Le Big Data est le flot d’informations dans lequel nous nous trouvons tous les jours (des zettaoctets de données provenant de nos ordinateurs, des terminaux mobiles et des capteurs). Ces données sont utilisées par les entreprises pour orienter la prise de décisions, améliorer les processus et les stratégies, et créer des produits, des services et des expériences centrés sur le client.
Le Big Data désigne non seulement de gros volumes de données, mais aussi des données de nature variée et complexe. Il dépasse généralement la capacité des bases de données traditionnelles à capturer, gérer et traiter ce type de données. De plus, le Big Data peut provenir de n’importe où et de tout ce que nous sommes en mesure de surveiller numériquement. Les satellites, les appareils IoT (Internet des Objets), les radars et les tendances des réseaux sociaux ne sont que quelques exemples parmi la multitude de sources de données explorées et analysées pour rendre les entreprises plus résilientes et compétitives.
L’importance de l’analyse du Big Data
La véritable valeur du Big Data se mesure d’après votre capacité à l’analyser et à le comprendre. L’intelligence artificielle (IA), le machine learning et les technologies de base de données modernes permettent de visualiser et d’analyser le Big Data pour fournir des informations exploitables en temps réel. L’analyse du Big Data aide les entreprises à exploiter leurs données en vue de saisir de nouvelles opportunités et de créer de nouveaux modèles de gestion. Comme l’a si bien dit Geoffrey Moore, auteur et analyste de gestion, « sans analyse du Big Data, les entreprises sont aveugles et sourdes, errant sur le Web comme des cerfs sur une autoroute ».

L’évolution du Big Data
Aussi inconcevable que cela puisse paraître aujourd’hui, l’Apollo Guidance Computer a emmené l’homme sur la lune avec moins de 80 kilo-octets de mémoire. Depuis, la technologie informatique s’est développée à un rythme exponentiel, de même que la génération de données. La capacité technologique mondiale à stocker des données a doublé tous les trois ans depuis les années 1980. Il y a un peu plus de 50 ans, lors du lancement d’Apollo 11, la quantité de données numériques générées dans le monde aurait pu tenir dans un ordinateur portable. Aujourd’hui, l’IDC estime ce chiffre à 44 zettaoctets (soit 44 000 milliards de gigaoctets) et prévoit qu’il atteindra 163 zettaoctets en 2025.
44 zettaoctets de données numériques aujourd’hui, IDC
163 zettaoctets de données numériques en 2025, IDC
Plus les logiciels et la technologie se développent, moins les systèmes non numériques sont viables. Le traitement des données générées et collectées numériquement requiert des systèmes de data management plus avancés. En outre, la croissance exponentielle des plates-formes de réseaux sociaux, des technologies pour smartphones et des appareils IoT connectés numériquement ont contribué à l’émergence du Big Data.
Types de Big Data : que sont les données structurées et non structurées ?
Les ensembles de données sont généralement catégorisés en trois types, selon leur structure et la complexité de leur indexation.
- Données structurées : ce type de données est le plus simple à organiser et à rechercher. Il peut inclure des données financières, des machine logs et des détails démographiques. Une feuille de calcul Microsoft Excel, avec sa mise en forme de colonnes et de lignes prédéfinies, offre un moyen efficace de visualiser les données structurées. Ses composants peuvent facilement être catégorisés, ce qui permet aux concepteurs et administrateurs de bases de données de définir des algorithmes simples pour la recherche et l’analyse. Même lorsque les données structurées sont très volumineuses, elles ne sont pas nécessairement qualifiées de Big Data, car elles sont relativement simples à gérer et ne répondent donc pas aux critères qui définissent le Big Data. Traditionnellement, les bases de données utilisent un langage de programmation appelé SQL (Structured Query Language) pour gérer les données structurées. SQL a été développé par IBM dans les années 1970 pour permettre aux développeurs de créer et gérer des bases de données relationnelles (de type feuille de calcul) qui commençaient à émerger à l’époque.
- Données non structurées : cette catégorie de données peut inclure des publications sur les réseaux sociaux, des fichiers audio, des images et des commentaires client ouverts. Ces données ne peuvent pas être facilement capturées dans les bases de données relationnelles standard en lignes et colonnes. Auparavant, les entreprises qui voulaient rechercher, gérer ou analyser de grandes quantités de données non structurées devaient utiliser des processus manuels laborieux. La valeur potentielle liée à l’analyse et à la compréhension de ces données ne faisait aucun doute, mais le coût associé était souvent trop exorbitant pour en valoir la peine. Compte tenu du temps nécessaire, les résultats étaient souvent obsolètes avant même d’être générés. Contrairement aux feuilles de calcul ou aux bases de données relationnelles, les données non structurées sont généralement stockées dans des lacs de données, des entrepôts de données et des bases de données NoSQL.
- Données semi-structurées : comme leur nom l’indique, les données semi-structurées intègrent à la fois des données structurées et non structurées. Les e-mails en sont un bon exemple, car ils incluent des données non structurées dans le corps du message, ainsi que d’autres propriétés organisationnelles telles que l’expéditeur, le destinataire, l’objet et la date. Les dispositifs qui utilisent le marquage géographique, les horodatages ou les balises sémantiques peuvent également fournir des données structurées avec un contenu non structuré. Une image de smartphone non identifiée, par exemple, peut indiquer qu’il s’agit d’un selfie et préciser l’heure et l’endroit où il a été pris. Une base de données moderne exécutant une technologie d’IA peut non seulement identifier instantanément différents types de données, mais aussi générer des algorithmes en temps réel pour gérer et analyser efficacement les ensembles de données disparates.
Les sources du Big Data
Les objets générateurs de données se développent à un rythme spectaculaire, depuis les drones jusqu’aux grille-pains. Toutefois, à des fins de catégorisation, les sources de données sont généralement divisées en trois types :
Données sociales
Comme leur nom l’indique, les données sociales sont générées par les réseaux sociaux : commentaires, publications, images et, de plus en plus, vidéos. En outre, compte tenu de l’ubiquité croissante des réseaux 4G et 5G, on estime que le nombre de personnes dans le monde qui regardent régulièrement des contenus vidéo sur leur smartphone atteindra 2,72 milliards en 2023. Bien que les tendances concernant les réseaux sociaux et leur utilisation évoluent rapidement et de manière imprévisible, leur progression en tant que générateurs de données numériques est incontestable.
Données machine
Les machines et appareils IoT sont équipés de capteurs et ont la capacité d’envoyer et de recevoir des données numériques. Les capteurs IoT aident les entreprises à collecter et traiter les données machine provenant des appareils, des véhicules et des équipements. Globalement, le nombre d’objets générateurs de données augmente rapidement, des capteurs météorologiques et de trafic jusqu’à la surveillance de la sécurité. Selon l’IDC, il y aura plus de 40 milliards d’appareils IoT en 2025, générant près de la moitié des données numériques mondiales.
