 Over the years, experts have repeatedly discussed the possible impact of mixed realities on web design. Concepts like AR and VR are expected to have the potential to change the way that we interact with websites on a fundamental level.
Over the years, experts have repeatedly discussed the possible impact of mixed realities on web design. Concepts like AR and VR are expected to have the potential to change the way that we interact with websites on a fundamental level.
Now that we’re in the year 2021, however, discussions about AR aren’t just observational anymore. The age of mixed-reality interfaces is here, in everything from Pokémon Go, to Snapchat filters.
The question is, how do web designers create incredible user experiences in a world where there are now multiple digital realities to consider?
The Benefits of Experimenting with AR
Before we look at some of the steps that web designers can take to enhance their projects with AR, it’s worth examining the benefits of interacting with augmented reality in the first place.
While virtual reality replaces the typical world around us completely with digital components, AR augments it. This means that developers and designers need to learn how to thrive in an environment where the real world and the digital one work together.
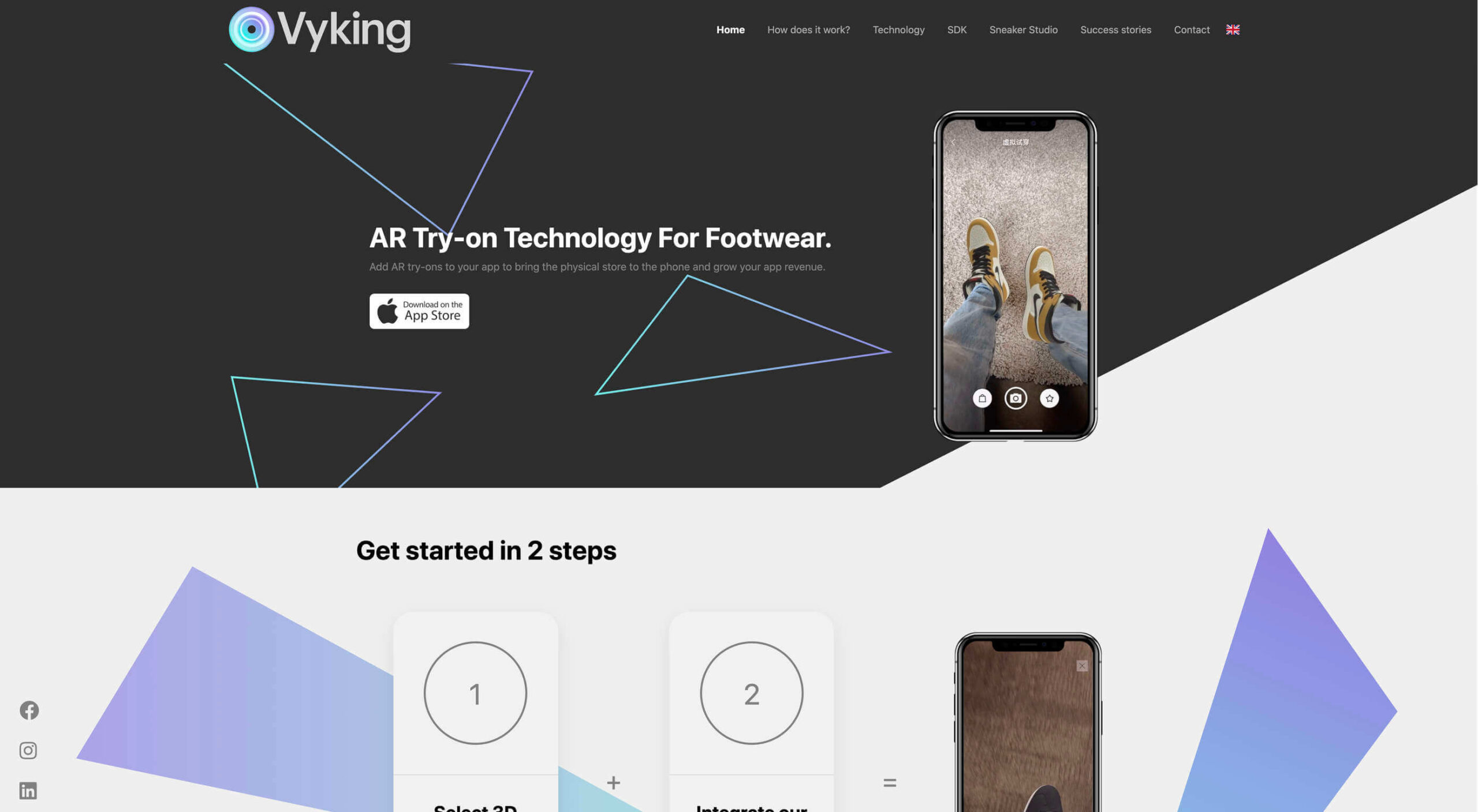
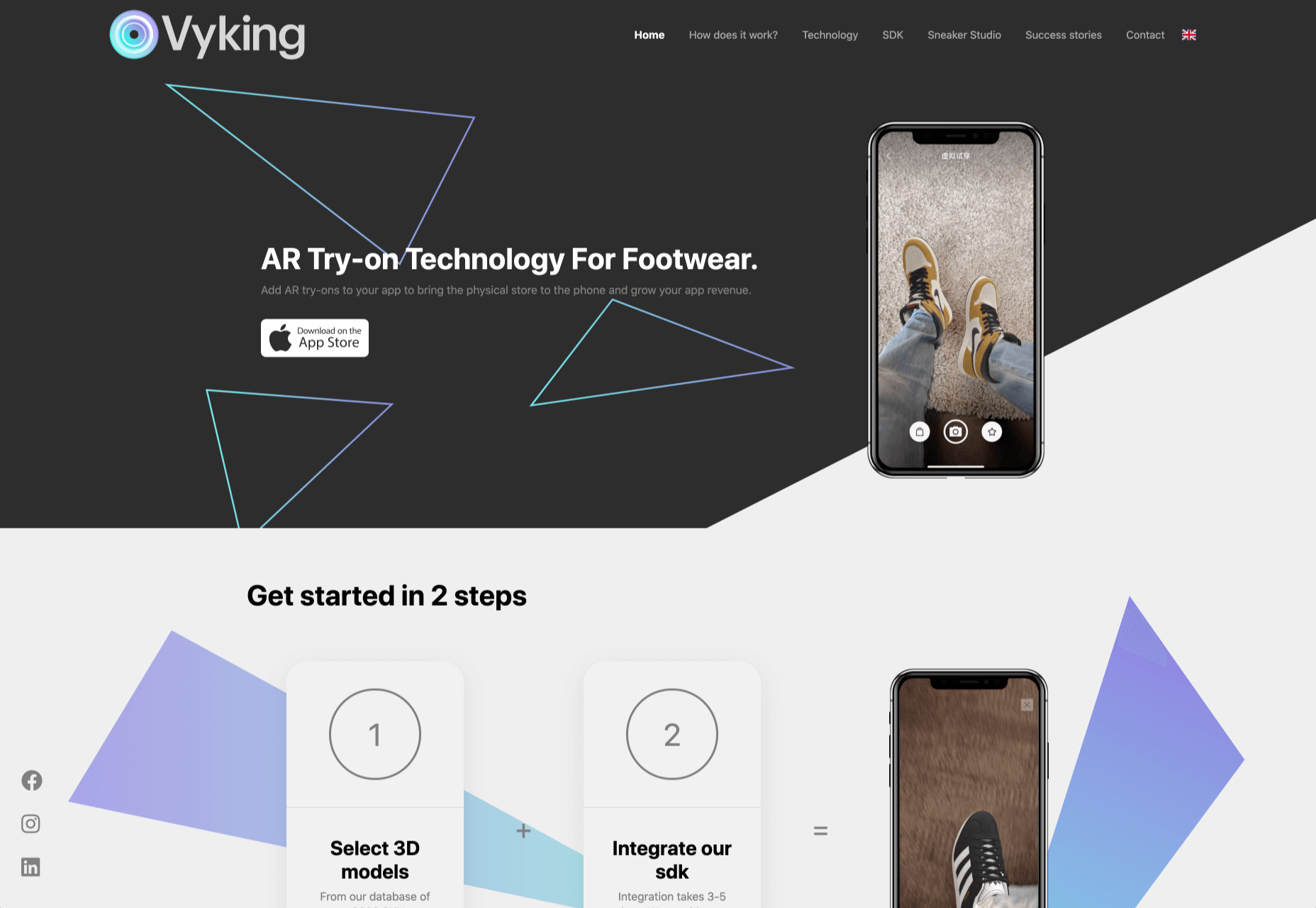
The most common AR application for website owners is to provide a solution for real-time and remote product visualization. Imagine being able to try on a pair of shoes before you buy them online. That’s a service that the Vyking brand can deliver by creating technology that “reinvents” the digital shopping experience.
