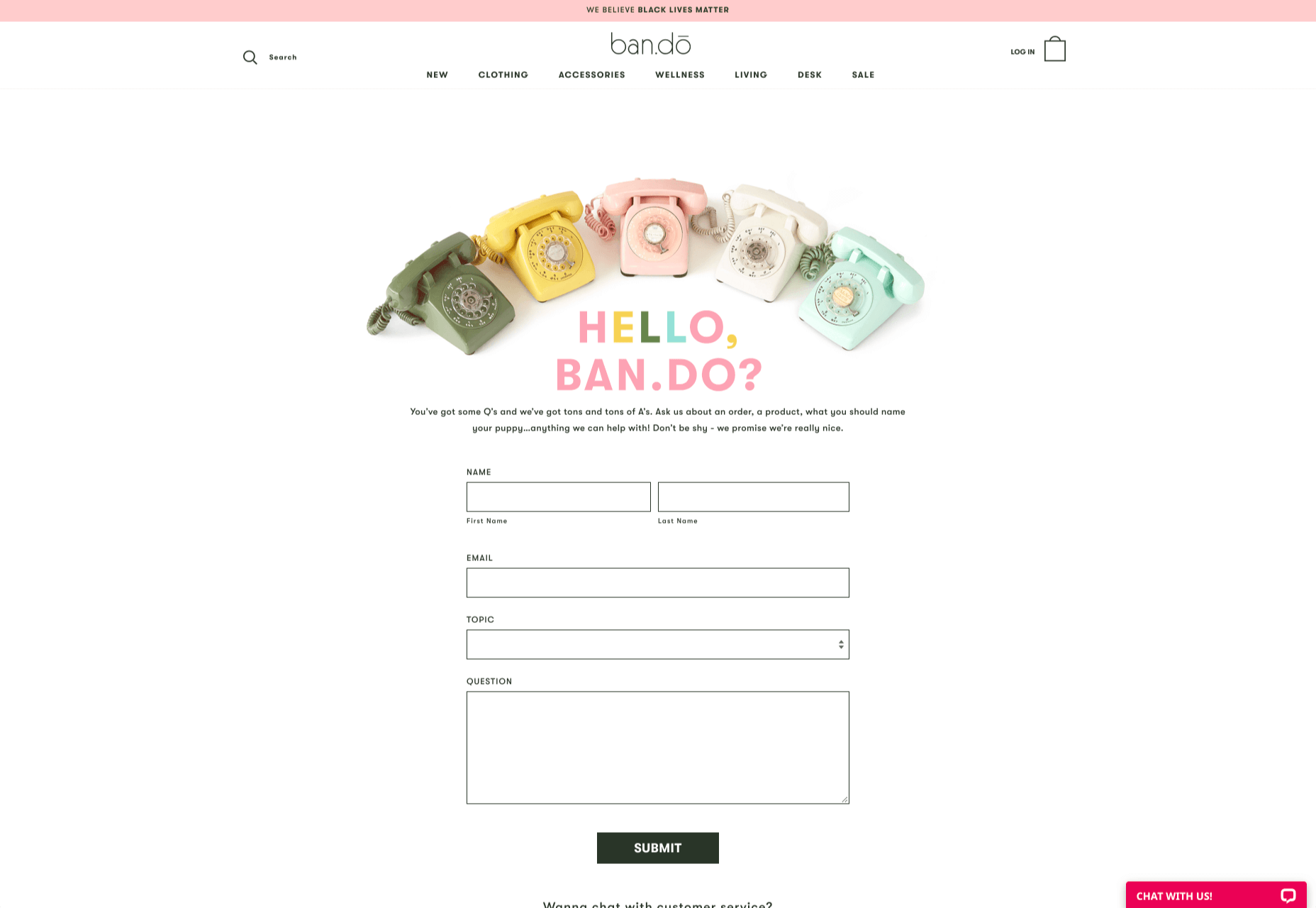
- Prompt for extra context: Although not every customer will take advantage of an opportunity to add extra information to a form, some will. Adding a box to your contact form for “anything we need to know?” is a great way to generate more information. Ban.do includes a simple “question” box where customers can add as much detail as they like. An option to add screen shots or documents might be a nice touch too.
Building Your Own Contact Us Page
Every customer has their own specific set of needs. The right contact page for another business might not be the right one for you. That’s why it’s so important to take some time getting to know your customers and speaking to your support team.
When you’re planning your contact page, it helps to ask yourself some basic questions about what you want to achieve. For instance:
- What kind of channels will our customers want to use to connect with us? Look at things like social media messaging, email, or phone calls. If you’ve got a relatively tech-savvy audience, then they might want to use things like instant messaging with chat bots too.
- How can we direct clients to the appropriate channels in as little time as possible? Having a system in place to automatically route your customers to the right agent will reduce the time to resolution for your customers. The faster you solve problems, the better your reputation becomes.
- What can we do to set customer expectations and build confidence before they speak to us? Designing a professional-looking contact page will increase customer confidence, while an FAQ section shows that you’re ready to answer common questions.
- How can we showcase a unique brand personality without making the page complicated? Everything from using distinct brand colors on a contact page, to adding images and illustrations reminds customers that they’re in the right place.
- What can we do to reduce the friction points in a customer’s path to contact? Avoid adding too many input options to a contact form and ensure that it’s easy to reach out when your clients have a problem.
Understanding exactly what your audience needs from you, and what they’re looking for when they come to your team for help reduces the effort involved for your client when they reach out for help. Remember, today’s digitally-savvy customers expect their interactions with companies to be as streamlined and simple as possible.
Make the Most of Your Contact Page
Contact pages are frequently an afterthought in the website design process. However, they’re one of the most valuable tools your company has. With a good contact page, you ensure that your customers can always reach you when they have problems. What’s more, you boost your chances of people wanting to reach out to the sales team too!
