As we turn the corner into the final part of the year, many of the new websites and redesigns that we see during much of the rest of the year tend to slow down. Many businesses are focusing on fourth quarter and holiday sales.
As we turn the corner into the final part of the year, many of the new websites and redesigns that we see during much of the rest of the year tend to slow down. Many businesses are focusing on fourth quarter and holiday sales.
With that being said, there are plenty of holiday flourishes already showing up on many websites. But there are still a few trends that don’t have a holiday theme.
Here’s what’s trending in design this month.
1. Beautiful Connectivity
Web elements that merge and flow into one another can be difficult to design but the payoff is totally worthwhile. This website design trend exemplifies connected elements in a way that’s beautiful and mesmerizing.
You can accomplish it with static elements or interactivity; the common theme is that design parts enter the space of one another and merge in ways that are seamless and visually interesting.
The thing that makes it exceptionally tricky is responsiveness. To ensure that pieces work well at all sizes when they overlap or encroach on the space of one another takes a lot of planning and testing.
Here are a few examples of projects that do it well – and each one does it in a different way.
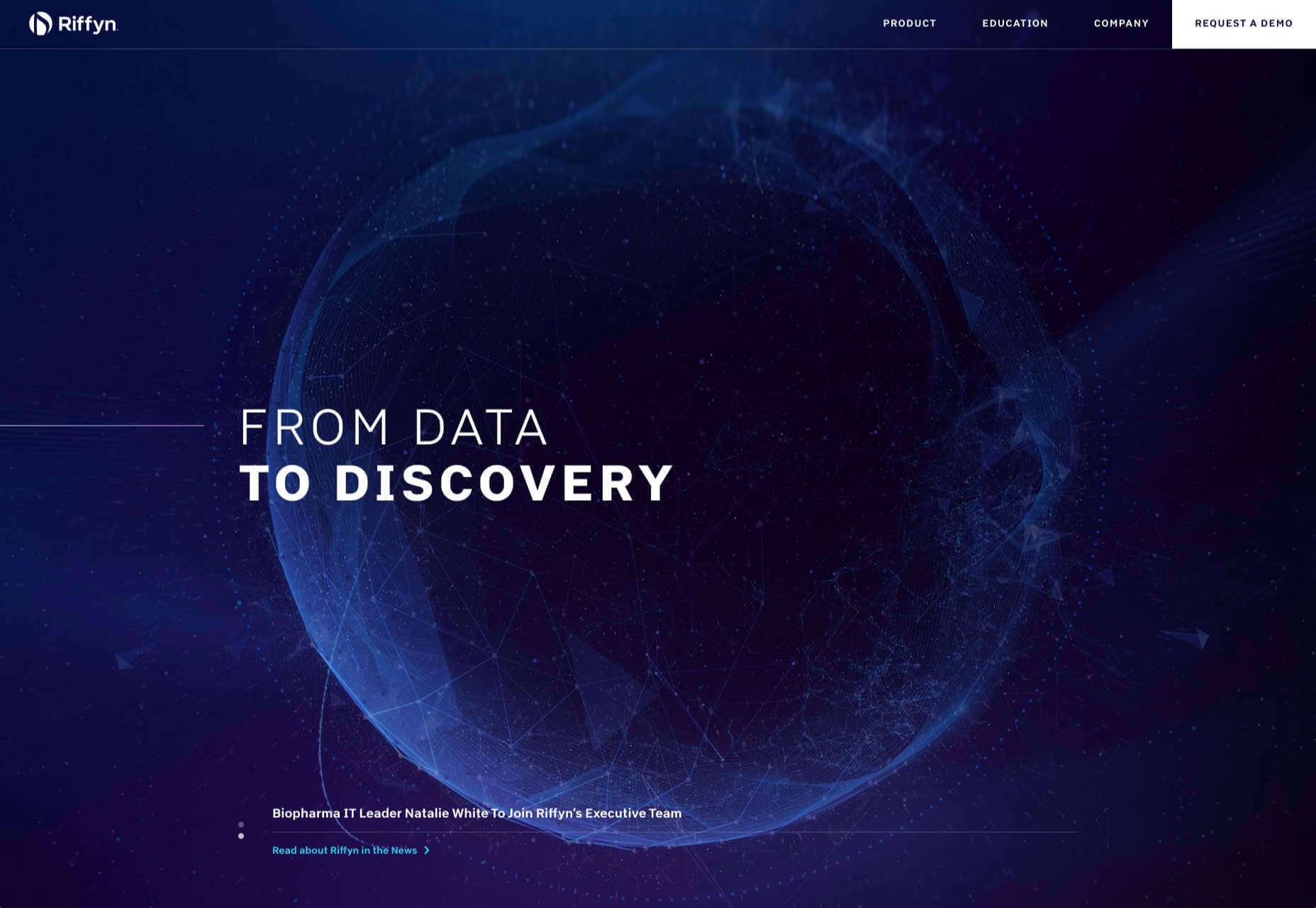
Kirk Whayman’s website uses a floating ice cube over simple lettering. The interactivity is spot on here with hover actions that allow you to move the block with the letters refracting in an expected manner. (It would be easy to play with it all day.) But the coolest interaction happens when you “break it” (click on the cube). The elements continue to merge and interact in a new and different way.
Kikk Festival uses animations and giant scrollable illustrations and plenty of elements that overlap within the space. What’s neat is that everything on this canvas seems to touch everything else. The staircase design encourages scrolling and lettering and smaller animated elements all connect to the steps in the sky motif.
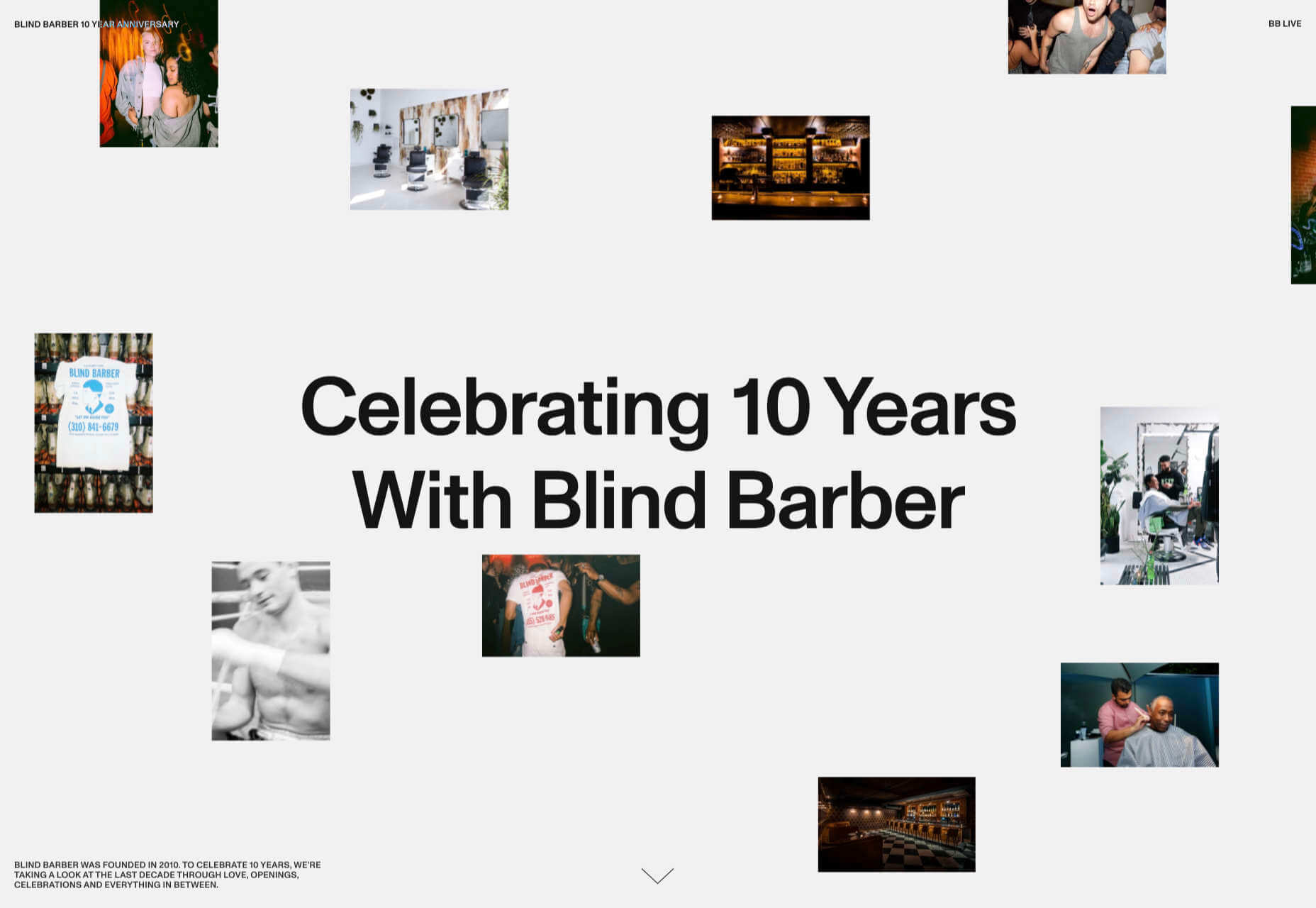
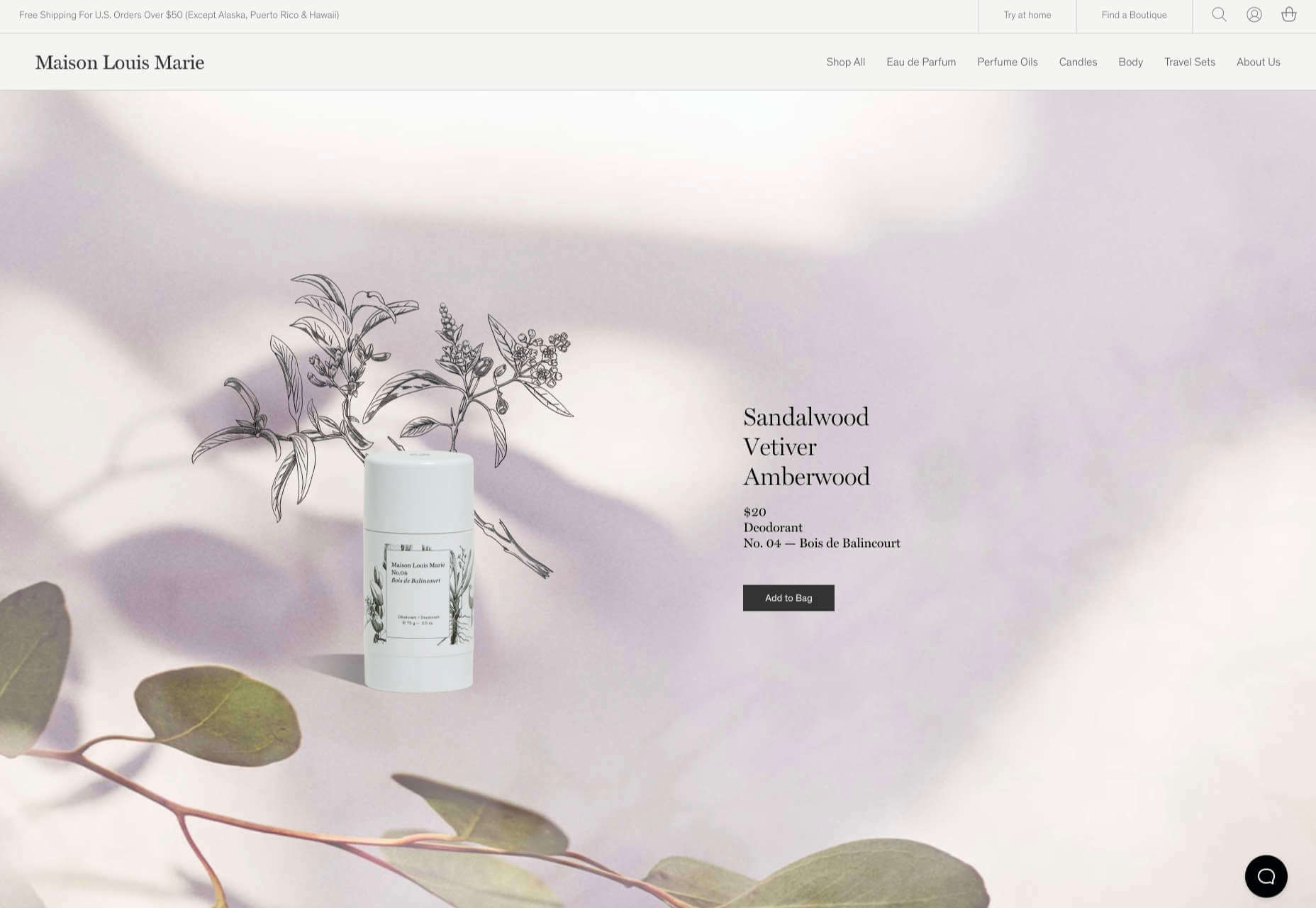
Multi Options Nursing takes a totally different approach. It uses a static split screen with a photo on the right side that merges into a round graphic element. It takes two not-s-interesting images and makes something out of them. The design carries this theme below the scroll as well and this style of image presentation carries a nice visual weight without feeling heavy.
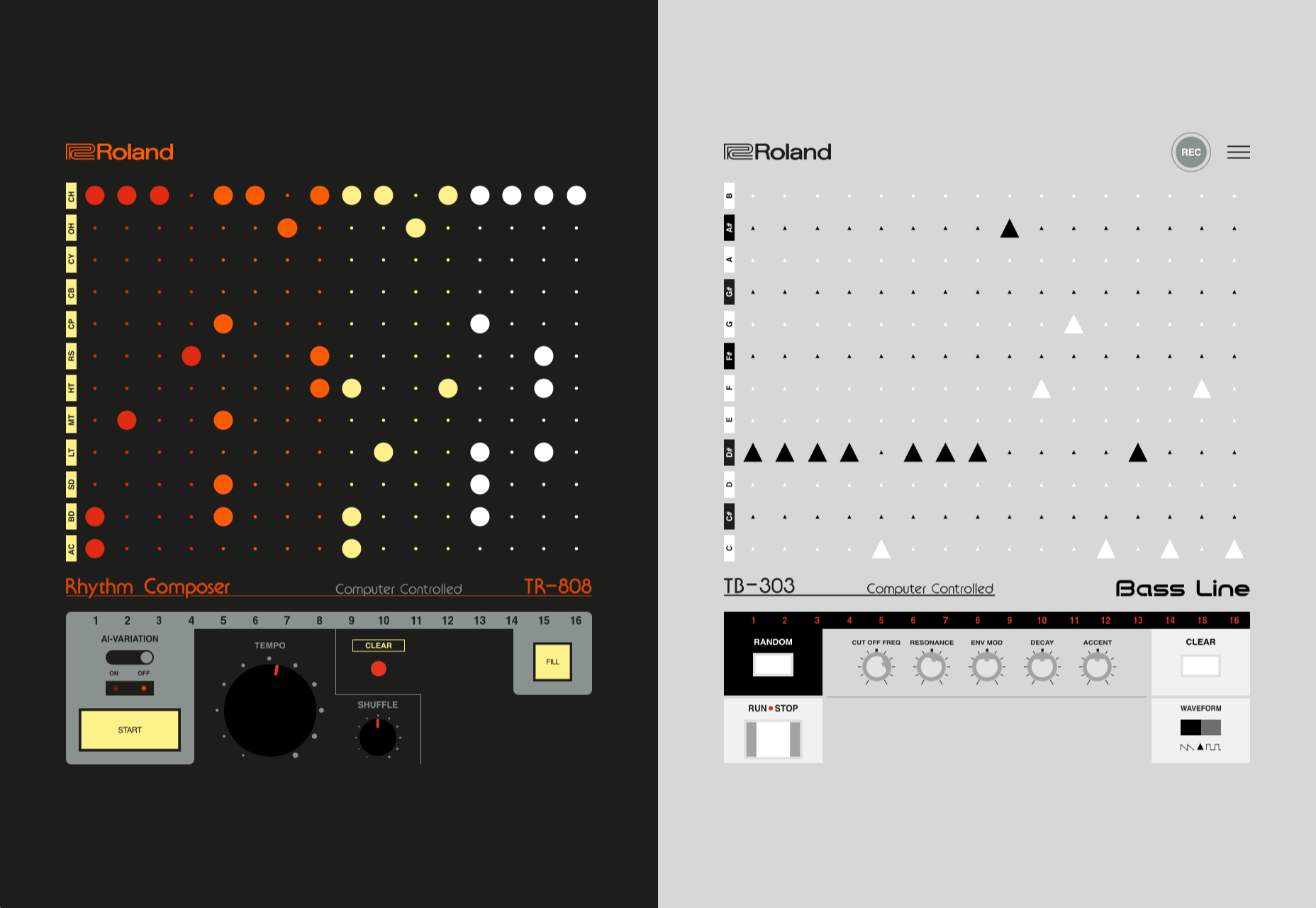
2. Almost Brutalism
Brutalism just seems to keep coming back around. For those that love this trend, it keeps evolving as well.
