Yesterday’s creativity won’t keep pace with tomorrow’s requirements; businesses need speed and agility without sacrificing creative quality.
Yesterday’s creativity won’t keep pace with tomorrow’s requirements; businesses need speed and agility without sacrificing creative quality.
“The creativity that was needed in the past is not the creativity that is needed today,” according to Matthew Rayback, a creative director at Adobe. He’s not talking about the function of creativity but rather about the process of creative management in a marketing context.
What is needed today? Speed and agility without sacrificing quality.
Why? Because the pace of change has accelerated. As Rex Salisbury, a deal partner for the venture firm a16z noted early in the pandemic, “Businesses of all kinds are experiencing two years’ worth of digitization compressed into months.”
This accelerated digital transformation has put pressure on marketing teams to turn campaigns around faster. In turn, that places pressure on creative teams to generate the requisite creative for those campaigns. Leaders need to sharpen their awareness of the unfolding creative management trends to keep pace. To that end, below are five such trends to watch in 2022.
1. In-House Creative Teams Continue to Grow
Companies have been building in-house creative teams for the better part of a decade. A 2018 study by Forrester Research and the In-House Agency Forum (IHAF) found the number of in-house teams has grown 22% in the last ten years or so. As The Wall Street Journal reported, more than half of advertisers (64%) have shifted their creative organizations to an in-house team.
According to a more recent version of that same study, the in-housing movement didn’t stop throughout the pandemic. It revealed, “80% of respondents said they have brought more marketing assignments in-house since the onset of the pandemic, with 50% saying the increase was directly triggered by the events of the past two years.”
Businesses seem well-satisfied with the results because the urge to in-house is poised to grow beyond creative teams. For example, a recent survey by the customer intelligence company Axciom found about 50% of respondents believe the “in-housing is currently a top marketing objective, and 40% expect it will remain a top priority in the coming years.”
2. Outside Agencies Hired for Specialized Skills
Despite the in-housing trend, there is still opportunity for agencies, consultants, and freelancers, particularly those with specialized skills. Even the consumer-packaged goods giant Proctor & Gamble, a leading example of brands bringing marketing and creative teams in-house, still needs outside service providers.
Indeed, while in-house creative teams produce the lion’s share of creative work, the vast majority (86%) also continue to partner with agencies and freelancers; according to our own research, published in our 2021 Creative Management Report, which was facilitated by Lytho (formerly inMotionNow) and based on a survey of 400 creatives and marketers.
When the survey asked creatives why they hire outside resources, the top reason was access to specialized skills (60%). That was followed in a distant second by a need for increased capacity (44%), help with developing strategy (24%), and, lastly, to get work done faster (20%).
“It is very unusual for an in-house team to have no outside resources that they lean on,” wrote Alex Blum of Blum Consulting Partners, Inc. in a written assessment of the survey results.
He says there are two primary ways to partner with agencies. “First, for overflow capacity. There is always a need for more creative resources, and agencies can offer that flexibility without the cost of maintaining larger teams,” he wrote. “Second, in-house teams can divide areas of ownership with an agency based on the skill sets they have in-house.”
3. The Creative Process Evolves
Marketing today is dominated by an insatiable thirst for fresh content, produced and polished by creative teams. The demand for that content continues to explode.
What does this portend for creative teams? Despite adding headcount, creative requests exceed the creative team’s capacity to produce it – even as lead times shrink. Matthew Rayback, the creative director at Adobe, suggested the creative process must evolve.
He likens creatives to an auto factory, where “creatives used to be the assembly line to make a single car.” However, today, creatives are tasked with creating more cars, each with unique adjustments such as personalization.
“The assembly line we built can’t accommodate that speed or volume,” he says. So the whole factory – the entire creative process – must be overhauled to adapt.
4. Quantitative Measurement Drives Creative Priorities
Current methods for measuring the value of creative teams center on outputs. That is to say, the metrics tracked tend to quantify the number of creative projects in progress, the rounds of review, and the number of projects completed over time.
