What stands out as an incredible web design project for you? Do you count your creation as a success if it’s modern, minimal, and accessible? Maybe you’re the kind of designer that’s constantly experimenting with the latest dynamic design tools or state-of-the-art technology. Perhaps your websites are vivid, animated, and brimming with unique components?
What stands out as an incredible web design project for you? Do you count your creation as a success if it’s modern, minimal, and accessible? Maybe you’re the kind of designer that’s constantly experimenting with the latest dynamic design tools or state-of-the-art technology. Perhaps your websites are vivid, animated, and brimming with unique components?
Sometimes, creating the ideal design means thinking carefully about what you want to accomplish for your client. The purpose of your web creation has a significant impact on the components that you need to consider. For instance, if you’re hoping for a highly emotive and human design, it may be worth combining some of your sleek lines and graphics with hand-drawn elements.
The Value of Hand-Drawn Graphics in Web Design
Hand-drawn elements are just like the other components of web design; that way may use to express individuality in a cluttered digital environment. In a world where everyone focuses on futuristic and virtual creations, hand-drawn elements can pull attention back to the importance of humanity in your content.
As web designers, we know that visual components often impact people more than text-based content. Illustrations are highly engaging functional elements that capture audience attention and convey relevant information.
The main difference between hand-drawn elements and graphics built with vectors and other digital components is that one appears to be more influenced by the human hand than the other. Even if your illustrations are created on a screen, just like any other web design component, it pushes an audience to see something more straightforward, more natural, and authentic.
For a brand trying to convey innocence and humanity in its personality, hand-drawn design can speak to the part of the human psyche that’s often unappreciated by web design. Perhaps more than any other visual, the content reminds your audience that there’s a human behind the web page.
The Value of Hand-Drawn Features in Web Design
Any image can have a massive impact on the quality of your web design. Visuals deliver complex information in an easy-to-absorb format. In today’s world of fast-paced browsing, where distractions are everywhere, visuals are a method of capturing attention and delivering value fast.
However, with hand-drawn elements, you go beyond the basic functionality of images to embrace the emotional side of the content. Benefits include:
- A memorable experience: Web illustrations are becoming more popular among leading brands like Innocent Smoothies and Dropbox. However, the time that goes into these components means that they’re still scarce. If you want to stand out online, illustrations can help you do that.
- Brand personality: One of the most significant benefits of hand-drawn web design is showcasing your brand personality. The blocky lines of imperfect content that go into illustrated images highlight the human nature of your company. So many businesses are keen to look “perfect” today to make the human touch much more inviting.
- Differentiation: As mentioned above, hand illustrations are still rare in the digital design landscape. If you’re struggling to find a way to make your brand stand out, this could be it. Although there needs to be meaning behind your design, the result could be a more unique brand if you can convey that meaning properly.
Tips for Using Hand Drawn Elements in Web Design
Hand-drawn components, just like any other element of visual web design, demand careful strategy. You don’t want to overwhelm your websites with these sketches, or you could end up damaging the user experience in the process.
As you work on your web designs, pulling hand-drawn elements into the mix, think about how you can use every illustration to accomplish a crucial goal. For instance:
Create Separation
Hand-drawn design components can mix and match with other visual elements on your website. They work perfectly alongside videos and photos and help to highlight critical points.
On the Lunchbox website, the company uses hand-drawn elements. This helps make the site stand out, and it provides additional context for customers scanning the website for crucial details.
Engage Your Audience
Sometimes, hand-drawn elements are all about connecting with end-users on a deeper, more emotional level. One of the best ways to do this is to make your hand-drawn elements fun and interactive pieces in the design landscape.
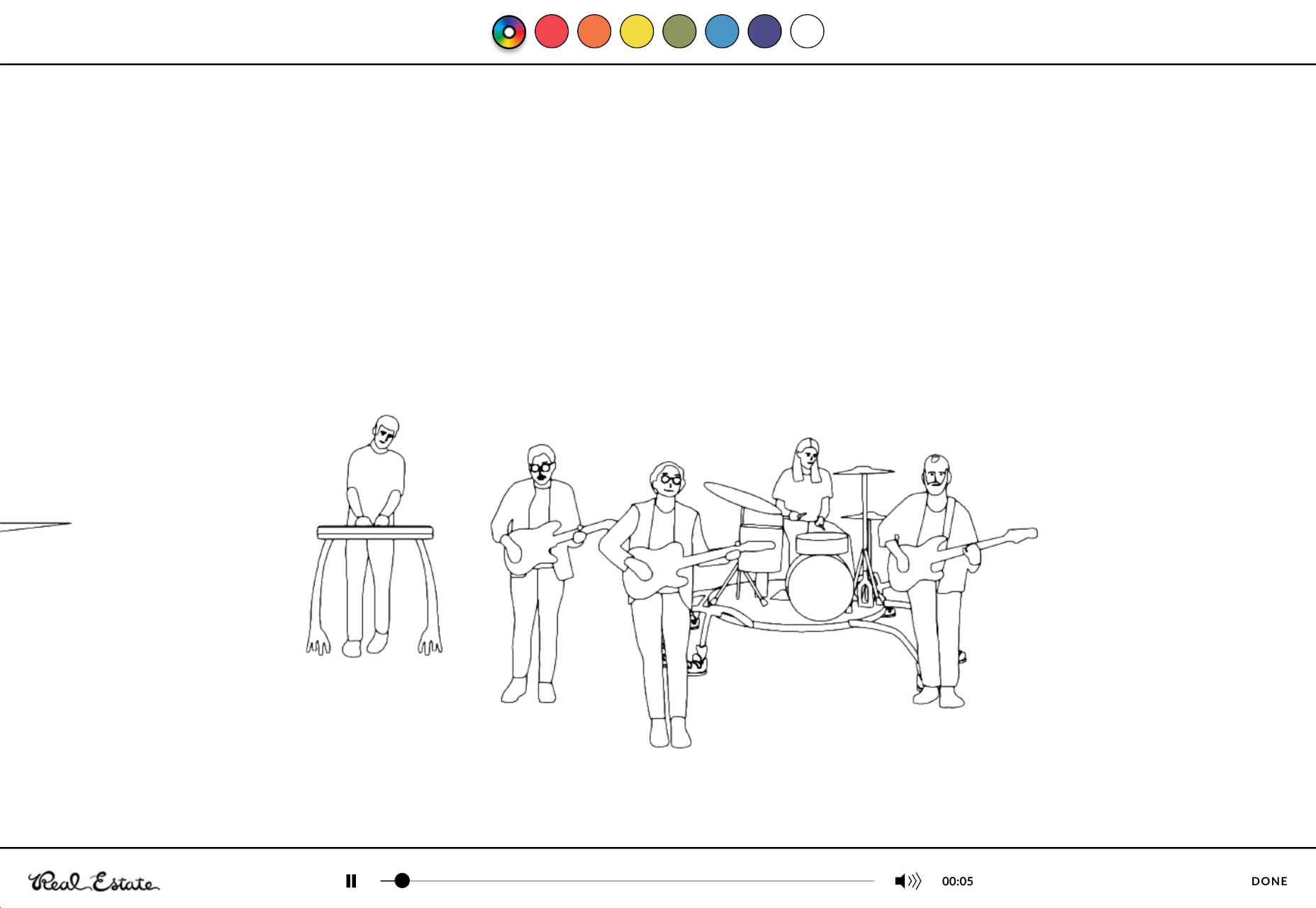
One excellent example of this is in the Stained Glass music video here. This interactive game combines an exciting web design trend with creative interactive components so that users can transform the web experience into something unique to them.
Highlight Headers with Typography
Sometimes, the best hand-drawn elements aren’t full illustrations or images. Hand-drawn or doodle-like typography can also give depth to a brand image and website design.
Typography styles that mimic natural, genuine handwriting are excellent for capturing the audience’s attention. These captivating components remind the customer of the human being behind the brand while not detracting from the elegance of the website.