The latest styles of brutalism are a little less mono but still pretty sharp with harsh lines, questionable type readability, and a lot going on in a compressed space. These projects also seem to be embracing color and alternative font choices more readily.
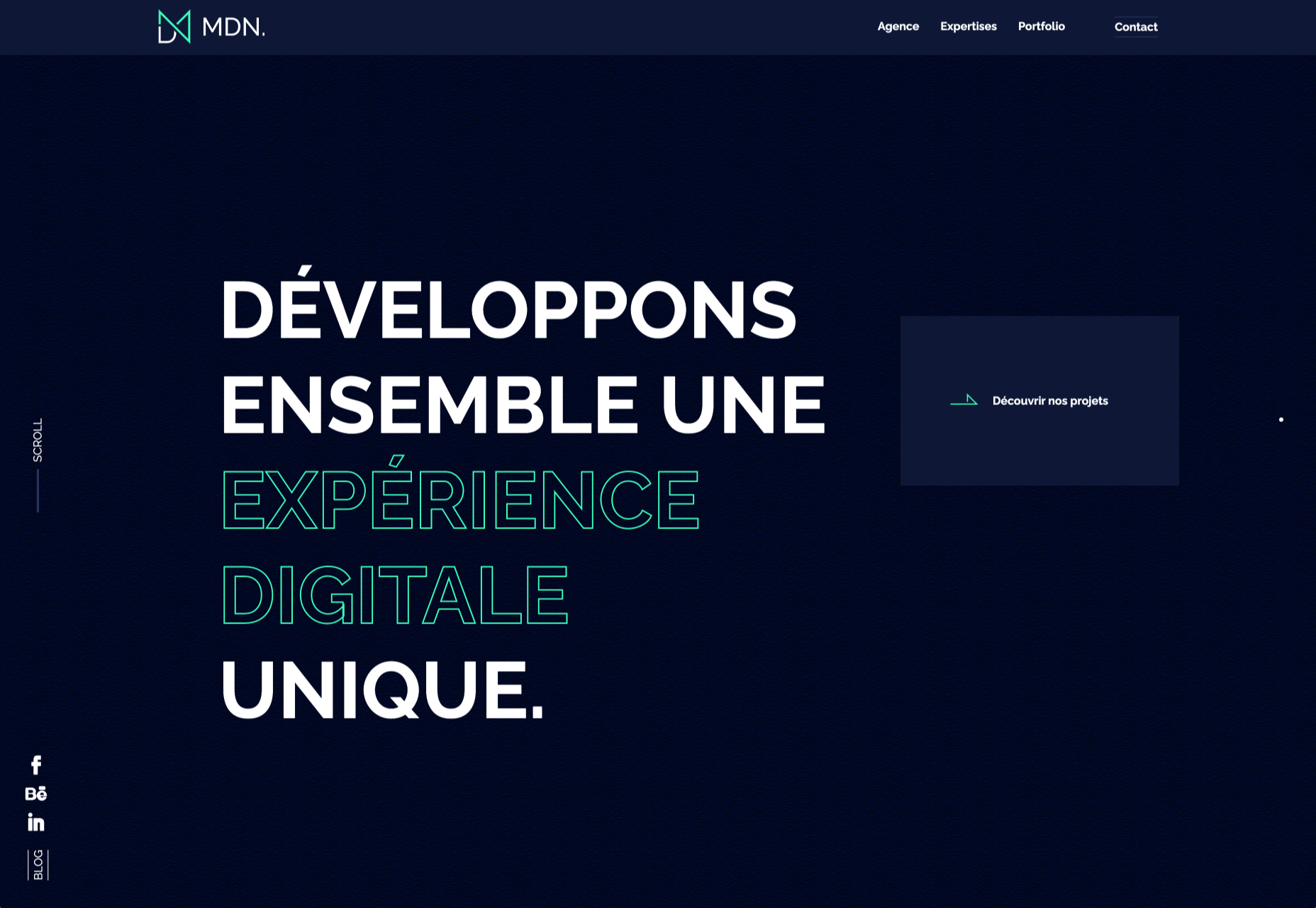
Fledge uses a split screen – still a dominant trend two years running – with a blue that’s almost too bright with an almost white offset color. The text is big and smooshed into the space tightly. Depending on the breakpoint, you might not even get the whole phrase on the left side. The design challenge is what are you supposed to do here? There are some hover animation cues, but they aren’t very direct.
Loeven Morcel’s design has hints of brutalism and elements of elegance. What makes this design skew toward the brutal side is use of space and typography. Like the previous example, it falls into the territory of “what should I do here” with some concerns about readability. Most of these issues are resolved on the scroll if you move beyond the homepage.
Szymon Michalczyl’s site is another that is close to brutal in style but has an element of sleekness that doesn’t quite carry it over the edge. The simple framework has that brutalist feel but the use of simple, clean fonts with plenty of space pulls it back into a more mainstream design scheme.
3. Beige Everything
Is a shade of beige the color of the year for 2020? Or is it just how we all feel?
Beige backgrounds are everywhere, making this one of those design trends that you can’t miss. The good news is that designers are playing with different shades of beige as well as warm and cool variations. Beige on its own can take on some of the color from accent hues and imagery, so that’s important to keep in mind when using this in the background.
The other variable is how saturated to make beige coloring. Most designs are using some of the more muted options while mostly playing with the levels of green and red. But darker beiges are also an option.
Simon Daufresne uses a beige that is the color that comes to mind when you think beige. It’s simple, a hint reddish, and is used with black only to maintain true color.
Discovered Wildfoods uses a more neutral feeling beige with a more green undertone (or is that color feel coming from other design elements). The neutral and natural color fits the brand and association this website is trying to create.
Aebele Interiors also uses a more traditional beige but with a bold mustard accent that makes the color feel exceptionally warm. What’s nice about this color combination is that in small sizes the mustard colored-type almost falls into the beige background, but at larger sizes seems to almost jump off the screen. It’s an interesting color juxtaposition.
Conclusion
Personally, this month’s trends are a mixed bag. I love the lines and interactivity of the beautifully connected examples. It shows that elements can cross and work together well.
On the flip side, brutalism and beige just aren’t my style. But apparently, they appeal to a lot of people based on the number of projects using these styles. What do you think? I’d love to know how you feel about these trends. Let me know on Twitter.











