 It would be way too easy to answer this question with: “Whoever pays your bills.” And, honestly, I don’t think you can be a very successful web designer if you’re only driven by what the person paying you tells you to do.
It would be way too easy to answer this question with: “Whoever pays your bills.” And, honestly, I don’t think you can be a very successful web designer if you’re only driven by what the person paying you tells you to do.
Then again, that doesn’t mean you should swing to the exact opposite end and say that you only serve the end user.
When you take an extreme view or approach to this, you’re bound to leave someone or something important out. Everyone along the chain of command — your boss (if you work at an agency), your client, and their customers — matters.
So, what I’d suggest you do instead is approach the idea of who you really work for the way you would Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
Establishing Your Own Hierarchy of Needs
Who do web designers really work for? I think the true answer to this question is: “Everyone.” But there’s a catch…
Think about some of the requests you’ve received from superiors, or clients in the past. How many times have you rolled your eyes at their wacky requests?
- “The contact form would be better in the header so visitors can always see it.”
- “Let’s use this stock photo of two women shaking hands that I’ve seen a few other companies use.”
- “Why don’t we redesign all of this and make it look like this site my brother built last night?”
You’re the design professional. That’s why they’re paying you to design their website and they’re not doing it themselves. So, there comes a point where you have to push aside what they want for what they need. And this will ultimately help you figure out who you work for and what you actually owe them (because fulfilling every nitpicky and unreasonable request will never lead to anything good).
So, here’s where the Hierarchy of Needs comes in. If we’re creating our own, it would look like this to start:
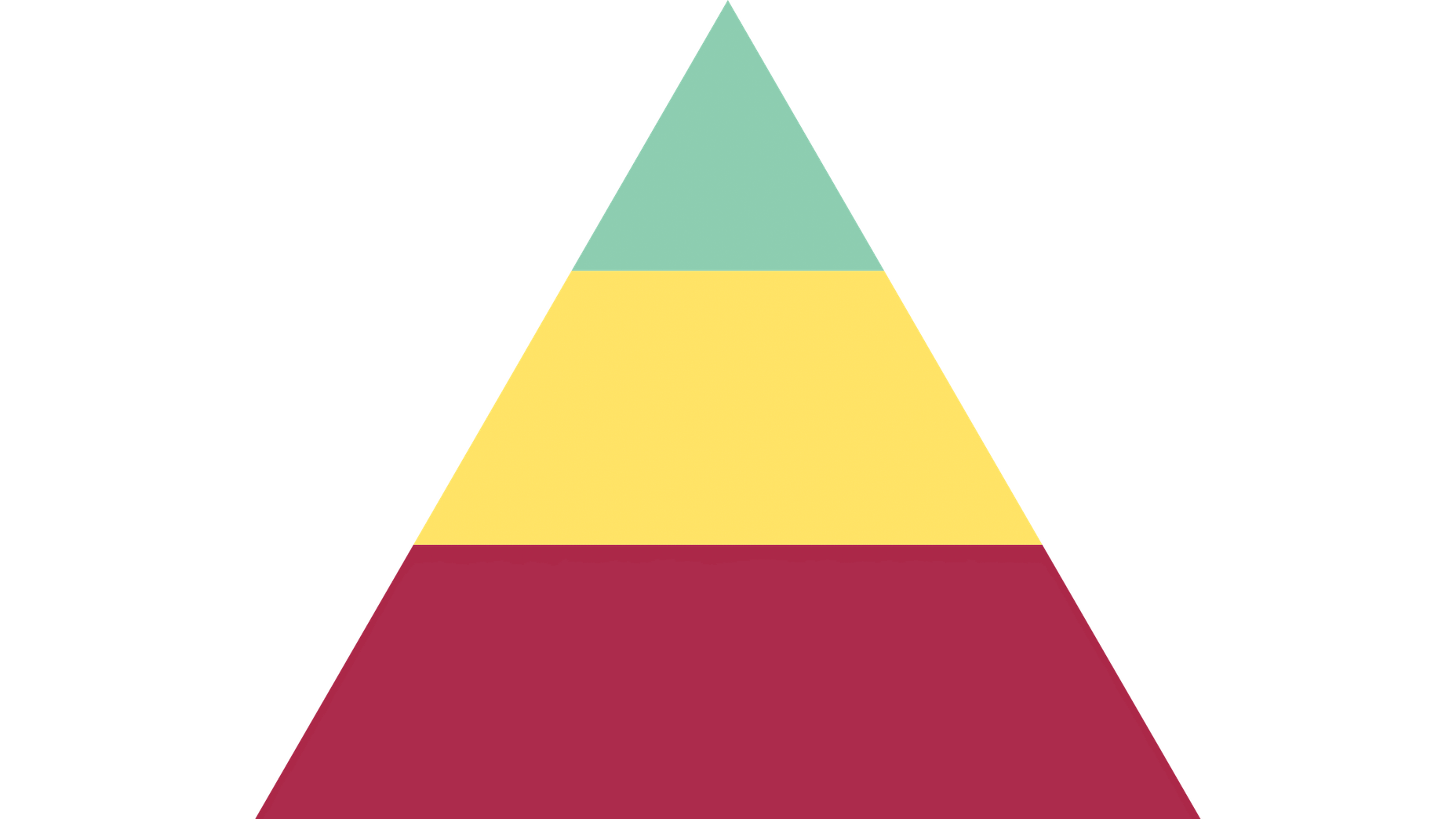
Working for the Boss
According to Dr. Neel Burton on Psychology Today:
Maslow called the bottom… levels of the pyramid ‘deficiency needs’ because we do not feel anything if they are met but become anxious or distressed if they are not.