This test functionality plays a massive role in purchasing decisions. In a world where people can’t see a shade of make-up in person when they’re shopping online, or check how an item of furniture looks in their home, AR has a crucial role to play.
In simple terms, AR helps shoppers to make more informed purchases.
Here’s how you can use augmented reality to deliver incredible UX.
1. Focus on Real-Time Feedback
Augmented reality is all about connecting the real world to the virtual world.
Doing this provides users a unique experience – one that’s filled with real-time feedback that can deliver crucial and insightful information. For instance, an augmented reality system in a GPS app can calculate the average time before reaching a destination based on previous trips.
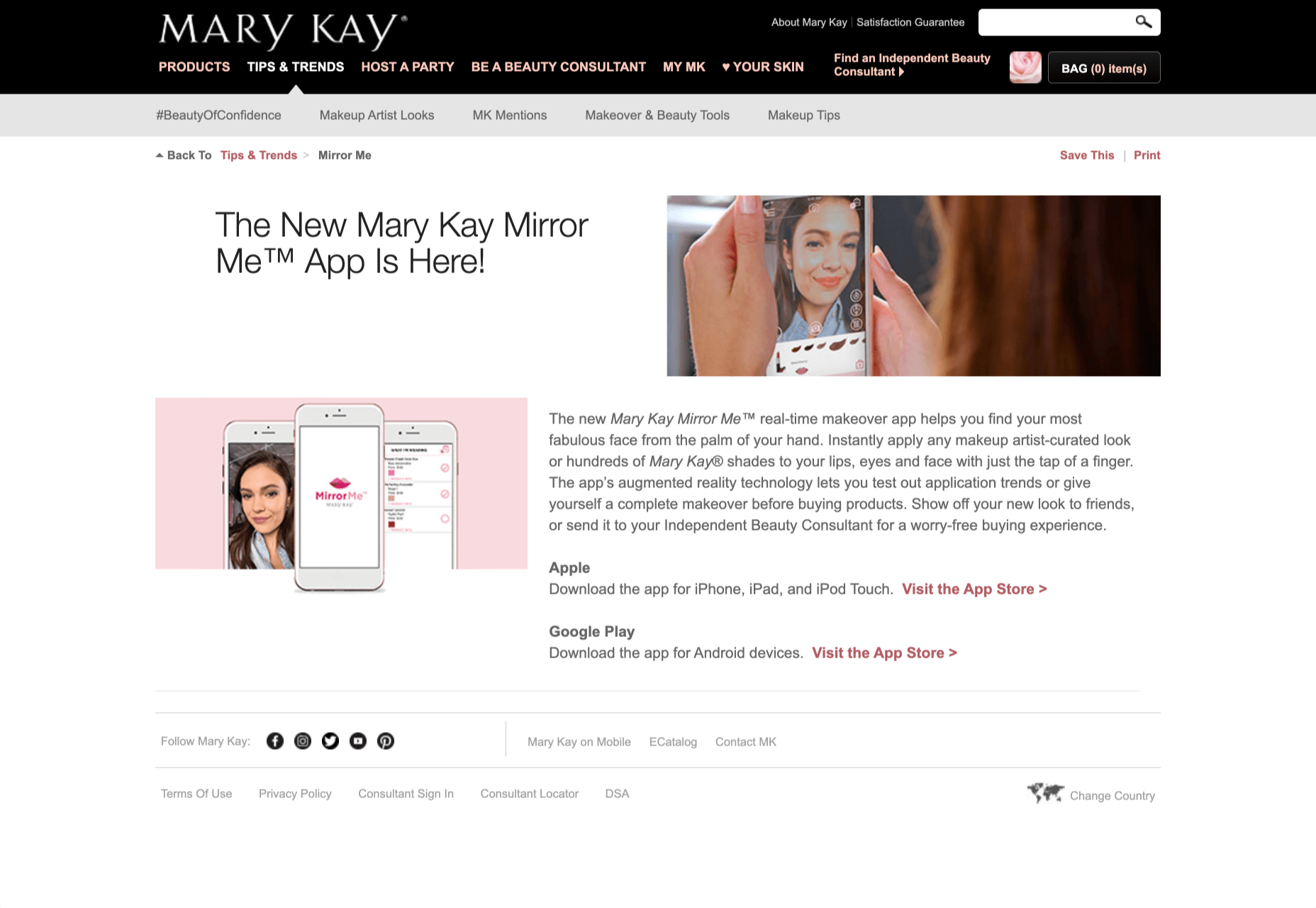
Another option is for an augmented reality to use solutions like face-mapping to help customers determine how a certain makeup product will look before they buy it. For instance, that’s the case for the Mary Kay Mirror Me app, which simplifies the process of shopping for make-up.
When designing for AR, experts need to consider how they can provide customers with real-time information that they can use to make better purchasing decisions.
2. Define input and output
Although you’ve probably performed similar exercises when designing for traditional websites and applications in the past, defining inputs and outputs of UX in AR environments can be tough.
Defining inputs and outputs allows you to determine which elements of an interface your user can actually interact with, in your interface. This gives you a better idea of what to “augment.” For instance, you might decide that physical gestures like a swipe of the hand will be essential for AR inputs. However, you’ll also need to consider how each mobile device offers different input possibilities.
Outputs are a little simpler. For instance, you could offer a three-dimensional model of a product that your customers are interested in. Once you have that output, you can think about how the customer will interact with it by changing colors or position.
3. Embrace Customer-Friendly Performance
Another feature at the heart of AR applications is interactivity.
Good designs in the augmented reality world need to be simple to access and use, otherwise customers will end up avoiding them. For instance, 60% of customers say they want to use AR when they’re shopping for furniture. However, they’re only going to use your app if it actually works.
