Voice is one aspect of technology that is getting bigger and bigger, and showing little sign of relenting. In fact, 2019 data revealed that 22% of UK households owned a voice-controlled digital home assistant device such as an Amazon Echo or Google home. This is double the figure recorded in 2017 and it is predicted that over the next five years nearly 50% of all homes will have one. Smart home adoption rates are increasing, and it shows how voice control is something we are all becoming more accustomed to.
Voice is one aspect of technology that is getting bigger and bigger, and showing little sign of relenting. In fact, 2019 data revealed that 22% of UK households owned a voice-controlled digital home assistant device such as an Amazon Echo or Google home. This is double the figure recorded in 2017 and it is predicted that over the next five years nearly 50% of all homes will have one. Smart home adoption rates are increasing, and it shows how voice control is something we are all becoming more accustomed to.
With these high figures, does it follow that voice should be something web designers build into sites? Or is it merely a gimmick that will die out and render sites with hardware and complex design issues? You only have to look at the failed introduction of Google glass to see that certain technological advancements don’t always have the outcome that might be expected.
Multiple Voices
One of the first issues with voice is establishing whether you want sites to recognise everyone’s voices, or just those who have registered. If you’re using the site in a crowded room will it pick up on snippets of conversation from others and think these are instructions? Google Home has a feature whereby you have to register your voice with its app to use more personalised features such as the shopping list. Is this the sort of thing websites would need?
Accents
The implementation of voice is complex, not only does it need to understand certain languages (such as English), but all the accents and variations too. With 160 English dialects alone, that is a lot that the technology needs to understand – not including mispronunciations, slang, and colloquialisms. Also, if a site is used all over the world (which many are) how many languages will it need to know?
Privacy Issues
if there are clips of your voice out there on the web…it can easily be imitated
If a website involves a feature such as online shopping or other functions which require sensitive details to be input, this could put people off using voice. Users need to know where this saved data is being stored, how it will be used and if it is secure. In 2018, HMRC had signed up about 6.7 million people to its voice ID service and HSBC said over 10,000 were registering each week. This shows many trust the service, but experts say that if there are clips of your voice out there on the web (such as in a podcast) it can easily be imitated. Bringing with it security and privacy issues.
According to futurologist Dr Ian Pearson, who invented the text message back in 1991, it won’t be long until we can complete a financial transaction with just a few words and a gesture. This can be a time-saver for things such as online shopping, but we need to ensure there are the correct security steps in place.
Users Don’t Talk The Way They Type
When speaking we tend to use shortened and more colloquial language as opposed to when we type. The voice function on a website will need to be able to adapt for this. One example is if you are filling in a form or comment box by voice for a website, you will need to tell it what to punctuate, letting it know where to add a comma, exclamation mark etc.
Website Processes Need to be Simpler
With the web as we use it now, we often browse through pages, reading other snippets of information before clicking through to the page we want. With voice recognition it will cut out these middle steps. For example, if you are looking for a recipe of something specific, you will just say the command “Show me the … recipe” and it will take you straight there. This direct access to what we are looking for could lead to a simplification of websites.
Regular Updates
With websites as they are now, they need updates semi-regularly, depending on how they are built, how complex they are, and what features we have built into them. A voice-based site will need updating regularly, whether to add new words or processes or to keep up with the fast-adapting technology. It might end up being quite a complex process.
Mistrust
While there are more of us now than ever using voice control via tech such as Alexa, Google, and Siri, there is still a level of mistrust over it. It’s still not quite clear where data is being stored, if it is being stored, and how easy it could be to abuse.
Larger Storage and Bandwidth
If a site is built for voice, will it utilise a ready-built plugin or will it have its own software built by developers? Will this feature require a greater amount of storage and bandwidth to cope with it? These are further factors to consider when thinking of the future of implementing voice to websites.
We Still Don’t Know Where It Will Go
Voice technology while working in some respects, is still a bit of a grey area when it comes to future use. Will it be the next big thing as many have predicted, or will it simply die down?
Look at Google Glass – highlighted as the big new technology, they soon died down and were eventually discontinued. Smart watches were another thing. You can see their initial downfall by reading an article published in 2017 about smartwatches – how major smartwatch makers such as Apple and Samsung rushed into the market before the technology was ready and they subsequently failed. Motorola exited the smartwatch market, Pebble and Jawbone shut down and Fitbit sold 2.3 million fewer devices than in their previous quarter. It was perceived as being a fad. However, fast forward to 2020 and more people than ever are wearing and using smartwatches. The smartwatch market was valued at shipment volumes of 47.34 million in 2019 and is expected to reach 117.51 by 2025, reaching a growth of 15.4 over the next five years.
