 Ten years ago, people began talking about the “Independent Web.” Although we don’t commonly use the term anymore, that doesn’t mean that it’s not still as vital a topic of discussion today as it was a decade ago.
Ten years ago, people began talking about the “Independent Web.” Although we don’t commonly use the term anymore, that doesn’t mean that it’s not still as vital a topic of discussion today as it was a decade ago.
Today, I want to look at where the term came from, what it refers to today, and why it’s something that all of us in business, marketing, and web design should be thinking about.
What Is The Independent Web?
The Independent Web is a term that was coined back in 2010 by John Battelle.
In “Identity and The Independent Web,” Battelle broaches the subject of internet users losing control of their data, privacy, and decision-making to the likes of social media and search engines.
“When we’re ‘on’ Facebook, Google, or Twitter, we’re plugged into an infrastructure that locks onto us, serving us content and commerce in an automated but increasingly sophisticated fashion. Sure, we navigate around, in control of our experience, but the fact is, the choices provided to us as we navigate are increasingly driven by algorithms modeled on the service’s understanding of our identity.”
That’s the Dependent Web.
This is how Battelle explains the Independent Web:
“There is another part of the web, one where I can stroll a bit more at my own pace, and discover new territory, rather than have territory matched to a presumed identity. And that is the land of the Independent Web.”
In 2010, this referred to websites, search engines, and apps where users and their activity were not tracked. But a lot has changed since then, and many websites that were once safe to peruse without interference or manipulation are no longer.
What Happens When the Dependent Web Takes Over?
Nothing good.
I take that back. It’s not fair to make a blanket statement about Dependent Web platforms and sites. Users can certainly benefit from sharing some of their data with them.
Take Facebook, for instance. Since its creation, it’s enabled people to connect with long-lost friends, stay in touch with distant relatives, enable freelance professionals like ourselves to find like-minded communities, etc.
The same goes for websites and apps that track and use visitor data. Consumers are more than willing to share relevant data with companies so long as they benefit from the resulting personalized experiences.
But the Dependent Web also has a darker side. There are many ways that the Dependent Web costs consumers and businesses control over important things like:
Behavior
If you’ve seen The Social Dilemma, then you know that platforms like Facebook and Google profit from selling their users to advertisers.
That’s right. They’re not just selling user data. They’re selling users themselves. If the algorithms can change the way users behave, these platforms and their advertisers get to cash in big time.
Many websites and apps are also guilty of using manipulation to force users to behave how they want them to.
Personal Data
This one is well-known thanks to the GDPR in the EU and the CCPA in California. Despite these initiatives to protect user data and privacy, the exploitation of personal data on the web remains a huge public concern in recent years.
Content and Branding
This isn’t relevant to websites so much as it is to social media platforms and Google.
Dependent Web platforms ultimately dictate who sees your content and when. And while they’re more than happy to benefit from the traffic and engagement this content brings to their platforms, they’re just as happy to censor or pull down content as they please, just as Skillshare did in 2019 when it deleted half of its courses without telling its course creators.
What’s more, while social media and search engines have become the place to market our businesses, some of our branding gets lost when entering such oversaturated environments.
Income
When algorithms get updated, many businesses often feel the negative effects almost immediately.
For example, Facebook updated its algorithm in 2018 to prioritize “meaningful content.” This pushed out organic business content and pulled regular user content to the top of the heap.
This, in turn, forced businesses to have to pay-to-play if they wanted to use Facebook as a viable marketing platform.
Access
The Dependent Web doesn’t just impact individuals’ experiences. It can have far-reaching effects when one company provides a critical service to a large portion of the population.
We saw this happen in November when AWS went down.
It wasn’t just Amazon’s servers that went down, though. It took out apps and sites like:
- 1Password
- Adobe Spark
- Capital Gazette
- Coinbase
- Glassdoor
- Roku
- The Washington Post
And there’s absolutely nothing that these businesses or their users could do but sit around and wait… because Amazon hosts a substantial portion of the web.
Innovation
When consumers and businesses become dependent on platforms that predominantly control the way we live and work, it’s difficult for us to stand up for the little guys trying to carve out innovative pathways.
And that’s exactly what we see happen time and time again with Big Tech’s buy-and-kill tactics.