These metrics are important, but alone they are insufficient. A complementary way to prioritize large volumes of creative requests is focusing on those tasks most likely to move the business needle. The barrier to achieving this is that most creatives aren’t kept informed as to the outcomes of marketing campaigns fueled by their creative efforts. This must change.
With the growing demand for content, the margin of error for applying creative resources to projects that don’t correlate to business results shrinks. Marketing organizations must build a feedback loop that brings quantitative results back to the creative team. In turn, creative teams must learn to use the data to drive their work priorities in collaboration with marketing.
5. Creative Resource Management Becomes Essential
Resource management is both a leadership concept and technology (or a combination of technologies). It’s a means to plan, track, collaborate and measure creative operations, including people, processes, and budgets.
Traditionally, planning and tracking of all things creative and marketing occurred in a spreadsheet. It works well when the future is generally predictable – yet cliché as it may be to say it – we are living in a state of uncertainty.
Like many trends over the last 18-24 months, the global pandemic “forced virtual experiences, disrupted marketing channels and campaigns, and accelerated companies’ transition to digital marketing,” according to Forrester. The research firm calls resource management “essential” because it helps move “planning from static spreadsheets to a dynamic and real-time environment.”
Final Thoughts
Yogi Berra paraphrased an old Danish proverb when he said, “It’s tough to make predictions, especially about the future.” Even so, the pandemic has accelerated trends that were already underway, and these five trends are good examples. More than just watching them, creative and marketing leaders should take steps now to get ahead of them.
Featured image via Pexels.
The post 5 Creative Management Trends to Watch in 2022 first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.

 So here we are, in a brand spanking new year—time for looking forward with fresh ideas and renewed hope for the year ahead. We are kicking off 2022 with a mixed bag and, we hope, something for everyone.
So here we are, in a brand spanking new year—time for looking forward with fresh ideas and renewed hope for the year ahead. We are kicking off 2022 with a mixed bag and, we hope, something for everyone.












 Few things are more important to a web designer or developer’s chances of success than having the proper workflow. The term “workflow” applies to the set of standardized steps you or your company uses to create, test, and deploy designs or products.
Few things are more important to a web designer or developer’s chances of success than having the proper workflow. The term “workflow” applies to the set of standardized steps you or your company uses to create, test, and deploy designs or products.
 Picture a dark office, blinds drawn. Picture a UX designer smoking a cigar. See the light filtered through the smoke whipped to fog by a spinning ceiling fan. Watch as the UX designer sits at a desk and considers the website.
Picture a dark office, blinds drawn. Picture a UX designer smoking a cigar. See the light filtered through the smoke whipped to fog by a spinning ceiling fan. Watch as the UX designer sits at a desk and considers the website.
 There was a point at which I was very close to losing my business, and I didn’t realize how close.
There was a point at which I was very close to losing my business, and I didn’t realize how close.