 We have become so used to using web sites just to buy stuff that it is easy to forget that the web has more to offer. So this month we’ve included some because-it’s-interesting sites, some micro-sites and some just-for-the-sake-of-it projects.
We have become so used to using web sites just to buy stuff that it is easy to forget that the web has more to offer. So this month we’ve included some because-it’s-interesting sites, some micro-sites and some just-for-the-sake-of-it projects.









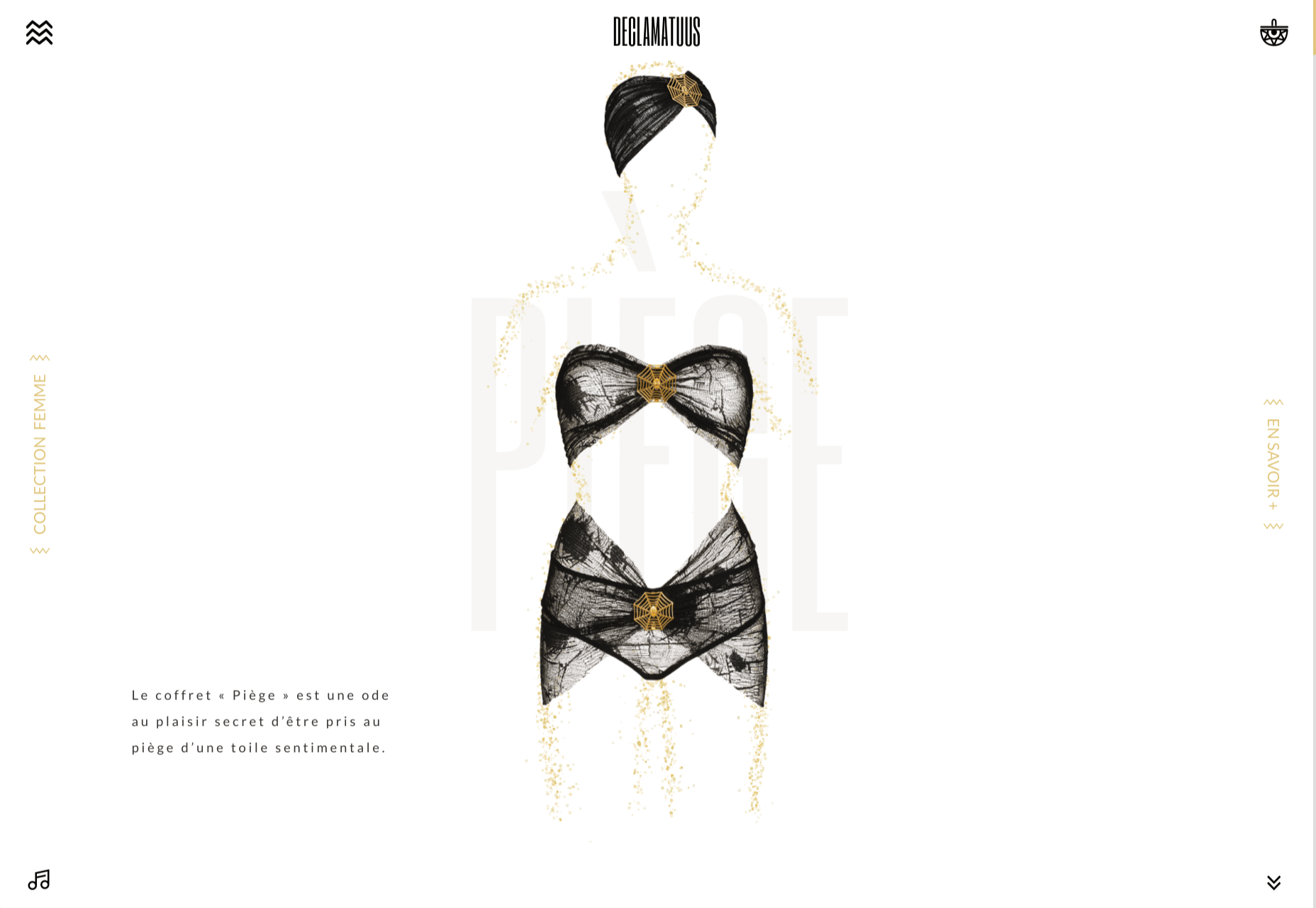
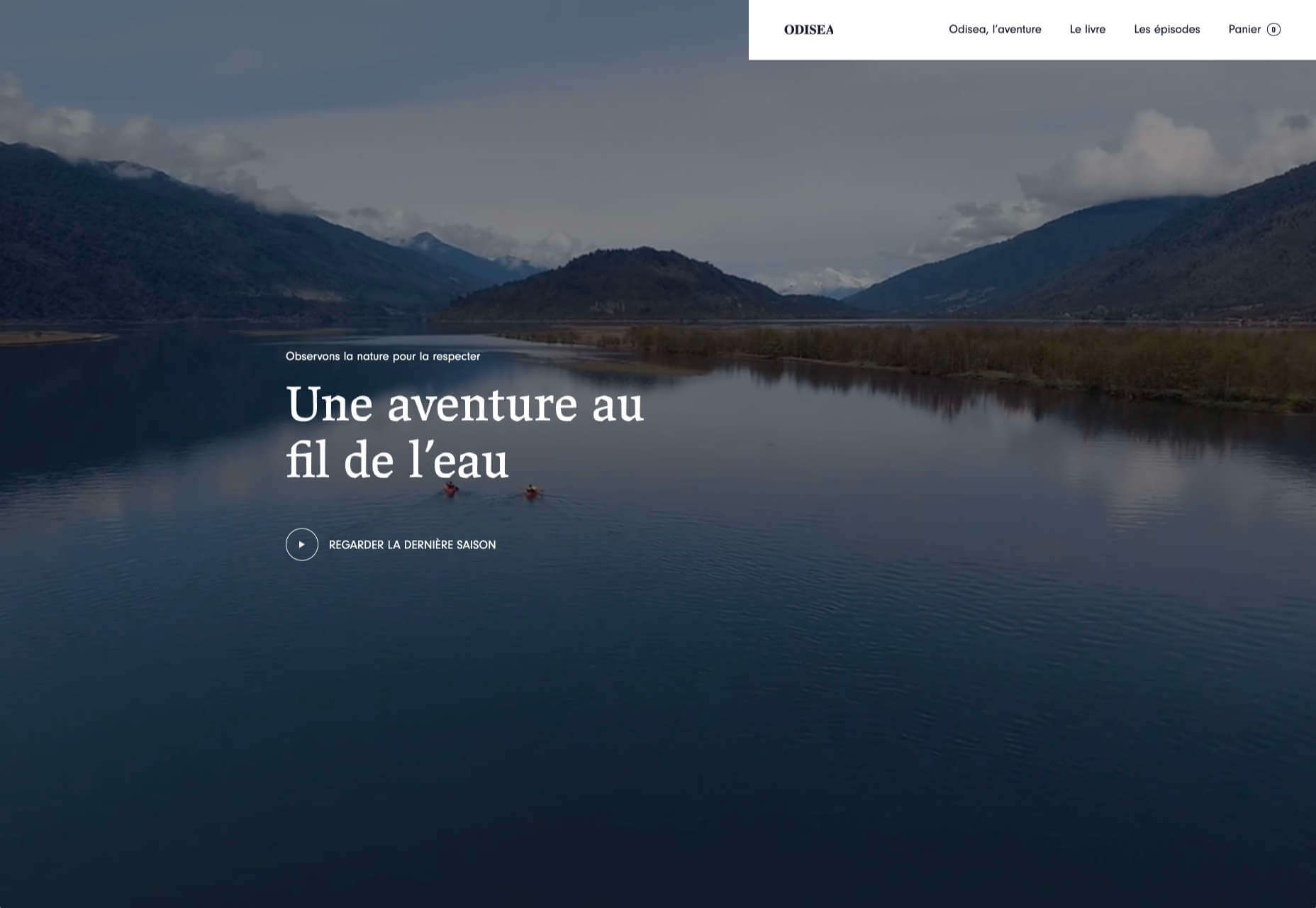
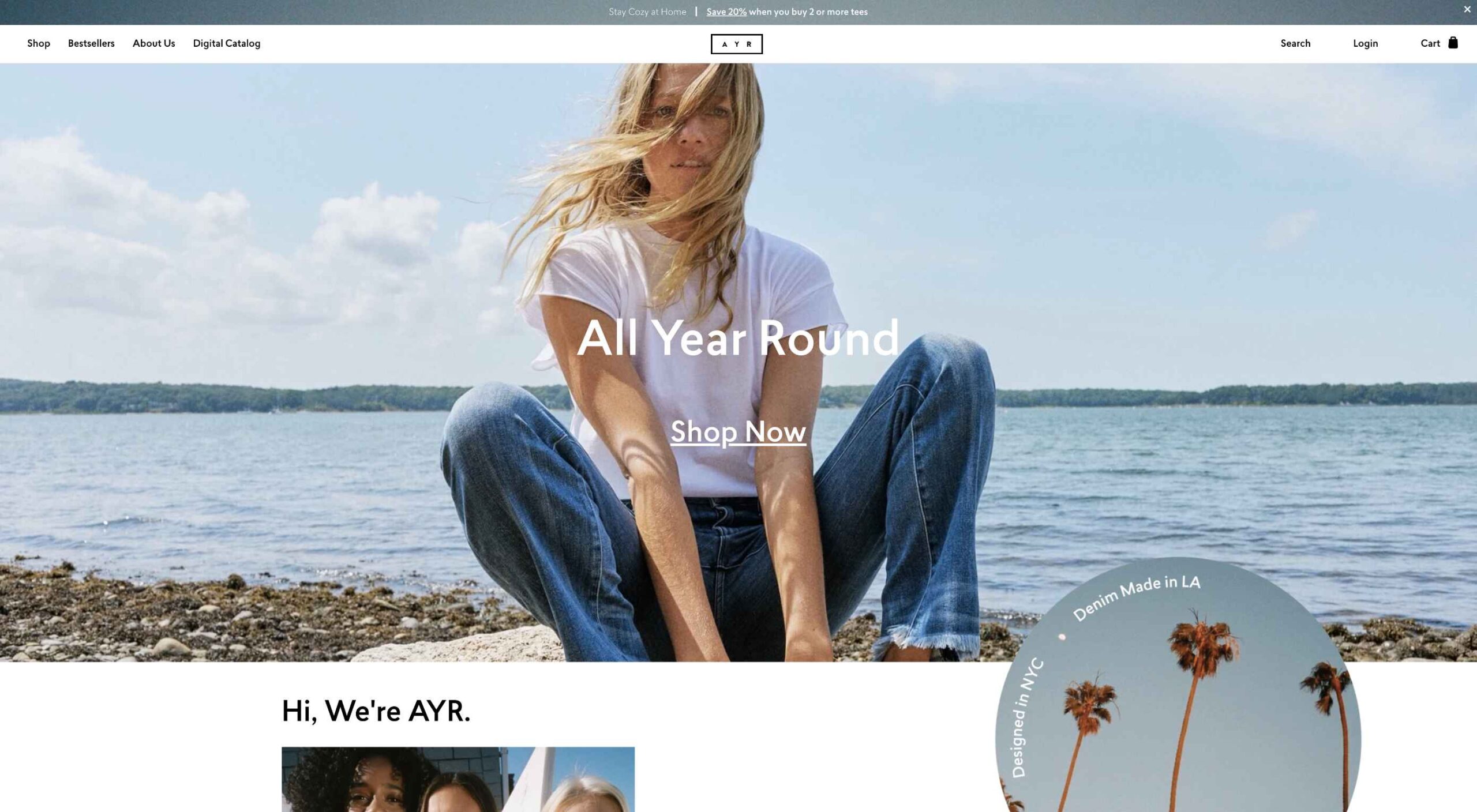 Today, great design isn’t just about conveying the right amount of information in a certain number of pages.