I’d argue that these basic needs are like the ones we fulfill for bosses (or clients, if you’re a freelancer and work for yourself). It would look something like this:
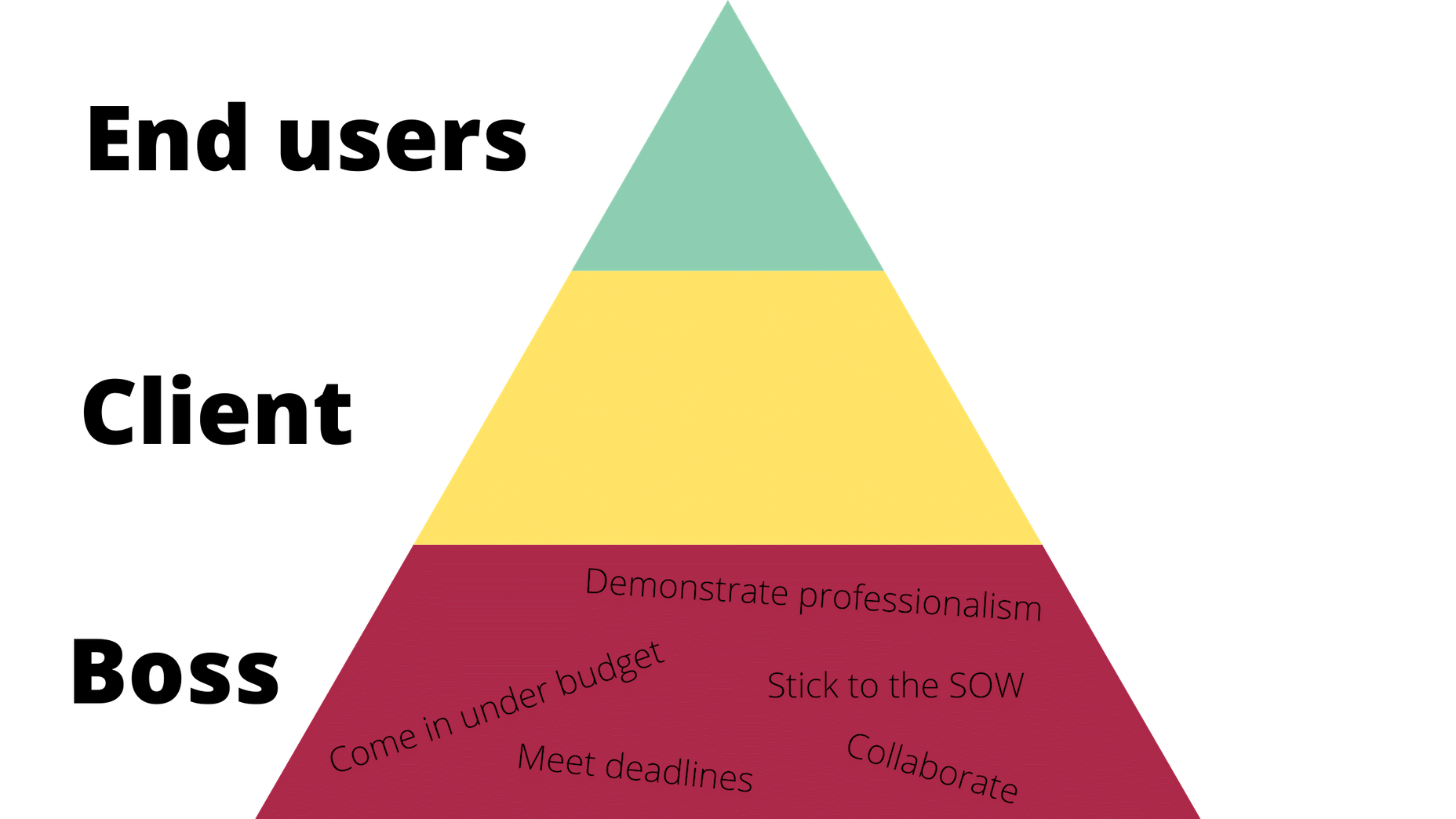
Of course, you’ll feel a sense of accomplishment by meeting these needs, but, as a creator, how important are these really to you? These are the basic things you have to do in order to make your boss happy and to stay gainfully employed. They also help to ensure that the client is happy with the boss and agency in the end.
Bottom line: Without these needs fulfilled, you won’t be able to move any deeper into the triangle/hierarchy. So, when focusing on working for your boss, make sure the basic needs are met so you can move on and serve others as they need you to.
Working for the Client
Now, if your boss and client are two different people, you’ll have a second layer of needs to attend to here.