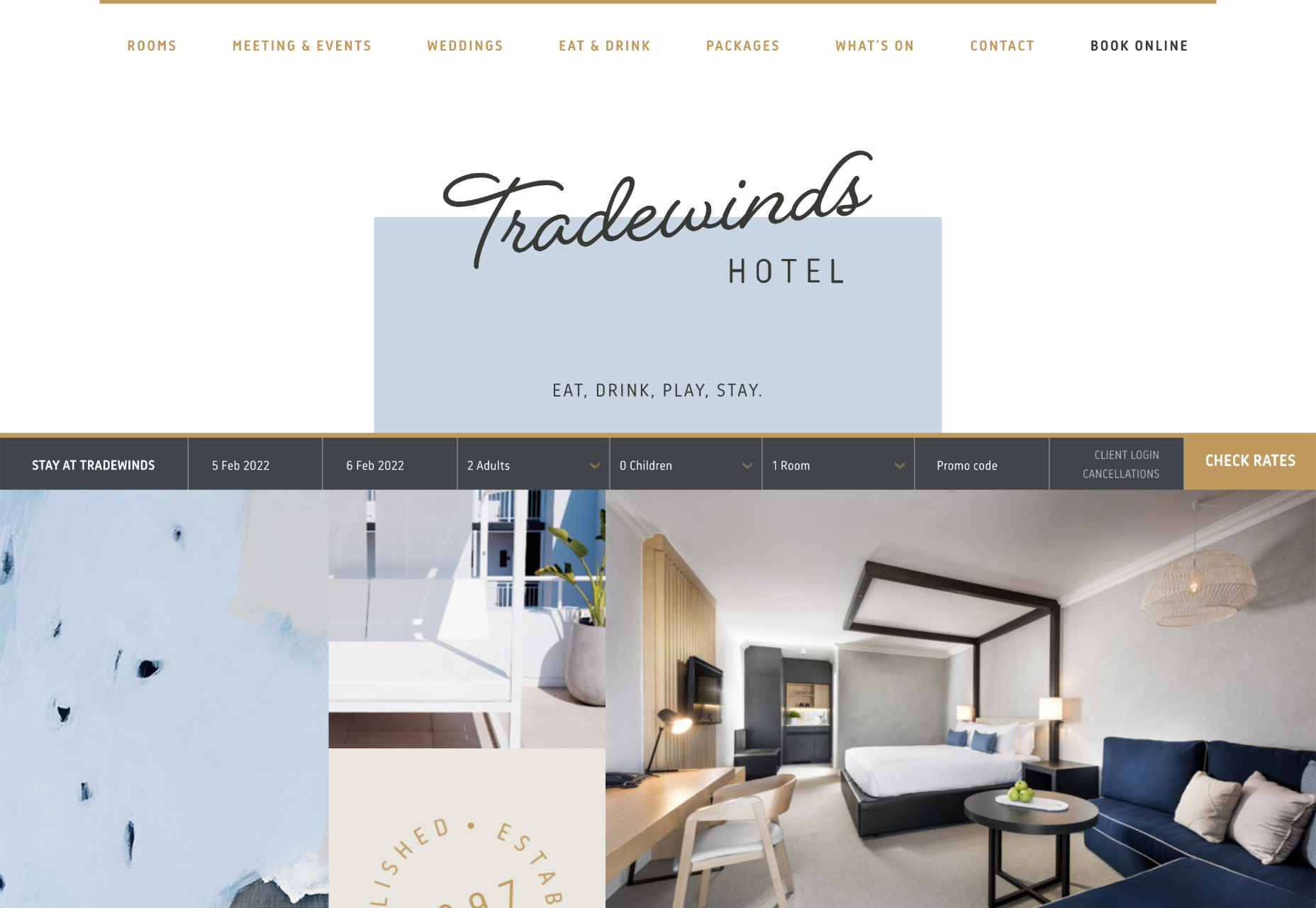
This example of hand-drawn typography from the Tradewinds hotel shows how designers can use script fonts to immediately capture customer attention. Notice that the font is still easy to read from a distance, so it’s not reducing clarity.
Set the Mood
Depending on the company that you’re designing for, your website creation choices can have a massive impact on the emotional resonance that the brand has with its audience. Hand-drawn elements allow websites to often take on a more playful tone. They can give any project a touch of innocence and friendliness that’s hard to accomplish elsewhere.
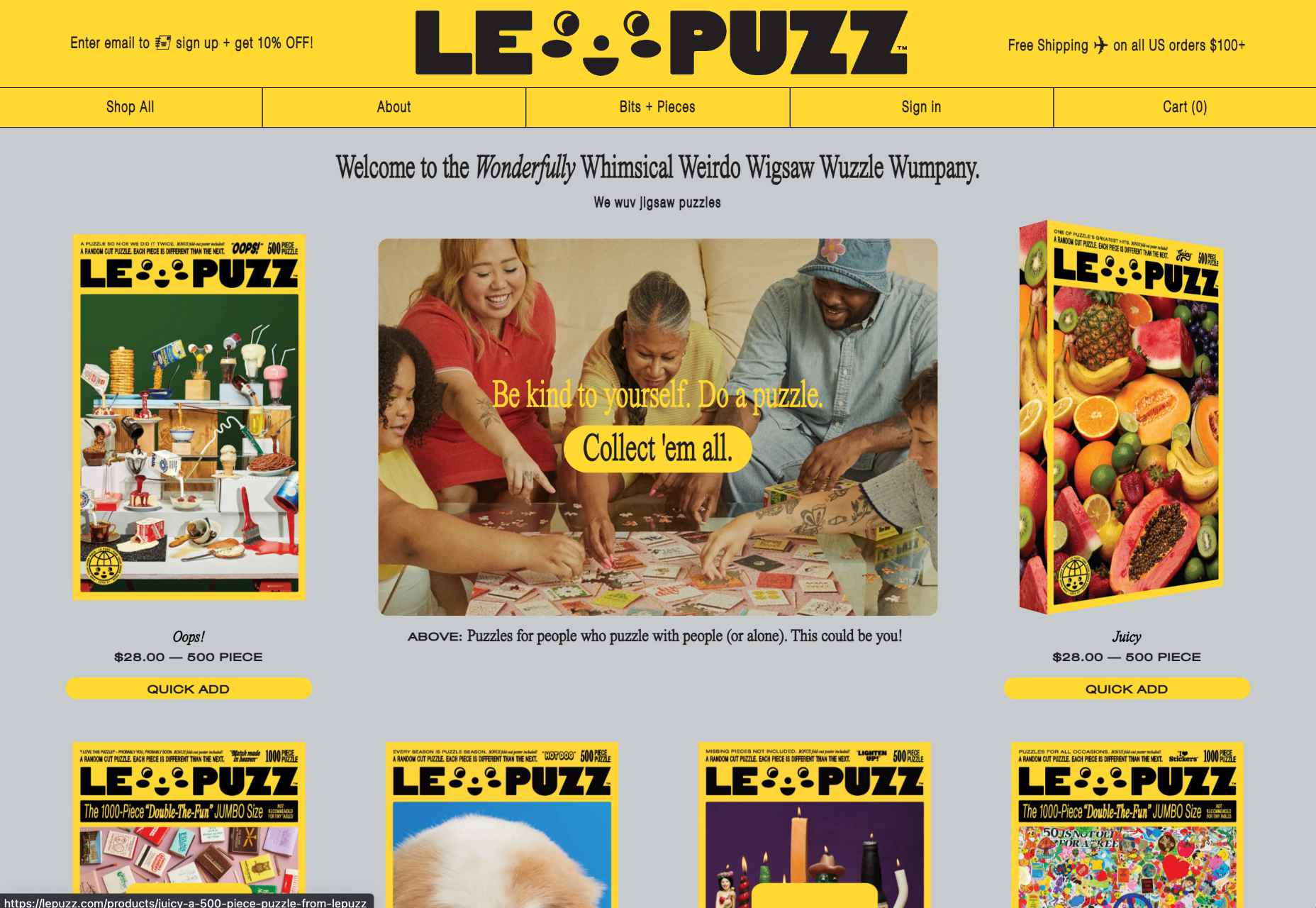
A child-like aesthetic with bright colors and bulky fonts combines with hand-drawn elements on the Le Puzz website. This is an excellent example of how web designers can use hand-drawn elements to convey a mood of creativity and fun.
Animated Elements
Finally, if you want to combine the unique nuances of hand-drawn design with the modern components of what’s possible in the digital world today, why not add some animation. Animated elements combined with illustrations can help to bring a website to life.
In the Kinetic.com website, the animated illustrated components help to highlight the punk-rock nature of the fanzine. It’s essential to ensure that you don’t go too over-the-top with your animations here. Remember that too many animations can quickly slow down a website and harm user-friendliness.
Finishing Thoughts on Hand-Drawn Elements
Hand-drawn elements have a lot to offer to the web-design world.
Even if you’re not the best artist yourself, you can still simulate hand-drawn components in your web design by using the right tools and capabilities online.
Although these features won’t fit well into every environment, they can be perfect for businesses that want to show their human side in today’s highly digitized world. Hand-drawn components, perhaps more than any other web design feature, showcase the innocence and creativity of the artists that often exist behind portfolio pages and startup brands.
Could you experiment with hand-drawn design in your next project?
The post How to Use Hand-Drawn Elements in Web Design first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.



 User Experience (UX) design and User Interface (UI) design are two terms people sometimes mistakenly use interchangeably. While aspects of each are interconnected, there are distinct differences between UI/UX design.
User Experience (UX) design and User Interface (UI) design are two terms people sometimes mistakenly use interchangeably. While aspects of each are interconnected, there are distinct differences between UI/UX design.