Today, great design isn’t just about conveying the right amount of information in a certain number of pages. 
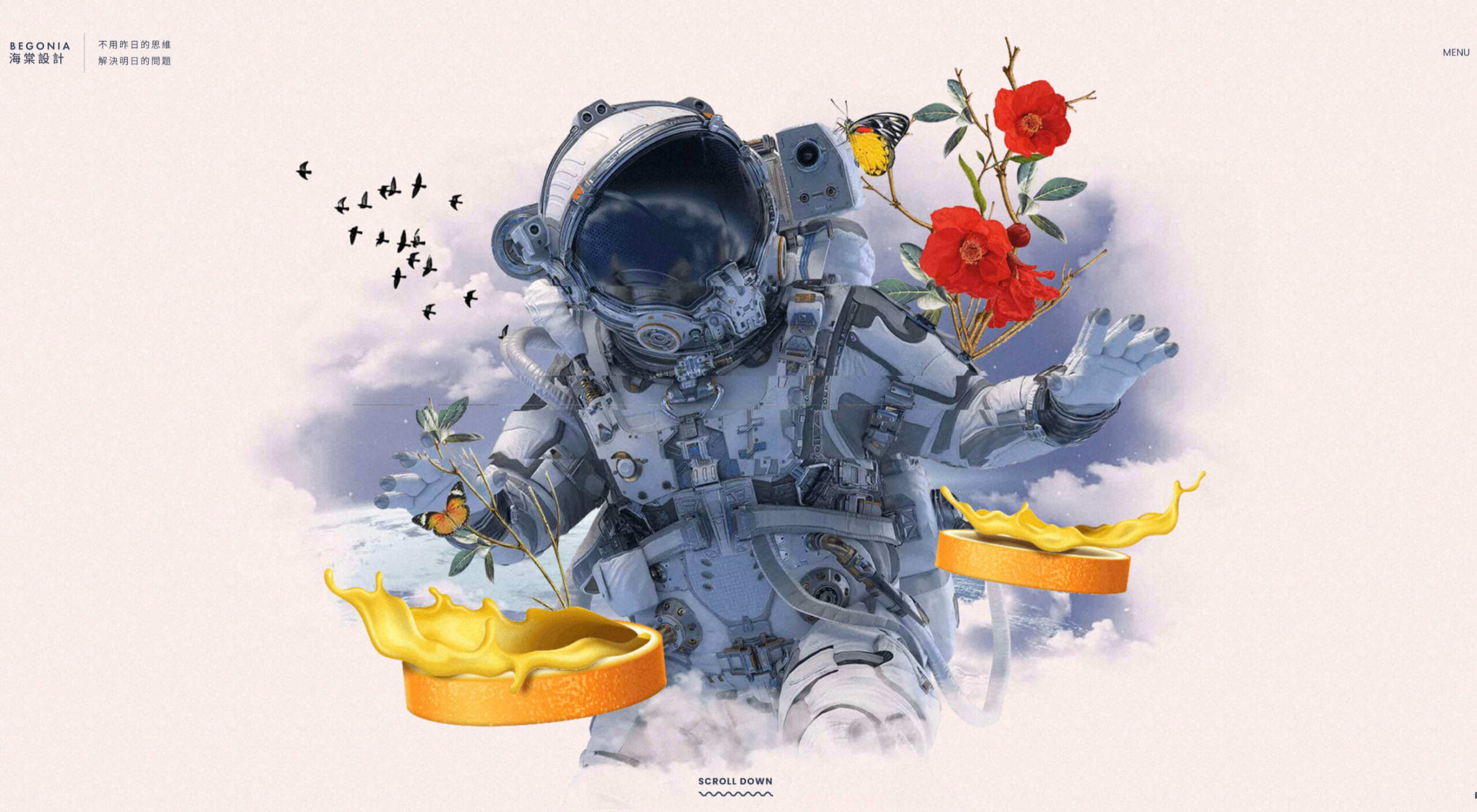
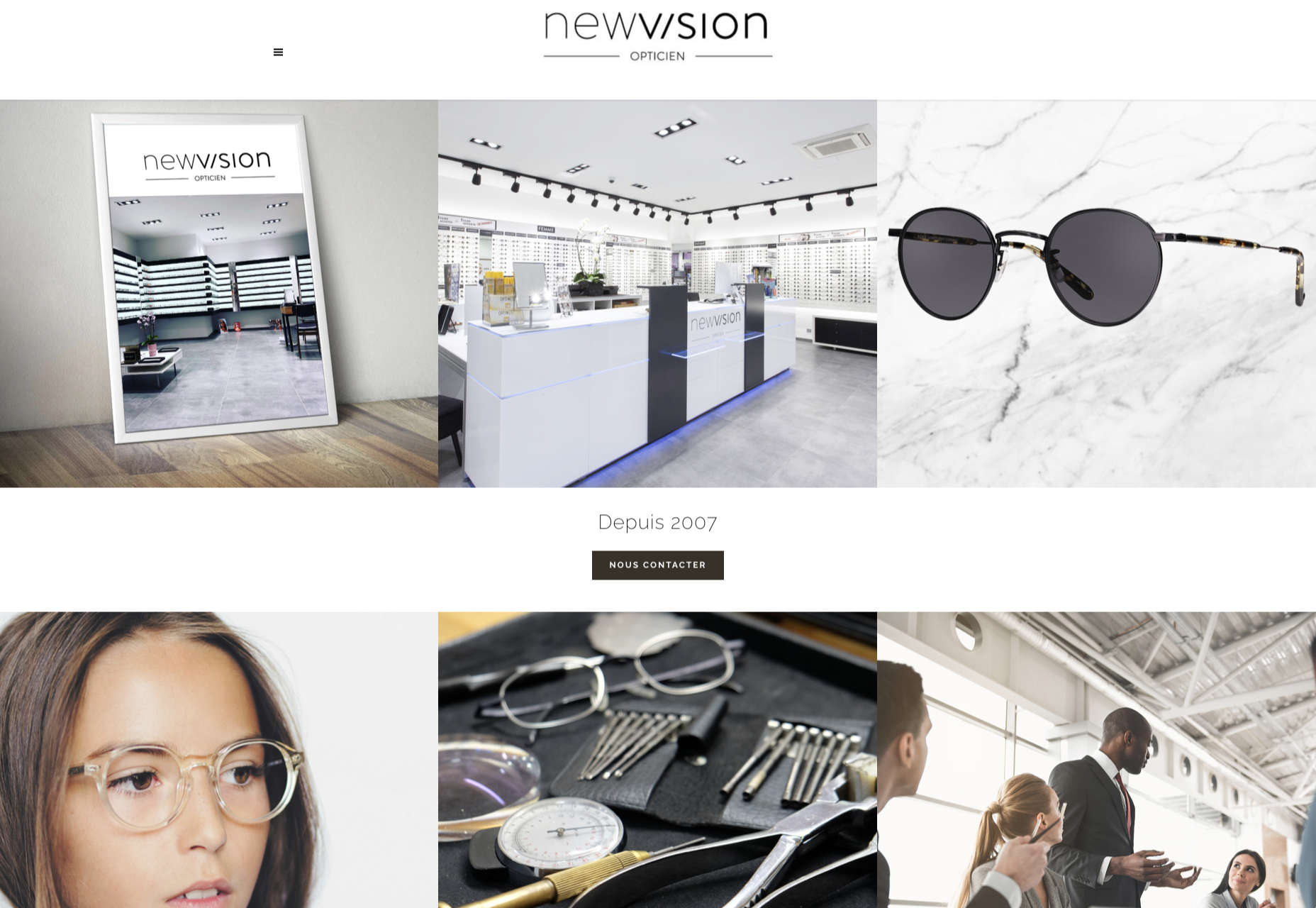
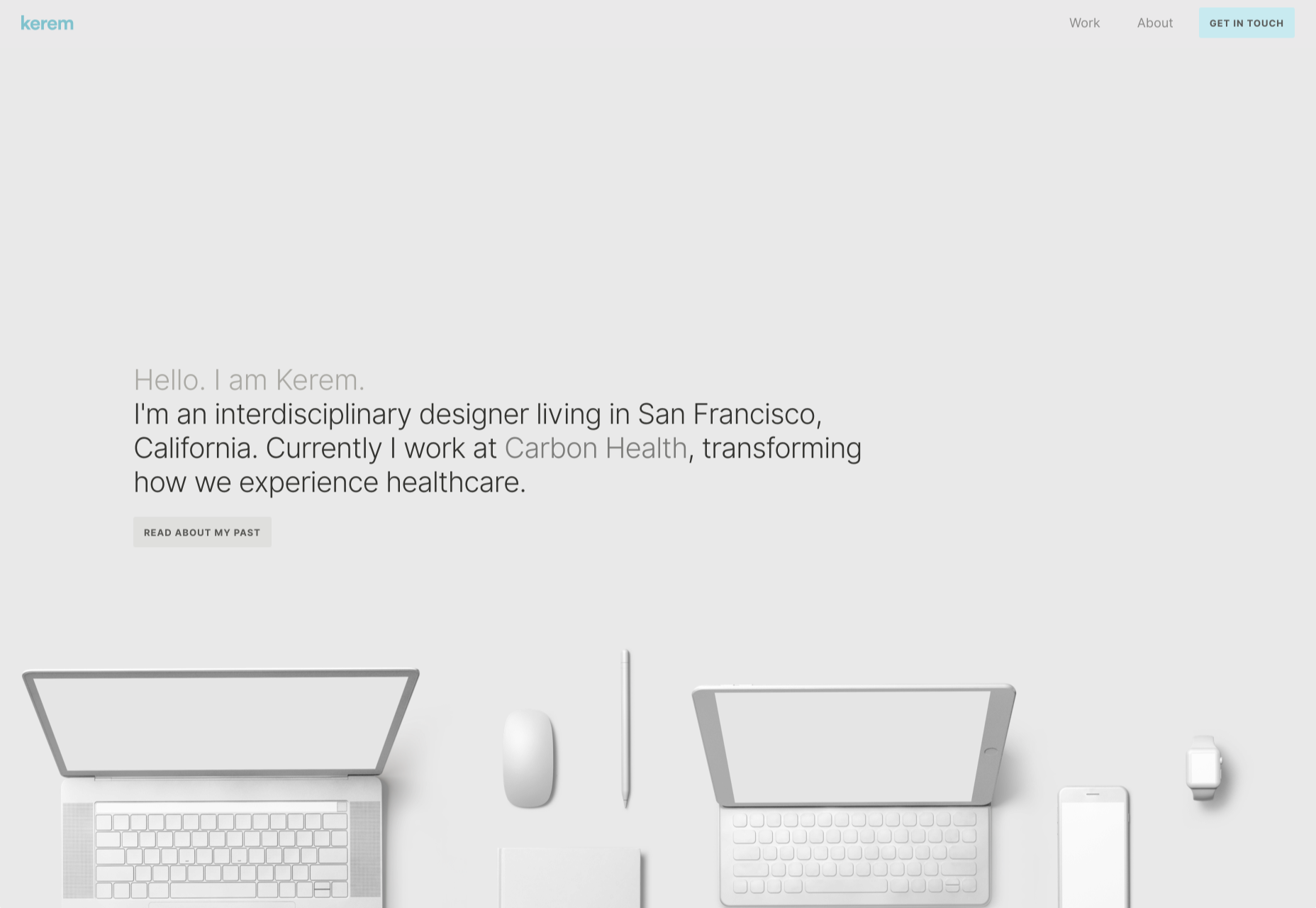


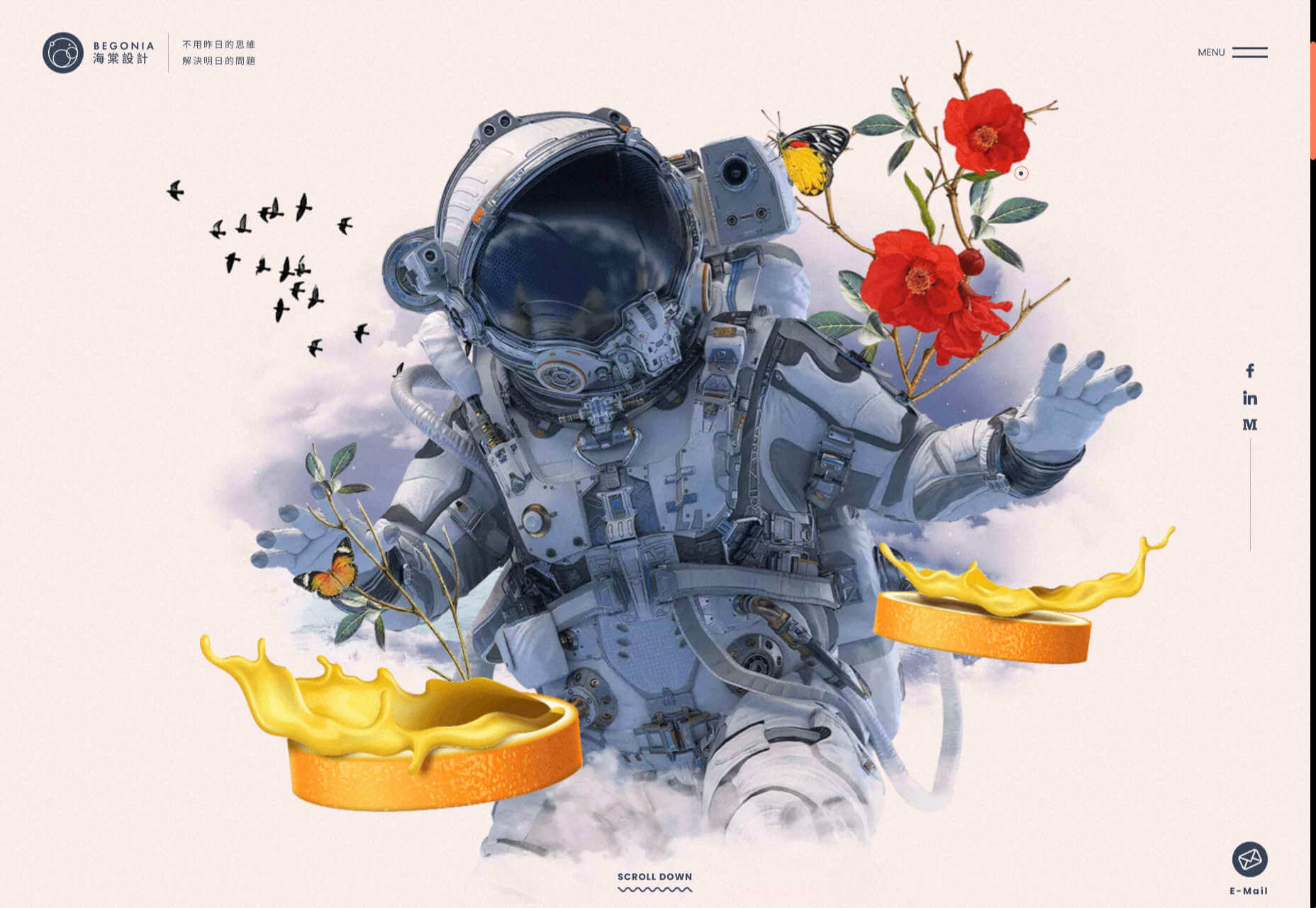