Just as your boss wants you to help them make more money and earn a strong reputation within their space, so too does your client. However, the work you owe them is different. Here’s how it would be represented in the triangle:
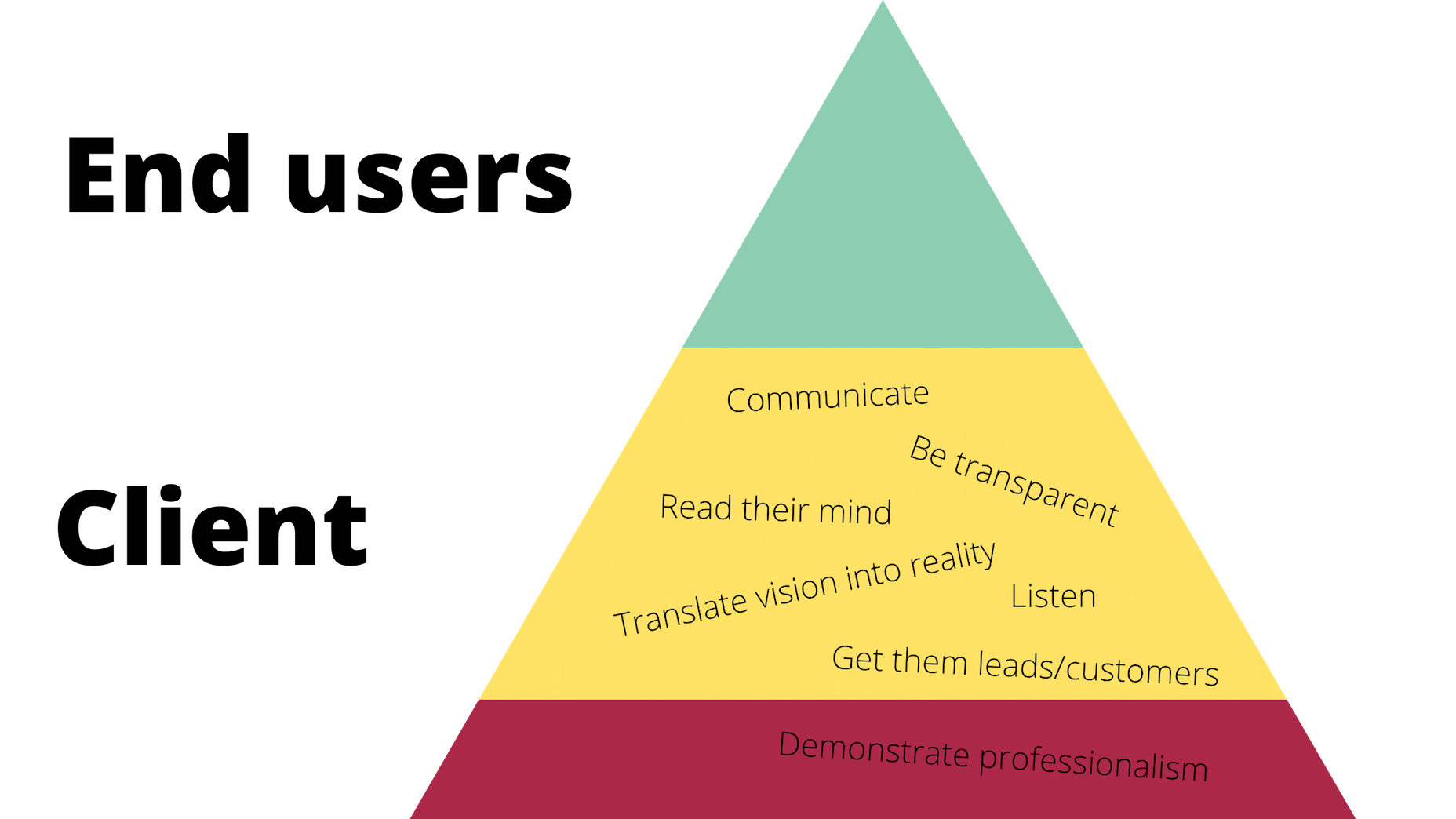
Again, you’ll be pleased if you can do and be all these things that your client needs, but is this ultimately what drives you as a designer? Sure, you want to build great relationships with clients so they return to you time and time again with all their website and marketing needs. But in terms of being fulfilled by being a good listener or a timely communicator? Probably not.
All the same, it’s important to be skilled in this type of work and to know how to serve your clients in order to get to that top level. It’ll also help you prioritize their needs accordingly, so you’re not jumping at every single thing or request they claim to “need” and blowing the budget or scope of the job.
For example, if they start demanding more of you (like bombarding you with emails every day wanting to know what’s going on), you can confidently remind them that things are under control (because you’re adhering to the project deadlines, per your boss) and you’ve already scheduled the next client check-in for this week (because you’ve been a good communicator, just as they need you to be).
Working for the End User (Customer)
Maslow refers to the top-level of the pyramid as the growth need. And here’s how Dr. Burton sums this one up for us:
Once we have met our deficiency needs, the focus of our anxiety shifts to self-actualization, and we begin, even if only at a sub- or semi-conscious level, to contemplate our bigger picture. However, only a small minority of people are able to self-actualize because self-actualization calls upon uncommon qualities such as independence, awareness, creativity, originality, and, of course, courage.
These characteristics perfectly sum up everything you want to and should be as a web designer. Unfortunately, it’s those employer and client needs that can stand in your way before you can truly flex your muscles as a creative.
Once you’ve attended to the basics, though, you’ll get your chance to design the kinds of user experiences you know will delight your client’s customers.