Will voice follow a similar trend?
No More Impulse Buying
People enjoy browsing websites and many businesses rely on user’s impulse buying and ask their websites to be designed to reflect this. With voice taking you directly to the page’s users want to find, will they bypass these potential selling traps and just buy what they want – rather than added extras? Will it end up being a negative for businesses and see users not as satisfied for the experience?
Voiceless Still Matters
You will also have to remember that not all devices might work with voice, or people might be browsing somewhere where voice cannot be used. This means in the design process it needs to work both for voice instruction and manual use. It needs to work just as well for both to ensure the customer journey isn’t affected.
There are many ways voice can affect how we design websites in the upcoming future. It’s important to take note of market trends and usage – seeing how people use voice and thinking of the customer journey. It’s vital we don’t forget the end goals of websites – whether it’s to inform or to sell, the implementation of voice needs to assist this process not make it harder.
Featured image via Unsplash.


 When analysts for professional sports teams noticed that marketing promotions that included the team’s logo vastly outperformed similar creative assets that featured player imagery — something which, to the casual observer, this may simply sound like good analyst work — it showed something significant: creatives rarely receive an analytical assessment of their work.
When analysts for professional sports teams noticed that marketing promotions that included the team’s logo vastly outperformed similar creative assets that featured player imagery — something which, to the casual observer, this may simply sound like good analyst work — it showed something significant: creatives rarely receive an analytical assessment of their work.