Données altérables
Il s’agit des données parmi les plus évolutives au monde. Par exemple, un détaillant international traite plus d’un million de transactions client par heure. Si l’on ajoute à cela les transactions d’achat et bancaires au niveau mondial, on comprend mieux le volume phénoménal de données générées. En outre, les données altérables contiennent de plus en plus de données semi-structurées, y compris des images et des commentaires, ce qui les rend d’autant plus complexes à gérer et à traiter.
Les cinq V du Big Data
Ce n’est pas parce qu’un ensemble de données est volumineux qu’il s’agit nécessairement de Big Data. Pour être qualifiées en tant que telles, les données doivent posséder au minimum les cinq caractéristiques suivantes :
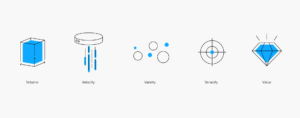
- Volume : même si le volume n’est pas le seul composant qui constitue le Big Data, il s’agit d’une de ses caractéristiques principales. Pour gérer et exploiter pleinement le Big Data, des algorithmes avancés et des analyses pilotées par l’IA sont nécessaires. Mais avant tout cela, il doit exister un moyen fiable et sécurisé de stocker, d’organiser et d’extraire les téraoctets de données détenus par les grandes entreprises.
- Vitesse : auparavant, les données générées devaient ensuite être saisies dans un système de base de données traditionnel (souvent manuellement) avant de pouvoir être analysées ou extraites. Aujourd’hui, grâce à la technologie du Big Data, les bases de données sont capables de traiter, d’analyser et de configurer les données lorsqu’elles sont générées, parfois en l’espace de quelques millisecondes. Pour les entreprises, cela signifie que les données en temps réel peuvent être exploitées pour saisir des opportunités financières, répondre aux besoins des clients, prévenir la fraude et exécuter toute autre activité pour laquelle la rapidité est un facteur clé.
- Variété : les ensembles de données contenant uniquement des données structurées ne relèvent pas nécessairement du Big Data, quel que soit leur volume. Le Big Data comprend généralement des combinaisons de données structurées, non structurées et semi-structurées. Les solutions de gestion des données et les bases de données traditionnelles n’offrent pas la flexibilité et le périmètre nécessaires pour gérer les ensembles de données complexes et disparates qui constituent le Big Data.
- Véracité : bien que les bases de données modernes permettent aux entreprises d’accumuler et d’identifier des volumes considérables de Big Data de différents types, elles ne sont utiles que si elles sont précises, pertinentes et opportunes. S’agissant des bases de données traditionnelles alimentées uniquement avec des données structurées, le manque de précision des données était souvent dû à des erreurs syntaxiques et des fautes de frappe. Les données non structurées présentent toute une série de nouvelles difficultés en matière de véracité. Les préjugés humains, le « bruit social » et les problèmes liés à la provenance des données peuvent avoir un impact sur la qualité des données.
- Valeur : les résultats de l’analyse du Big Data sont souvent fascinants et inattendus. Mais pour les entreprises, l’analyse du Big Data doit fournir une visibilité qui les aident à gagner en compétitivité et en résilience, et à mieux servir leurs clients. Les technologies modernes du Big Data offrent la possibilité de collecter et d’extraire des données susceptibles de procurer un avantage mesurable à la fois en termes de résultats et de résilience opérationnelle.
Avantages du Big Data
Les solutions modernes de gestion du Big Data permettent aux entreprises de transformer leurs données brutes en informations pertinentes avec une rapidité et une précision sans précédent.
- Développement de produits et de services :l’analyse du Big Data permet aux développeurs de produits d’analyser les données non structurées, telles que les témoignages clients et les tendances culturelles, et de réagir rapidement.
- Maintenance prédictive : dans le cadre d’uneenquête internationale, McKinsey a constaté que l’analyse du Big Data émanant des machines IoT pouvait réduire les coûts de maintenance des équipements jusqu’à 40 %.
- Expérience client :dans le cadre d’une enquête réalisée en 2020 auprès de responsables d’entreprises du monde entier, Gartner a déterminé que « les entreprises en croissance collectent plus activement des données sur l’expérience client que les entreprises à croissance nulle ». L’analyse du Big Data permet aux entreprises d’améliorer et de personnaliser l’expérience de leurs clients avec leur marque.
- Gestion de la résilience et des risques :la pandémie de COVID-19 a été une véritable prise de conscience pour de nombreux dirigeants d’entreprise qui se sont rendu compte à quel point leur activité était vulnérable. La visibilité offerte par le Big Data peut aider les entreprises à anticiper les risques et à se préparer aux imprévus.
- Économies et efficacité accrue : lorsque les entreprises effectuent une analyse avancée du Big Data pour tous les processus de l’organisation, elles peuvent non seulement détecter les inefficacités, mais aussi déployer des solutions rapides et efficaces.
- Amélioration de la compétitivité : les informations obtenues grâce au Big Data peuvent aider les entreprises à réaliser des économies, à satisfaire leurs clients, à concevoir de meilleurs produits et à innover dans les opérations de gestion.
IA et Big Data
La gestion du Big Data repose sur des systèmes capables de traiter et d’analyser efficacement de gros volumes d’informations disparates et complexes. À cet égard, le Big Data et l’IA ont une relation de réciprocité. Sans l’IA pour l’organiser et l’analyser, le Big Data n’aurait pas grande utilité. Et pour que l’IA puisse générer des analyses suffisamment fiables pour être exploitables, le Big Data doit contenir des ensembles de données suffisamment étendus. Comme l’indique Brandon Purcell, analyste chez Forrester Research, « les données sont au cœur de l’intelligence artificielle. Un système d’IA doit apprendre des données pour remplir sa fonction ».
« Les données sont au cœur de l’intelligence artificielle. Un système d’IA doit apprendre des données pour remplir sa fonction ».
Brandon Purcell, analyste, Forrester Research
Machine learning et Big Data
Les algorithmes de machine learning définissent les données entrantes et identifient des modèles associés. Ces informations permettent de prendre des décisions avisées et d’automatiser les processus. Le machine learning se nourrit du Big Data, car plus les ensembles de données analysés sont fiables, plus le système est susceptible d’apprendre, de faire évoluer et d’adapter ses processus en continu.
Technologies du Big Data
Architecture du Big Data
À l’instar de l’architecture du bâtiment, l’architecture du Big Data fournit un modèle pour la structure de base déterminant la manière dont les entreprises gèrent et analysent leurs données. L’architecture du Big Data mappe les processus requis pour gérer le Big Data à travers quatre « couches » de base, des sources de données au stockage des données, puis à l’analyse du Big Data, et enfin via la couche de consommation dans laquelle les résultats analysés sont présentés en tant que Business Intelligence.
Analyse du Big Data
Ce processus permet de visualiser les données de manière pertinente grâce à l’utilisation de la modélisation des données et d’algorithmes spécifiques aux caractéristiques du Big Data. Dans le cadre d’une étude approfondie et d’une enquête de la MIT Sloan School of Management, plus de 2 000 dirigeants d’entreprise ont été interrogés sur leur expérience en matière d’analyse du Big Data. Comme on pouvait s’y attendre, ceux qui s’étaient impliqués dans le développement de stratégies de gestion du Big Data ont obtenu les résultats les plus significatifs.