As a result, we really lose the option to choose what we use to improve our lives and our businesses. And innovative thinkers lose the ability to bring much-needed changes to the world because Big Tech wants to own the vast majority of data and users.
How Can We Take Back Control From The Dependent Web?
Many things are happening right now that are trying to push consumers and businesses towards a more Independent Web:
Consumer Privacy Protection: GDPR and CCPA empower consumers to control where their data goes and what it’s used for.
Big Tech Regulations: The Senate held tech regulation hearings with Facebook’s and Twitters’s CEOs.
Public Awareness Initiatives: Films like The Social Dilemma bring greater awareness to what’s happening on social media.
Ad Blocker Adoption: Adblocker usage is at an all-time high.
Private Search Engine Usage: Although Google dominates search engine market share, people are starting to use private search engines like Duck Duck Go.
Private Browsing Growth: Over 60% of the global population is aware of what private browsing is (i.e., incognito mode), and roughly 35% use it when surfing the web.
Self-hosted and Open Source CMS Popularity: The IndieWeb community encourages people to move away from Dependent platforms and build their own websites and communities. This is something that Matt Mullenweg, the founder of WordPress, talked about back in 2012.
“The Internet needs a strong, independent platform for those of us who don’t want to be at the mercy of someone else’s domain. I like to think that if we didn’t create WordPress something else that looks a lot like it would exist. I think Open Source is kind of like our Bill of Rights. It’s our Constitution. If we’re not true to that, nothing else matters.”
As web designers, this is something that should really speak to you, especially if you’ve ever met a lead or client who didn’t understand why they needed a website when they could just advertise on Facebook or Instagram.
A Decentralized Web: Perhaps the most promising of all these initiatives are Solid and Inrupt, which were launched in 2018 by the creator of the Web, Tim Berners-Lee.
As Berners-Lee explained on the Inrupt blog in 2020:
”The Web was always meant to be a platform for creativity, collaboration, and free invention — but that’s not what we are seeing today. Today, business transformation is hampered by different parts of one’s life being managed by different silos, each of which looks after one vertical slice of life, but where the users and teams can’t get the insight from connecting that data. Meanwhile, that data is exploited by the silo in question, leading to increasing, very reasonable, public skepticism about how personal data is being misused. That in turn has led to increasingly complex data regulations.”
This is something we should all keep a close eye on. Consumers and businesses alike are becoming wary of the Dependent Web.
Who better than the creator of the web to lead us towards the Independent Web where we can protect our data and better control our experience?
Featured Image via Pexels.
Source
The post What Is The Independent Web And Does It Matter In 2021? first appeared on Webdesigner Depot.

Source de l’article sur Webdesignerdepot
 Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site, Webdesigner News. Our colleagues sift through it, selecting the very best stories from the design, UX, tech, and development worlds and posting them live on the site.
Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site, Webdesigner News. Our colleagues sift through it, selecting the very best stories from the design, UX, tech, and development worlds and posting them live on the site.