 A seasonal change is on the horizon and that always has me looking to refresh projects. This month’s design trends provide a few different ways to do that without ripping up your entire website.
A seasonal change is on the horizon and that always has me looking to refresh projects. This month’s design trends provide a few different ways to do that without ripping up your entire website.









 I often see freelancers on social media asking what the secret is to working fewer hours, making more money, and helping new clients to find them. While those things tend to happen the longer you’ve been freelancing, it doesn’t happen without some effort.
I often see freelancers on social media asking what the secret is to working fewer hours, making more money, and helping new clients to find them. While those things tend to happen the longer you’ve been freelancing, it doesn’t happen without some effort.





 Google resembles an iceberg: there’s the part above the water we can see and use everyday; there’s also the part beneath the water, that we don’t see and know little about.
Google resembles an iceberg: there’s the part above the water we can see and use everyday; there’s also the part beneath the water, that we don’t see and know little about.


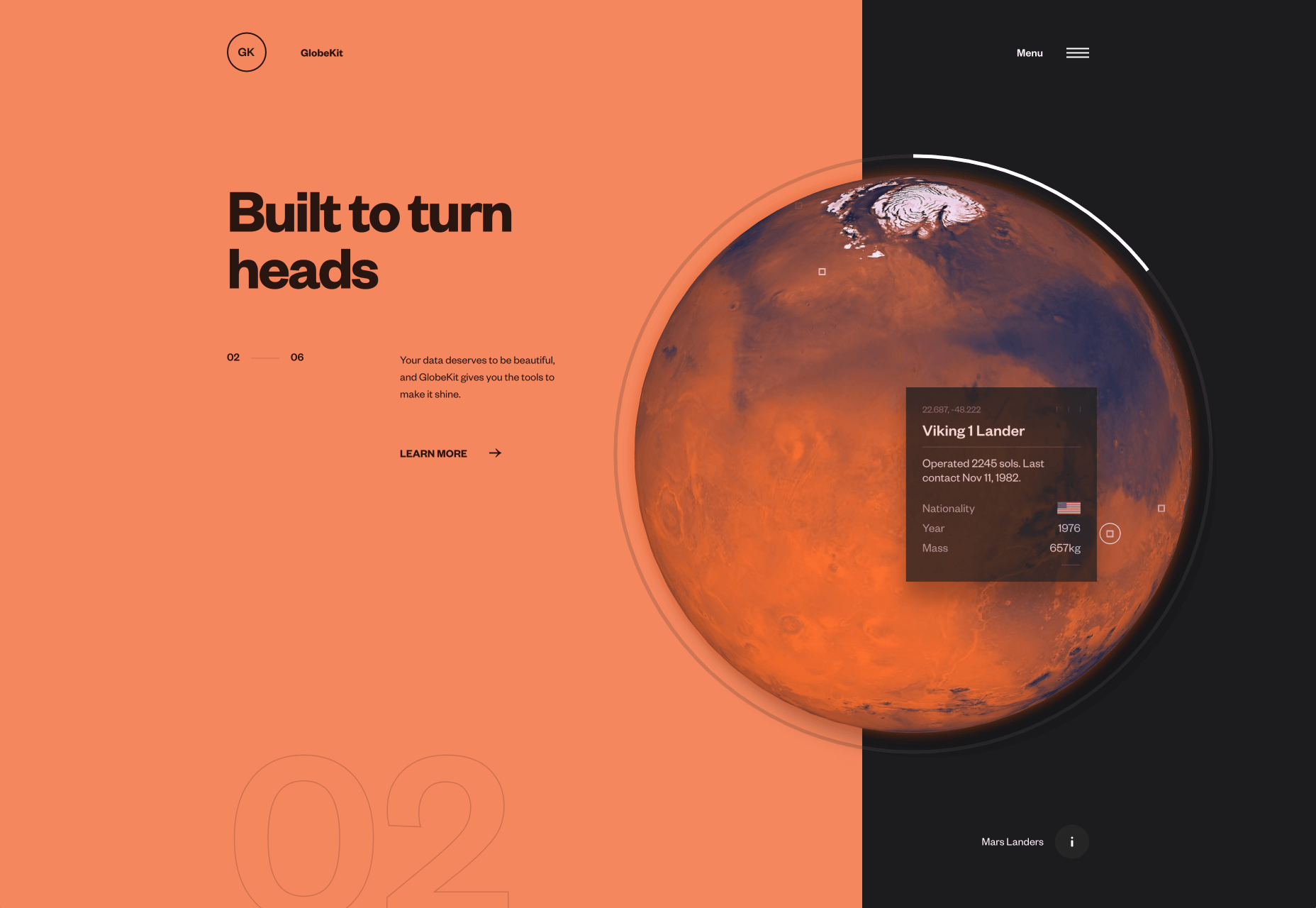
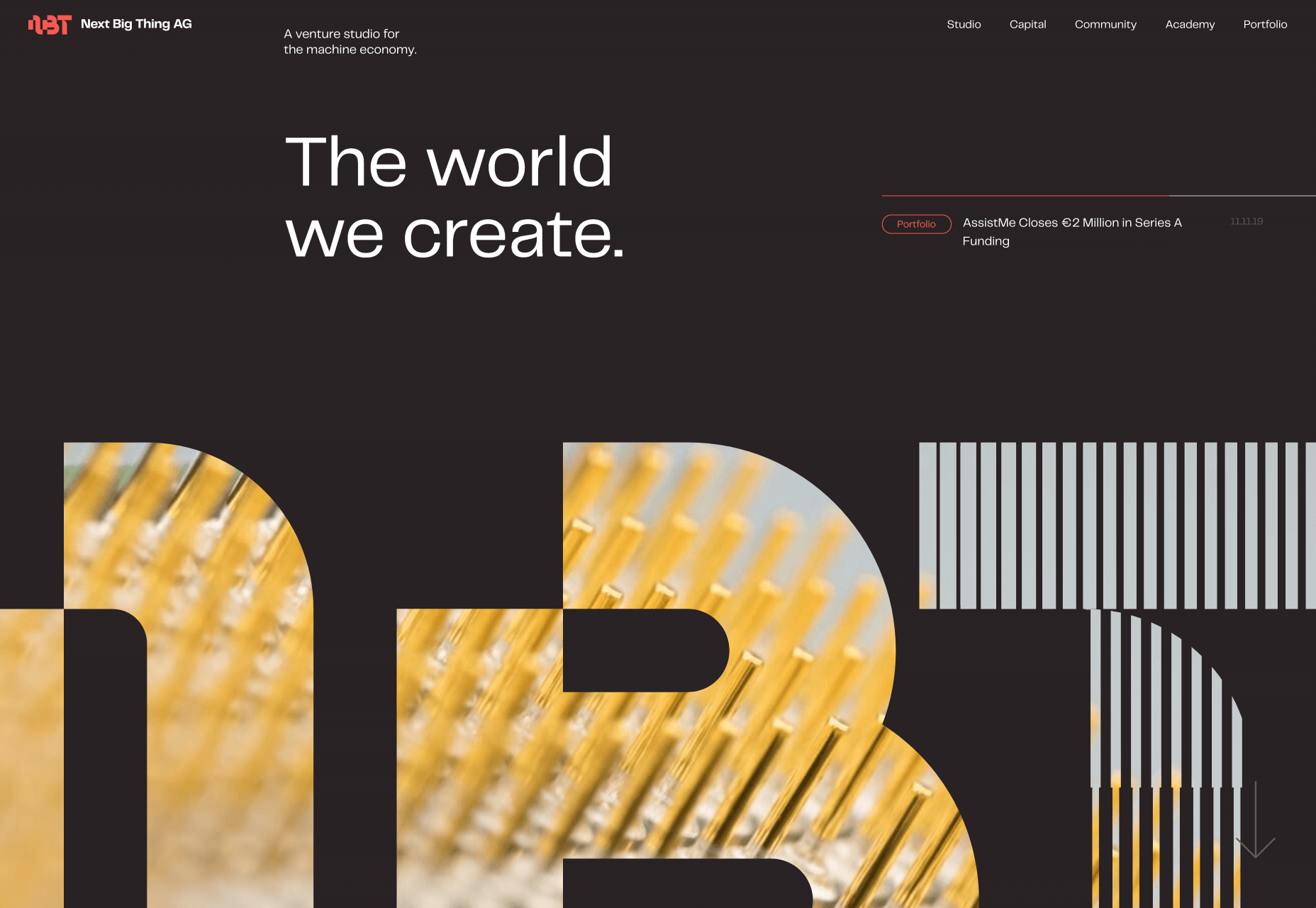
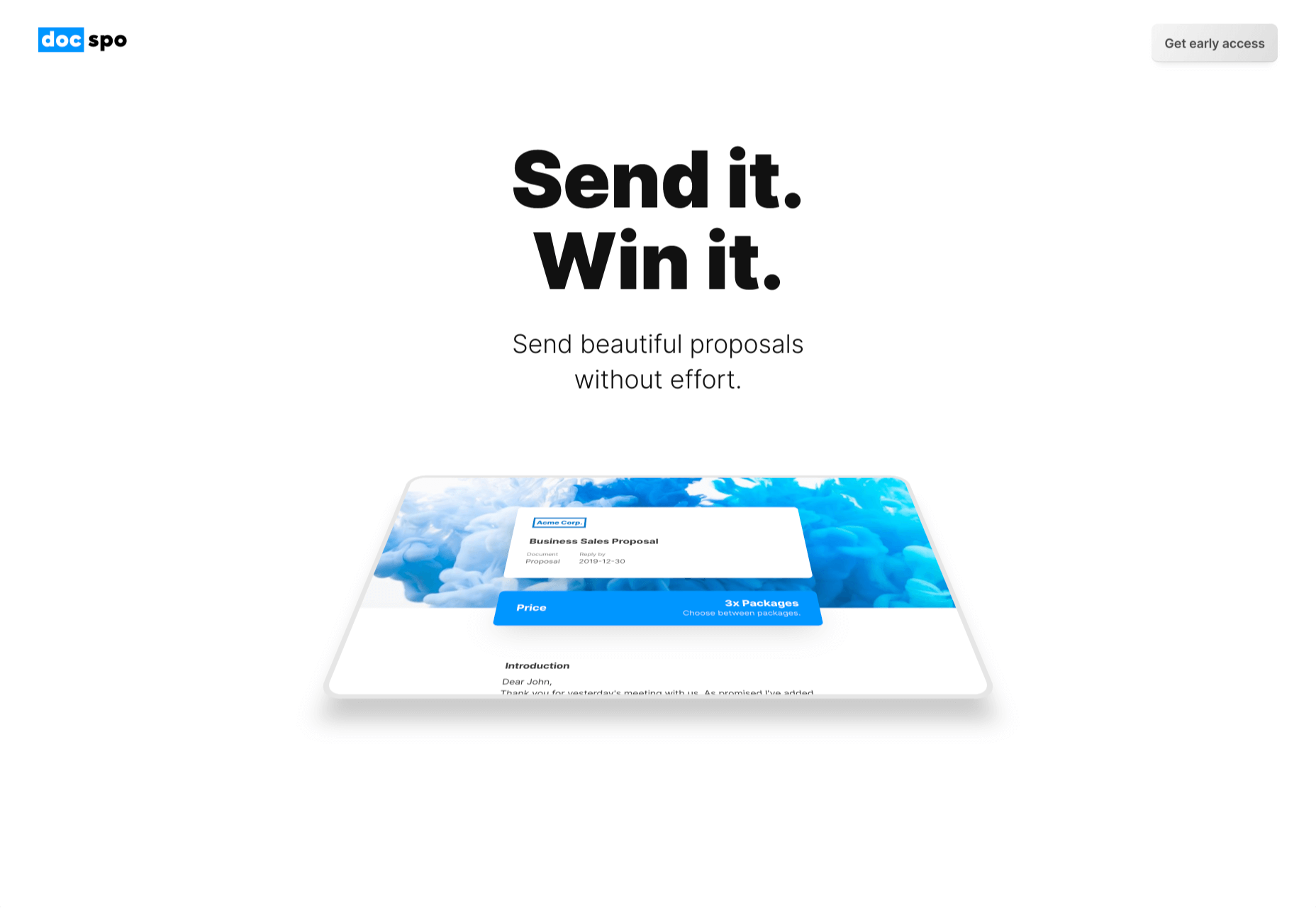
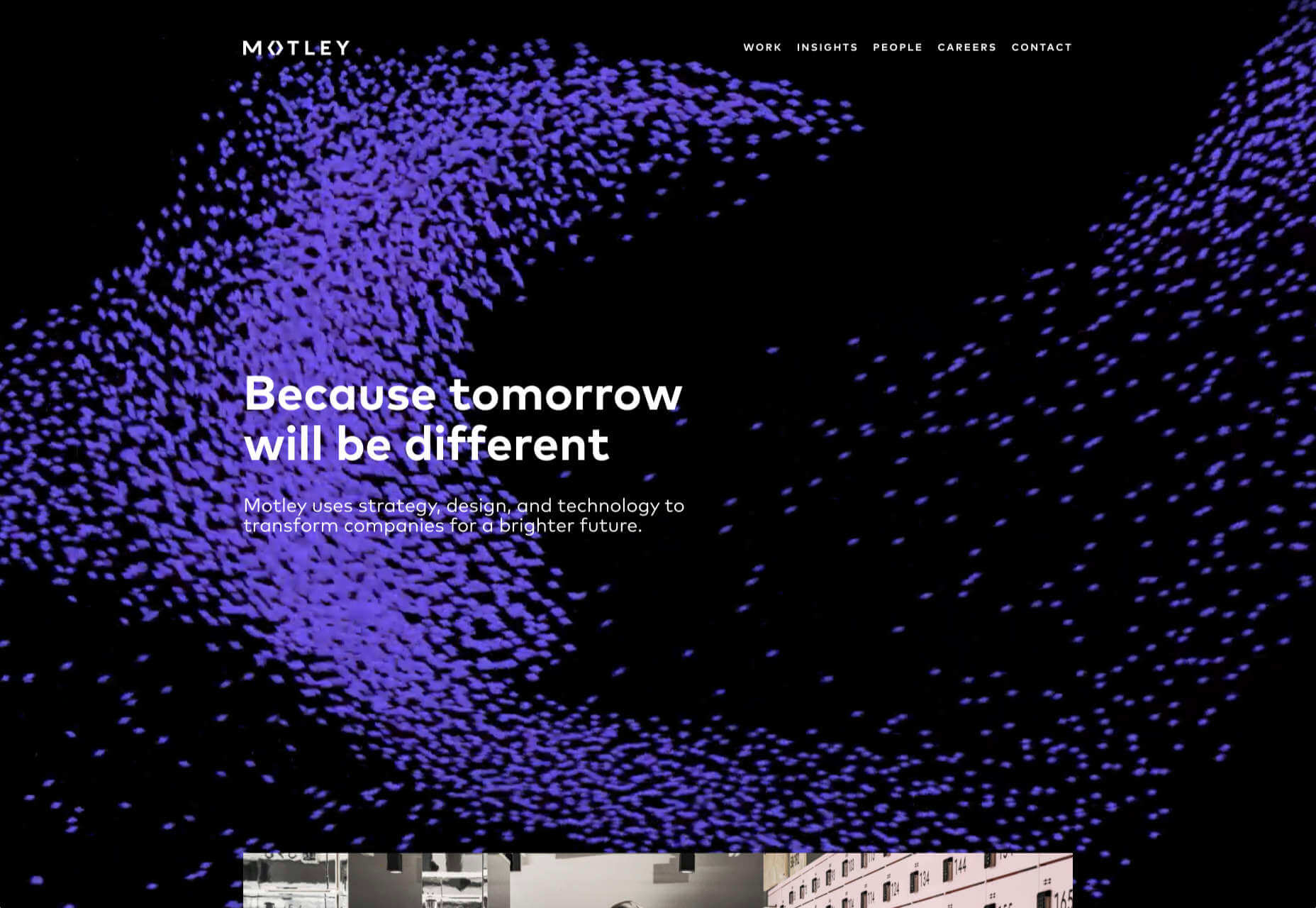
 In this month’s collection of the freshest web designs from the last four weeks the dominant trend is attention to detail.
In this month’s collection of the freshest web designs from the last four weeks the dominant trend is attention to detail.