Here’s how their part of the triangle should look:
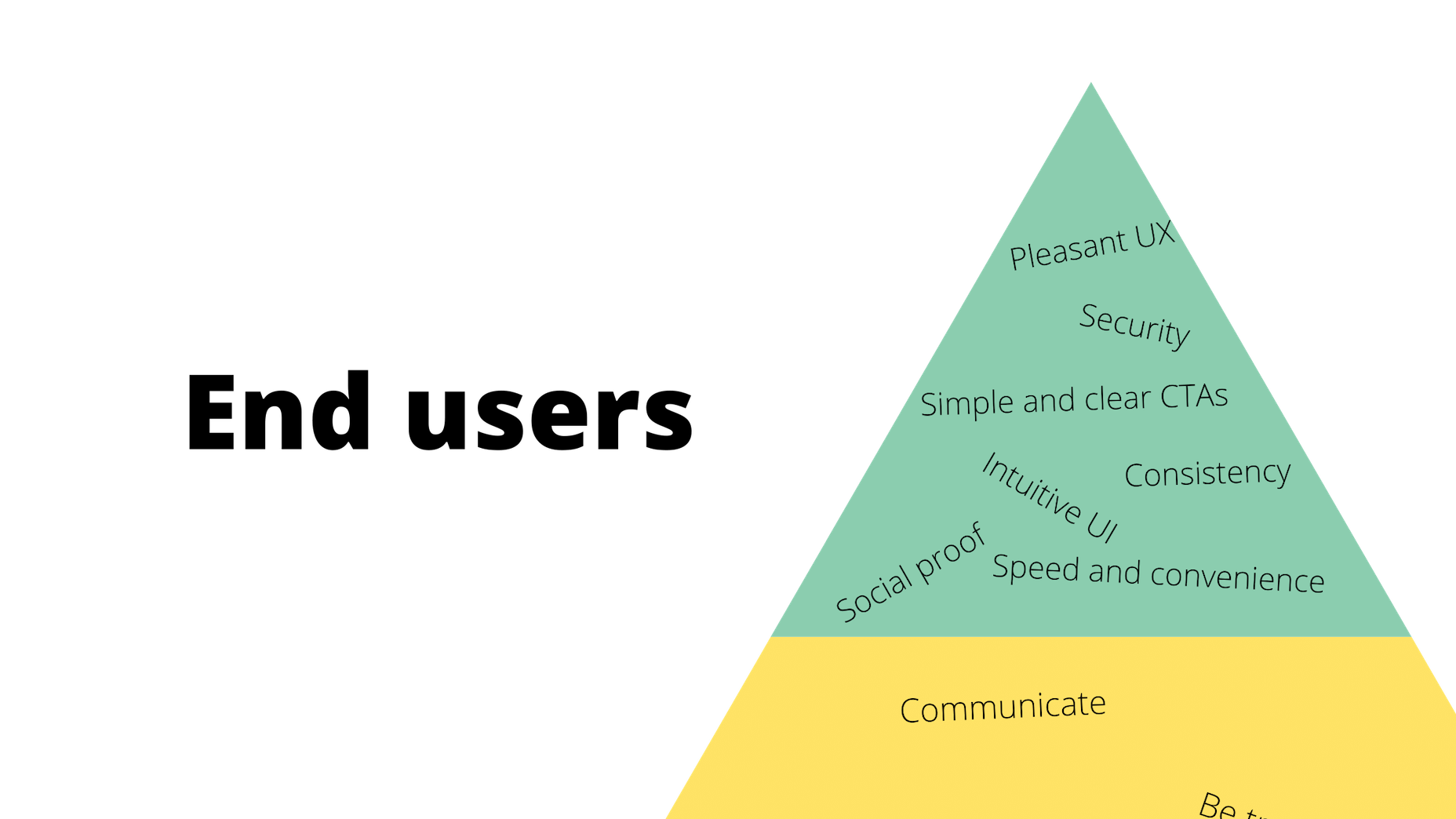
These are universally applicable needs and cannot be ignored.
After you’ve addressed them, though, you will have fulfilled your responsibility to all three parties: your boss, your client, and your end users. And once you’ve done that, you are free to be the creative designer that you are.
Wrap-Up
What I want you to take away from this, is that there are certain basic needs which you must fulfill when working as a web designer. These are the ones you’ll put into your own hierarchy of needs.
Take a systematic approach, starting with your boss and ending with the customer:
- What do you have to do to ensure that your boss is happy to have you on the team?
- And that the client is pleased with the site you’ve built them?
- So you can design a website and experience that end users respond to positively?
Once you’ve figured all this out, you’ll unlock the answer to whom you work for and, more importantly, how you should work for them.
Featured image via Pexels.


 Design can make a statement. It evokes feeling and can encourage thought and conversation. That’s the common theme among the three trends in website design this month.
Design can make a statement. It evokes feeling and can encourage thought and conversation. That’s the common theme among the three trends in website design this month.






 Artificial intelligence. Just hearing the phrase has been a trigger for many in the technology world since that creepy Haley Joel Osment film circa 2001. But more recently, artificial intelligence and machine learning strike fear into the hearts of skilled workers for an entirely different reason: job security, or lack thereof.
Artificial intelligence. Just hearing the phrase has been a trigger for many in the technology world since that creepy Haley Joel Osment film circa 2001. But more recently, artificial intelligence and machine learning strike fear into the hearts of skilled workers for an entirely different reason: job security, or lack thereof.