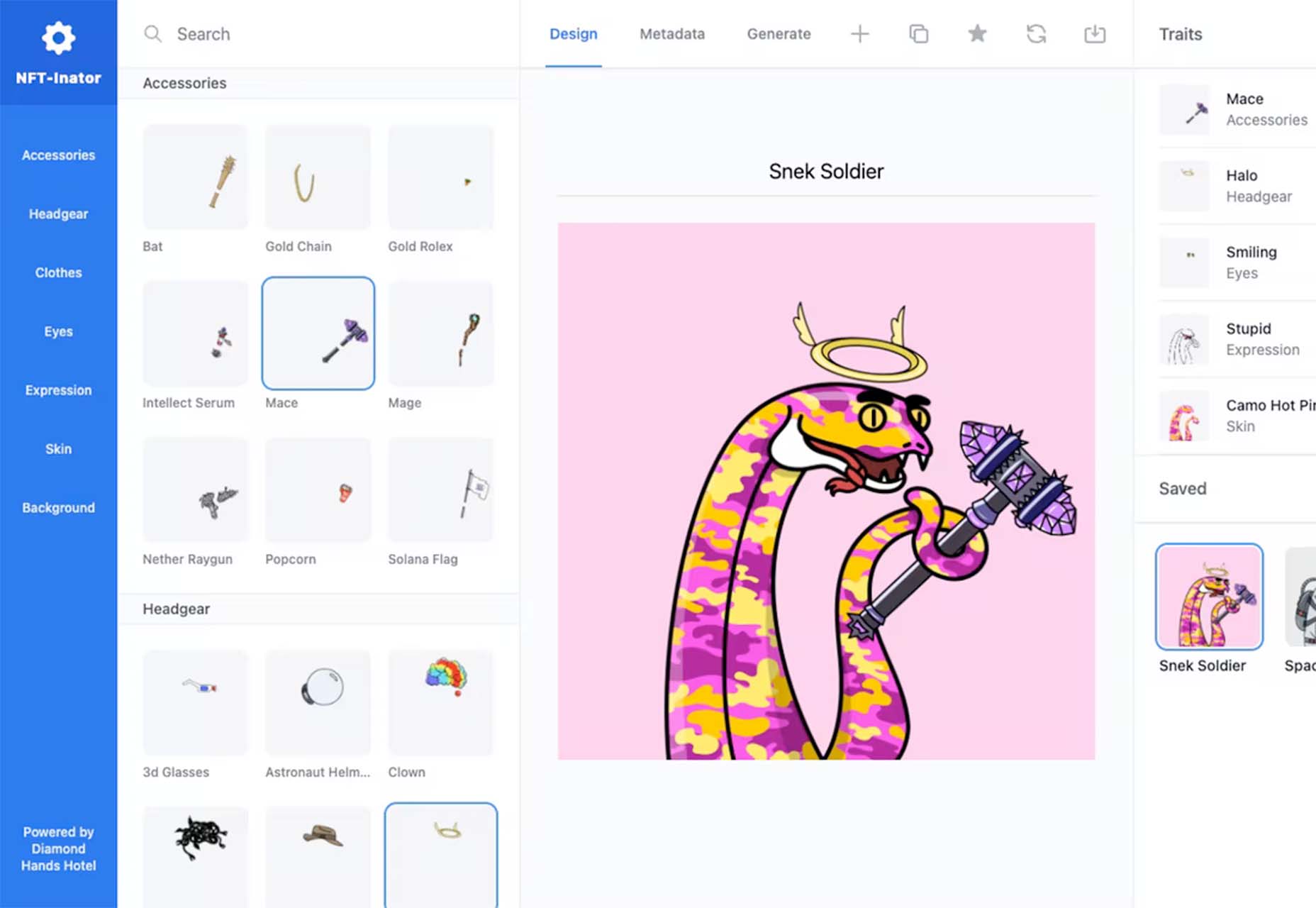
 One of the most talked-about digital elements of the new year leads our roundup of tools and resources this month – NFTs. The NFT landscape seems to be exploding right now and that includes tools for designers to get in on the game as well.
One of the most talked-about digital elements of the new year leads our roundup of tools and resources this month – NFTs. The NFT landscape seems to be exploding right now and that includes tools for designers to get in on the game as well.
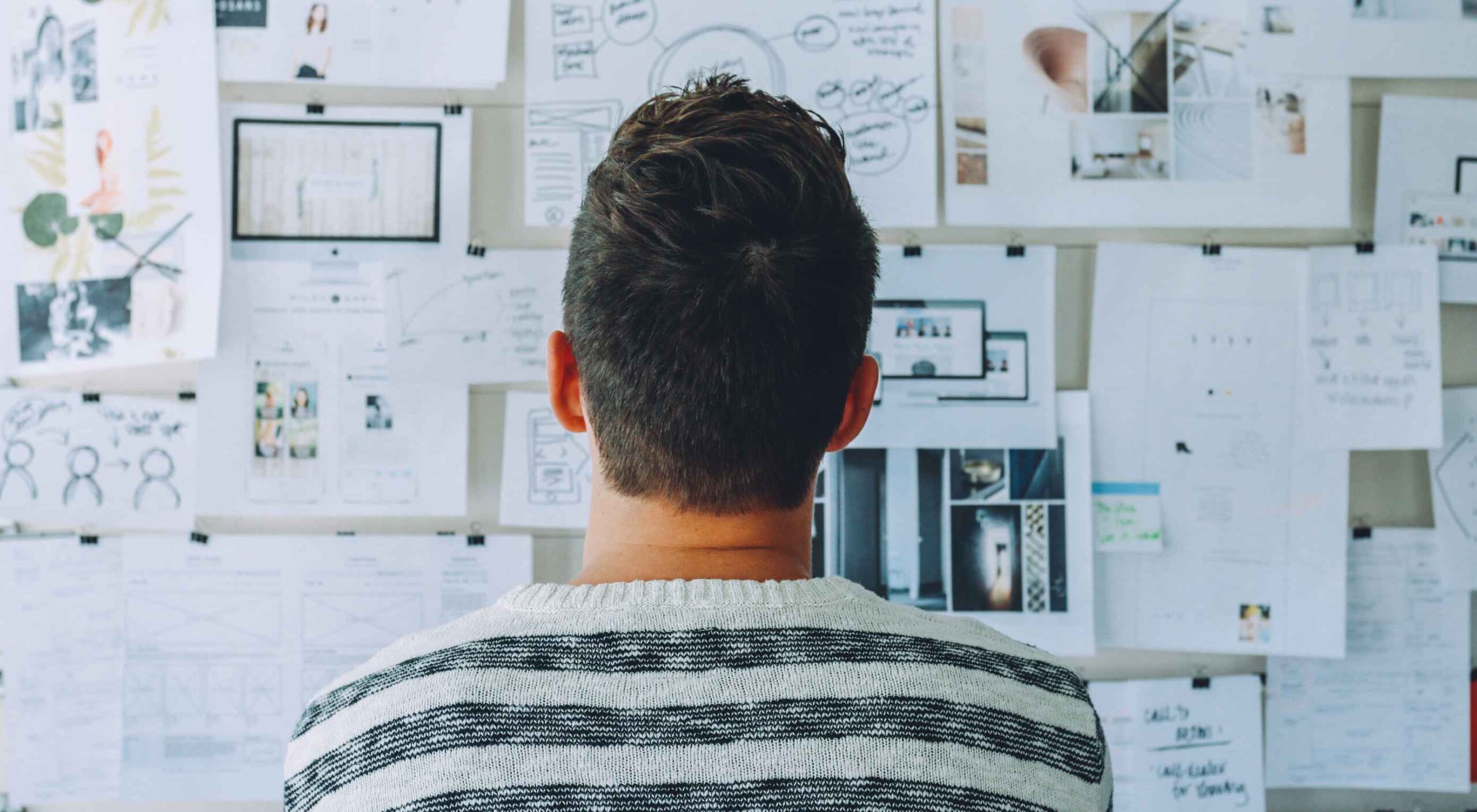













 The importance of scientific research cannot be overstated. User research is crucial to the success of any UX design, and this article will explain all the reasons why.
The importance of scientific research cannot be overstated. User research is crucial to the success of any UX design, and this article will explain all the reasons why.