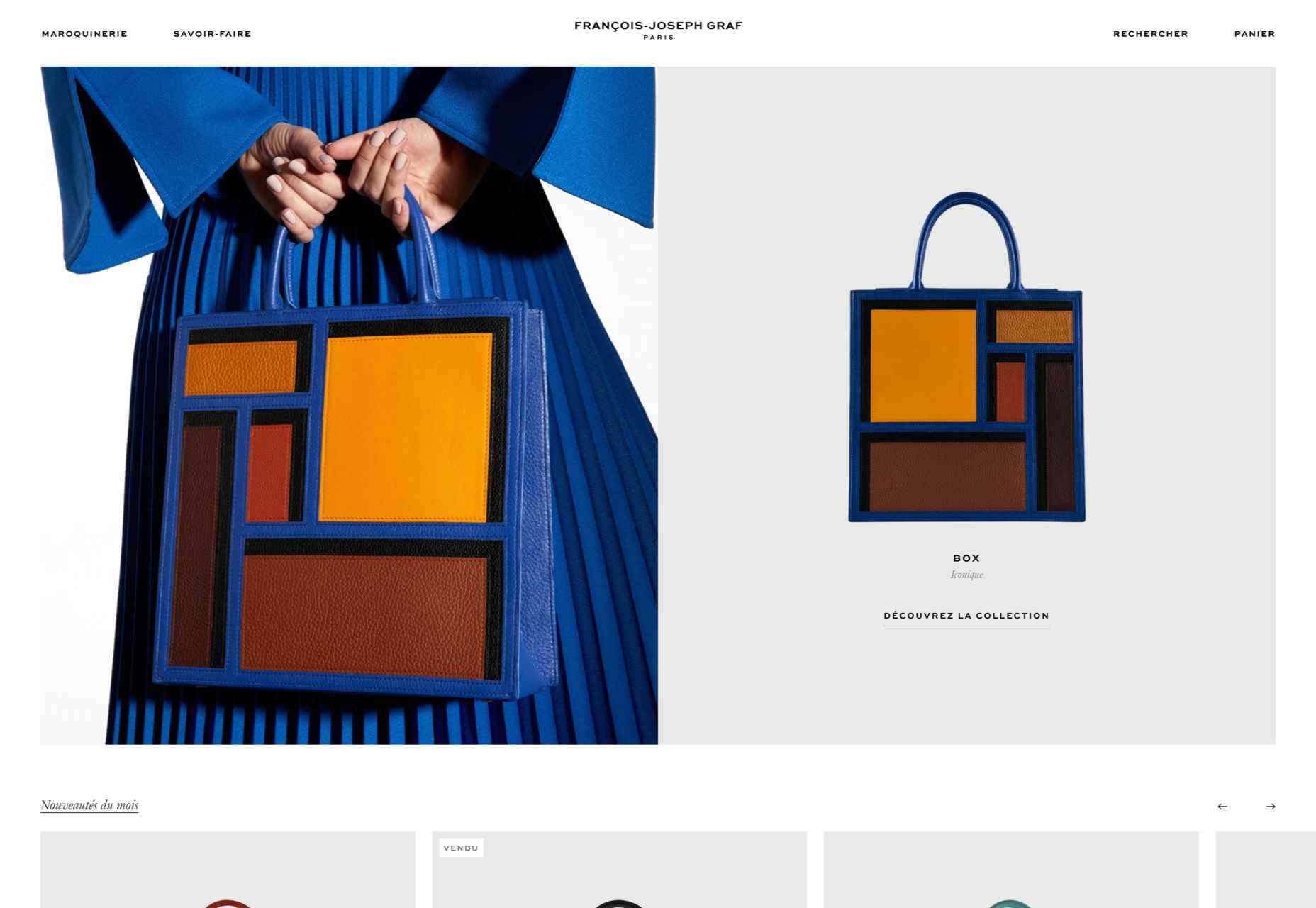
 Happy New Year, fabulous new website design trends!
Happy New Year, fabulous new website design trends!





 There are a lot of factors that contribute to a
There are a lot of factors that contribute to a 






 Every year, at this time, blogs like this one like to try and predict what’s going to happen in the year ahead. It’s a way of drawing a line under the archive and starting afresh. A rejuvenation that, as humans, we find life-affirming.
Every year, at this time, blogs like this one like to try and predict what’s going to happen in the year ahead. It’s a way of drawing a line under the archive and starting afresh. A rejuvenation that, as humans, we find life-affirming.
 Many people believe that UX design is all about creating slick, engaging images and top-notch user flows. While those things have their merits, UX designers do much more than that.
Many people believe that UX design is all about creating slick, engaging images and top-notch user flows. While those things have their merits, UX designers do much more than that.