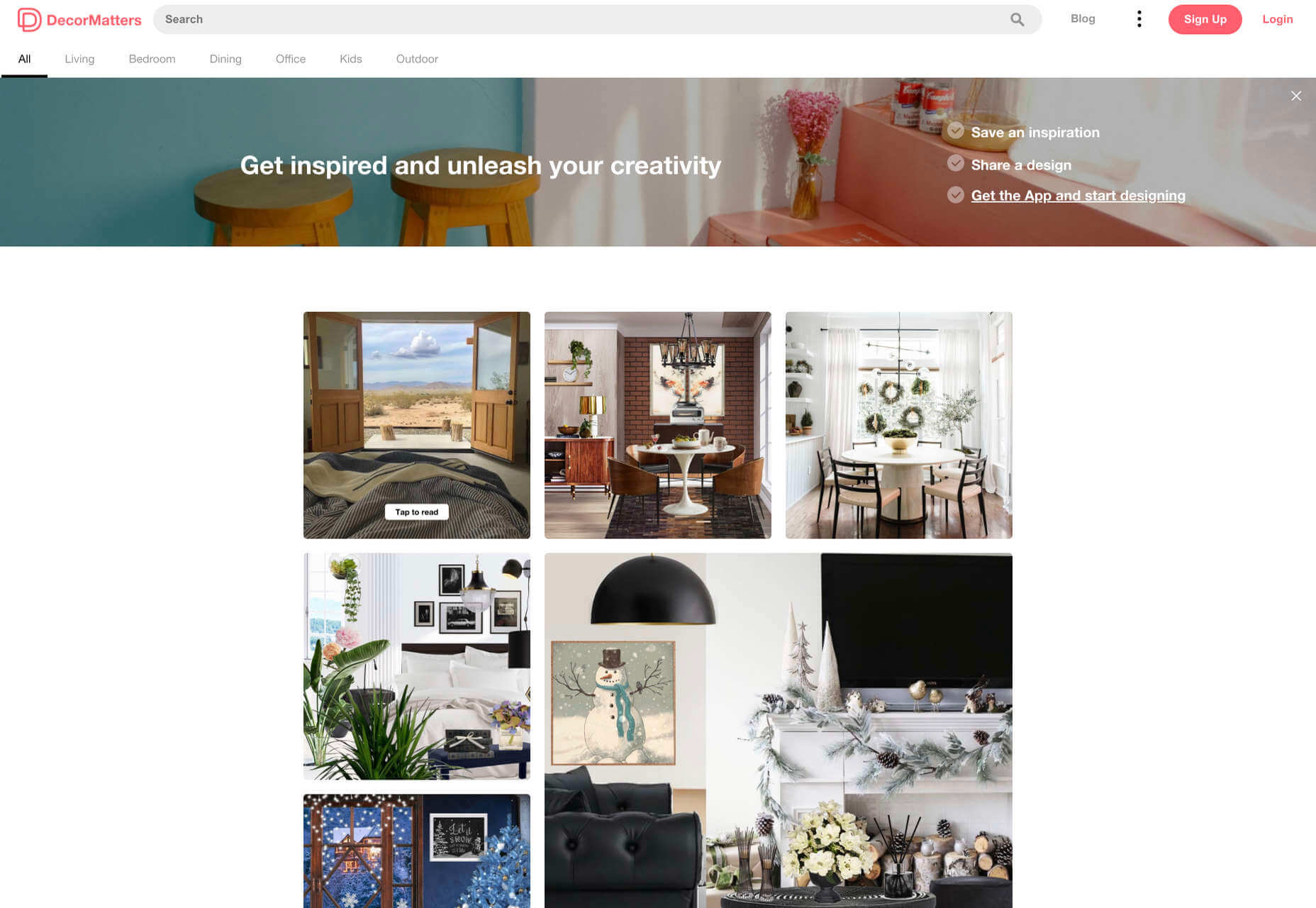
The Décor Matters website and app mix gamification with home decorating features that help customers get a better view of the home goods they’re planning on buying. The website even has inspiration pages available to help users find and try new design options with their AR technology.
When designing for AR, think about how you can make your applications or technology as simple to use as possible, so customers actually want to interact with it.
4. Address the Environment
In augmented and virtual reality applications, it’s important to remember that interfaces aren’t bound by physical screens. The viewport will move with the user, shifting perspectives in response. Most AR designers will use four different signifiers to describe AR environments:
- Public environment: The entire body of the user is involved as a controller, like with the Xbox Kinect or Nintendo Wii;
- Intimate environment: Where a user can be seated – often in a desktop environment;
- Personal environment: AR on smartphones, mobile devices, and tablets, like Pokémon Go;
- Private environments: Completely private spaces, such as with wearable technology like the Google Glass solution.
The environment that you’re designing for will be crucial for your project outcomes. Remember, spatial considerations need to be carefully considered when accounting for how users will interact with objects in a frame.
5. Remember User Fatigue
Another thing to keep in mind when designing for AR technology is that user fatigue is likely to be a much more significant consideration. After all, people interact with websites and applications in a much more intimate and in-depth way when AR is involved.