 There are a lot of factors that contribute to a
There are a lot of factors that contribute to a 
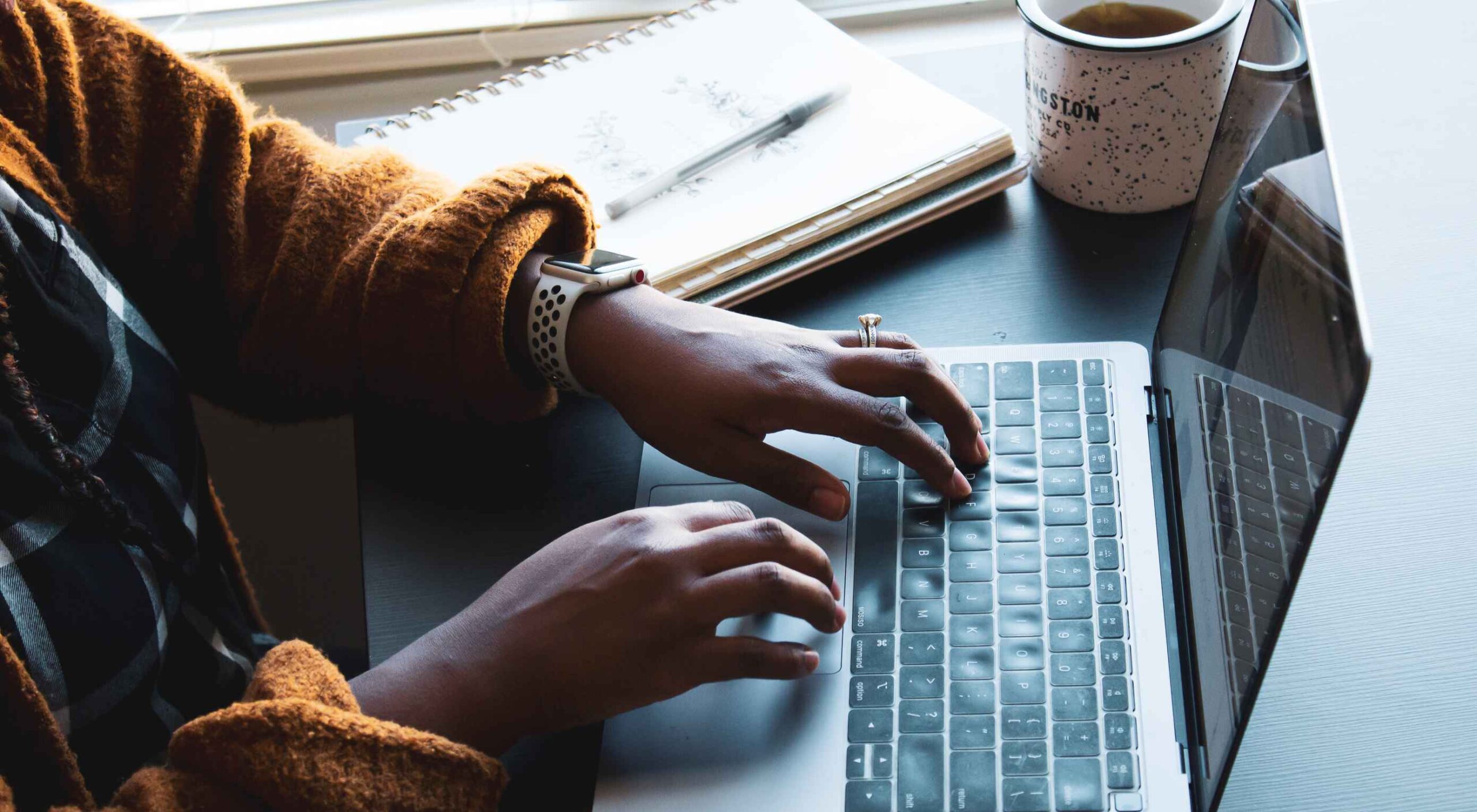





 Many people believe that UX design is all about creating slick, engaging images and top-notch user flows. While those things have their merits, UX designers do much more than that.
Many people believe that UX design is all about creating slick, engaging images and top-notch user flows. While those things have their merits, UX designers do much more than that.
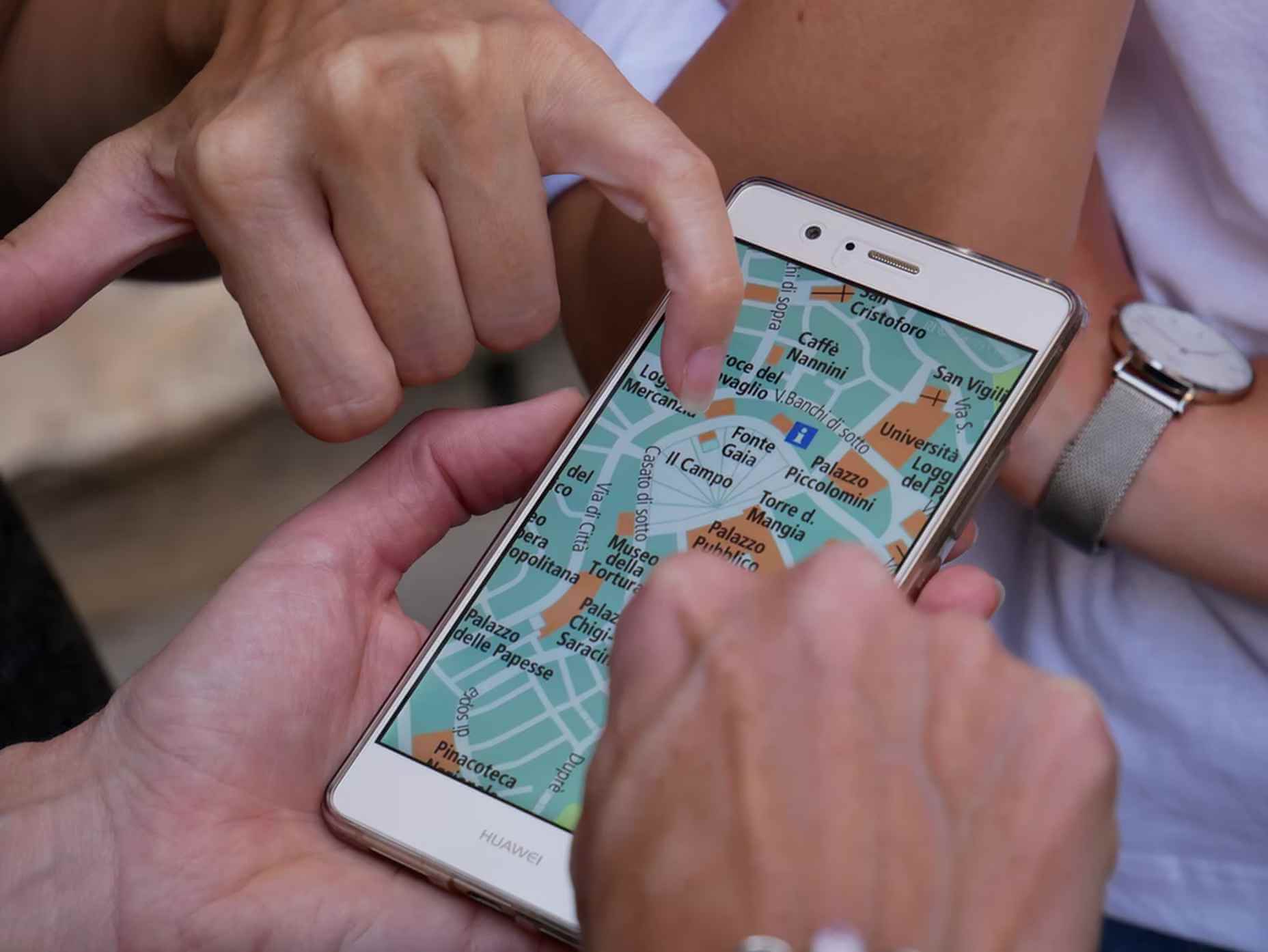
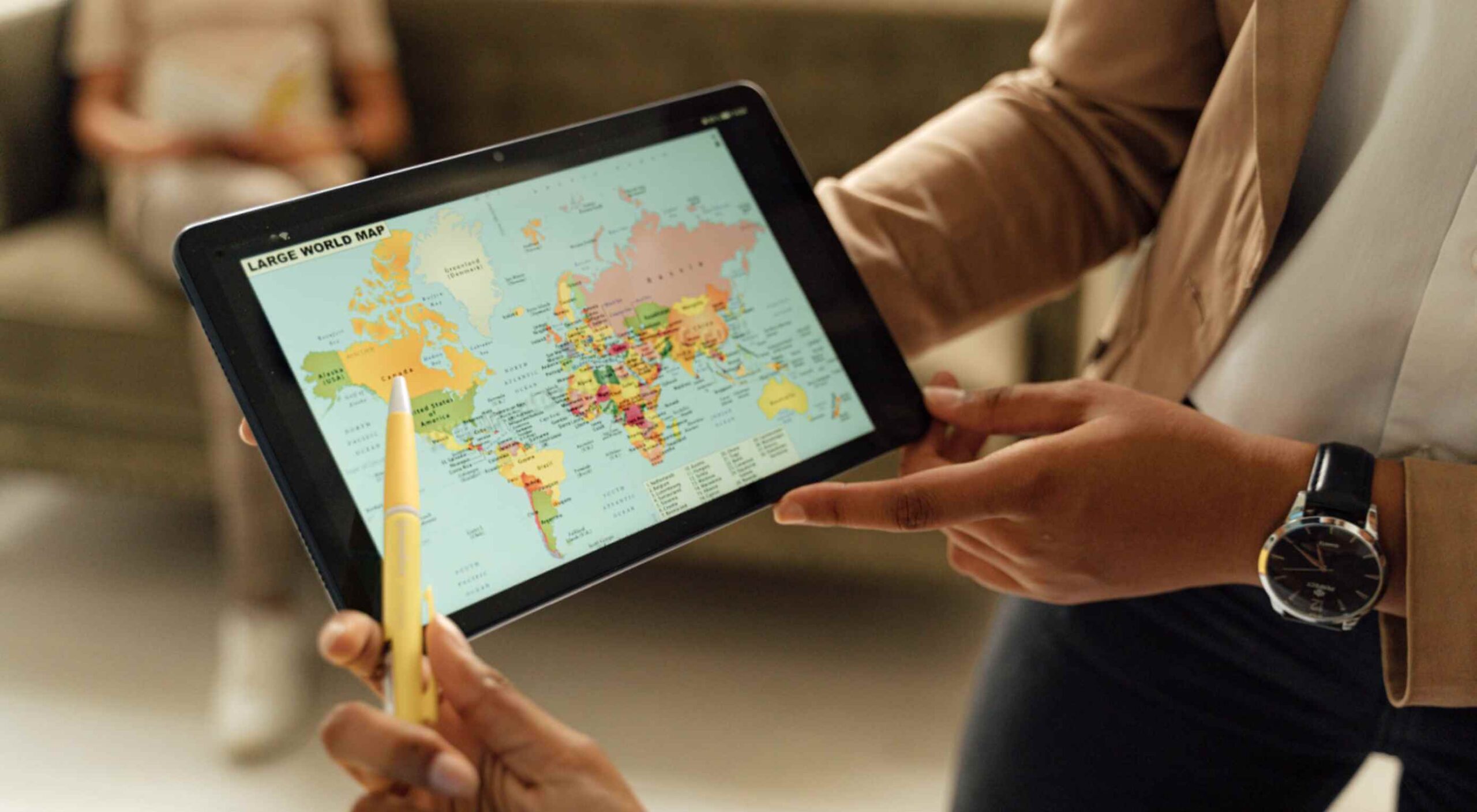 Maps are a fascinating method for delivering content. At their best, they can create an intuitive way of presenting information and interacting with it. This is the advantage that digital maps, through mobile apps and websites, have over print maps and images where no interactivity is possible.
