Many websites today use some type of traditional Content Delivery Network (CDN), which means improvements in website load times, decreases in bandwidth, and better redundancy and security. But not everything is optimized, specifically when it comes to images, and image CDNs can help with that!
Many websites today use some type of traditional Content Delivery Network (CDN), which means improvements in website load times, decreases in bandwidth, and better redundancy and security. But not everything is optimized, specifically when it comes to images, and image CDNs can help with that!
Traditional vs. Image CDNs
A traditional CDN treats images as static. If you want to tailor images to better match various mobile device types, then you need to create many variants of each image and upload them to your web server. It also means you must develop responsive code that will tell the server and CDN which image variant to deliver. This is clunky, time-consuming, and inefficient. For a large website, the amount of code needed can be astronomical. Using this static image model, there’s just no realistic way for each image to be effectively sized and compressed for every possible device model – at this point, there are thousands of them. The combination of these two unfortunate factors leads to potentially slow load times and poor UX caused by oversized images delivered to mobile devices.
So what is an image CDN? An image CDN builds on the traditional CDN model with the addition of device detection and image optimization. Instant detection of the device model and browser requesting the images is done right at the device-aware edge server (true edge computing!) Additional information, including screen resolution and dimension, pixels per inch, and support for next-gen image formats (such as WebP, JPEG 2000/JP2, and AVIF), provides even more details crucial for superior image optimization. Using this information derived from device-aware edge servers, the image CDN optimizes each image and serves the perfect version for each device and resolution, meaning users get the finest webpage experience faster.
A Bit About the Edge (Whoa, Living on the Edge?)
With a single server website, a web request would have to travel from the requestor, back to the origin server (wherever that was geographically located), be processed, and then travel back to the requestor. Depending on the physical distance between the requestor and the origin server, this could introduce a great deal of latency, which means lag time on page loads.
A traditional content delivery network (CDN) is a global network of servers that optimizes web performance by using the node geographically closest to the user for faster delivery of assets. It takes static content like images and stores them on the edge. But usually, these edge servers are relatively simple in terms of their role in business processes. They mostly index, cache, and deliver content. And traditional CDNs like to keep edge servers simple because of concerns over CPU usage, storage, and scalability.
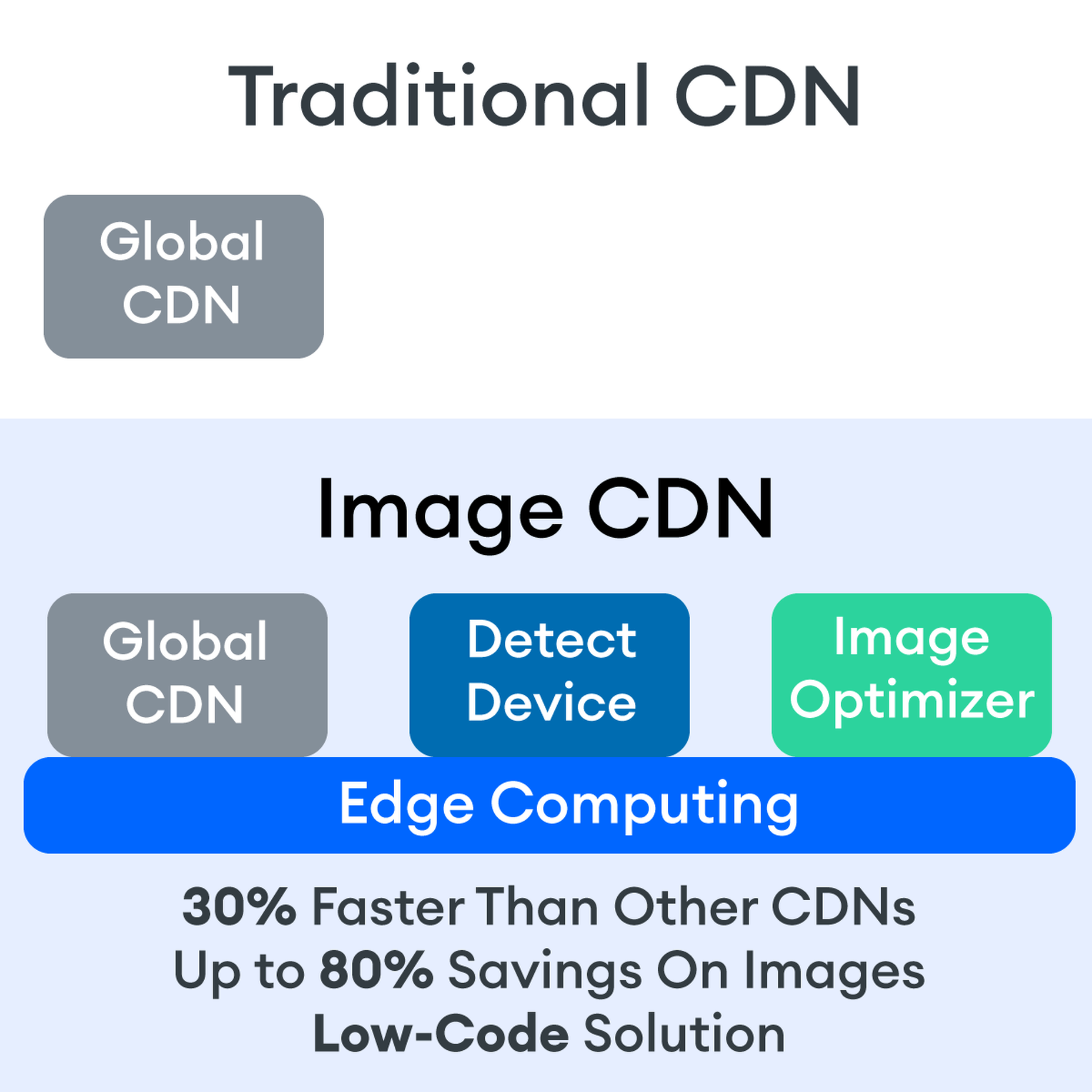
But what if these edge servers could also provide computing power that enhances performance and business processes? This is called edge computing. Slowly, CDNs are starting to open their edge servers to allow enterprises to deploy apps/services on the edge. Likewise, Cloud computing networks (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) provide virtualized server capacity around the world for those who want to use geographically distributed servers. In a sense, Edge Computing is a marriage of the CDN (where edge servers synchronize/work with each other) and Cloud computing (where servers are open to applications).