Big Data et Apache Hadoop
Imaginez une grande boîte contenant 10 pièces de 10 centimes et 100 pièces de 5 centimes. Puis imaginez 10 boîtes plus petites, côte à côte, contenant chacune 10 pièces de 5 centimes et une seule pièce de 10 centimes. Dans quel scénario sera-t-il plus facile de repérer les pièces de 10 centimes ? Hadoop fonctionne sur ce principe. Il s’agit d’une structure en open source permettant de gérer le traitement du Big Data distribué sur un réseau constitué de nombreux ordinateurs connectés. Ainsi, au lieu d’utiliser un gros ordinateur pour stocker et traiter toutes les données, Hadoop regroupe plusieurs ordinateurs sur un réseau pouvant évoluer presque à l’infini et analyse les données en parallèle. Ce processus utilise généralement un modèle de programmation appelé MapReduce, qui coordonne le traitement du Big Data en regroupant les ordinateurs distribués.
Lacs de données, entrepôts de données et NoSQL
Les bases de données traditionnelles de type feuille de calcul SQL servent à stocker les données structurées. Le Big Data non structuré et semi-structuré nécessite des modèles de stockage et de traitement uniques, car il ne peut pas être indexé et catégorisé. Les lacs de données, les entrepôts de données et les bases de données NoSQL sont des référentiels de données capables de gérer les ensembles de données non traditionnels. Un lac de données est un vaste pool de données brutes qui n’ont pas encore été traitées. Un entrepôt de données est un référentiel de données qui ont déjà été traitées à des fins spécifiques. Les bases de données NoSQL fournissent un schéma flexible qui peut être modifié en fonction de la nature des données à traiter. Ces systèmes présentent chacun des avantages et des inconvénients, c’est pourquoi de nombreuses entreprises utilisent plutôt une combinaison de ces référentiels de données pour répondre au mieux à leurs besoins.
Bases de données in-memory
Les bases de données traditionnelles sur disque ont été conçues pour SQL et les bases de données relationnelles. Bien qu’elles soient capables de traiter de gros volumes de données structurées, elles ne sont pas adaptées au stockage et au traitement des données non structurées. Dans le cas des bases de données in-memory, le traitement et l’analyse se font entièrement dans la RAM, pour ne pas avoir à extraire les données d’un système sur disque. Les bases de données in-memory reposent également sur des architectures distribuées. Cela signifie qu’elles peuvent atteindre des vitesses beaucoup plus élevées en utilisant le traitement parallèle, par rapport aux modèles de base de données sur disque à un seul nœud.
Fonctionnement du Big Data
Le Big Data remplit ses fonctions lorsque son analyse fournit des informations pertinentes et exploitables qui améliorent l’activité de manière significative. Pour se préparer à la transition vers le Big Data, les entreprises doivent s’assurer que leurs systèmes et processus sont en mesure de collecter, de stocker et d’analyser le Big Data.
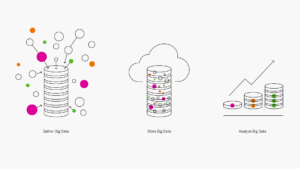
- Collecter le Big Data.Une grande partie du Big Data est constituée d’énormes ensembles de données non structurées qui émanent de sources disparates et incohérentes. Les bases de données traditionnelles sur disque et les mécanismes d’intégration des données ne sont pas suffisamment performants pour les gérer. La gestion du Big Data requiert des solutions de base de données in-memory et des solutions logicielles spécifiques de l’acquisition de ce type de données.
- Stocker le Big Data.Comme son nom l’indique, le Big Data est volumineux. De nombreuses entreprises utilisent des solutions de stockage sur site pour leurs données existantes et espèrent réaliser des économies en réutilisant ces référentiels pour traiter le Big Data. Toutefois, le Big Data est plus performant lorsqu’il n’est pas soumis à des contraintes de taille et de mémoire. Les entreprises qui n’intègrent pas dès le départ des solutions de stockage Cloud dans leurs modèles de Big Data le regrettent souvent quelques mois plus tard.
- Analyser le Big Data. Il est impossible d’exploiter pleinement le potentiel du Big Data sans utiliser les technologies d’IA et de machine learning pour l’analyser. L’un des cinq V du Big Data est la « vitesse ». Pour être utiles et exploitables, les informations du Big Data doivent être générées rapidement. Les processus d’analyse doivent s’auto-optimiser et tirer régulièrement profit de l’expérience, un objectif qui ne peut être atteint qu’avec l’IA et les technologies modernes de bases de données.
Applications du Big Data
La visibilité offerte par le Big Data est bénéfique à la plupart des entreprises ou secteurs d’activité. Cependant, ce sont les grandes entreprises aux missions opérationnelles complexes qui en tirent souvent le meilleur parti.
|
Finance |
Dans le Journal of Big Data, une étude de 2020 souligne que le Big Data « joue un rôle important dans l’évolution du secteur des services financiers, en particulier dans le commerce et les investissements, la réforme fiscale, la détection et les enquêtes en matière de fraude, l’analyse des risques et l’automatisation ». Le Big Data a également contribué à transformer le secteur financier en analysant les données et les commentaires des clients pour obtenir les informations nécessaires à l’amélioration de la satisfaction et de l’expérience client. Les ensembles de données altérables figurent parmi les plus importants et les plus évolutifs au monde. L’adoption croissante de solutions avancées de gestion du Big Data permettra aux banques et aux établissements financiers de protéger ces données et de les utiliser d’une manière qui bénéficie à la fois au client et à l’entreprise. |
|
Hygiène et santé |
L’analyse du Big Data permet aux professionnels de santé d’établir des diagnostics plus précis, fondés sur des données avérées. De plus, le Big Data aide les administrateurs d’hôpitaux à identifier les tendances, à gérer les risques et à limiter les dépenses inutiles, afin de consacrer le maximum de fonds aux soins des patients et à la recherche. En cette période de pandémie, les chercheurs du monde entier s’efforcent de traiter et de gérer au mieux la COVID-19, et le Big Data joue un rôle fondamental dans ce processus. Un article de juillet 2020 paru dans The Scientist explique comment des équipes médicales ont pu collaborer et analyser le Big Data afin de lutter contre le coronavirus : « Nous pourrions transformer la science clinique en exploitant les outils et les ressources du Big Data et de la science des données d’une manière que nous pensions impossible ». |
|
Transport et logistique |
L’« effet Amazon » est un terme qui définit la manière dont Amazon a fait de la livraison en un jour la nouvelle norme, les clients exigeant désormais la même vitesse d’expédition pour tout ce qu’ils commandent en ligne. Le magazine Entrepreneur souligne qu’en raison de l’effet Amazon, « la course logistique au dernier kilomètre ne fera que s’intensifier ». Les entreprises du secteur s’appuient de plus en plus sur l’analyse du Big Data pour optimiser la planification des itinéraires, la consolidation des charges et les mesures d’efficacité énergétique. |
|
Éducation |
Depuis l’apparition de la pandémie, les établissements d’enseignement du monde entier ont dû réinventer leurs programmes d’études et leurs méthodes d’enseignement afin de faciliter l’apprentissage à distance. L’un des principaux défis a été de trouver des moyens fiables d’analyser et d’évaluer la performance des étudiants et l’efficacité globale des méthodes d’enseignement en ligne. Un article paru en 2020 au sujet de l’impact du Big Data sur la formation et l’apprentissage en ligne indique, au sujet des enseignants, que « le Big Data les aide à gagner en confiance pour personnaliser l’enseignement, développer l’apprentissage mixte, transformer les systèmes d’évaluation et promouvoir l’apprentissage continu ». |
|
Énergie et services publics |
Selon le U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, le service public consacre plus de 1,4 milliard de dollars aux relevés de compteurs et s’appuie généralement sur des compteurs analogiques et des lectures manuelles peu fréquentes. Les relevés de compteurs intelligents fournissent des données numériques plusieurs fois par jour et, grâce à l’analyse du Big Data, ces informations permettent d’accroître l’efficacité de la consommation énergétique, ainsi que la précision des prix et des prévisions. En outre, lorsque les agents n’ont plus à se charger des relevés de compteurs, la saisie et l’analyse des données peuvent permettre de les réaffecter plus rapidement là où les réparations et les mises à niveau sont les plus urgentes. |
Publié en anglais sur insights.sap.com
The post Qu’est-ce que le Big Data ? appeared first on SAP France News.