Maps are a fascinating method for delivering content. At their best, they can create an intuitive way of presenting information and interacting with it. This is the advantage that digital maps, through mobile apps and websites, have over print maps and images where no interactivity is possible.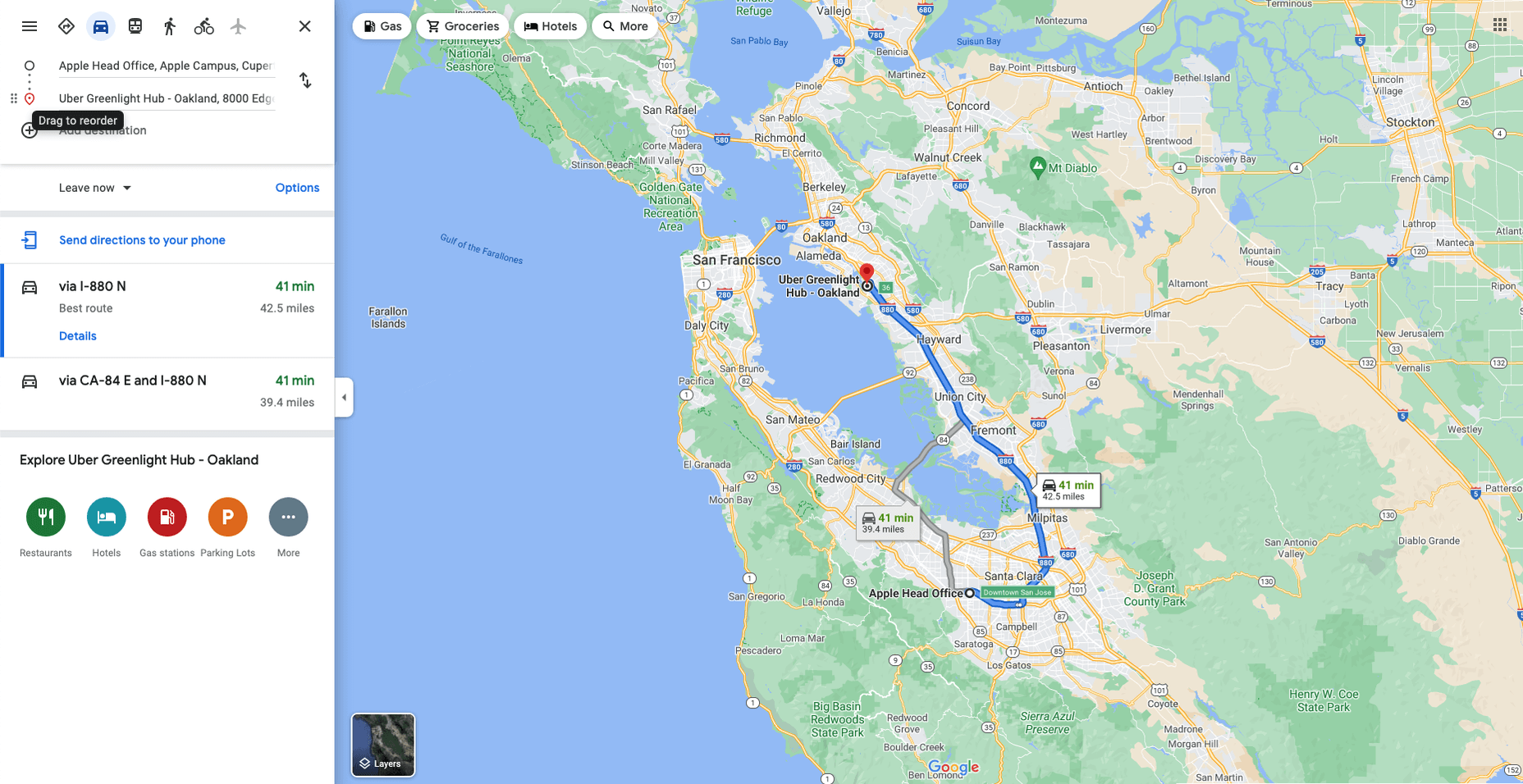
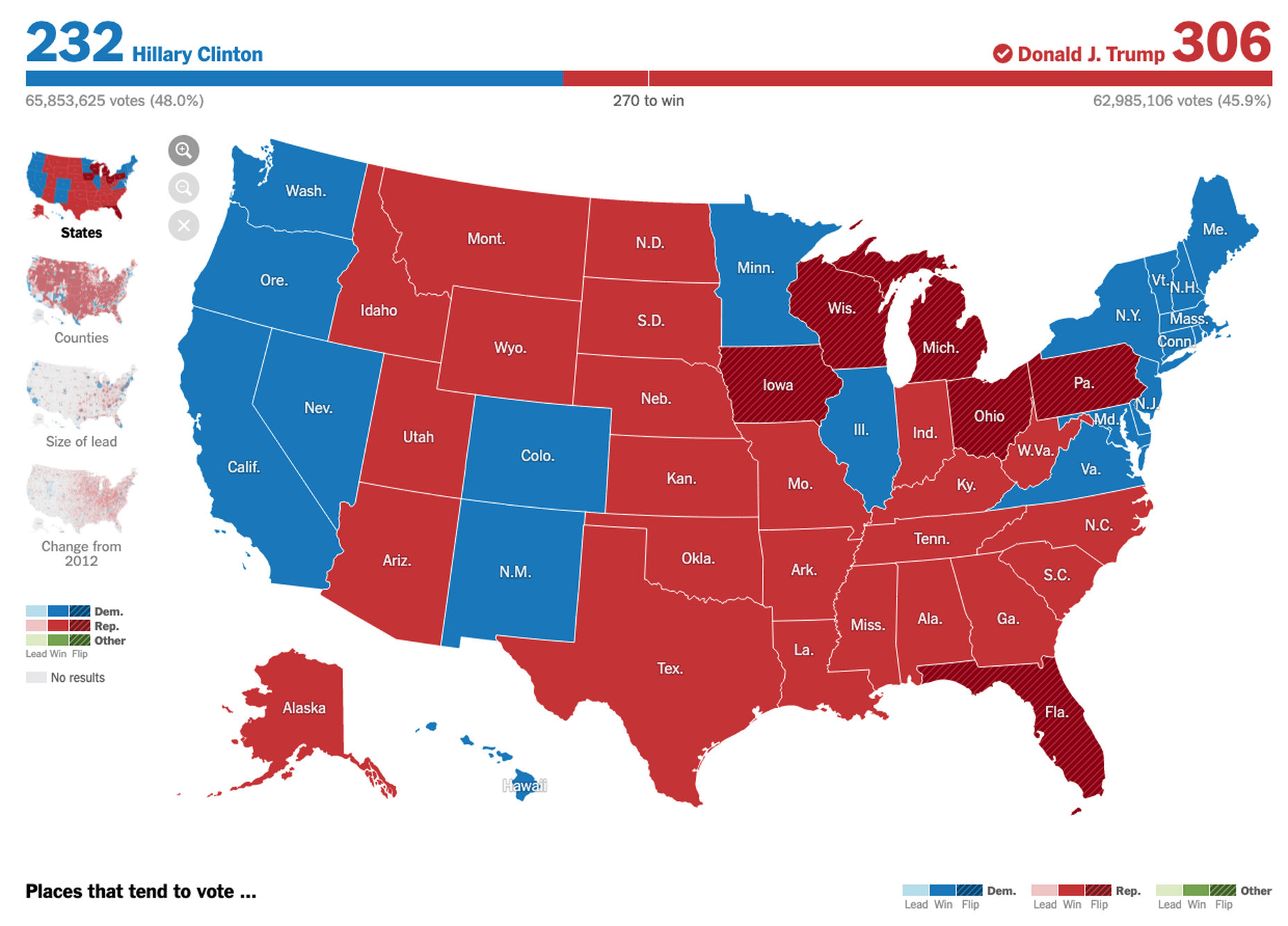


 According to Klipfolio research, users spend on average