AR applications can often use the entire body of a customer as a controller. Because of this, designers need to be careful about exhausting interactions. High-effort and repetitive interactions could tire the user out mentally and physically, causing them to give up on the interaction.
When designing, you’ll need to consider how you might over-stimulate the user with too many interaction-focused elements at once. Keep it simple.
6. Remember the Essential Principles of UX Design
Remember, just because you’re tapping into a relatively new technology doesn’t mean that you should abandon all the basic tenets of user experience design that you’ve come to understand over the years. Although UX is constantly evolving and changing, it’s always going to keep a few fundamental principles in mind.
For instance, you’ll always strive to give users the best digital experience in exchange for the lowest amount of effort on their part. Additionally, you’ll need to think about how you can make end-users as comfortable as possible when they’re interacting with new types of technology on websites and apps.
For instance, since AR is most commonly associated with gaming in the current environment, it might be a good idea to implement gamification concepts into your AR design. What can you do to make sure your customers are having fun?
For instance, Inkhunter is an app that allows users to try on tattoos just like using a filter on Snapchat. The experience feels familiar, comfortable, and exciting.
Unlocking the Potential of AR Web Design
Augmented Reality technology has come a long way over the years. Today, developers and designers can access simple plug-in tools like WordPress VR, allowing designers to upload 360-degree videos into WordPress sites and other unique web extensions.
Augmented reality is becoming much more readily available on sites and apps of all shapes and sizes. Additionally, customers are accessing more ways to unlock AR’s power through everything from headsets to mobile interfaces.
However, just like any new technology in the web design world, designers need to think carefully about how they will overcome the challenges in user experience that AR can present. For instance, though AR can offer more information for a customer and help them make purchasing decisions faster, there are also risks. For instance, add too many interactive features to a single website or application, and you could scare users off with too much information.
In the short-term, web designers need to explore the new tools that are available to them and think about the customers they’re designing for. Only this way will we be able to make any considerable advances in the possibilities of AR.
Are You Ready to Embrace AR?
Designing for augmented reality applications and websites can be an intimidating concept – even for seasoned designers. However, this is just another technology that creatives can use to drive better experiences for end-users.
Learn how the latest technology works and get an insight into your customers’ needs, and you’ll be amazed at what you can accomplish in the AR world.


 Naturally, there are bad clients out there, but 90% of the time, it’s not really the client who is at fault. Poor communication, a lack of setting expectations, and a failure to qualify clients beforehand is usually the problem.
Naturally, there are bad clients out there, but 90% of the time, it’s not really the client who is at fault. Poor communication, a lack of setting expectations, and a failure to qualify clients beforehand is usually the problem.

 Animation is a fun and interesting way to bring life to a website. Used correctly, it can capture audience attention, make your website more engaging, and even improve your chances of delivering conversions for your clients.
Animation is a fun and interesting way to bring life to a website. Used correctly, it can capture audience attention, make your website more engaging, and even improve your chances of delivering conversions for your clients.