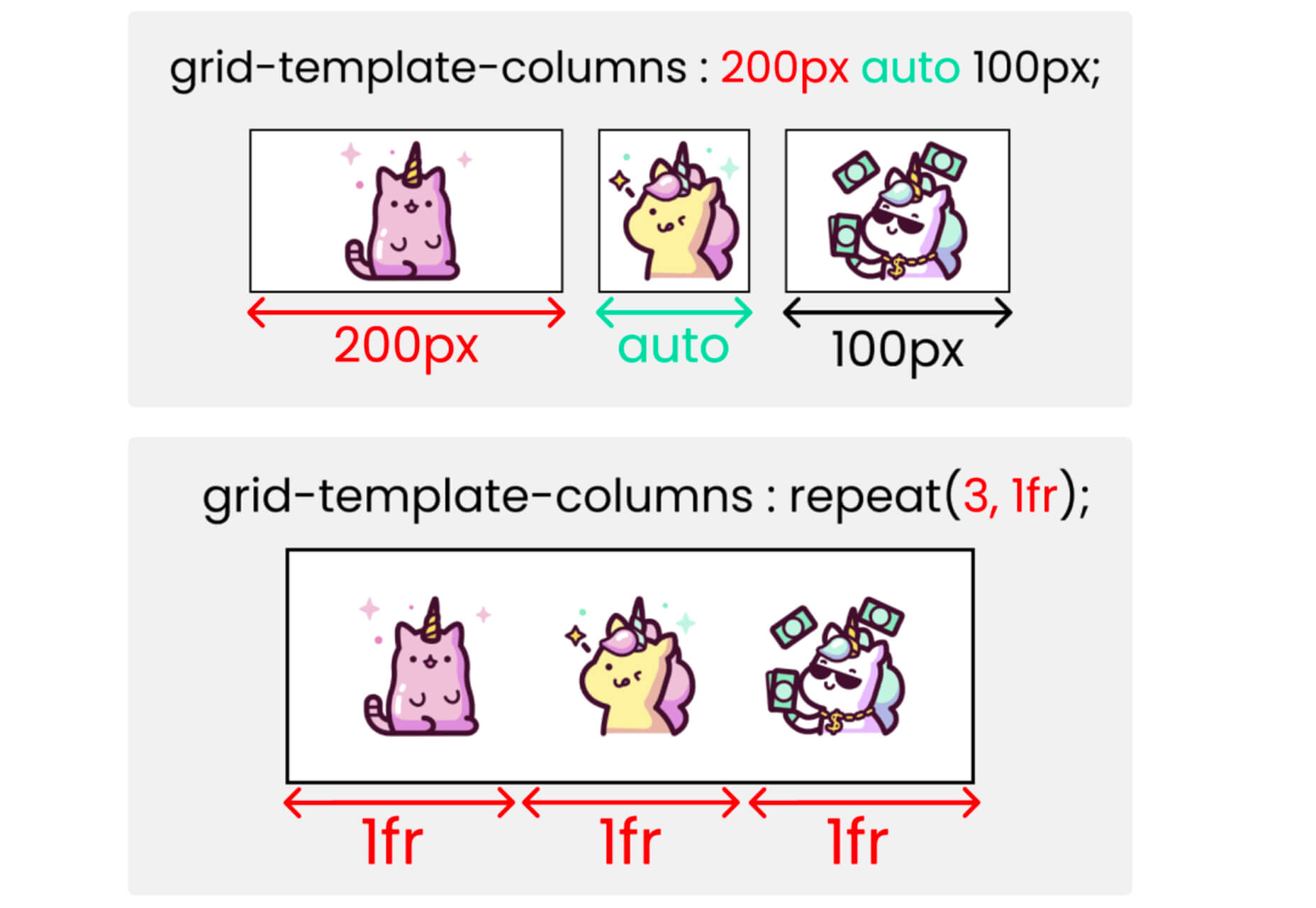
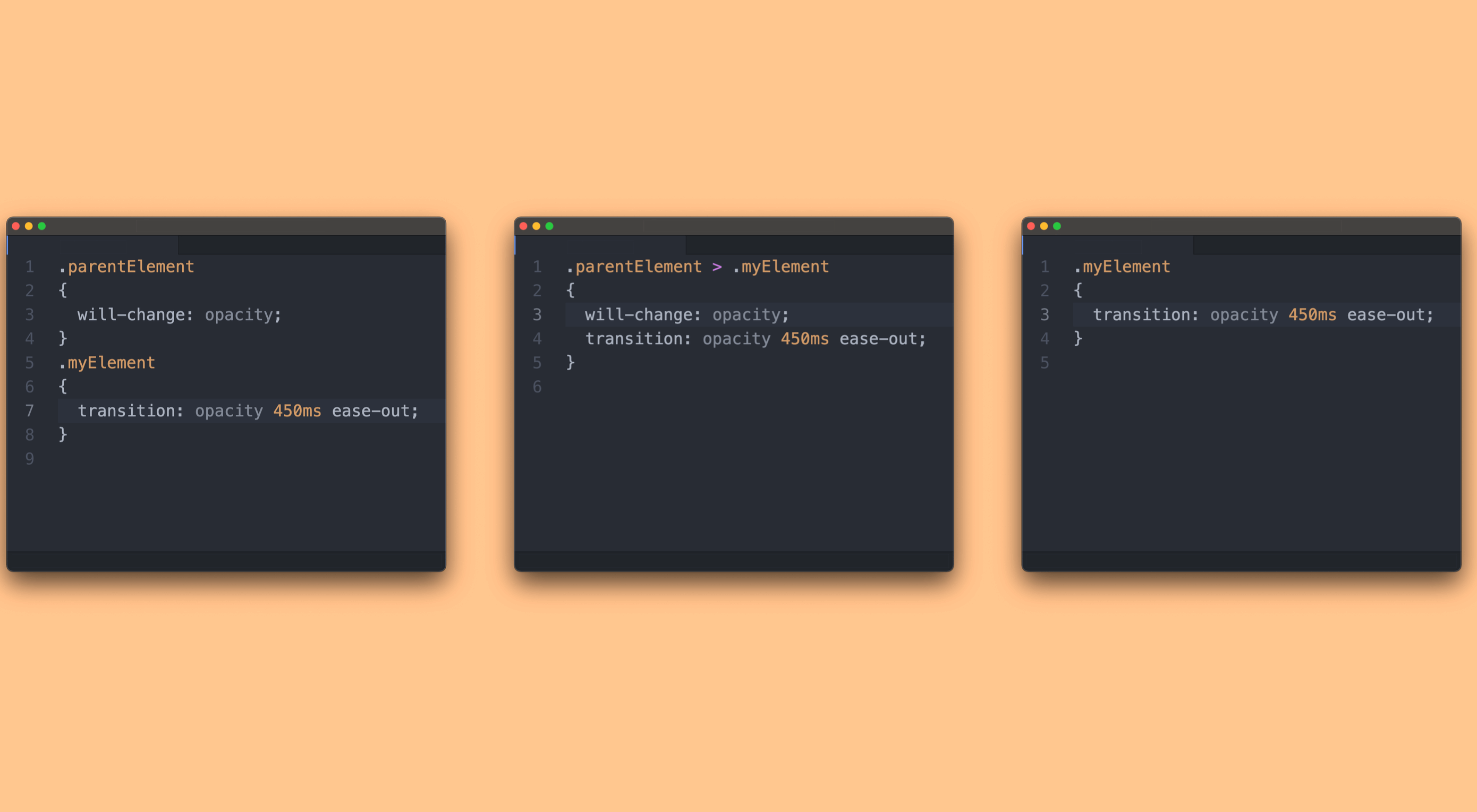 CSS is an awesome tool for styling websites. It’s small, fast, and easy to learn. But like all code, there’s a right way, and a wrong way to write it. Badly written CSS renders slowly, impacting on the perceived speed of your site, and even damaging your SEO.
CSS is an awesome tool for styling websites. It’s small, fast, and easy to learn. But like all code, there’s a right way, and a wrong way to write it. Badly written CSS renders slowly, impacting on the perceived speed of your site, and even damaging your SEO.
 At the dawn of the web-era, there was much focus on how environmentally friendly websites were: we’d chop down fewer trees, ship fewer products, and travel less for business.