According to Klipfolio research, users spend on average 
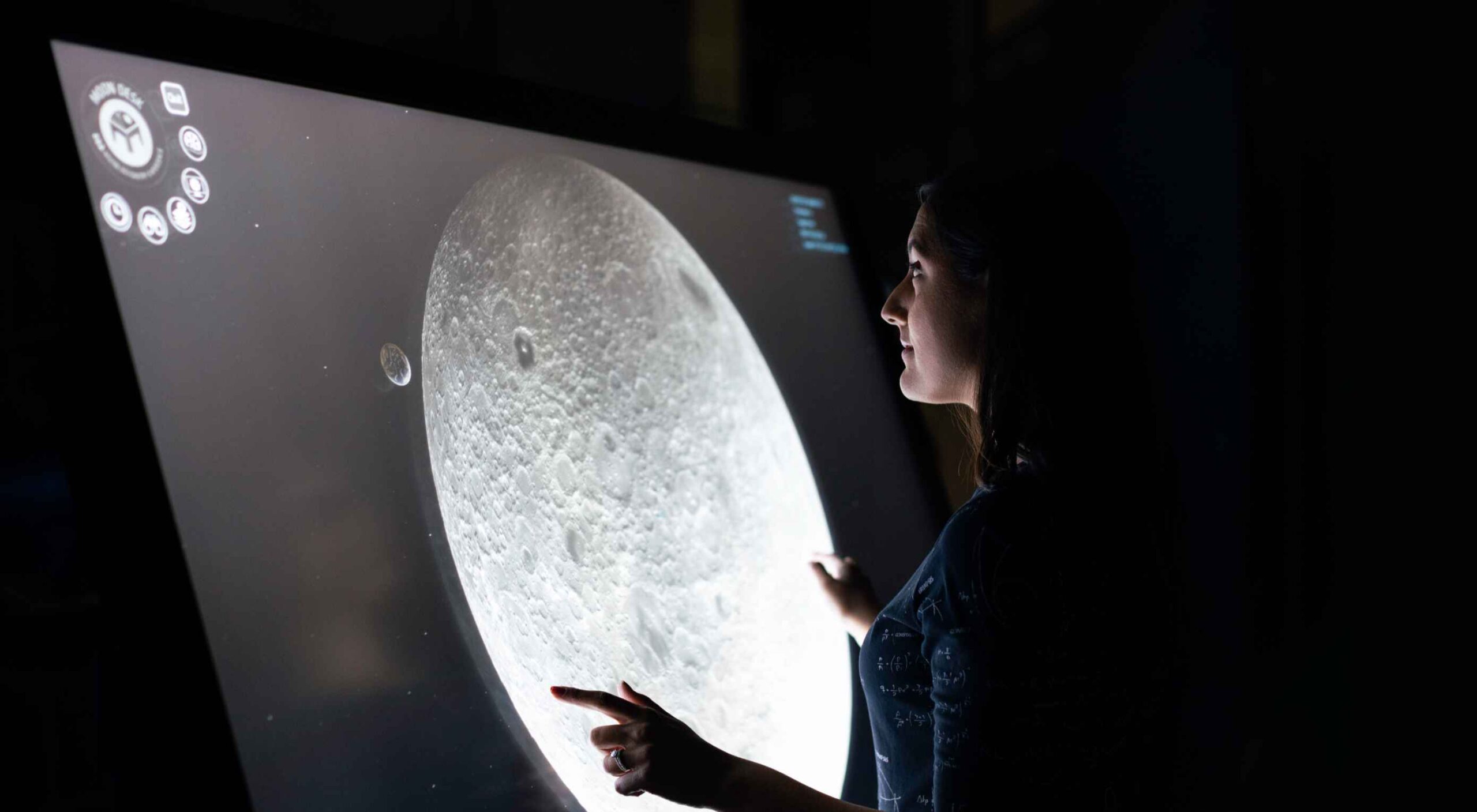

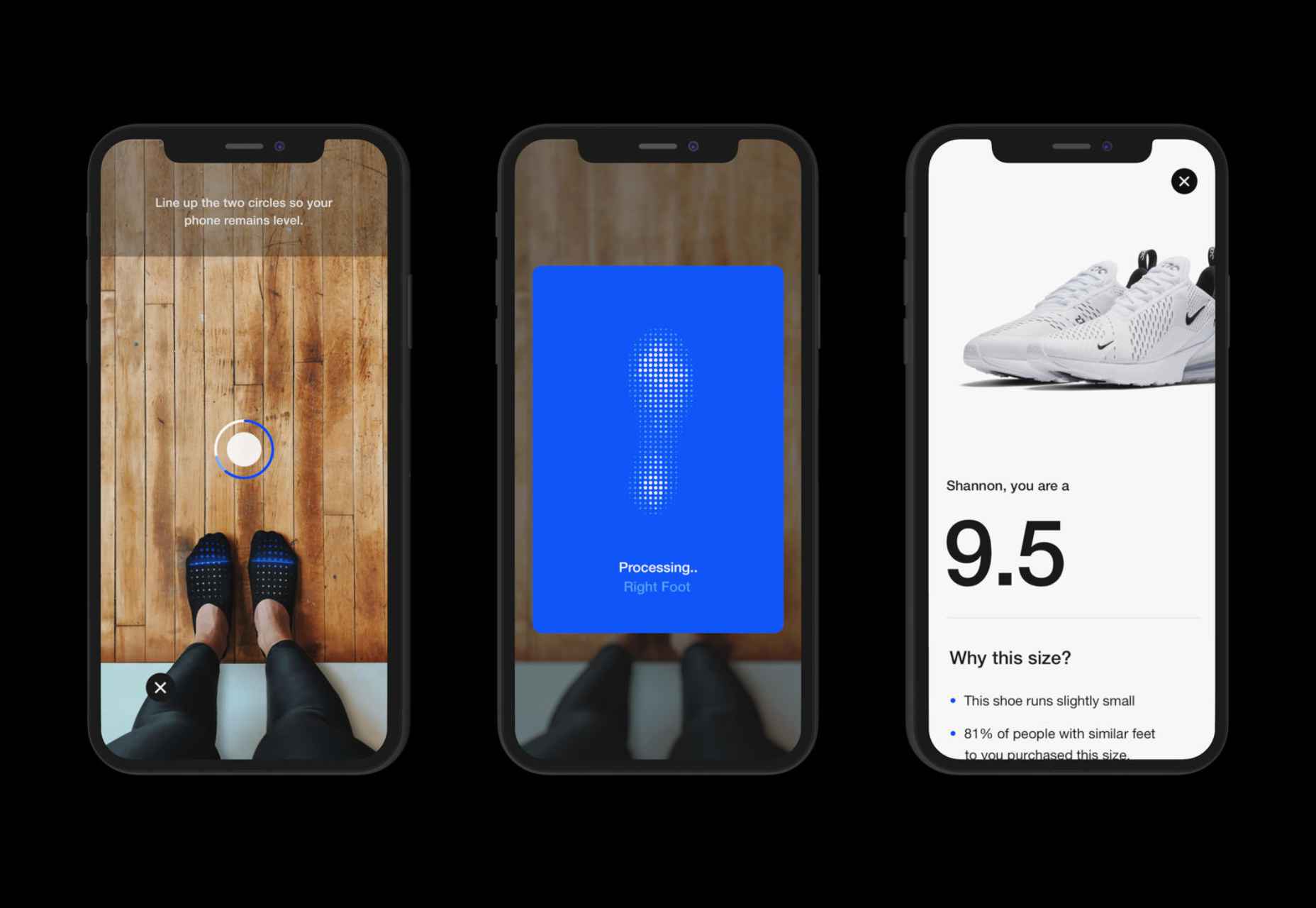

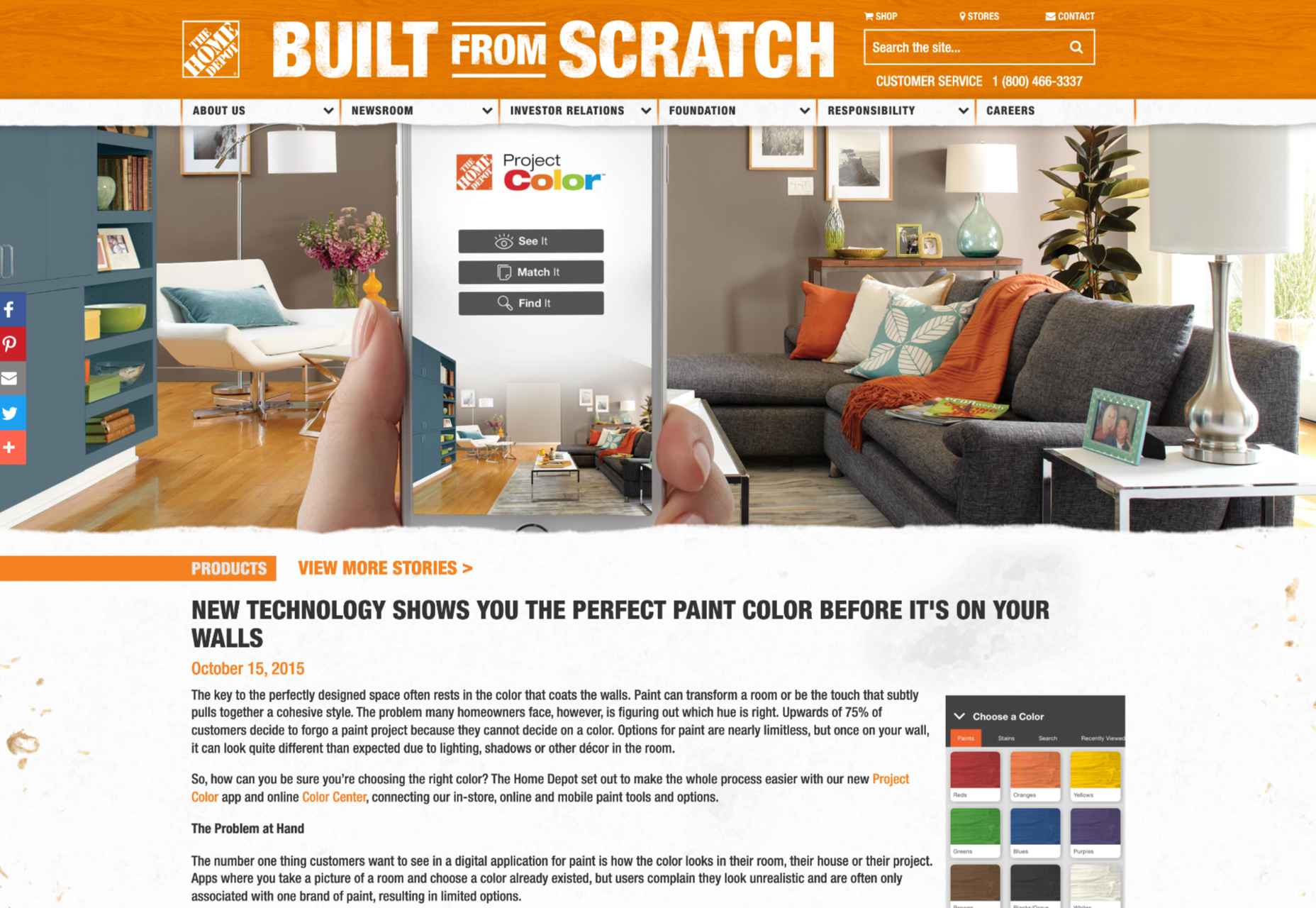
 AR (Augmented Reality) continues to build as one of the most exciting technology innovations to appear in recent years. More accessible than virtual reality experiences, since no specialist headset is required, AR has quickly emerged as a crucial tool for building unique experiences.