 Have you ever wondered why we’re so amazed by motion? A moving image is more likely to grab your attention than a static one. Motion is exciting and attention-grabbing – plus, it allows us to access more information in a short space of time.
Have you ever wondered why we’re so amazed by motion? A moving image is more likely to grab your attention than a static one. Motion is exciting and attention-grabbing – plus, it allows us to access more information in a short space of time. 

 Google has been talking about the Core Web Vitals tool and the Page Experience Update for about a year now.
Google has been talking about the Core Web Vitals tool and the Page Experience Update for about a year now.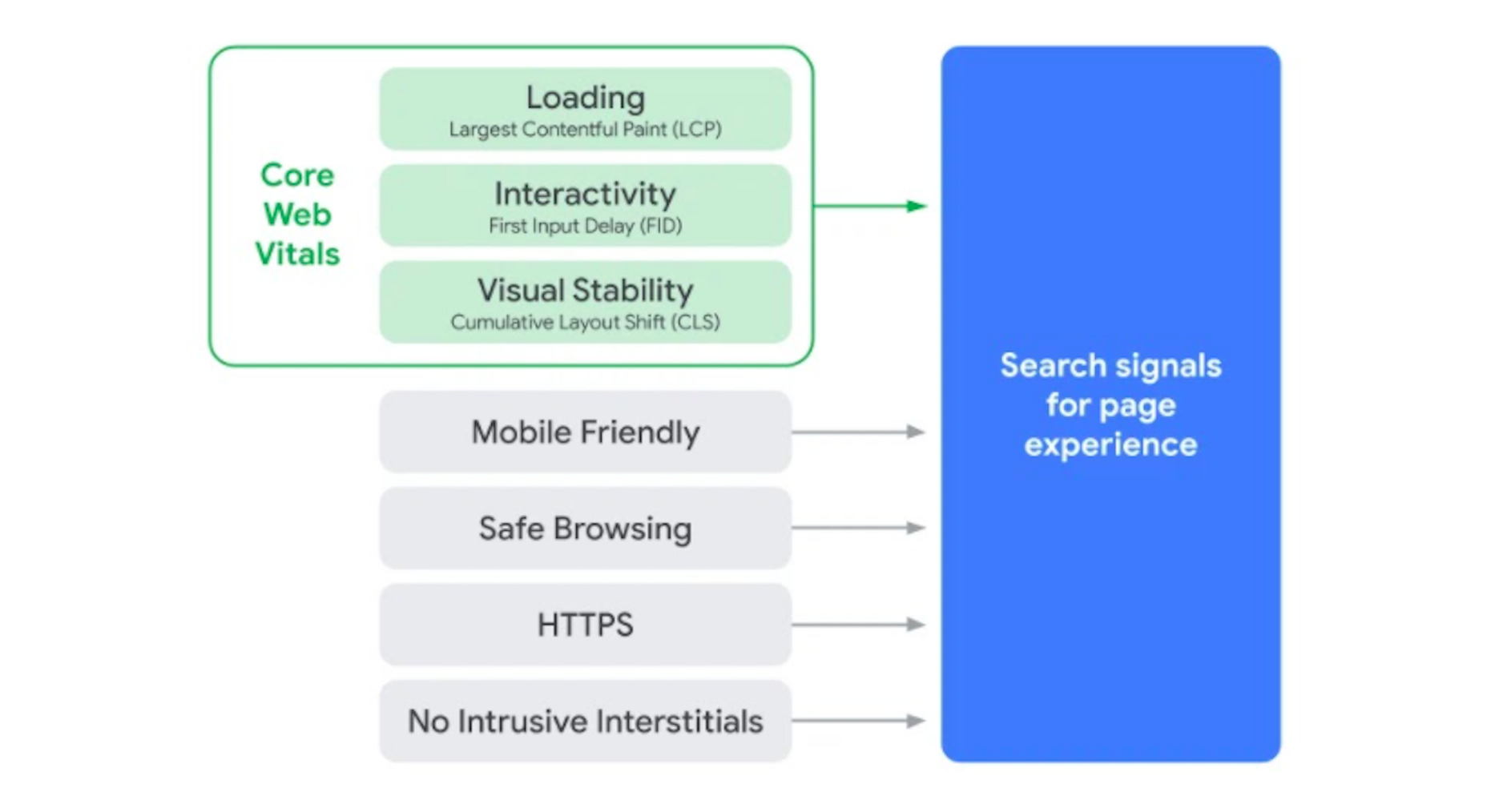
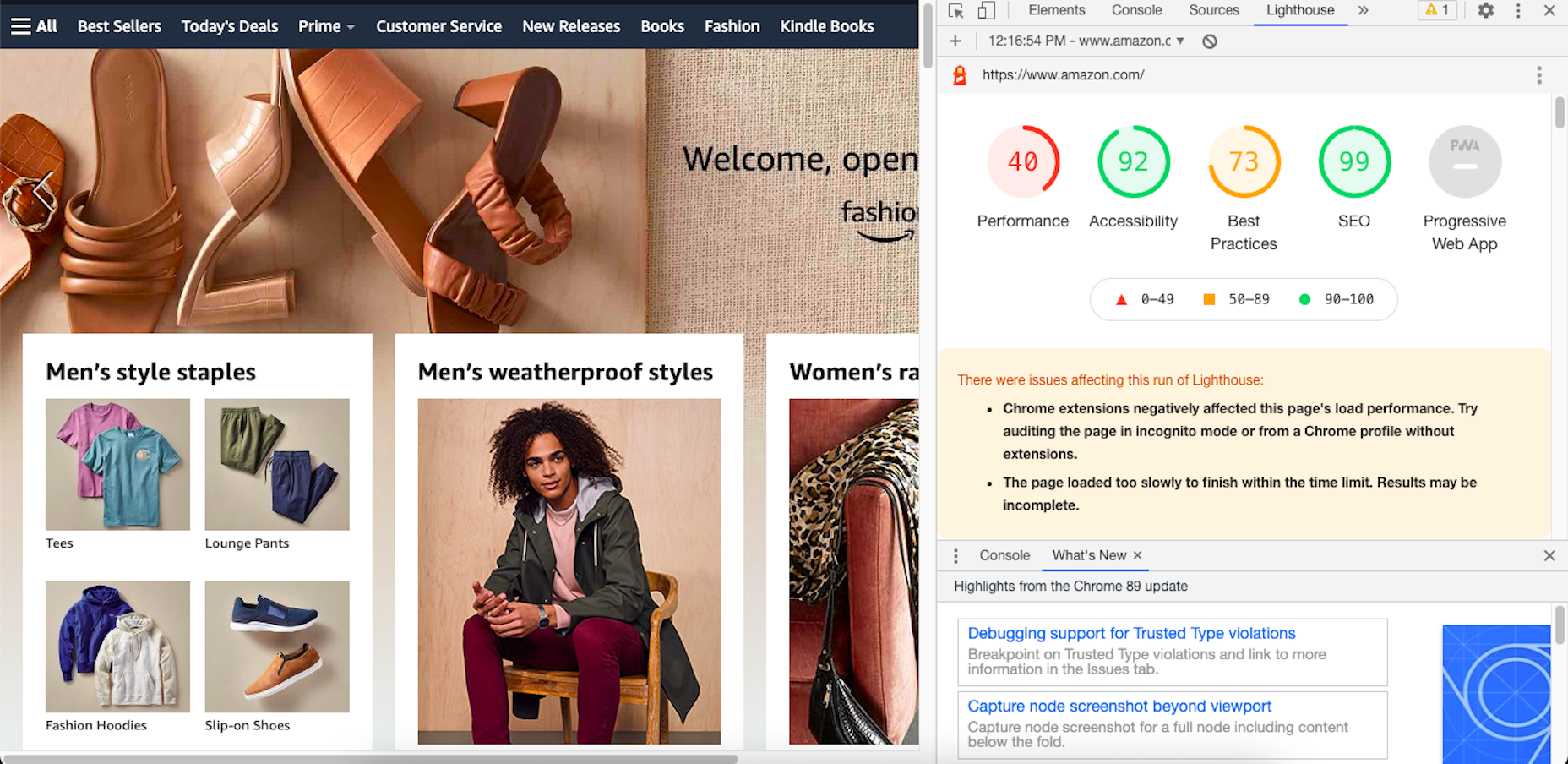
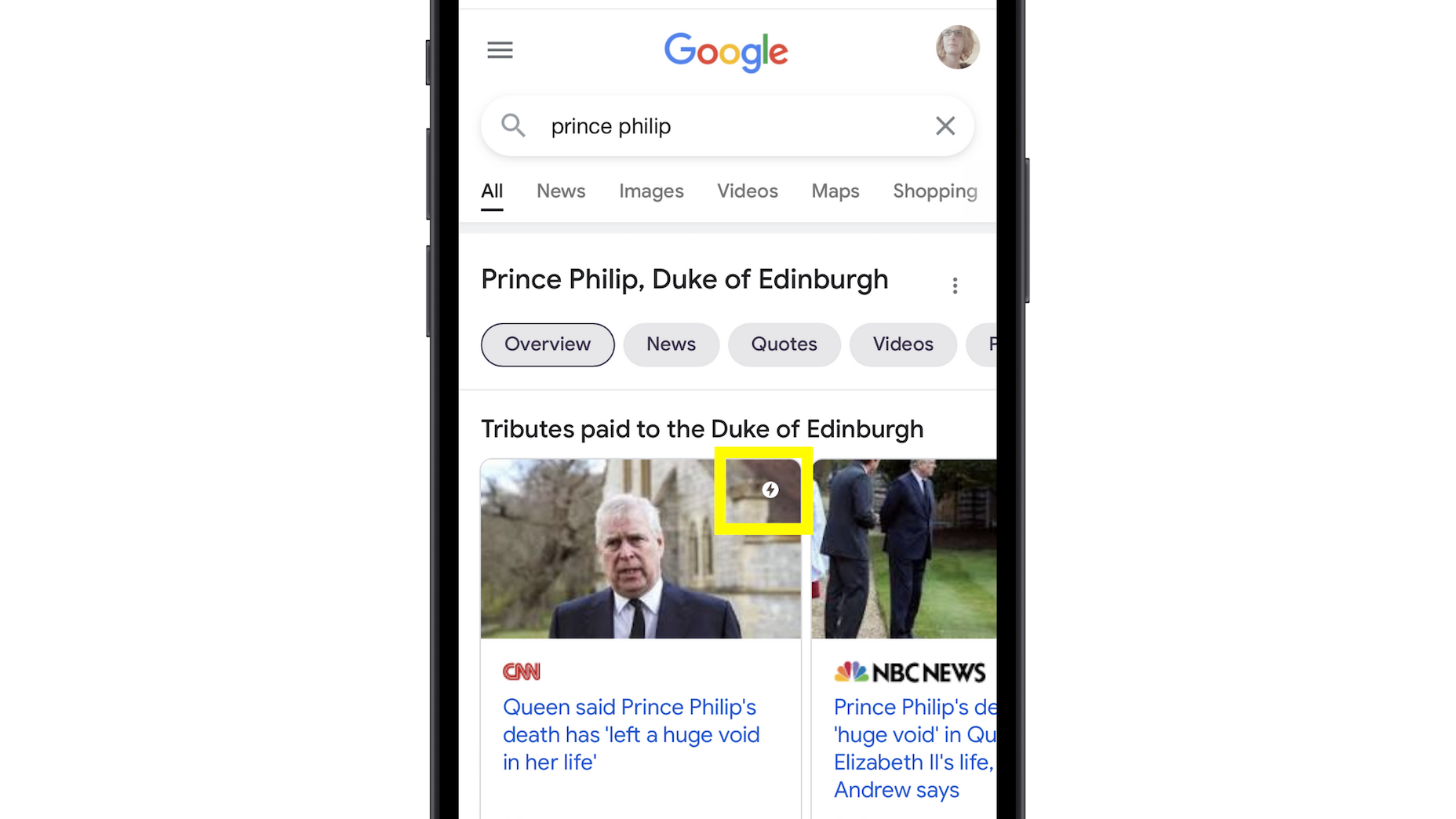
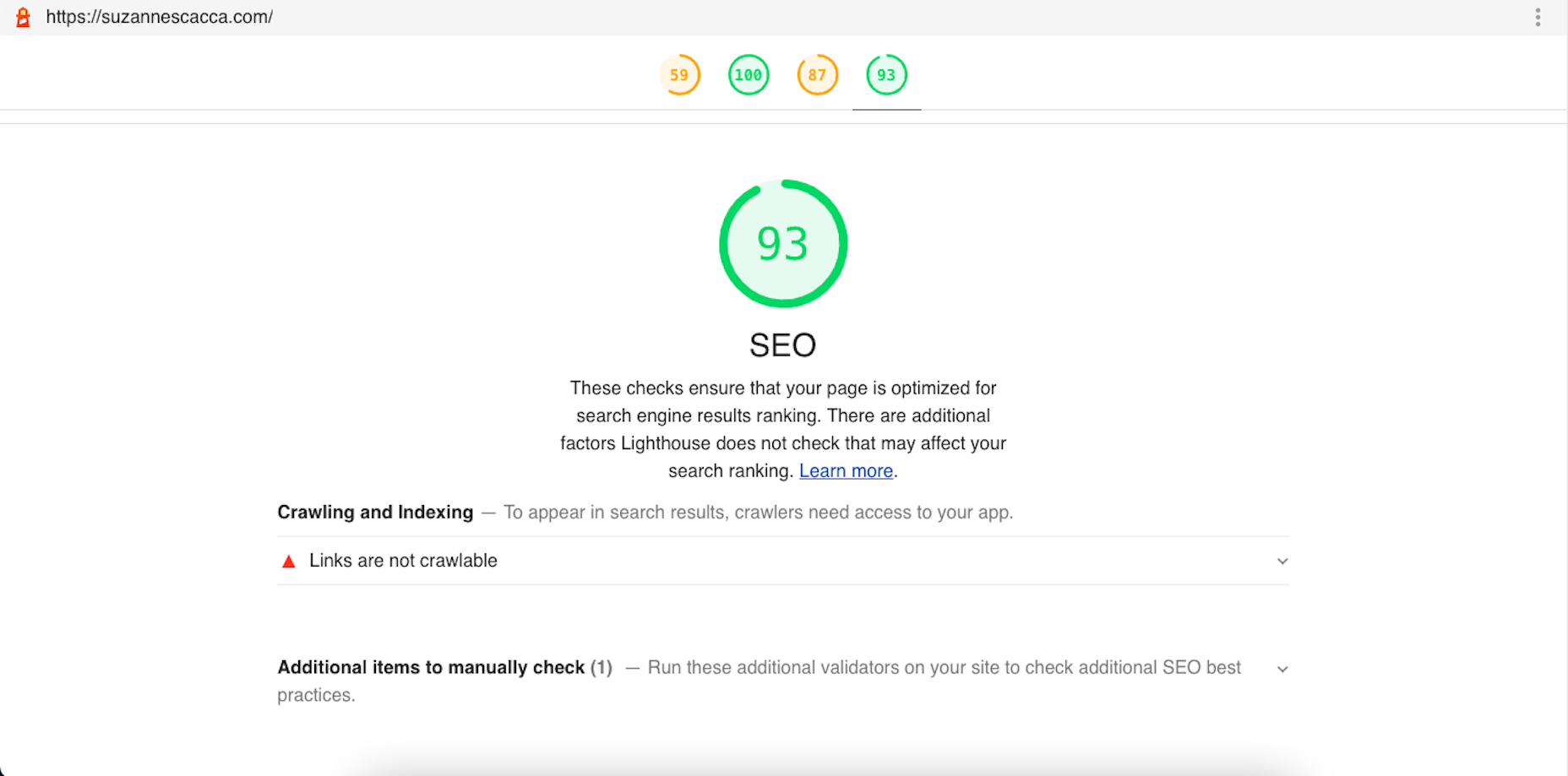

 As a web designer, you face plenty of challenges, both good and bad. One of the bad ones is