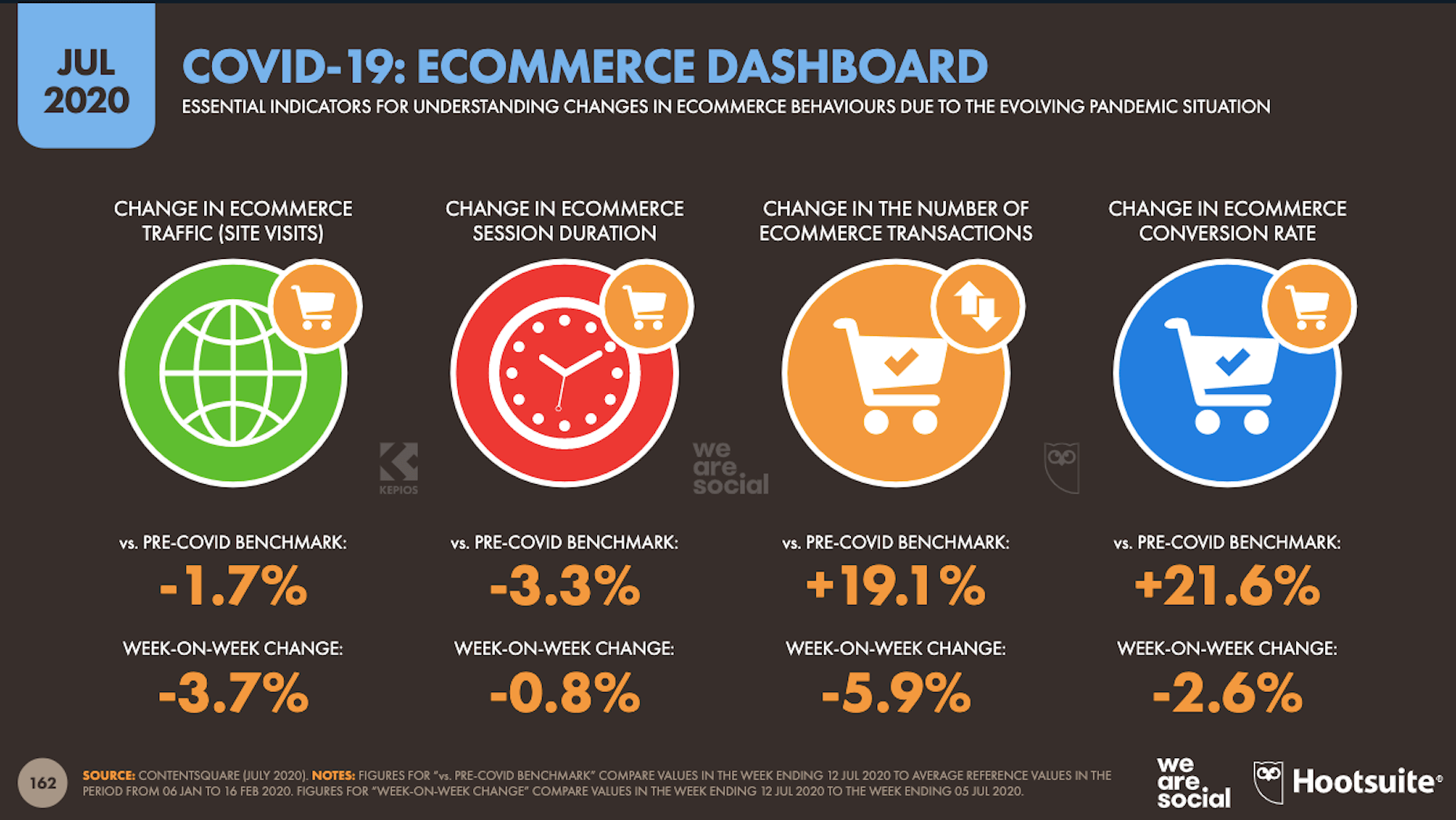
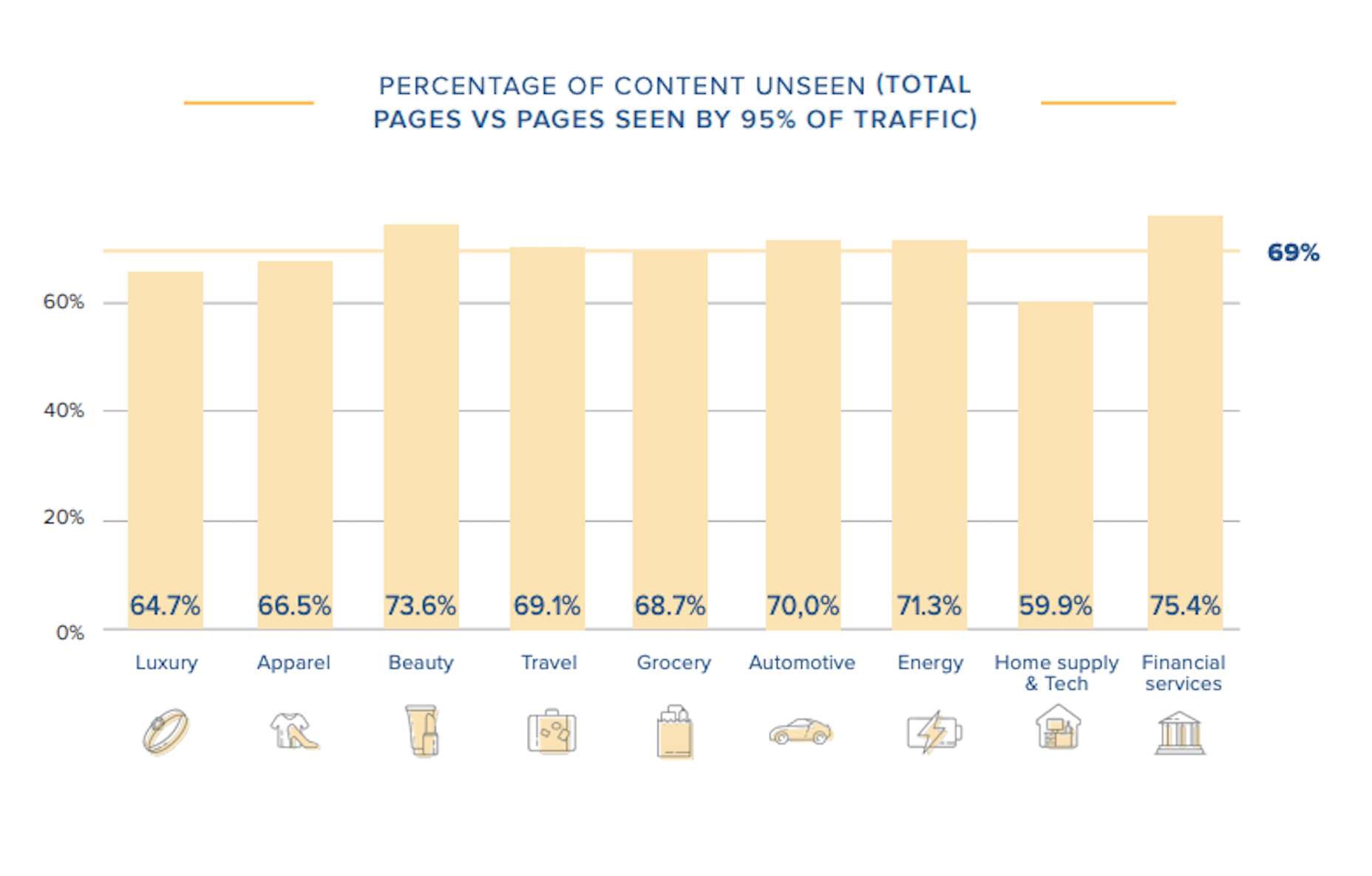
 In today’s look at the latest research for web designers, we’re going to look at studies and reports from Payoneer, Robert Half, Hootsuite, and Contentsquare to see what they have to say about things like:
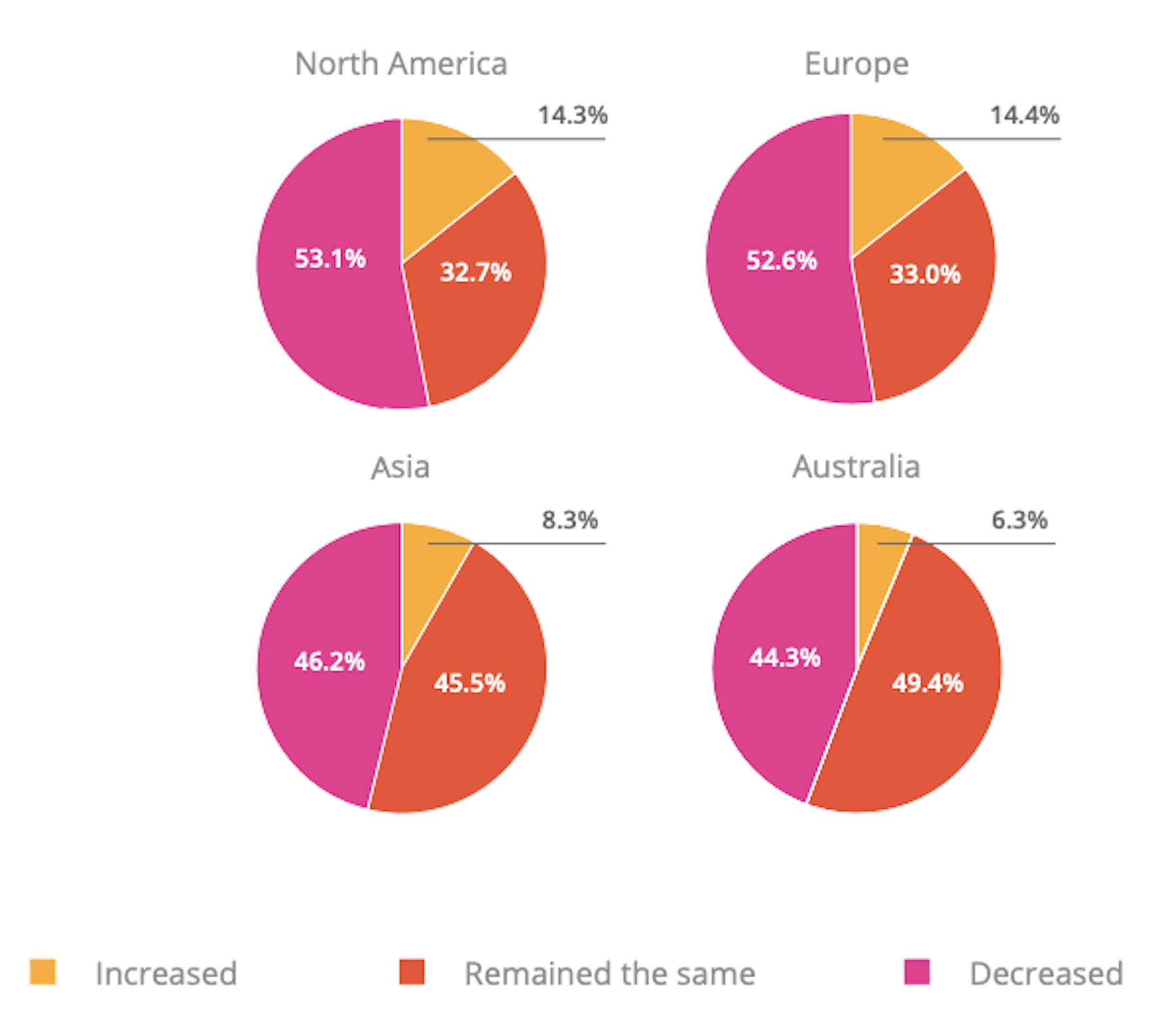
In today’s look at the latest research for web designers, we’re going to look at studies and reports from Payoneer, Robert Half, Hootsuite, and Contentsquare to see what they have to say about things like: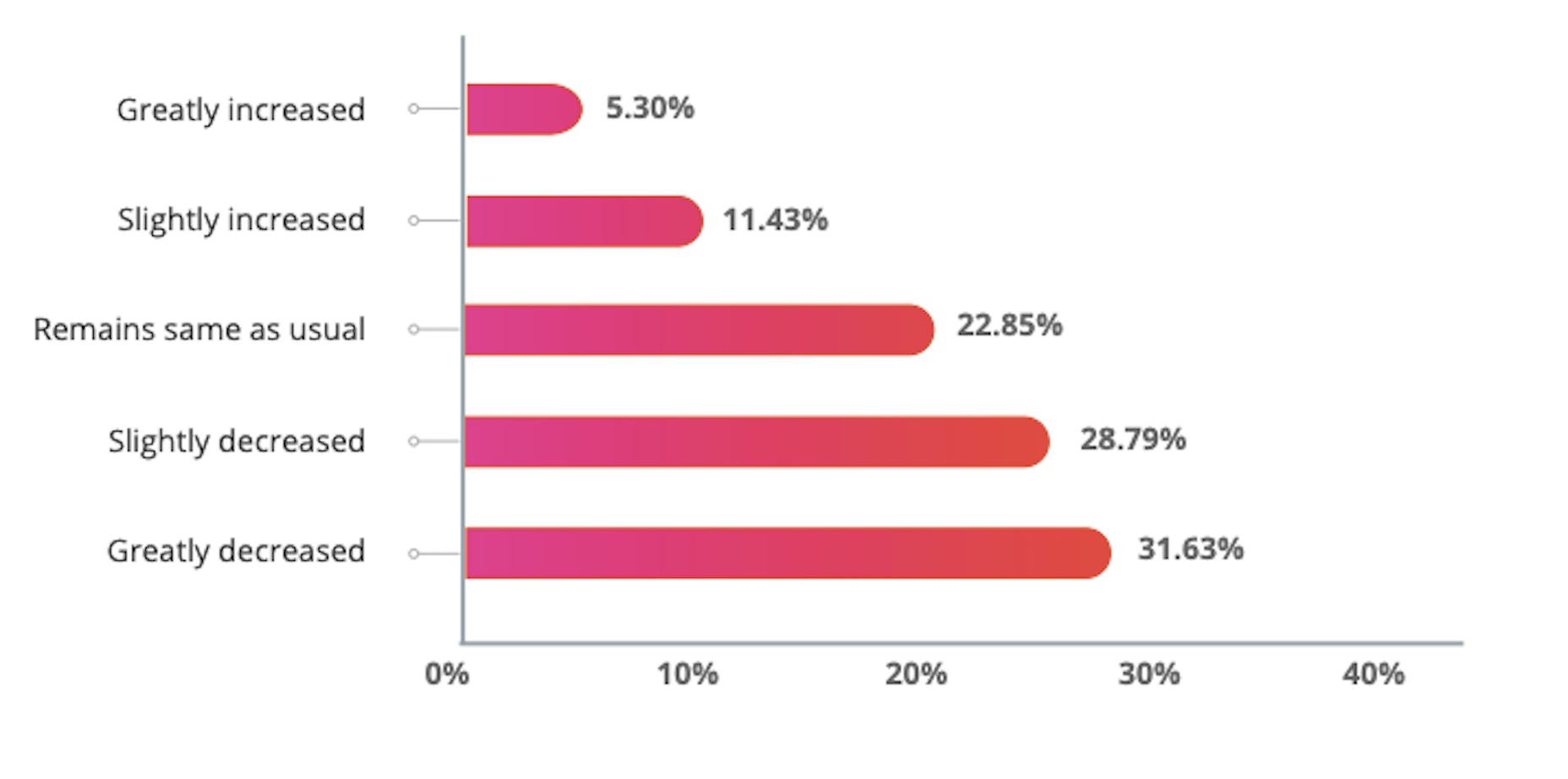


 I often see freelancers on social media asking what the secret is to working fewer hours, making more money, and helping new clients to find them. While those things tend to happen the longer you’ve been freelancing, it doesn’t happen without some effort.
I often see freelancers on social media asking what the secret is to working fewer hours, making more money, and helping new clients to find them. While those things tend to happen the longer you’ve been freelancing, it doesn’t happen without some effort.




 To understand why user onboarding is such an indispensable tool, we need to empathize with the people using our products; we all come from different backgrounds and cultures, we make different assumptions, and we see the world differently.
To understand why user onboarding is such an indispensable tool, we need to empathize with the people using our products; we all come from different backgrounds and cultures, we make different assumptions, and we see the world differently.

 Every week users submit a lot of interesting stuff on our sister site Webdesigner News, highlighting great content from around the web that can be of interest to web designers.
Every week users submit a lot of interesting stuff on our sister site Webdesigner News, highlighting great content from around the web that can be of interest to web designers.