AR (Augmented Reality) continues to build as one of the most exciting technology innovations to appear in recent years. More accessible than virtual reality experiences, since no specialist headset is required, AR has quickly emerged as a crucial tool for building unique experiences.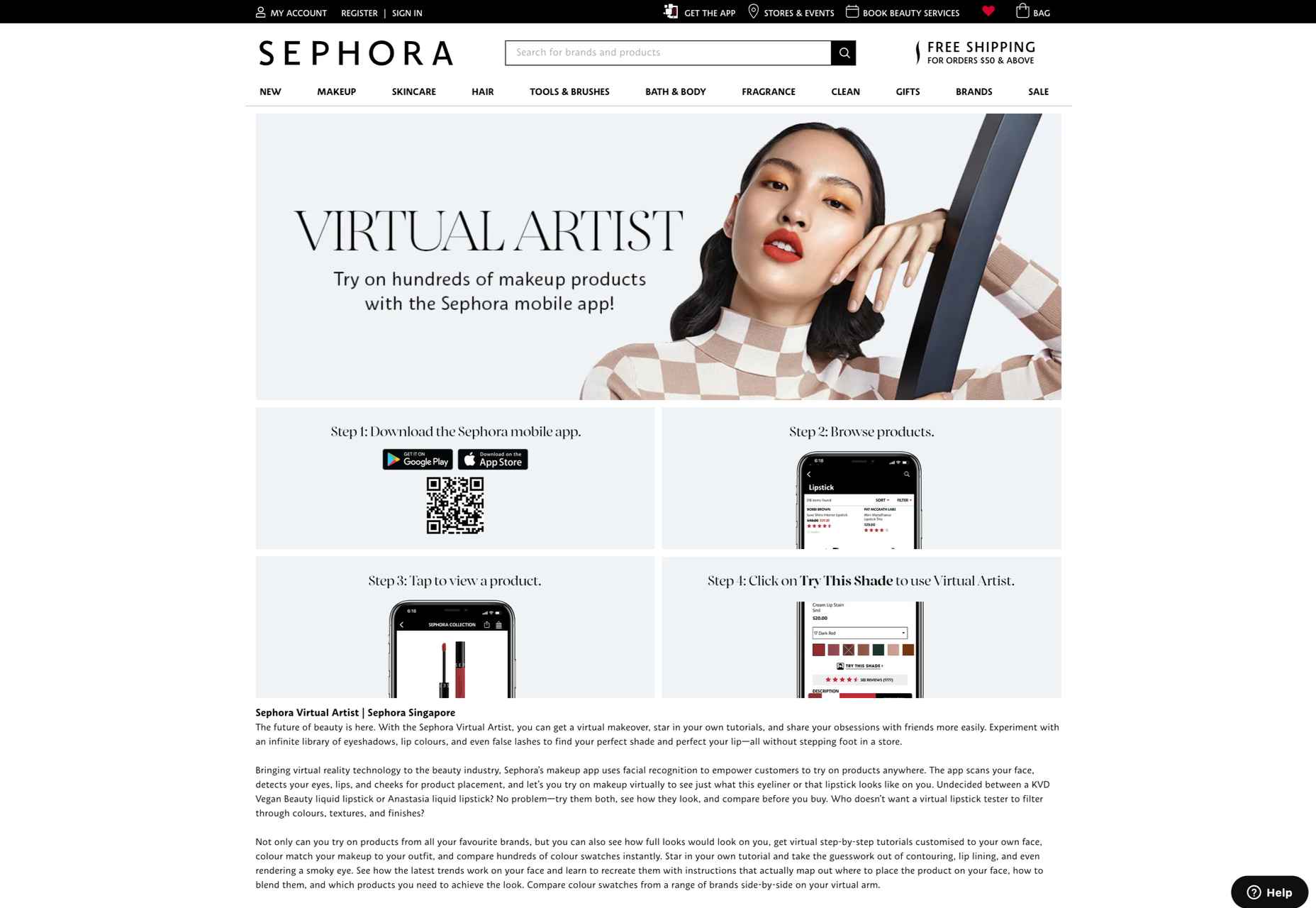

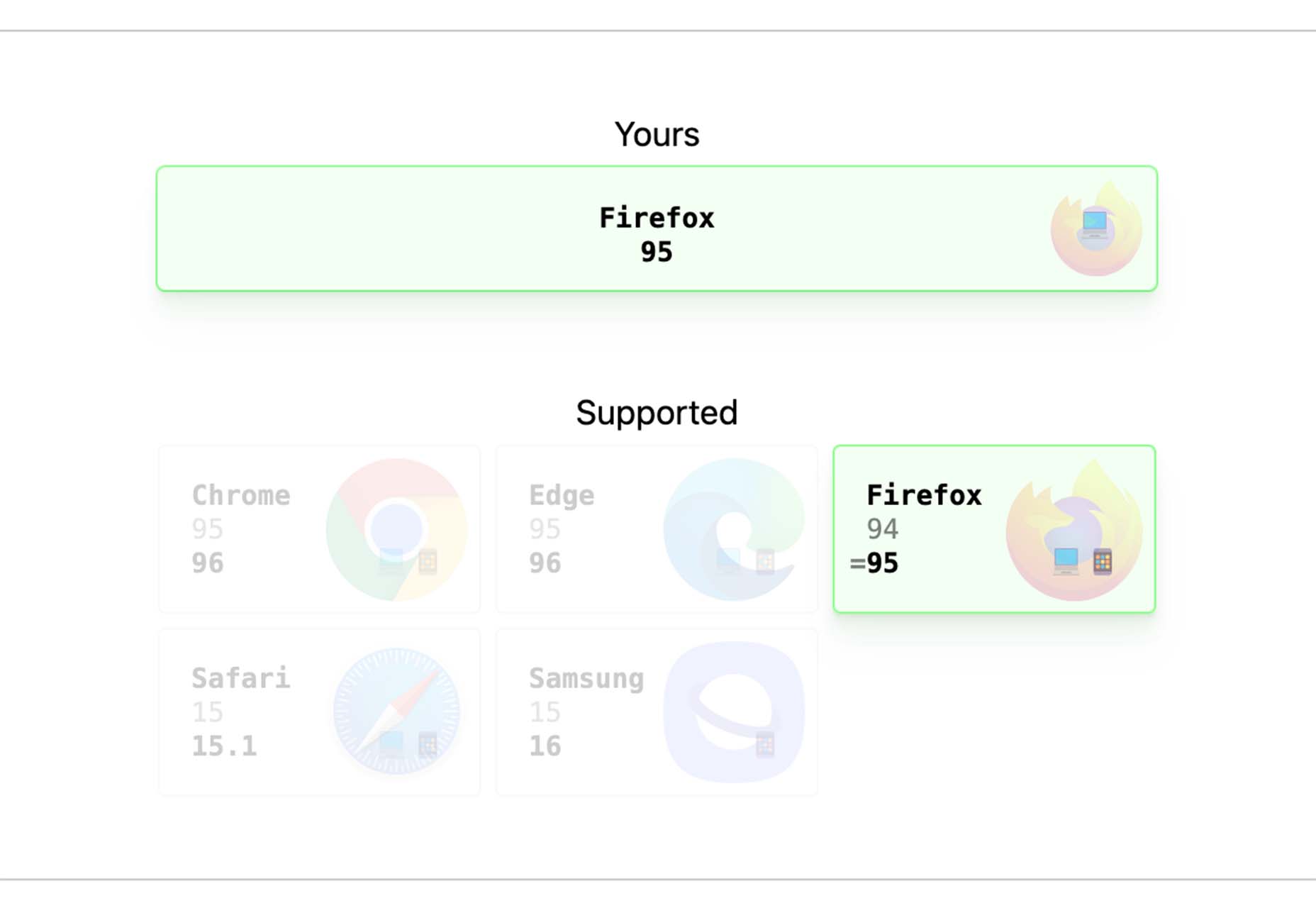
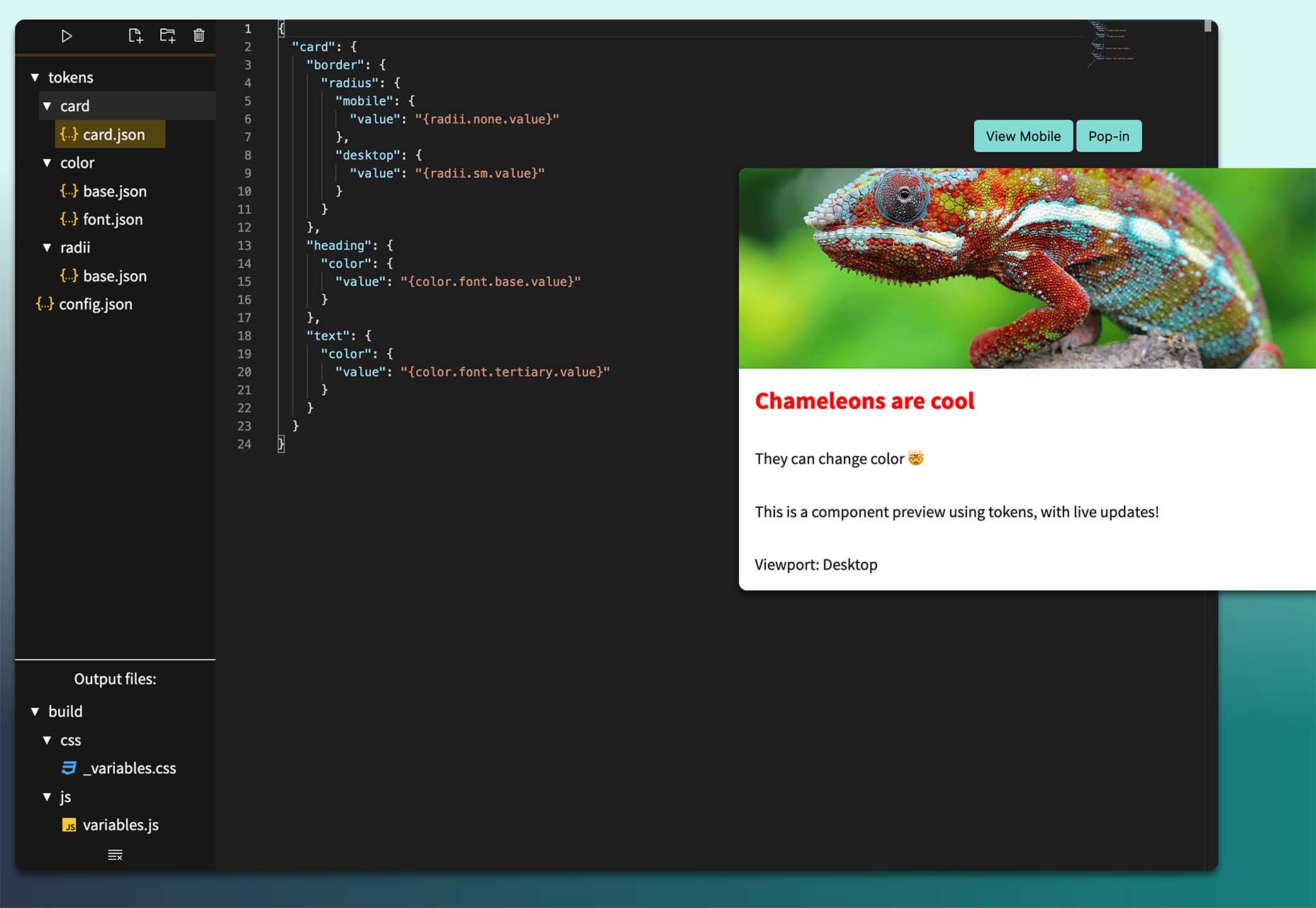