Good luck creating a contact page that encourages engagement from your target audience. Don’t forget to track your results from each design, and A/B test for optimization.


 When starting a new business (or even venturing into the world of freelancing for the first time), there are some really big, important steps you have to take.
When starting a new business (or even venturing into the world of freelancing for the first time), there are some really big, important steps you have to take.

 It would be way too easy to answer this question with: “Whoever pays your bills.” And, honestly, I don’t think you can be a very successful web designer if you’re only driven by what the person paying you tells you to do.
It would be way too easy to answer this question with: “Whoever pays your bills.” And, honestly, I don’t think you can be a very successful web designer if you’re only driven by what the person paying you tells you to do.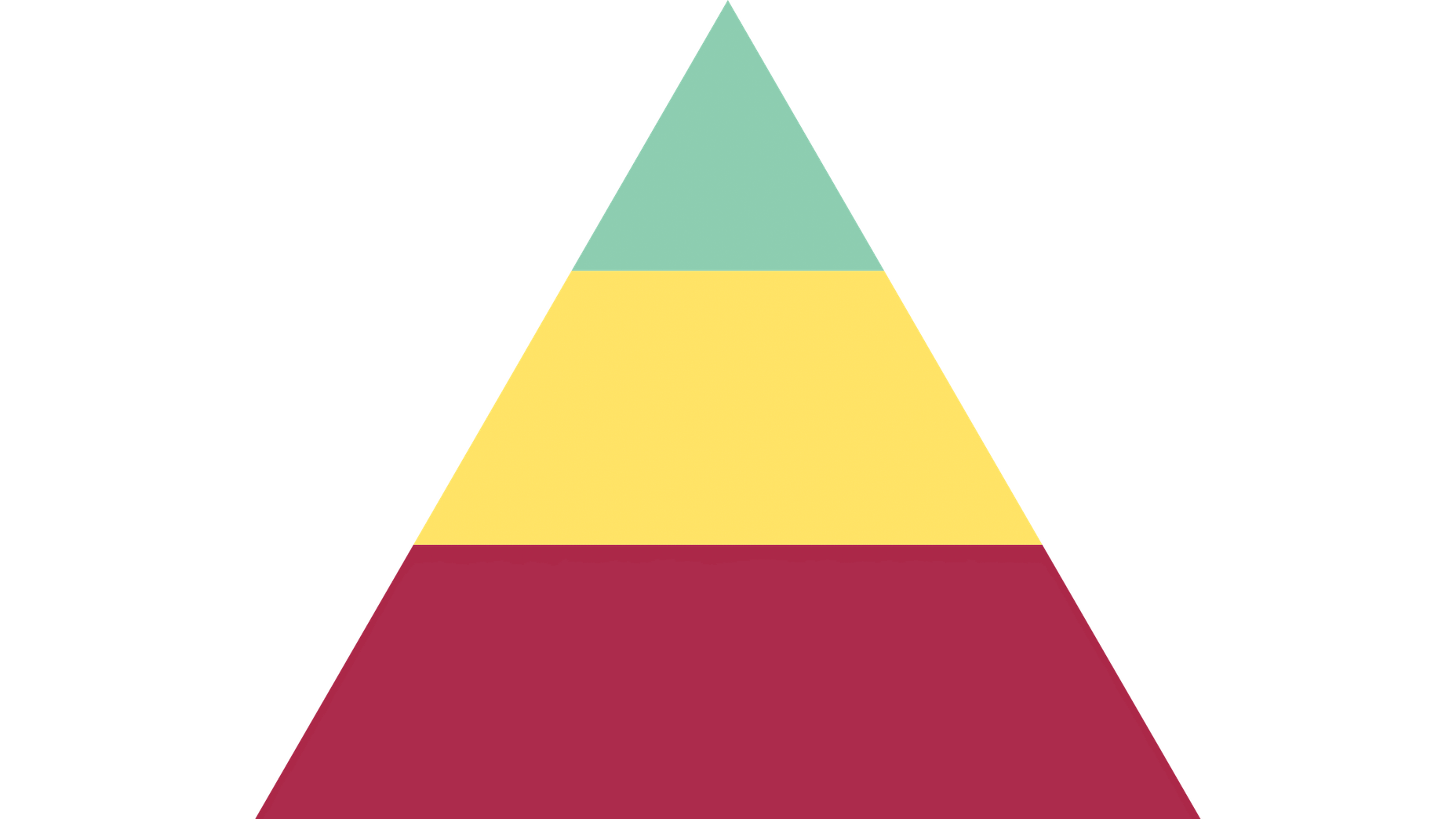
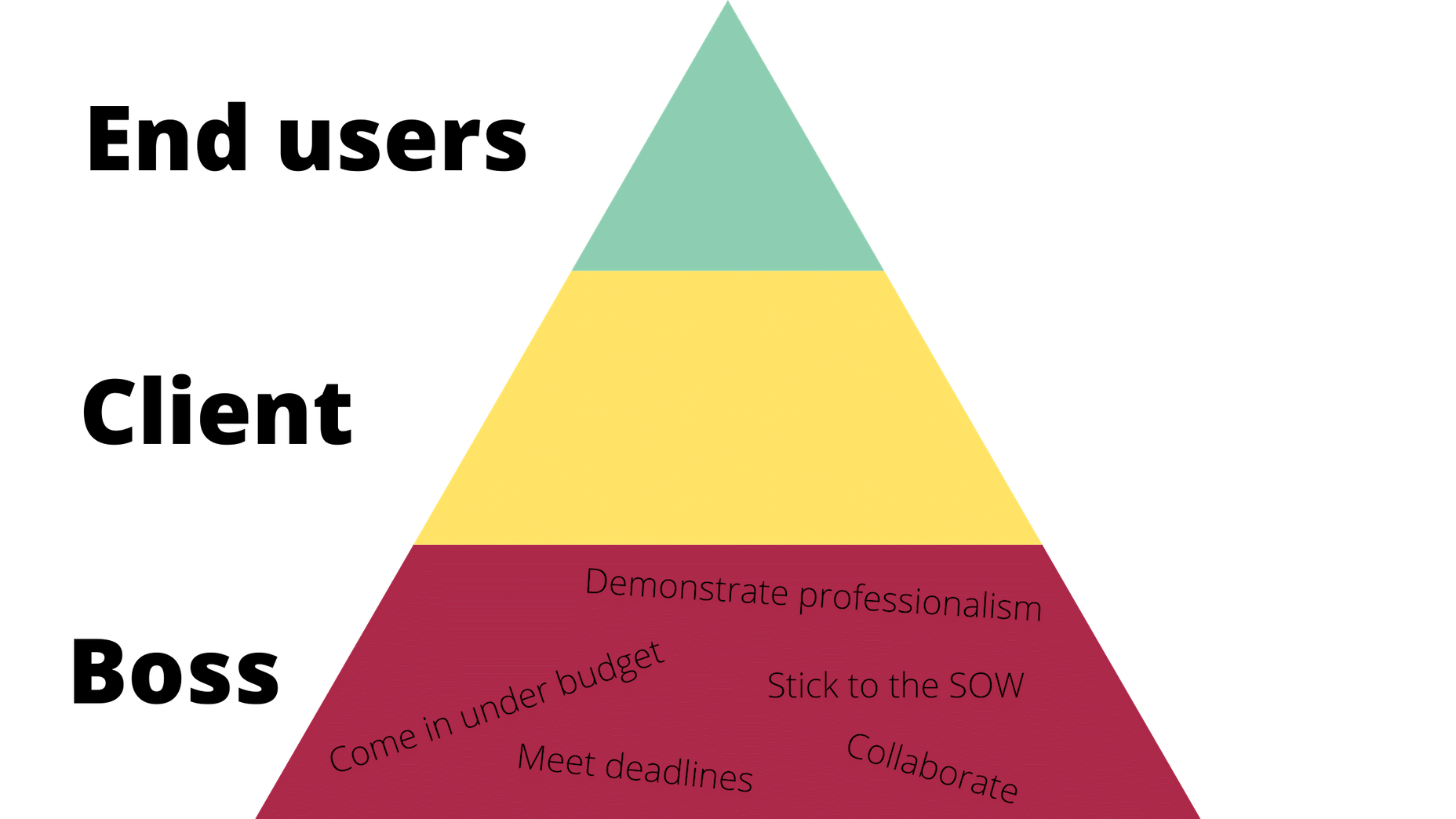
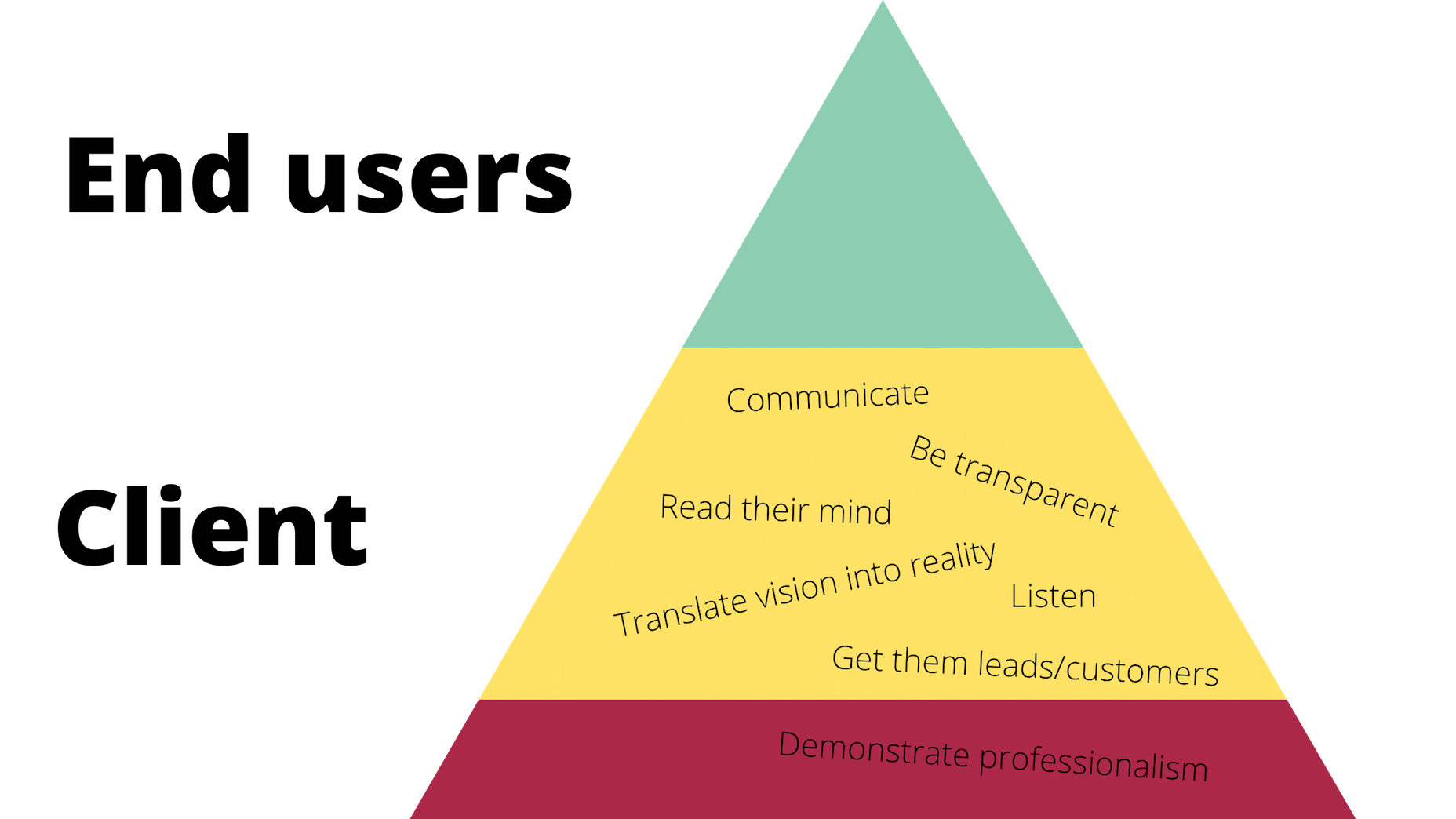
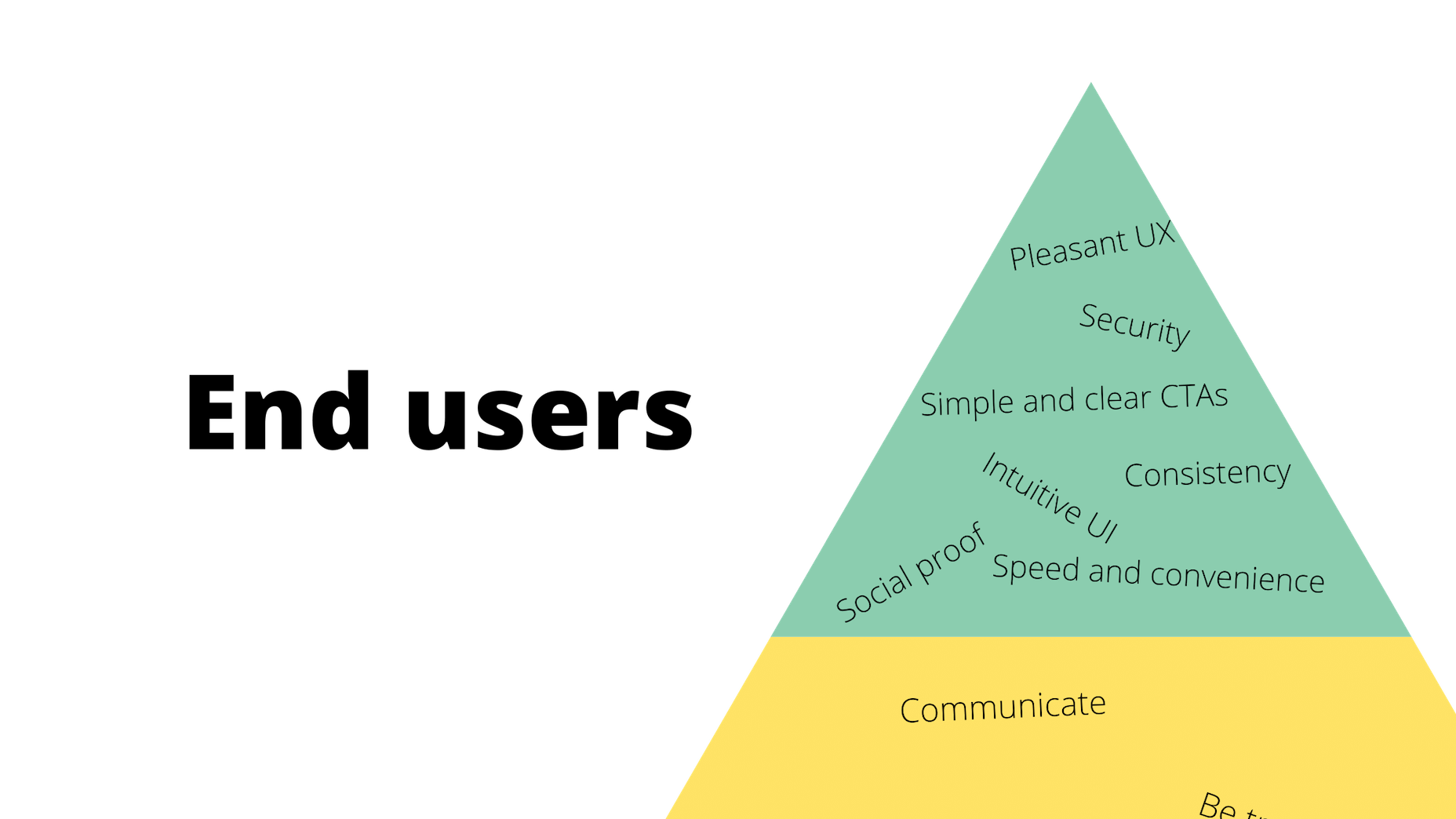

 I often see freelancers on social media asking what the secret is to working fewer hours, making more money, and helping new clients to find them. While those things tend to happen the longer you’ve been freelancing, it doesn’t happen without some effort.
I often see freelancers on social media asking what the secret is to working fewer hours, making more money, and helping new clients to find them. While those things tend to happen the longer you’ve been freelancing, it doesn’t happen without some effort.




 To understand why user onboarding is such an indispensable tool, we need to empathize with the people using our products; we all come from different backgrounds and cultures, we make different assumptions, and we see the world differently.
To understand why user onboarding is such an indispensable tool, we need to empathize with the people using our products; we all come from different backgrounds and cultures, we make different assumptions, and we see the world differently.

 While a lot of the research for web designers that’s come out this year has to do with COVID-19, we’re starting to see a light at the end of the tunnel. Many of these reports aren’t just looking at the effects of the pandemic on business and marketing today. They’re now looking at what consumers plan to do once the pandemic is gone.