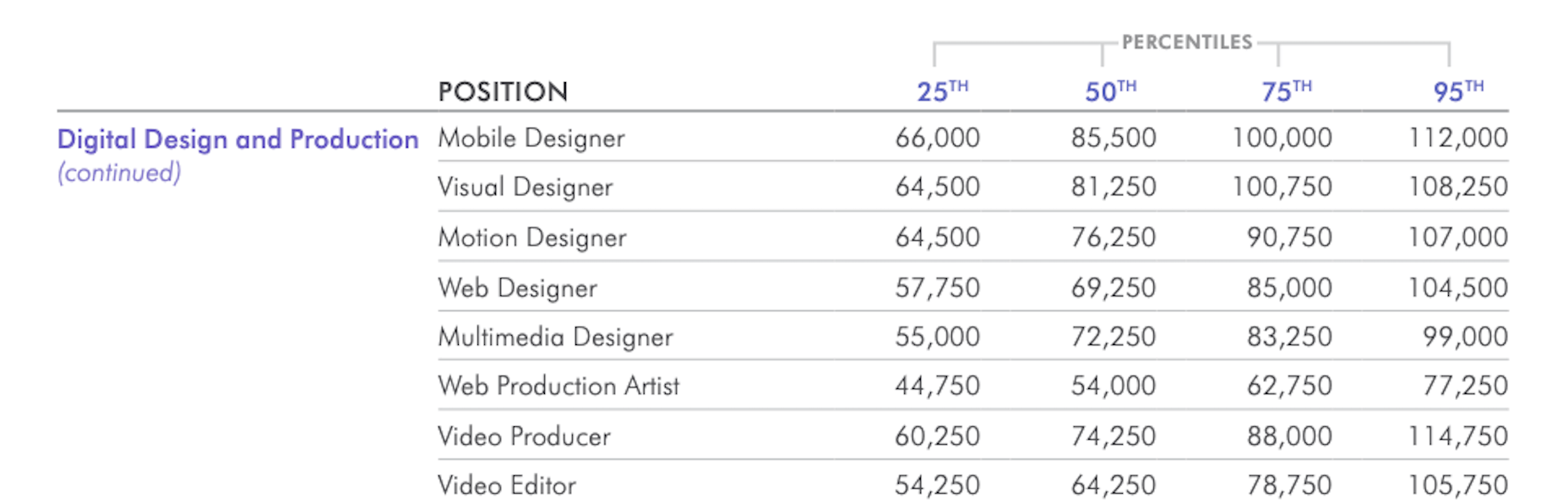
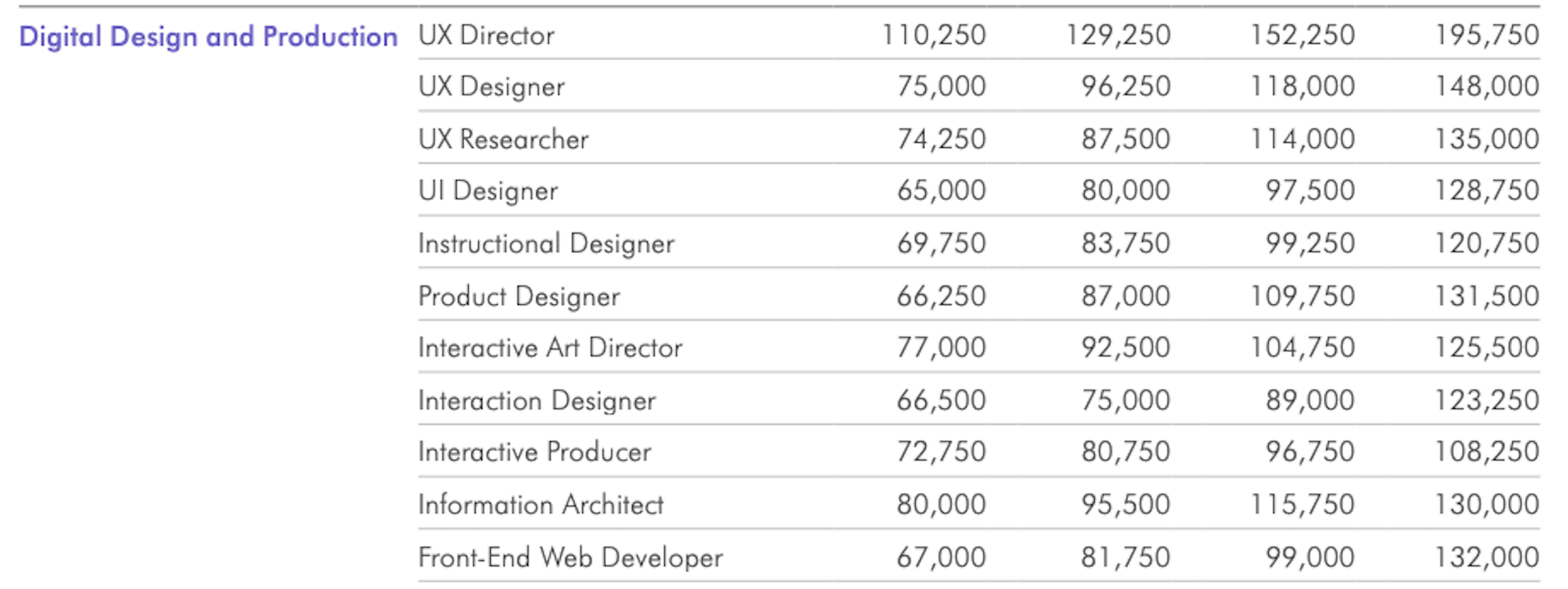
 Many people dream of a career in web design, but it may actually be more attainable than you think.
Many people dream of a career in web design, but it may actually be more attainable than you think.