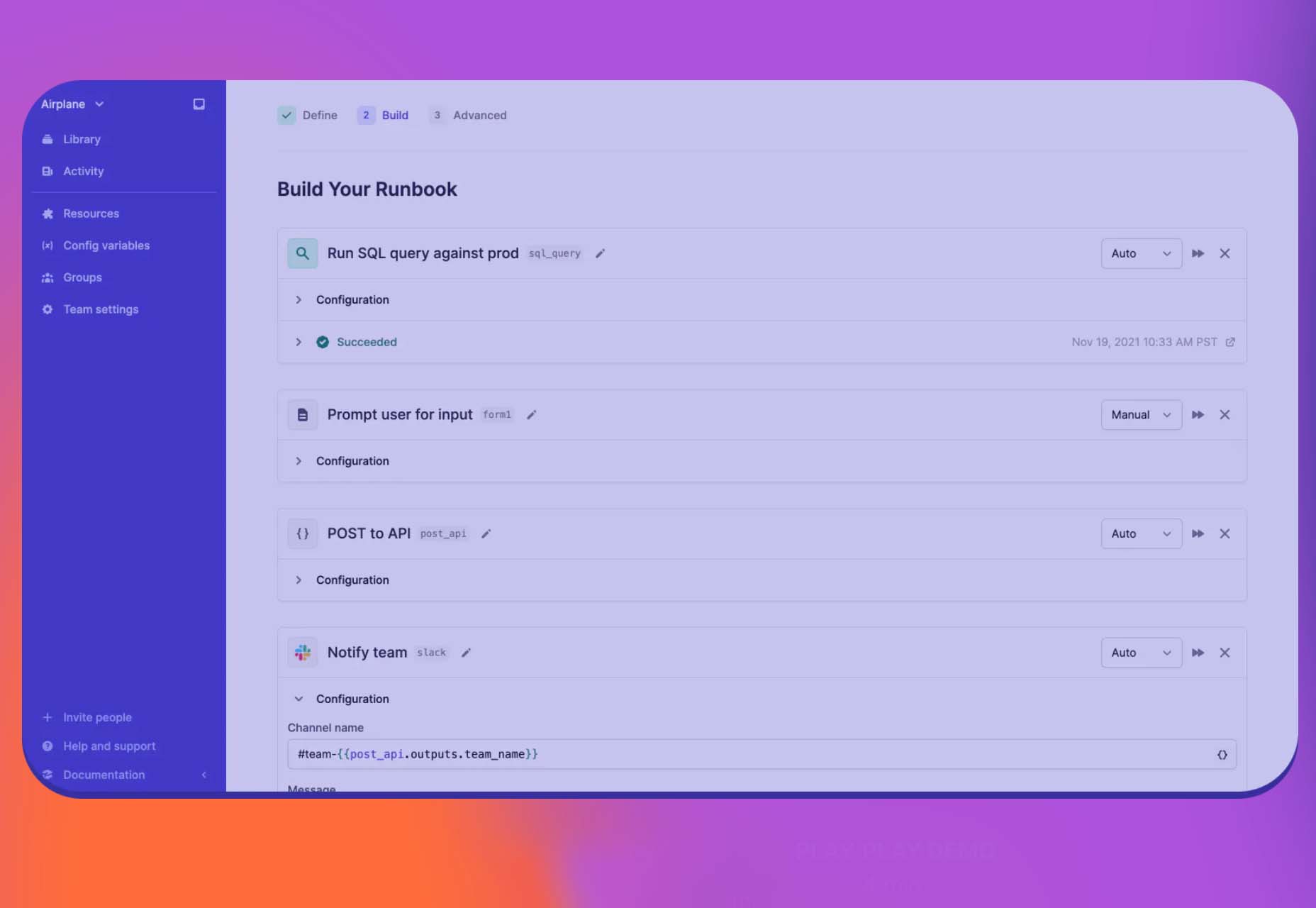
 The year’s winding down as everyone segues into a much-needed holiday R&R. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t some awesome new tools and resources for website design projects.
The year’s winding down as everyone segues into a much-needed holiday R&R. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t some awesome new tools and resources for website design projects.