to suddenly find out that you’re either in danger of missing a client’s deadline or will be unable to meet it at all.
As a web designer, you face plenty of challenges, both good and bad. One of the bad ones is to suddenly find out that you’re either in danger of missing a client’s deadline or will be unable to meet it at all.








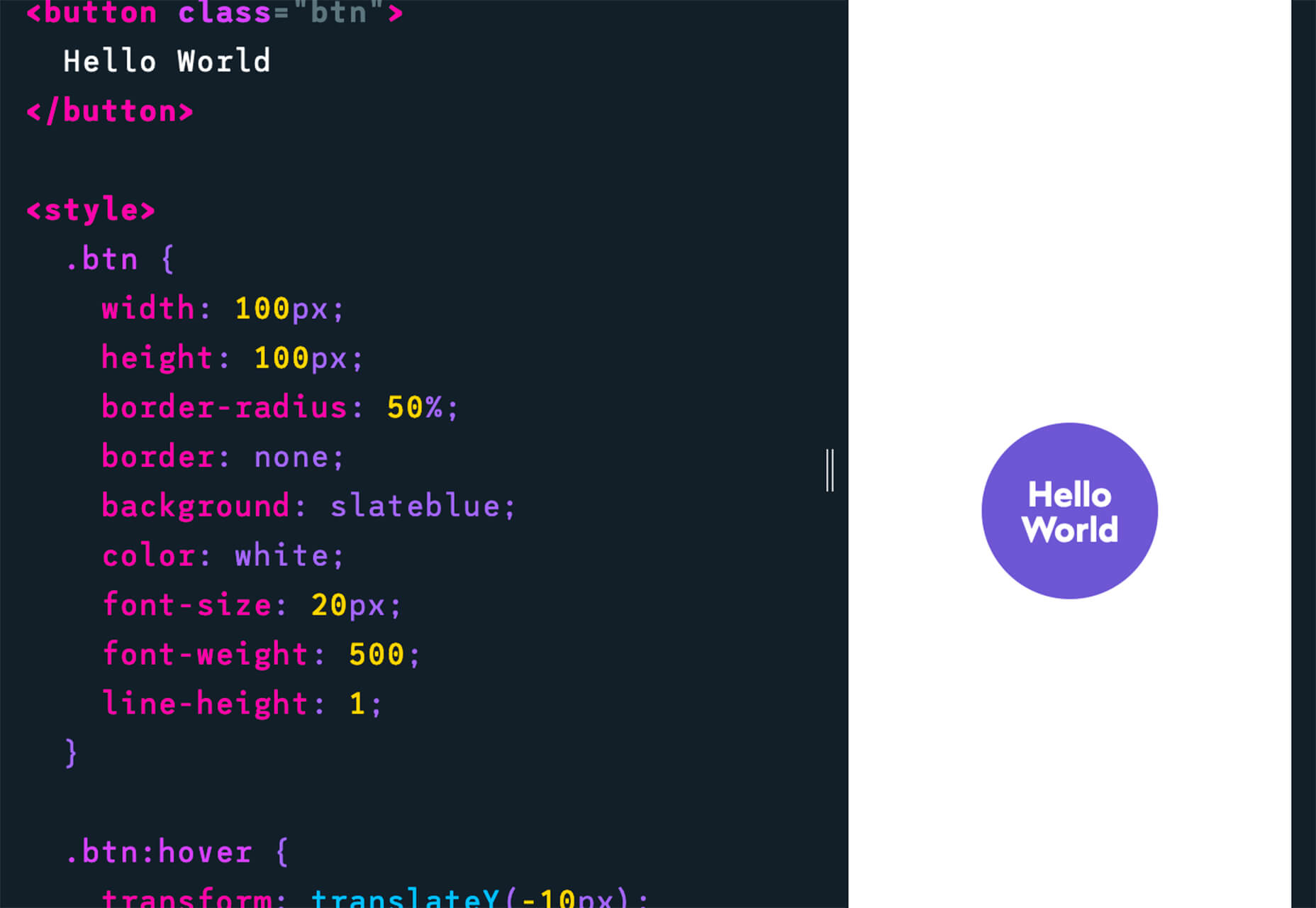
 It’s Friday, and we wanted to have a little fun with a design test that might make you go cross-eyed.