At the dawn of the web-era, there was much focus on how environmentally friendly websites were: we’d chop down fewer trees, ship fewer products, and travel less for business.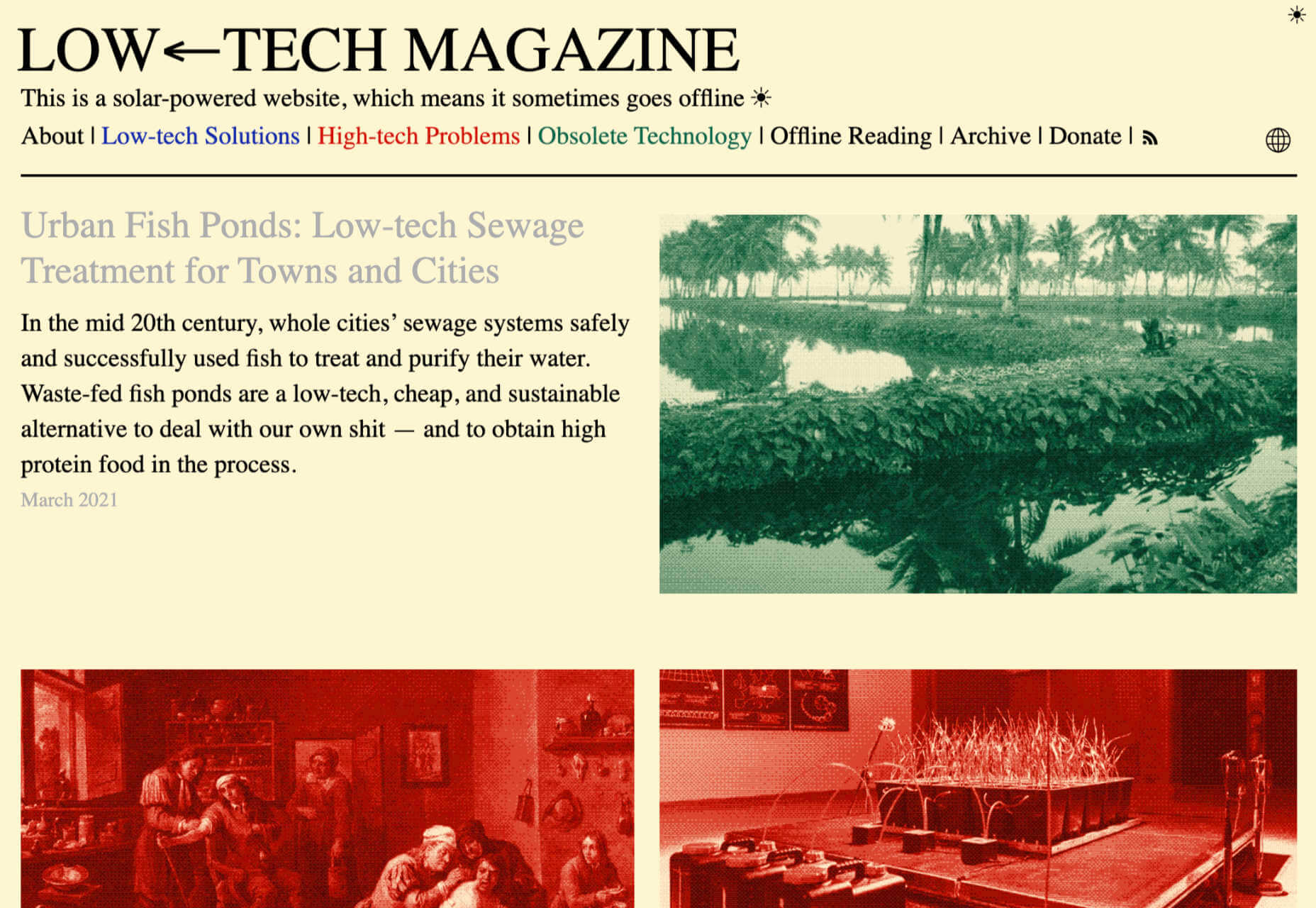

 Ten years ago, people began talking about the “Independent Web.” Although we don’t commonly use the term anymore, that doesn’t mean that it’s not still as vital a topic of discussion today as it was a decade ago.
Ten years ago, people began talking about the “Independent Web.” Although we don’t commonly use the term anymore, that doesn’t mean that it’s not still as vital a topic of discussion today as it was a decade ago.

 Rather than spring cleaning, do some spring “shopping” for tools that will make your design life easier. Packed with free options this month, this list is crammed full of tools and elements that you can use in your work every day.
Rather than spring cleaning, do some spring “shopping” for tools that will make your design life easier. Packed with free options this month, this list is crammed full of tools and elements that you can use in your work every day.













 Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site,
Every day design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site, 









 Over the last fortnight one site builder has gone toe-to-toe with another, as Wix launched a marketing campaign aimed at attracting WordPress users, and instead attracted universal ire.
Over the last fortnight one site builder has gone toe-to-toe with another, as Wix launched a marketing campaign aimed at attracting WordPress users, and instead attracted universal ire.
 We’re no longer arguing about whether climate change exists because climate change is now extensively documented. Instead, we’re arguing over whether climate change is a natural cycle or human-accelerated.
We’re no longer arguing about whether climate change exists because climate change is now extensively documented. Instead, we’re arguing over whether climate change is a natural cycle or human-accelerated.