While a lot of the research for web designers that’s come out this year has to do with COVID-19, we’re starting to see a light at the end of the tunnel. Many of these reports aren’t just looking at the effects of the pandemic on business and marketing today. They’re now looking at what consumers plan to do once the pandemic is gone.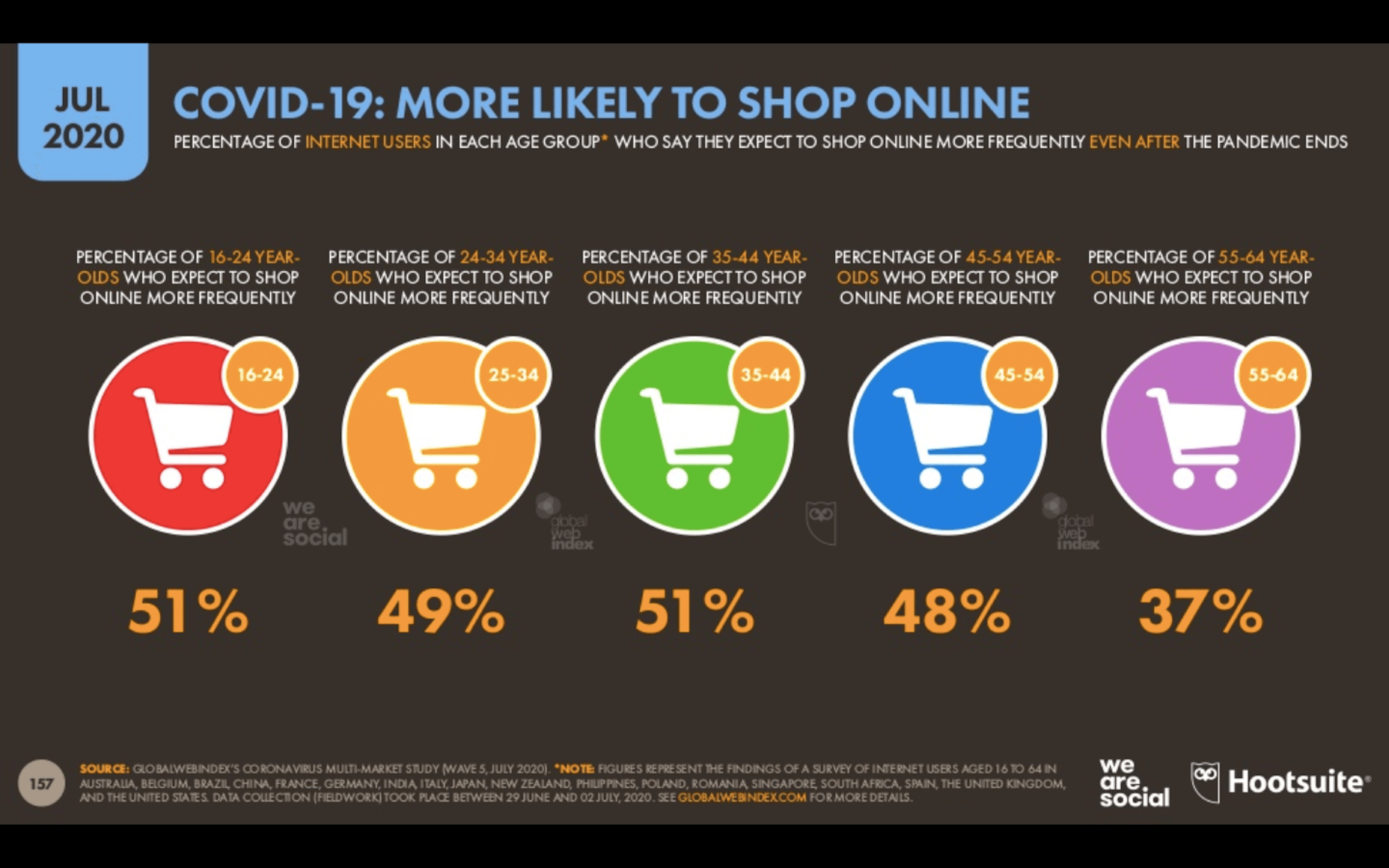
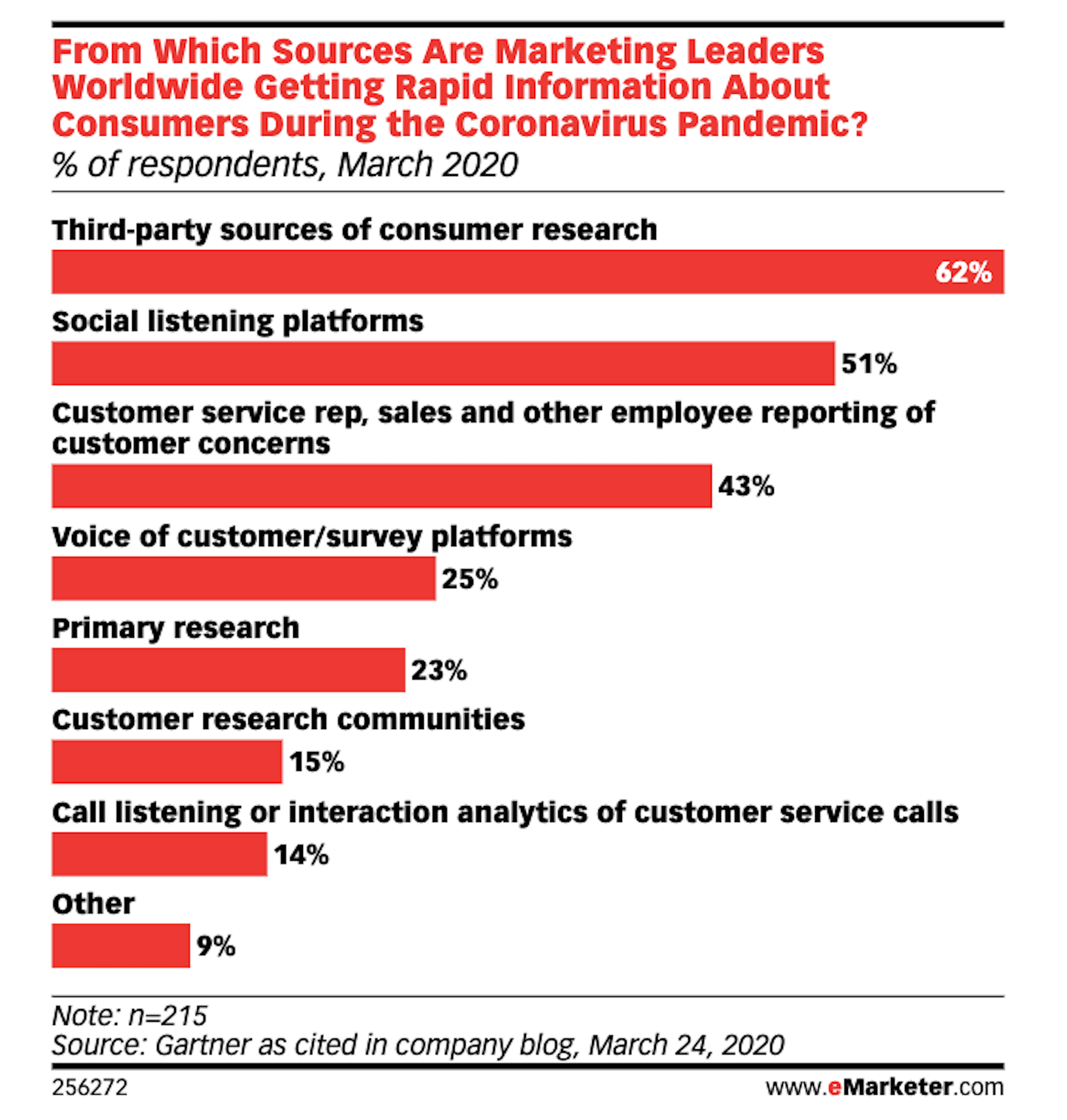
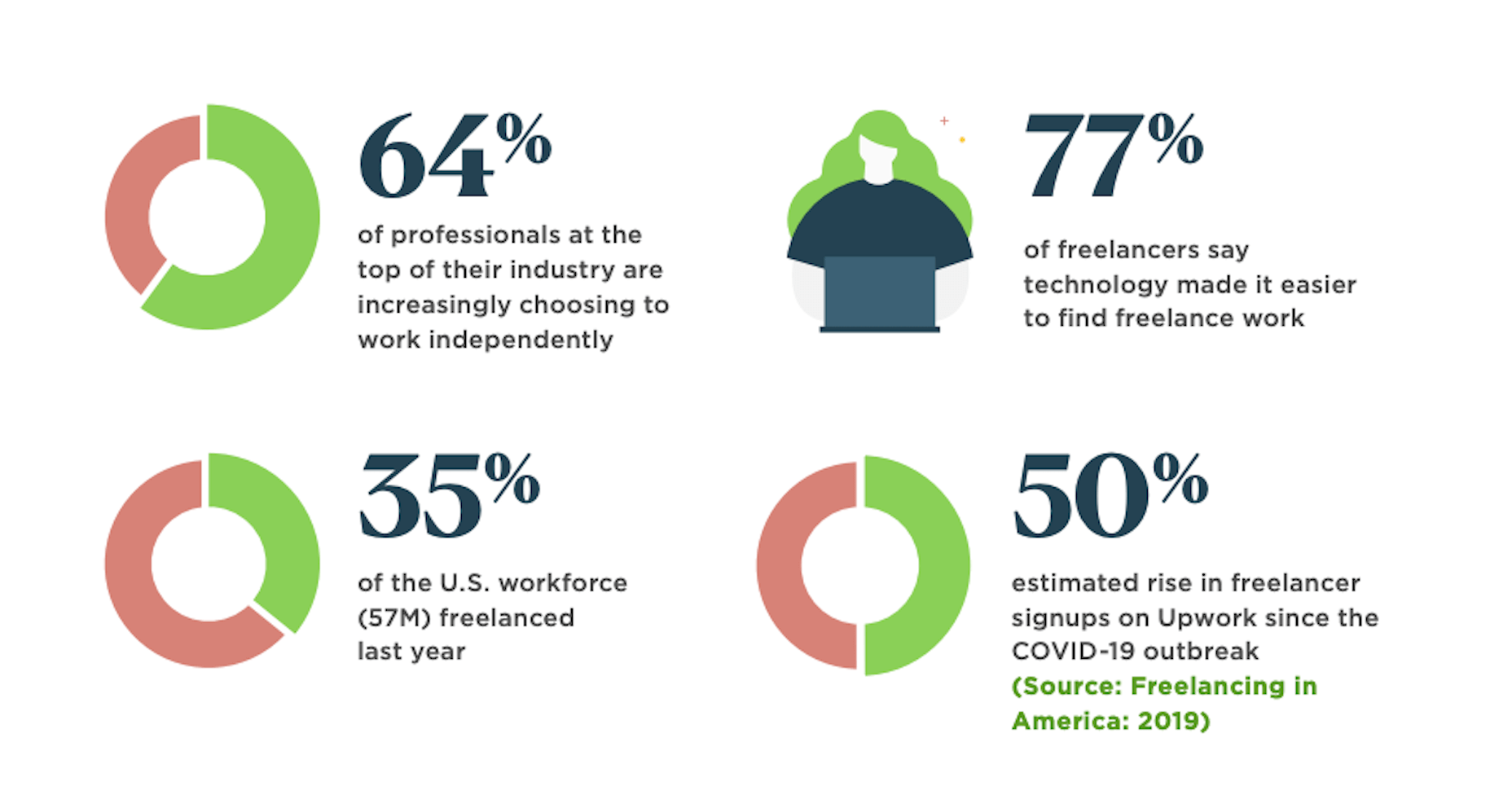