It’s Friday, and we wanted to have a little fun with a design test that might make you go cross-eyed.
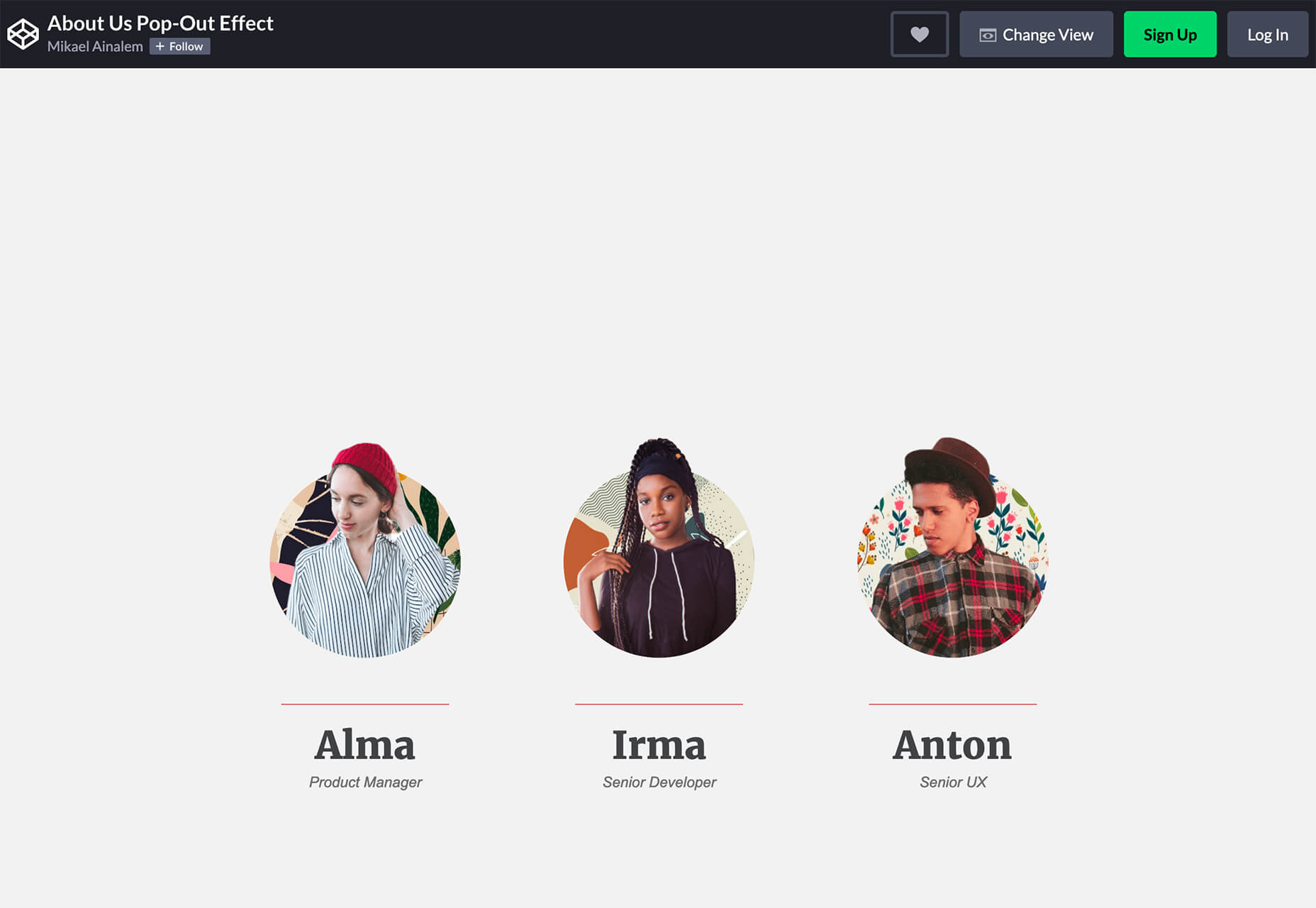
 So, really, you’re in the business of designing websites for your clients’ audiences.
So, really, you’re in the business of designing websites for your clients’ audiences.
 Looking for something new to get you excited about design work? This list is packed with all kinds of goodies to help you feel inspired and ready to work.
Looking for something new to get you excited about design work? This list is packed with all kinds of goodies to help you feel inspired and ready to work.














 Stock images are an essential tool for anyone working with clients who can’t afford to hire a photographer for a bespoke shoot, and with the cost of photography shoots running into thousands of dollars, that’s most clients.