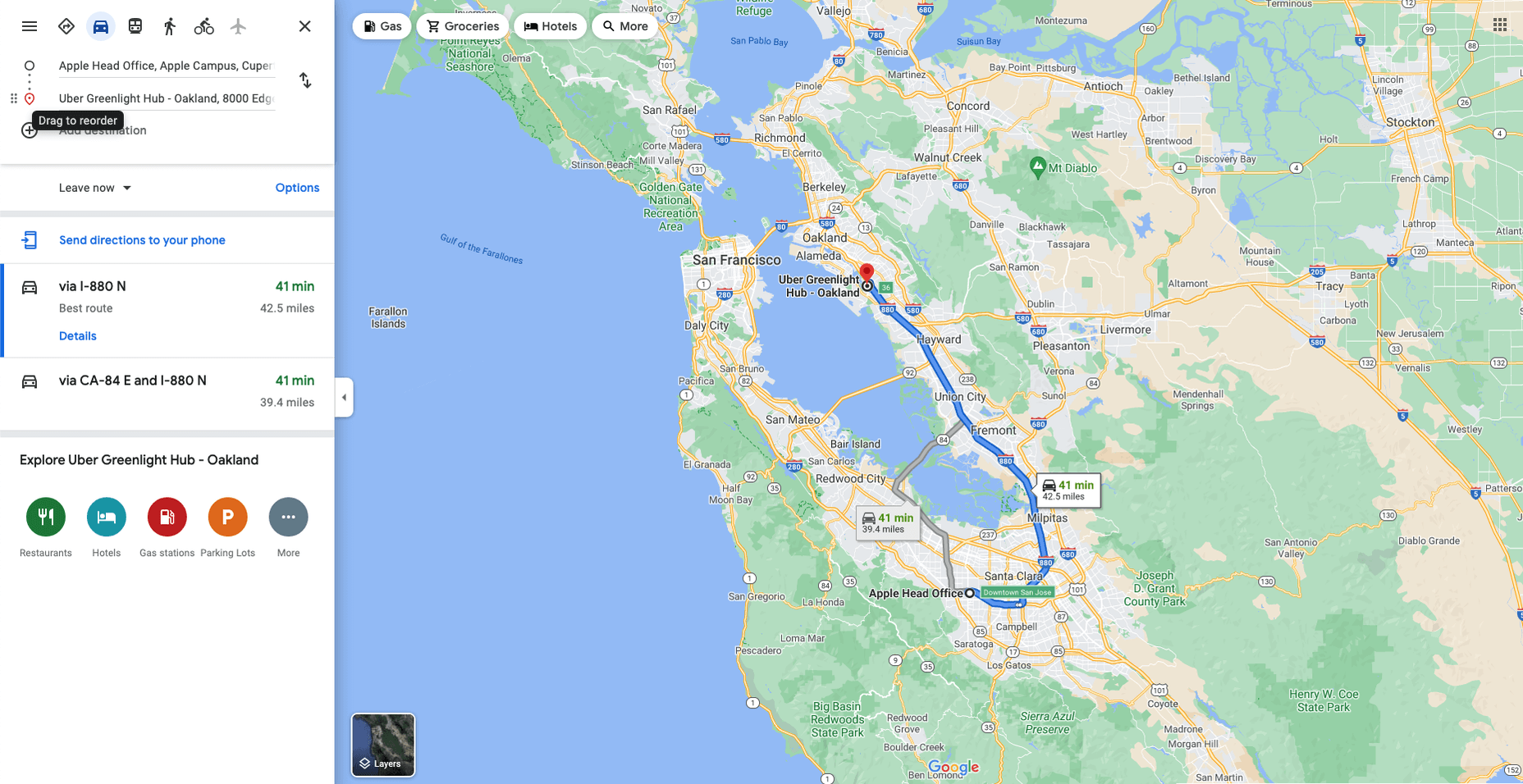
 Maps are a fascinating method for delivering content. At their best, they can create an intuitive way of presenting information and interacting with it. This is the advantage that digital maps, through mobile apps and websites, have over print maps and images where no interactivity is possible.
Maps are a fascinating method for delivering content. At their best, they can create an intuitive way of presenting information and interacting with it. This is the advantage that digital maps, through mobile apps and websites, have over print maps and images where no interactivity is possible.