Edge computing is a fascinating concept, but what is the killer app that will enhance business processes and improve website performance? The addition of device detection to edge computing provides the ability to transform from delivery of static images to a new model where images are dynamic and tailored exactly to devices.
Edge computing is computing that is done in a geographically distributed space, with many servers located at or near the source of the web request. This reduction in bandwidth and latency leads to fast processing times, increased site speed, and improved customer experience. And edge computing doesn’t require new infrastructure — it leverages the networks of existing providers to create Points of Presence (POP) around the globe.
The Edge Servers are…Aware?
Device-aware edge servers, like those used by the ImageEngine image CDN, take edge computing to a new level. Device detection is actually one of the use cases where edge computing really shines. Normally, the edge server would have to send a Javascript query to the device to figure out any information about a requesting device’s model, browser, operating system. But with a device-aware edge server, the User Agent string is captured and decoded. This contains all of the information necessary for device detection without the need for any back and forth – a definite speed improvement. So you’re starting ahead of the game!
Each time a new request comes to the device-aware edge server, the image is processed by that server (meaning optimized for that specific device parameters) and stored right there in cache, primed for future use. This is done in three stages: changing image size based on device resolution, compressing the image using an image optimization tool, and selecting the most efficient file format for the device.
If the device-aware edge server has already processed a request from a similar device model before, then it can serve the device-optimized image from its edge cache, leading to a lightning-fast server response — and ImageEngine’s device-aware edge servers can serve up cached images 98% of the time! Not only is there geographical proximity because of the distributed global POP network, but the smaller size of the optimized image compared to the full-sized original cuts up to 80% off the image payload. This can cut up to several seconds off page load times. When almost 70% of people say that page speed influences their likelihood of making a purchase, every single second counts!
Some image CDNs detect the device information and group the devices into “buckets” of similar types and serve an image based on that type. While this is certainly an advancement over a traditional CDN, and works passably well for some common devices, it still isn’t a truly optimal solution. There are so many variants of browser, screen size, resolution, etc., even among very similar devices, that images are still often oversized (too large payloads) and lead to poor load speed. A true image CDN, such as ImageEngine, serves the perfect image for every device, every time.
So Now You Want To Get Started (Don’t Worry, It’s Really Simple)
One of the best things about the ImageEngine image CDN is the ease of integration – and it can integrate into any platform that supports a 3rd-party CDN. All you need is to sign up for an account and receive a delivery address during your two (yes, 2!) minute signup process. This delivery address is used to redirect image traffic for optimization and superior delivery performance. Next, you’ll have to make some slight adjustments to img tags on your website, but that’s really all the work you’ll need to do. There are no DNS changes during a standard (generic delivery address) integration. You read that right, none at all. Contrast that to a traditional CDN integration, where there is just no way around some messing around in the DNS – in fact, usually some fairly extensive DNS changes.
This low-code, virtually no code, integration saves you time. It saves you money. It saves you the hassle of putting multiple team members on a new project. And it means that you can be up and running in about 15 minutes with a standard install. You can be serving optimized images to your site visitors at blazing fast speeds before lunch! And don’t worry, ImageEngine has an experienced integration support team available to answer any questions you might have.
There’s also no issue with adding the ImageEngine image CDN on top of an existing CDN. Traditional CDNs may have security features that you may prefer to keep for your site. It requires slightly more integration but provides the same benefits of a solo ImageEngine implementation — screaming fast image load times and perfectly optimized images from device-aware edge servers. All that is recommended is that the ImageEngine image CDN actually serve the images directly, not simply process them, to get maximum benefits.
Adopt an Image CDN and See The Benefits
We’ve learned that image CDNs bring numerous benefits to your site AND your business. Using device-aware edge servers, image CDNs provide measurably better UX to your visitors. Pages load potentially seconds faster with perfectly optimized images, meaning your customers get to the heart of your message right away, and you don’t lose potential sales.