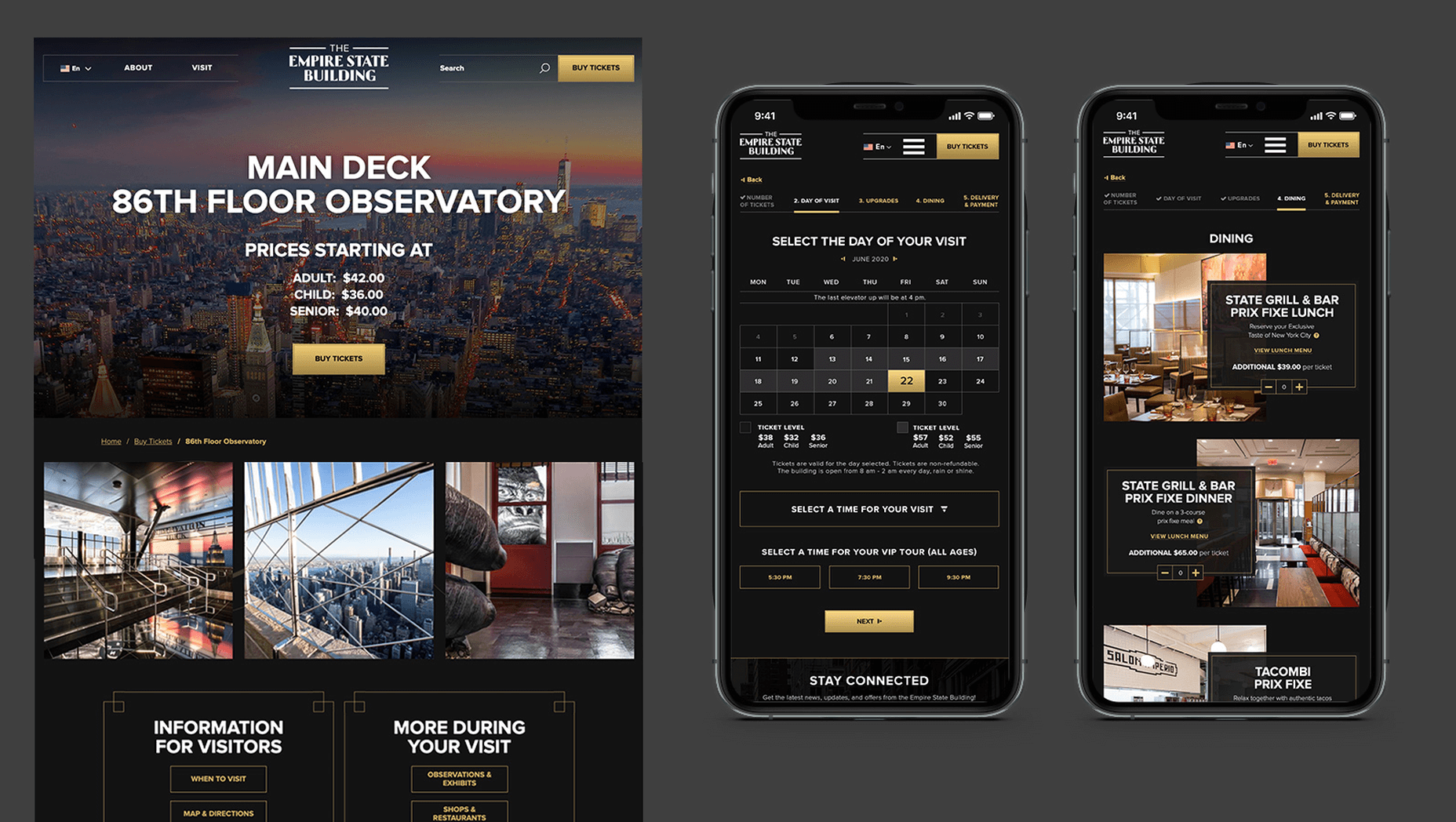
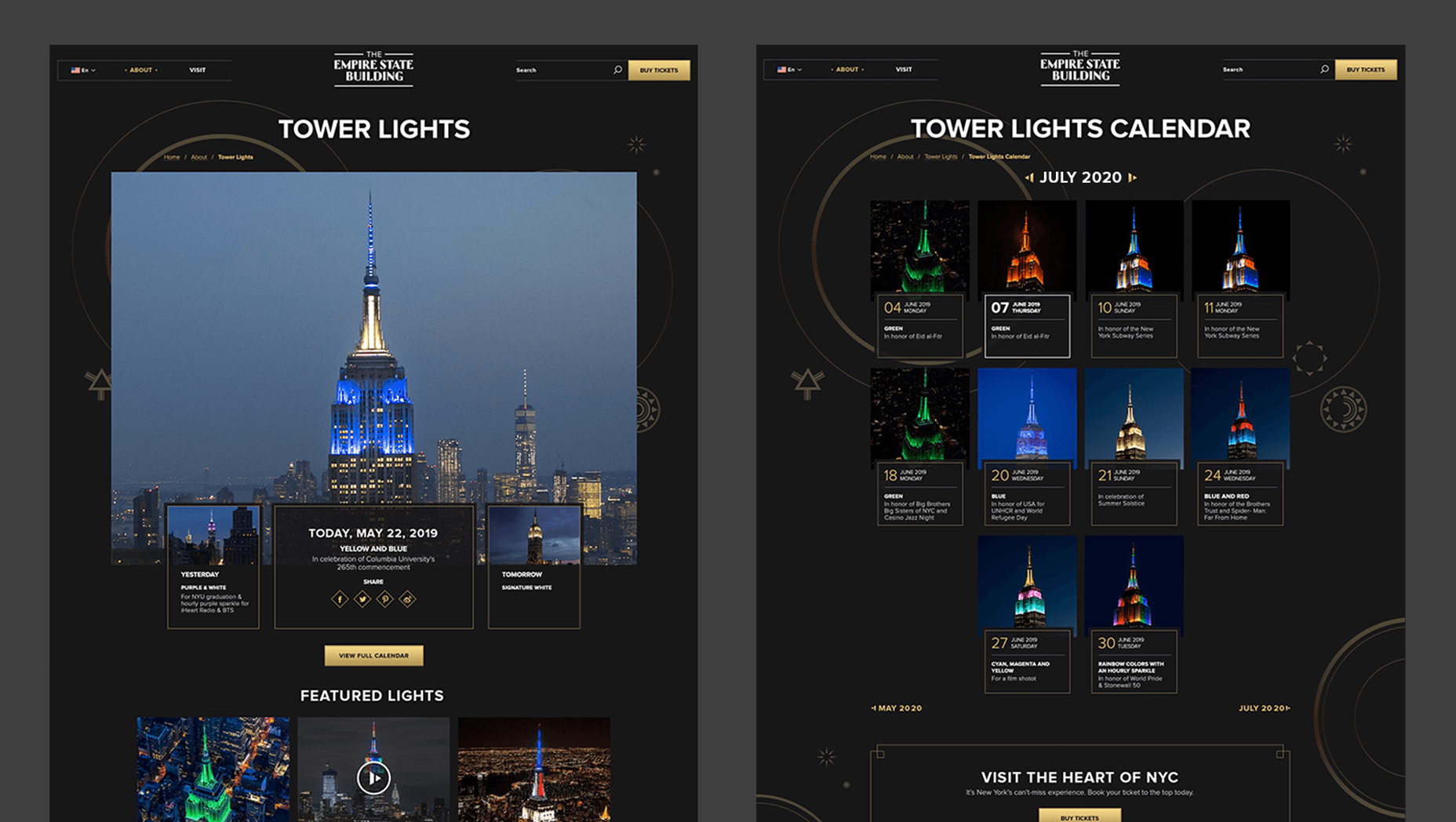
 In 2019, to keep pace with an interior redesign of its visitor experience, the
In 2019, to keep pace with an interior redesign of its visitor experience, the 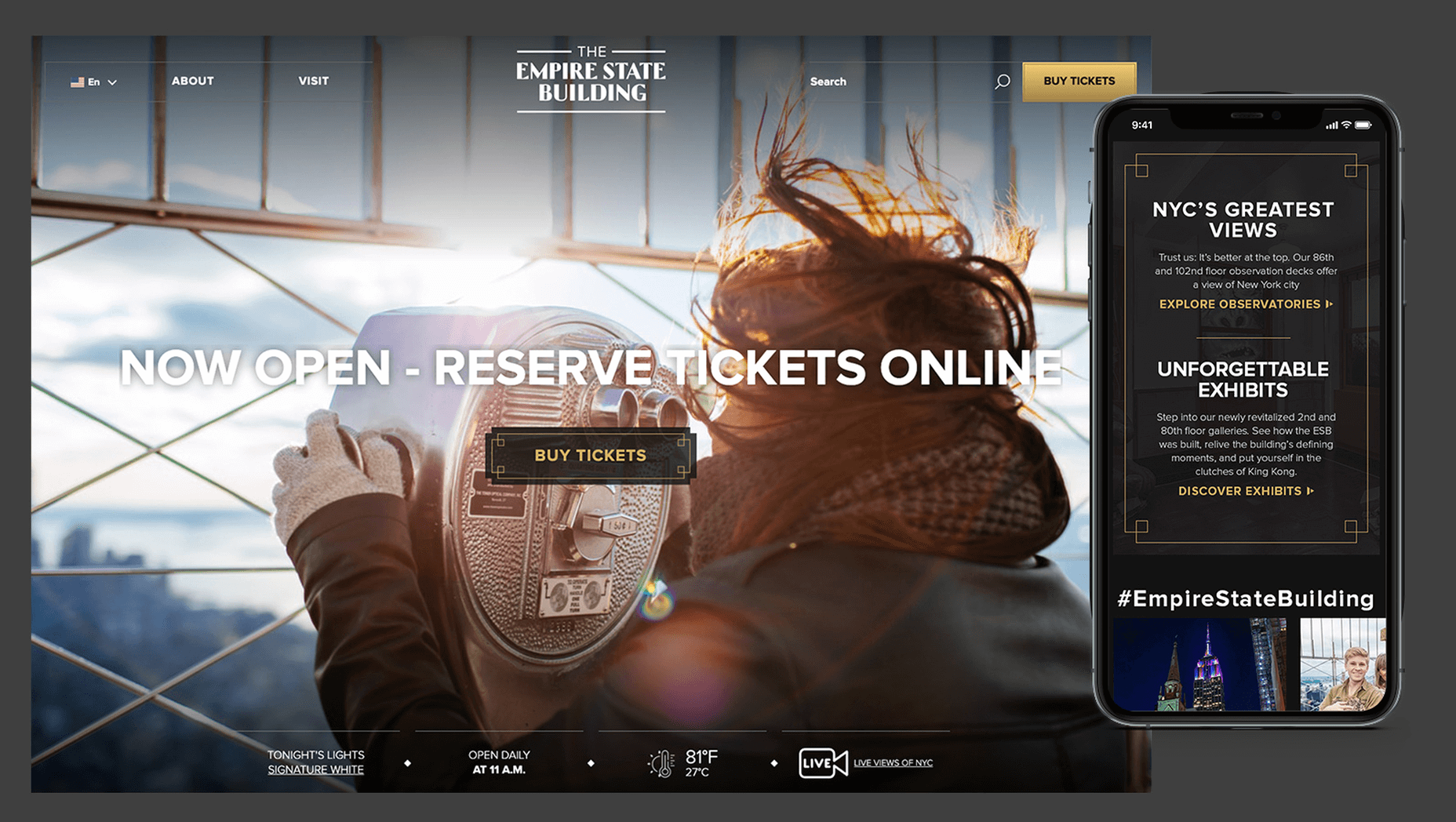

 Many people dream of a career in web design, but it may actually be more attainable than you think.
Many people dream of a career in web design, but it may actually be more attainable than you think.