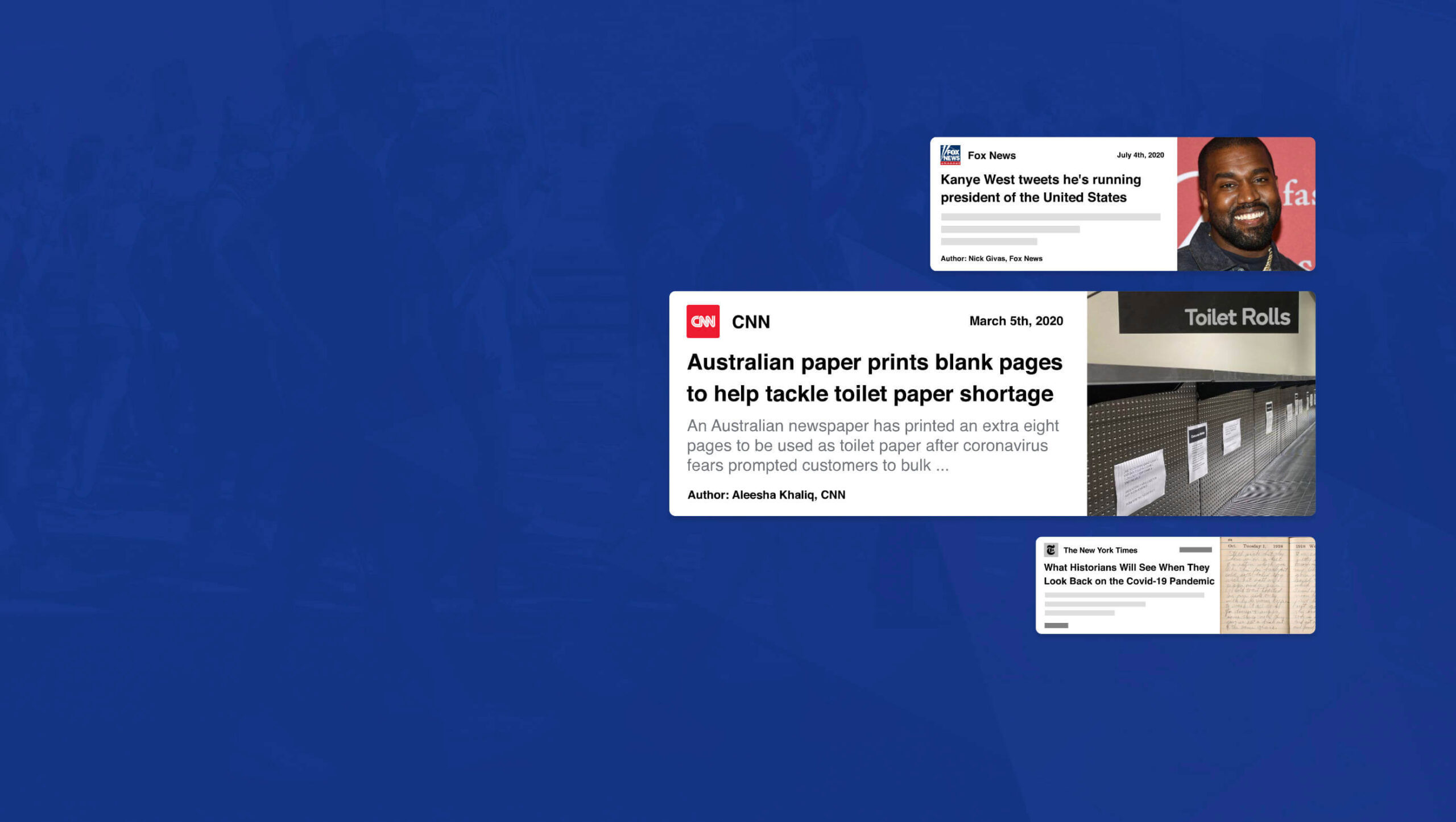 What an extraordinary year 2020 has been for the news! From the ongoing coronavirus crisis, to a turbulent US election, to the unrelenting march of Bitcoin, this year like no other we’ve been glued to our phones micro-analyzing every tidbit of news.