Image CDNs are actually 30%+ faster than most traditional CDNs, improving site speed accordingly. From an SEO perspective, that’s huge! And your SEO gets an additional boost from the improvement to your Largest Contentful Paint scores (which can help you gain valuable rank on Google’s SERPs). Implementation is simple and fast. You get all this, plus cost savings: since you have smaller payloads because of the fully optimized images, you’re delivering fewer gigabytes of data.
The post Image CDNs: How Edge Computing Provides a Faster Low Code Image Solution first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.



 1, 2, 3 – That’s exactly how long it takes you to start losing visitors if you have a slow-loading website.
1, 2, 3 – That’s exactly how long it takes you to start losing visitors if you have a slow-loading website.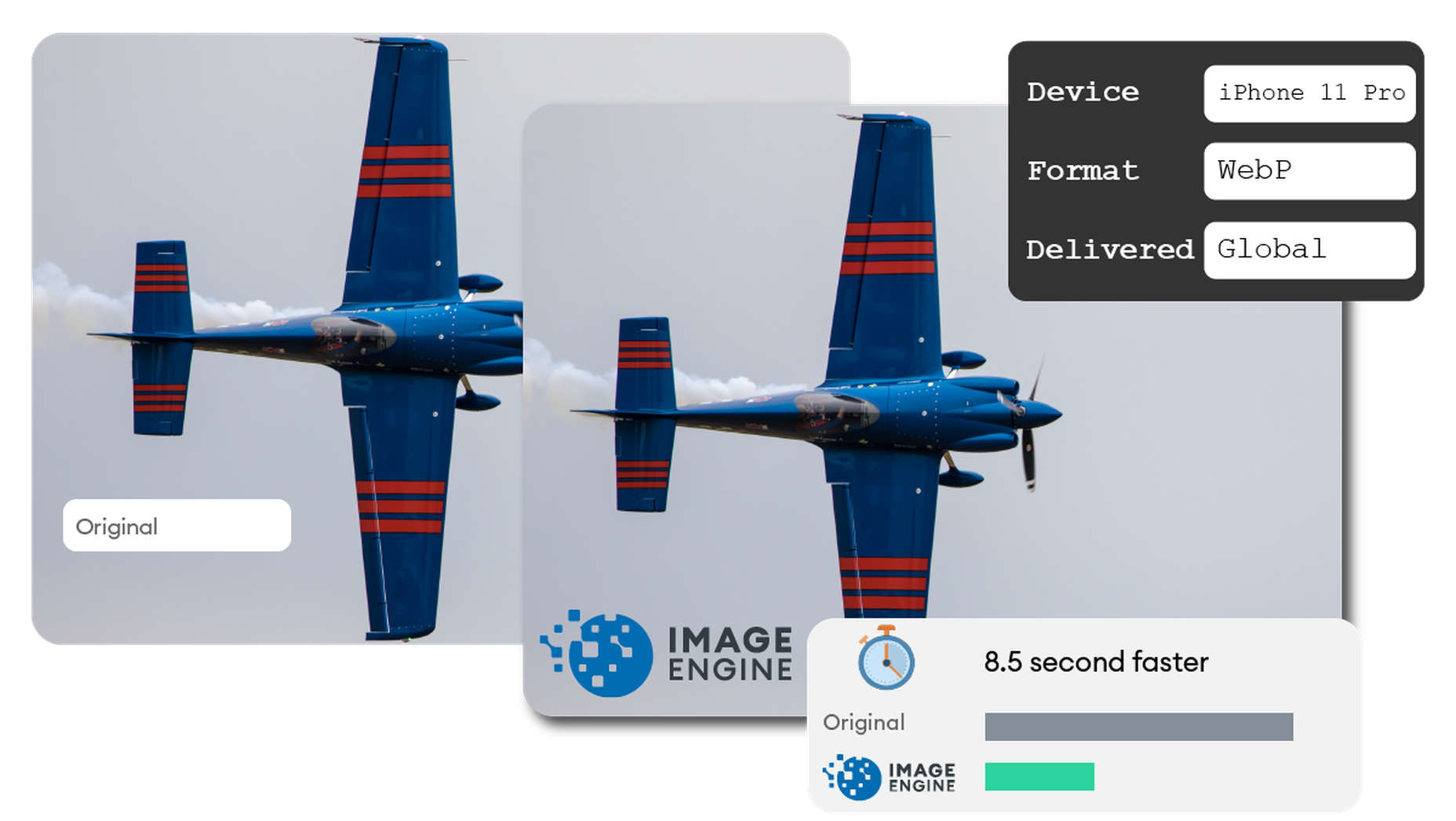


 There are some spook-tacular finds in this month’s October collection of resources and tools for designers and developers. From interesting tools that can help in the design process to boo-tiful typefaces, there’s something for everyone here.
There are some spook-tacular finds in this month’s October collection of resources and tools for designers and developers. From interesting tools that can help in the design process to boo-tiful typefaces, there’s something for everyone here.