 In this month’s collection of the freshest web designs from the last four weeks the dominant trend is attention to detail.
In this month’s collection of the freshest web designs from the last four weeks the dominant trend is attention to detail.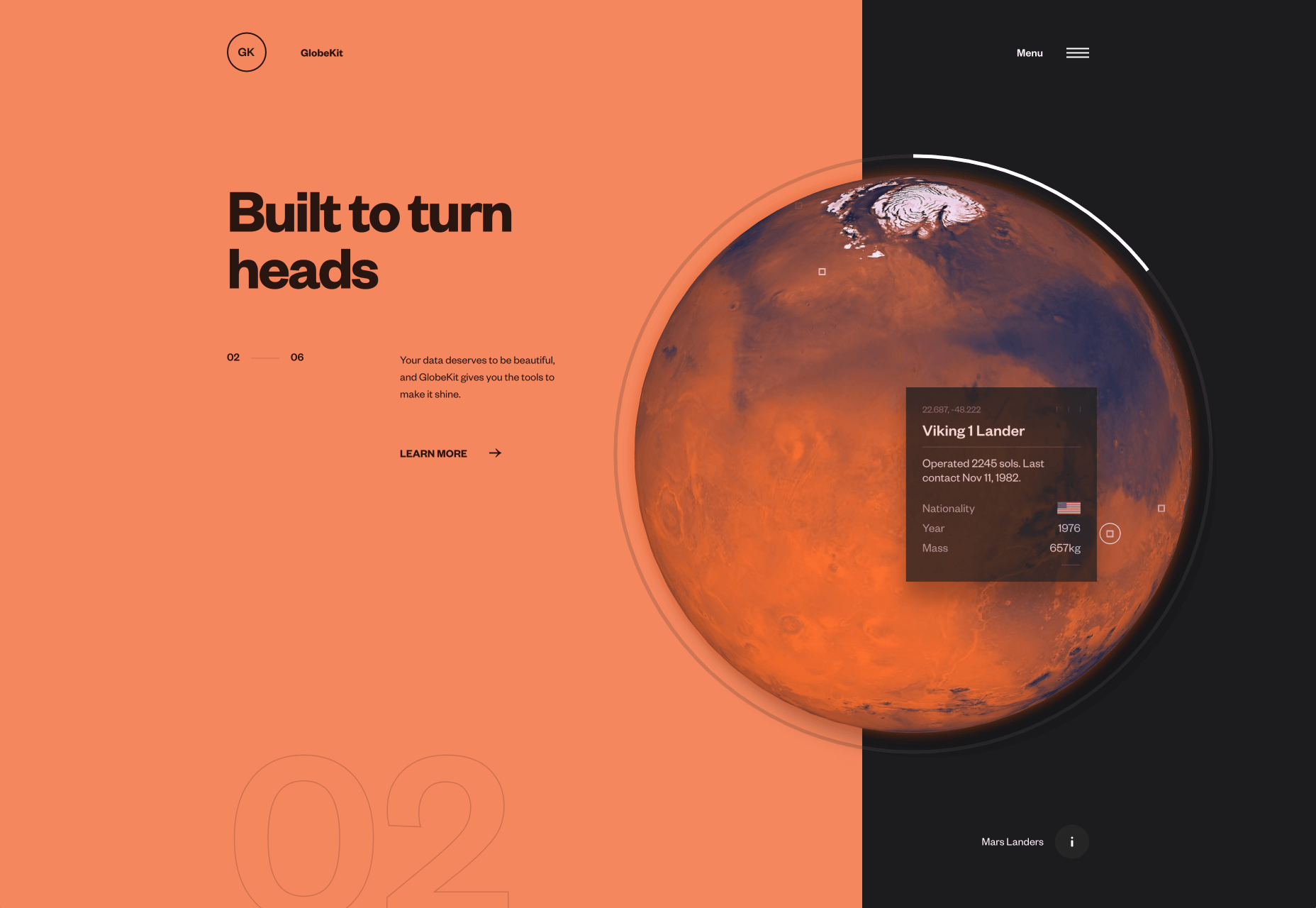

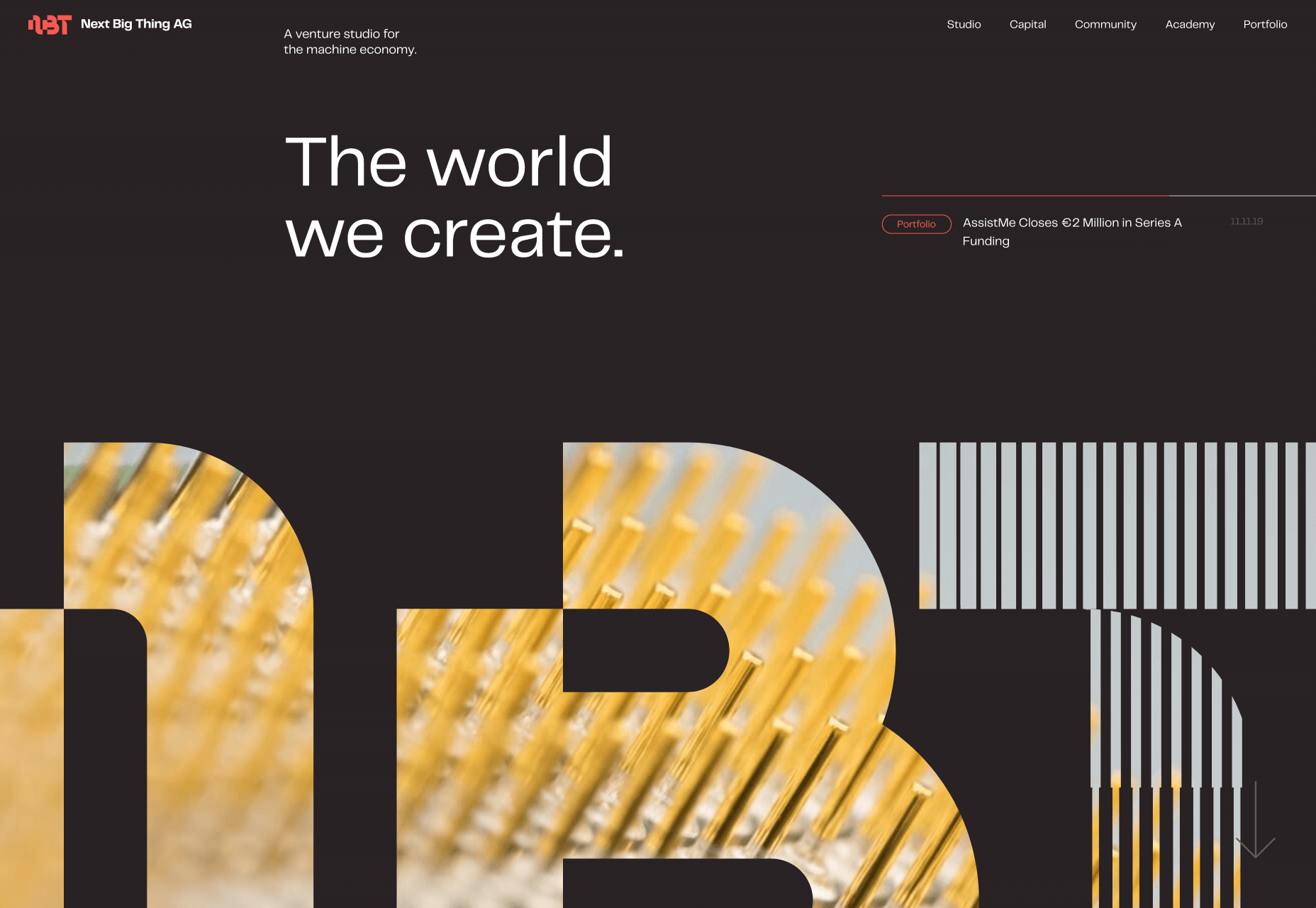









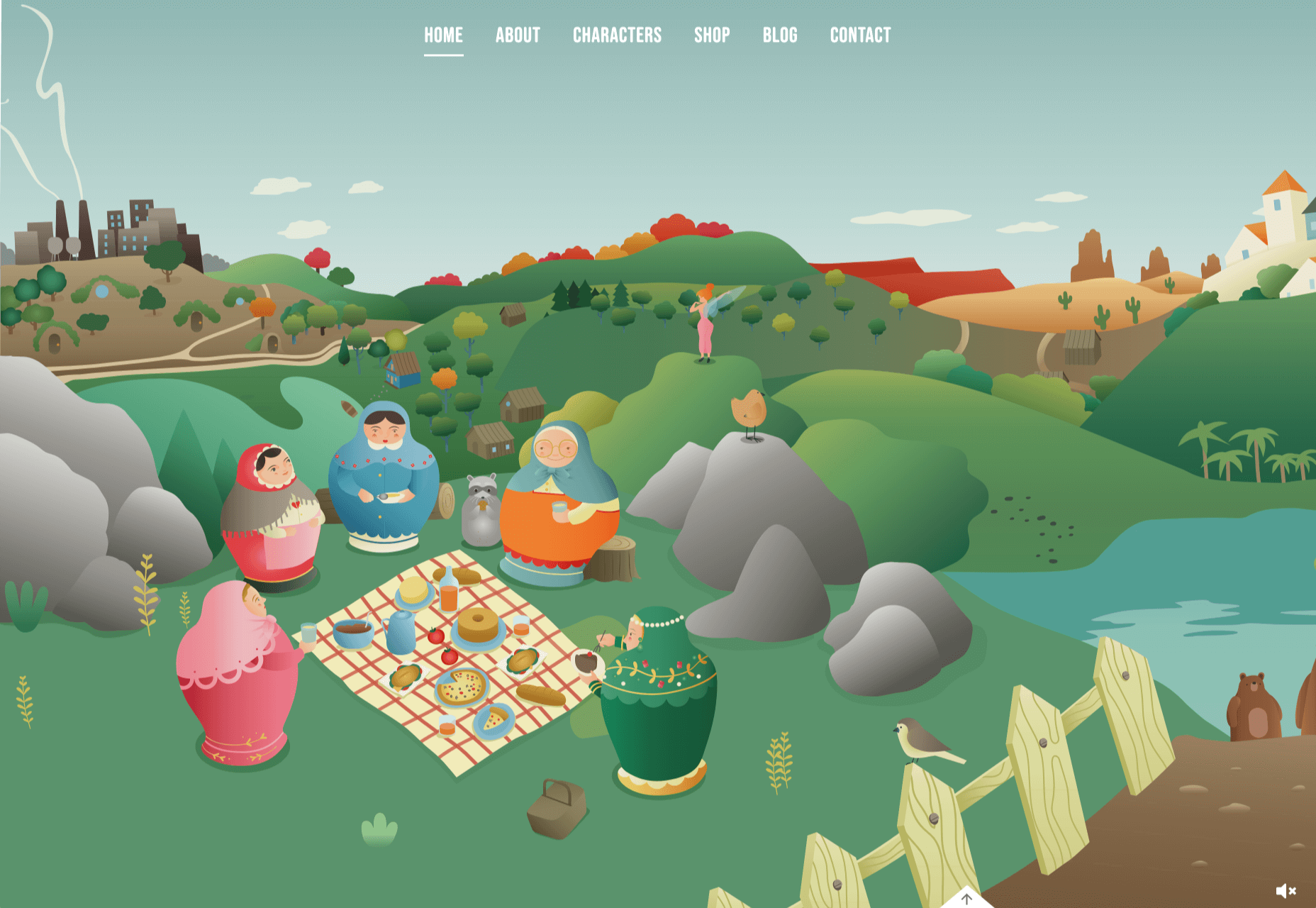



 If we don’t question this kind of design homogenization, do we put ourselves at risk of perpetuating the same mistakes in the years to come? Or is it even a mistake to begin with?
If we don’t question this kind of design homogenization, do we put ourselves at risk of perpetuating the same mistakes in the years to come? Or is it even a mistake to begin with?