What an extraordinary year 2020 has been for the news! From the ongoing coronavirus crisis, to a turbulent US election, to the unrelenting march of Bitcoin, this year like no other we’ve been glued to our phones micro-analyzing every tidbit of news.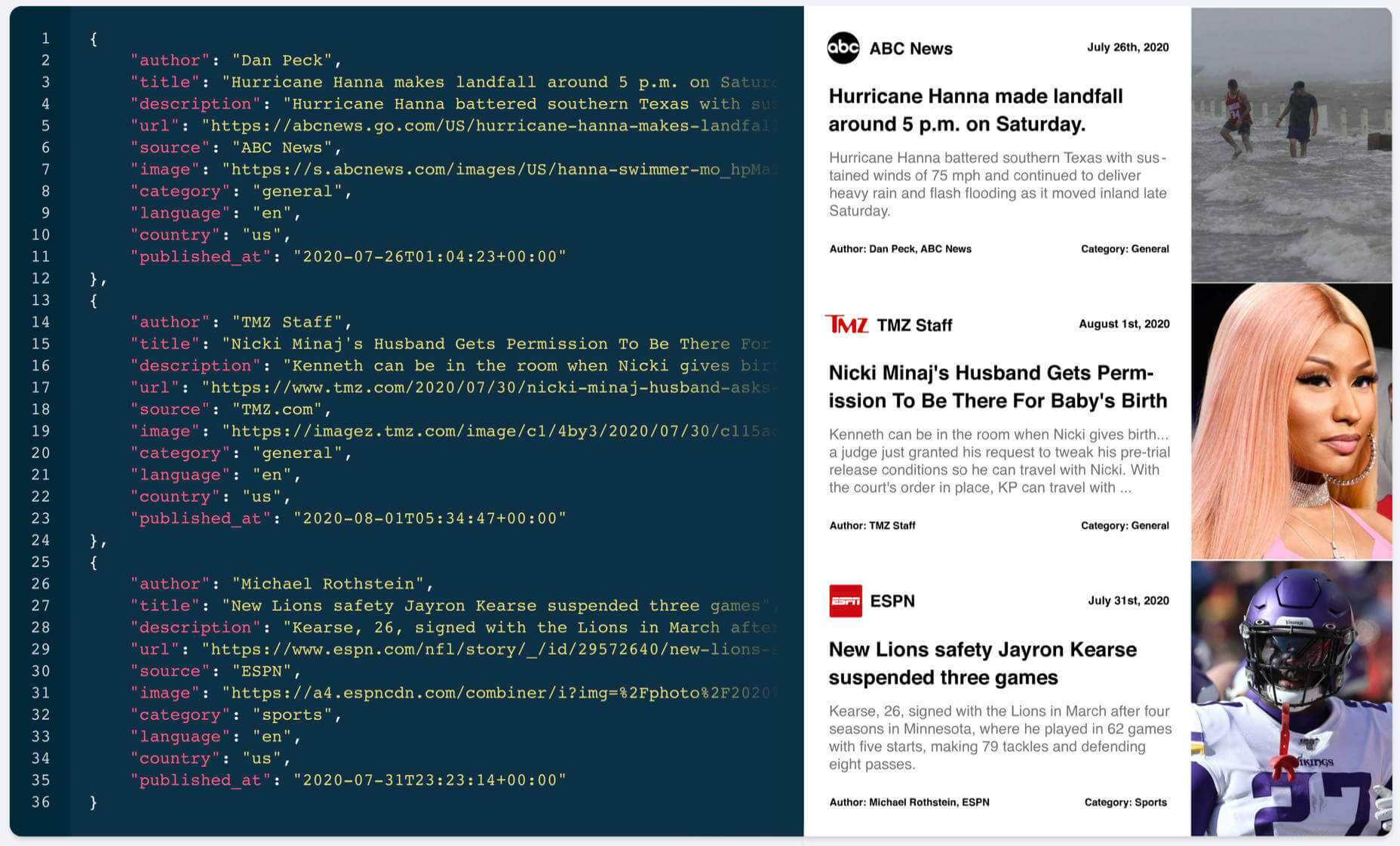
 Jumpstart your next design project or speed up a workflow with some of these new tools and resources. With so many new tools being developed all the time, you are almost certain to find something that can help you with projects.
Jumpstart your next design project or speed up a workflow with some of these new tools and resources. With so many new tools being developed all the time, you are almost certain to find something that can help you with projects.






 Sass – the extended arm of CSS; the power factor that brings elegance to your code.
Sass – the extended arm of CSS; the power factor that brings elegance to your code.
 By the end of the year, the number of global smartphone users is
By the end of the year, the number of global smartphone users is 

 As human beings, we like to think that we’re rational creatures.
As human beings, we like to think that we’re rational creatures.