Stock images are an essential tool for anyone working with clients who can’t afford to hire a photographer for a bespoke shoot, and with the cost of photography shoots running into thousands of dollars, that’s most clients.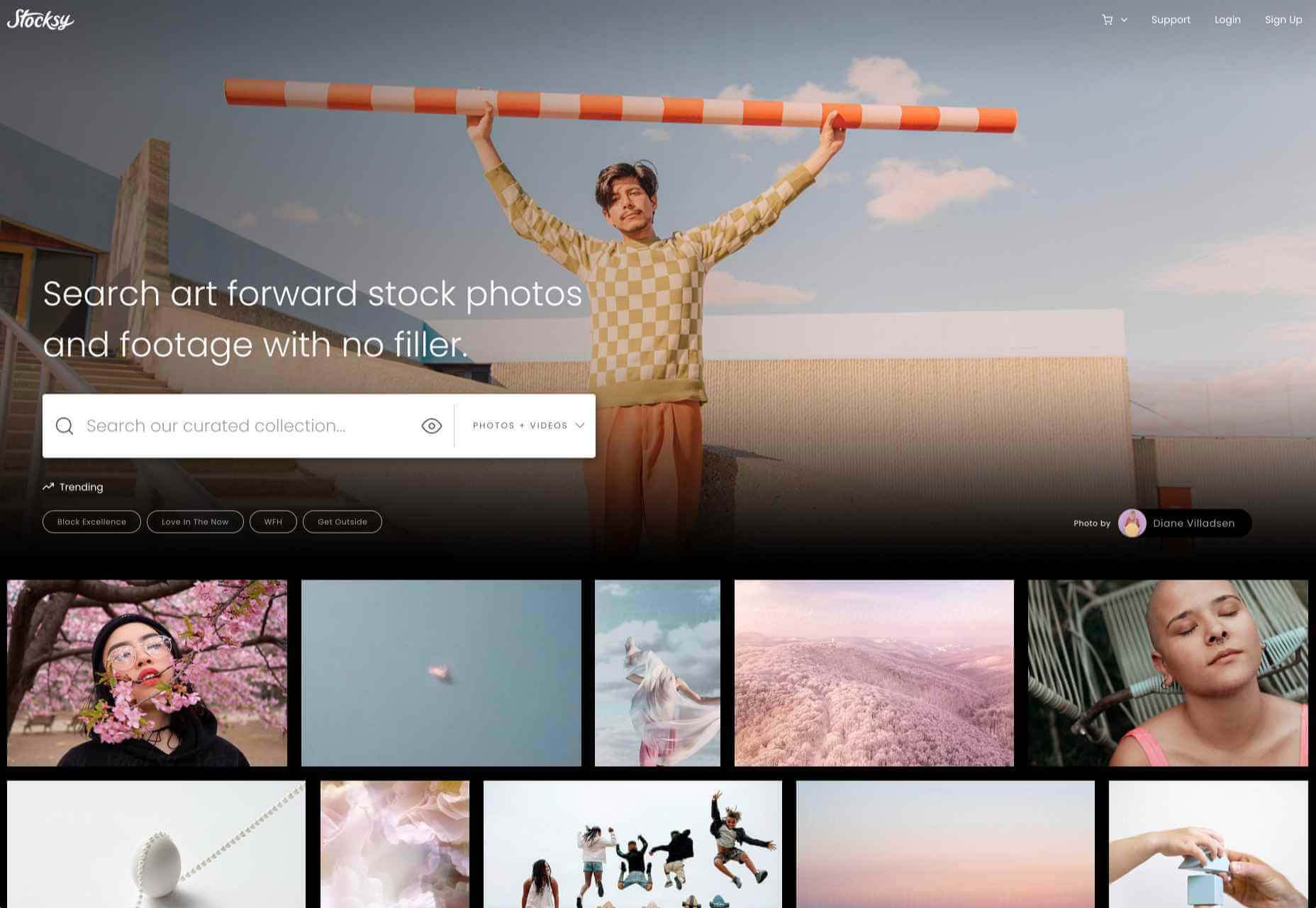
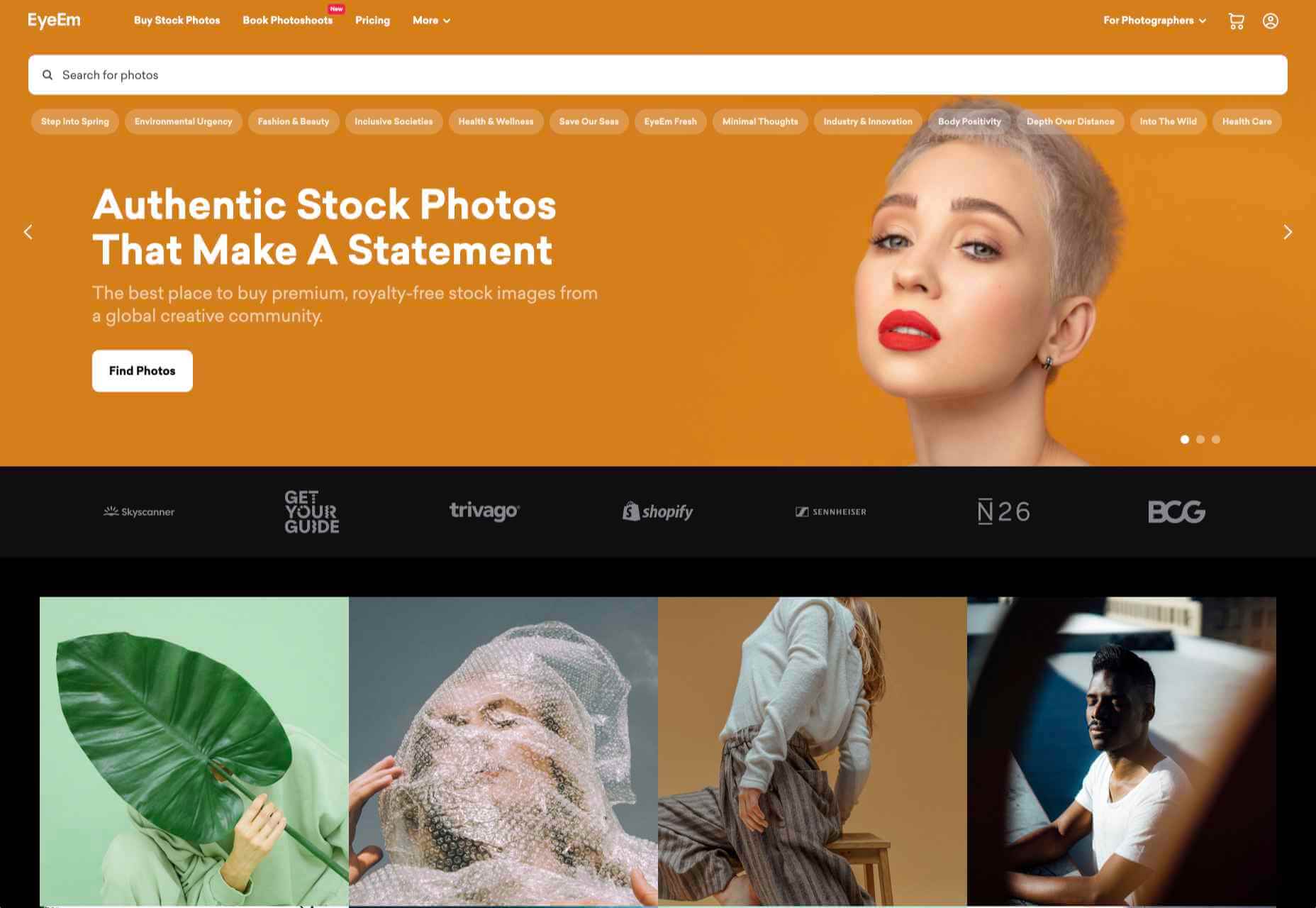


 March is that time of year where the feeling of newness starts, from the first Spring days to fresh design projects. These trends are no exception, with fun new takes on some classic concepts.
March is that time of year where the feeling of newness starts, from the first Spring days to fresh design projects. These trends are no exception, with fun new takes on some classic concepts.







 Everyday design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site,
Everyday design fans submit incredible industry stories to our sister-site,